MCSA job interviews are always brainstorming and significant for the applicants. Having being unbeaten in the MCSA interview questions denotes that the candidate has found the carrier to their dream career. Job interviews are always stressful. Therefore, to minimize the tension and nervousness caused before the interviews; the MCSA specialists, MCSA experts, and MCSA trainers of APTRON who have put their quality skill and considering while developing the MCSA interview questions and answers for freshers, and experience hopefuls. If MCSA job seekers pursue the MCSA interview questions provided below, their pressure can be minimized to zilch.
1. What is Active Directory in the context of MCSA?
Ans:
Active Directory is a Microsoft service that manages network resources, including user accounts, computers, and groups, providing centralized authentication and authorization. In the context of MCSA (Microsoft Certified Solutions Associate), Active Directory refers to Microsoft’s directory service used to manage and organize network resources. It provides a centralized authentication and authorization mechanism, allowing administrators to control access to resources like files, printers, and applications within a Windows Server environment.
2. Explain the purpose of DNS in a Windows Server environment.
Ans:
DNS (Domain Name System) resolves human-readable domain names to IP addresses, facilitating communication between devices on a network.DNS (Domain Name System) in a Windows Server environment is crucial to translating human-readable domain names into IP addresses and vice versa. This hierarchical system enables efficient communication across networks by locating resources using names instead of numerical IP addresses.
3. How do you troubleshoot a network connectivity issue on a Windows Server?
Ans:
- Begin with fundamental examinations: Verify cable connections, use `ipconfig` to confirm IP settings, and make sure DNS resolution is correct.
- Use programs like `tracert` to find possible network hops causing problems and `ping` to test connectivity to other devices.
- To diagnose and fix network connectivity issues on a Windows Server, check firewall settings, go through event logs for network-related errors, and check network adapter details for accurate setups.
4. What is the key role of DHCP in a Windows network?
Ans:
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) automatically assigns IP addresses to devices on a network, simplifying the management of IP configurations. The key role of DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) in a Windows network is automatically assigning IP addresses and related network configuration information to devices (such as computers and printers) within the network. This dynamic allocation simplifies network management by eliminating the need for manual IP address assignment.
5. How can you secure a Windows Server environment?
Ans:
- To reduce vulnerabilities, establish strong password restrictions, activate BitLocker for drive encryption, and update security software often.
- Use network segmentation, configure Windows Firewall with the appropriate rules, and utilize Group Policy to enforce security settings.
- To improve general security in the Windows Server environment, install and update antivirus software, turn on resource auditing, and disable unused services.
6. What is the purpose of Group Policy in Windows Server?
Ans:
Group Policy allows administrators to manage and configure settings for users and computers in an Active Directory environment. Group Policy in Windows Server is a tool that allows administrators to manage and enforce system settings for users and computers within an Active Directory environment. It helps maintain consistent configurations, security settings, and policies across a network, simplifying administration and ensuring compliance with organizational standards.
7. Explain the difference between RAID 0 and RAID 5.
Ans:
| RAID Level | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages | |
| RAID 0 | Striped Volume | Improved read/write performance | No data redundancy, no fault tolerance | |
| RAID 5 | Striped with Parity | Balanced performance and fault tolerance | Slower write speeds during parity update, higher disk overhead due to parity information |
8. How do you perform in Windows Server?
Ans:
- Use Windows Server Backup:
- Open “Server Manager.”
- Select “Tools” > “Windows Server Backup.”
- Choose “Backup Once” or “Backup Schedule.”
- Select backup type: “Full server” or “Custom.”
- Choose a destination: local, external, or network drive.
- Set a backup schedule if needed.
- Review selections.
- Click “Backup” to start.
9. What is PowerShell, and how is it used in Windows Server administration?
Ans:
PowerShell is a command-line shell and scripting language used for automating administrative tasks in Windows Server, enabling efficient management through scripts.PowerShell is a command-line shell and scripting language in Windows. In Windows Server administration, it automates tasks, manages server components, and enables remote administration through scripts.
10. Describe the process of adding a new user to Active Directory.
Ans:
- Open Active Directory Users and Computers (ADUC).
- Navigate to a desired container or OU.
- Right-click and select “New” > “User.”
- Enter user details and set a password.
- Assign groups and permissions.
- Review and confirm.
11. What is the purpose of a domain controller in Windows Server?
Ans:
A domain controller authenticates users, grants access to resources, and replicates directory information across a network in an Active Directory environment. A domain controller in Windows Server manages user authentication and controls access to network resources within a Windows domain. It stores user account information, enforces security policies, and facilitates centralized management of network resources.
12. Explain the difference between a workgroup and a domain. In a workgroup.
Ans:
- Computers are loosely connected.
- Each computer has its local user accounts.
- No centralized management or authentication.
- In a domain:
- A domain controller centrally manages computers.
- Users log in using domain accounts.
- Centralized authentication, security policies, and resource management.
13. How do you troubleshoot a Windows service that fails to start?
Ans:
The first step in troubleshooting a Windows service that won’t start is to go through the Windows Event Viewer for any pertinent error messages that can shed light on the problem. Check that the necessary services are operating, that the service account has the right permissions, and that the requirements for the service are met. In addition, have a look at the settings of the service, try restarting it with tools like `sc` or `services.msc`, and if needed, think about reinstalling or upgrading the service.
14. What is Hyper-V, and how is it used in Windows Server?
Ans:
Hyper-V is Microsoft’s virtualization platform. It allows you to create and manage virtual machines, enabling efficient utilization of server resources. Hyper-V is a virtualization platform in Windows Server that allows you to create and manage virtual machines (VMs).
15. How can you monitor server performance in Windows?
Ans:
To monitor important performance metrics including CPU, memory, disk, and network activities, use Performance Monitor (PerfMon). For a brief summary of resource use in real time, use Task Manager. For more thorough and extended performance monitoring on Windows servers, configure Data Collector Sets in PerfMon.
16. What are the different types of RAID configurations, and when would you use each?
Ans:
RAID 0 (Striping): Improved performance, no redundancy. Use for speed, not data protection.
RAID 1 (Mirroring): Redundancy, data mirrored. Suitable for critical data and fault tolerance.
RAID 5 (Striping with Parity): Balanced performance and data protection. It is good for general use.
RAID 6 (Striping with Dual Parity): Increased fault tolerance for large drives.
RAID 10 (Combining RAID 1 and 0): Balances performance and redundancy. Ideal for critical systems
17. How do you install updates on a Windows Server?
Ans:
- Windows Update:
- Open Settings.
- Go to “Update & Security.”
- Click “Check for updates.”
- WSUS (Windows Server Update Services):
- Configure and deploy updates centrally.
- Manual Installation:
- Download from Microsoft Update Catalog.
- Install using Windows Update Standalone Installer.
- PowerShell:
- Use Install-WindowsUpdate for automation.
18. Explain the concept of DHCP reservation.
Ans:
DHCP reservation associates a specific IP address with a device based on its MAC address. It ensures that a device receives the same IP address from the DHCP server.DHCP reservation is a feature that allows a DHCP server to permanently assign a specific IP address to a device.
19. What is the purpose of Remote Desktop Services (RDS) in Windows Server?
Ans:
RDS allows users to access applications and desktops remotely. It provides a scalable and secure solution for virtualizing desktops and applications. Remote Desktop Services (RDS) in Windows Server facilitates remote access, centralizes application management, optimizes resource usage, supports virtualization, and enables scalable solutions for users accessing desktops and applications.
20. How can you recover a Windows Server from a system failure?
Ans:
- Backup Restore: Use a backup created with tools like Windows Server Backup.
- System Restore: Attempt to revert to a previous state using System Restore.
- Repair/Reinstall: Boot from installation media for repair options or clean reinstall.
- WinRE: Access Windows Recovery Environment for troubleshooting tools.
- Hardware Check: Verify functioning hardware to rule out hardware issues.
21. What is the purpose of the DHCP Relay Agent in Windows Server?
Ans:
The DHCP Relay Agent forwards DHCP requests from clients in one subnet to the DHCP server in another subnet, facilitating dynamic IP address assignment. The DHCP Relay Agent in Windows Server facilitates the communication between DHCP clients and DHCP servers across different subnets. It forwards DHCP broadcast messages from clients to the DHCP server, ensuring that devices on different subnets can obtain IP addresses and configuration information from a centralized DHCP server.
22. Explain the concept of RAID 6.
Ans:
0 RAID 6 provides fault tolerance by using dual parity, allowing the array to withstand the failure of two drives without data loss.RAID 6 (Redundant Array of Independent Disks, Level 6 is a data storage configuration that provides fault tolerance and protection against data loss. It uses block-level striping like RAID 0 but adds dual-distributed parity for redundancy.
23. How do you configure a Windows Server to act as a file server?
Ans:
Install File Services Role:
Use Server Manager to add the “File and Storage Services” role.
Configure File Shares:
Create a share in Server Manager, specifying the folder path.
Set Permissions:
Adjust NTFS and sharing permissions for user or group access.
Enable Access-Based Enumeration (Optional):
Hide folders from unauthorized users in the share tab.
24. What is the purpose of the Windows Firewall in a server environment?
Ans:
Windows Firewall controls inbound and outbound network traffic, enhancing the server’s security by allowing or blocking specific communication based on predefined rules. The Windows Firewall in a server environment controls incoming and outgoing network traffic, enhancing security by allowing or blocking communication based on predefined rules.
25. How can you remotely manage a Windows Server?
Ans:
Use tools like Remote Desktop, PowerShell Remoting, or Server Manager to manage and administer a Windows Server remotely. You can remotely manage a Windows Server using tools like Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP), Windows Admin Center, or PowerShell Remoting. RDP allows direct desktop access, while Windows Admin Center provides a web-based interface for server management.
26. Explain the concept of VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks).
Ans:
VLANs logically segment a network, allowing multiple virtual networks to coexist on the same physical network, enhancing network security and performance.VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) are a network segmentation technique that logically divides a physical network into multiple isolated virtual networks.
27. What is the purpose of the Windows Task Scheduler?
Ans:
Task Scheduler automates the execution of tasks or programs at specified intervals or events, helping manage routine administrative processes. The Windows Task Scheduler is a built-in utility that allows users to automate the execution of tasks at specified intervals or in response to specific events.
28. How can you add redundancy to a Windows Server environment?
Ans:
Implementing failover clustering, network load balancing, and redundant hardware helps enhance system availability and minimize downtime. You can add redundancy to a Windows Server environment by implementing features like clustering, using redundant hardware, setting up failover clustering, and utilizing backup and recovery solutions.
29. Explain the difference between a full backup and an incremental backup.
Ans:
A full backup copies all selected data, while an incremental backup only copies the data that has changed since the last backup, saving storage space and time. A full backup copies all selected files and data in a system, creating a complete copy of the dataset.
30. What is the purpose of the Windows Registry?
Ans:
The Windows Registry stores system configuration settings and options, serving as a centralized database for applications, system components, and user preferences. The Windows Registry is a centralized database in Microsoft Windows that stores configuration settings and options for the operating system and installed applications.
31. How do you configure DNS forwarders in Windows Server?
Ans:
- On a Windows server, open DNS Manager.
- On the server, right-click, select “Properties,” then select the “Forwarders” tab.
- After entering the external DNS servers’ IP addresses, save the modifications.
32. Explain the role of Remote Desktop Gateway (RD Gateway) in Windows Server.
Ans:
RD Gateway allows secure remote access to internal network resources over the Internet, providing a way to connect to Remote Desktop Services outside the corporate network.RD Gateway enhances security by encapsulating RDP traffic within the HTTPS protocol, making it more resistant to potential threats. Users can connect to RD Gateway and access resources on the internal network without exposing those resources directly to the Internet.
33. What is Network Address Translation (NAT), and how is it used in Windows Server?
Ans:
NAT is a technique used to map private IP addresses to a public IP address, enabling devices in a private network to communicate with external networks, often used in routing scenarios. In Windows Server, NAT is often implemented using the Routing and Remote Access Service (RRAS).
34. How can you monitor and manage disk space in Windows Server?
Ans:
Use tools like Disk Management to view and manage disk partitions and Performance Monitor to monitor disk performance and space utilization. You can monitor and manage disk space in Windows Server by using tools like Disk Management, File Explorer, and PowerShell. Disk Management allows you to view and resize partitions, while File Explorer provides an overview of available space.
35. Explain the purpose of the Windows Event Viewer.
Ans:
The Event Viewer logs system, application, and security events, providing a centralized location for administrators to review and troubleshoot issues. The Windows Event Viewer is a tool in the Windows operating system that allows users to view and monitor system, security, and application events.
36. What is Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS)?
Ans:
AD FS enables single sign-on (SSO) across different applications and platforms by authenticating users against an identity provider, often used for federated identity management. Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS) is a Windows Server role that provides single sign-on (SSO) access to systems and applications across organizational boundaries.
37. How do you configure a Windows Server as a Domain Name System (DNS) server?
Ans:
Install the DNS Server role, create forward and reverse lookup zones, configure zone settings, and ensure proper DNS resolution for network clients. Configuring a Windows Server as a DNS server involves installing the DNS Server role via Server Manager and configuring zones, records, and other settings using the DNS Manager tool. Detailed steps can be found in Microsoft’s official documentation or tutorials online.
38. Explain the Group Policy Objects (GPOs) concept in Windows Server.
Ans:
GPOs are collections of settings that define how computers and users operate in an Active Directory environment, allowing administrators to manage policies centrally. Group Policy Objects (GPOs) in Windows Server are configurations that define various settings and security policies for users and computers within an Active Directory domain.
39. What is the purpose of the Windows Update Services (WSUS) role?
Ans:
WSUS allows administrators to manage the distribution of updates released by Microsoft for Windows operating systems and Microsoft applications within an organization. With WSUS, administrators can download updates from Microsoft’s servers to a central repository on the WSUS server.
40. How can you secure Remote Desktop Services in a Windows Server environment?
Ans:
Use a VPN: Employ a Virtual Private Network for secure remote access.
Strong Authentication: Implement strong password policies and enable Network Level Authentication.
SSL/TLS Encryption: Utilize SSL/TLS certificates to encrypt RDS traffic.
Keep Systems Updated: Regularly update and patch the server and RDS components.
Account Lockout Policies: Set account lockout policies to thwart brute force attacks.
Remote Desktop Gateway: Utilize RD Gateway with SSL and proper configuration.
Firewall Rules: Restrict access through Windows Firewall rules, allowing only necessary traffic.
41. What is the purpose of Dynamic Access Control (DAC) in Windows Server?
Ans:
DAC allows administrators to control resource access based on user attributes and conditions, providing fine-grained access control in an Active Directory environment. Dynamic Access Control (DAC) in Windows Server provides a centralized and dynamic way to control resource access based on user attributes and file classifications.
42. How do you configure Windows Server Backup for scheduled backups?
Ans:
Open “Server Manager” on your Windows Server.Navigate to “Local Server” and click “Manage” in the top right.Choose “Add Roles and Features” and install the “Windows Server Backup” feature. After installation, open “Windows Server Backup” from the “Tools” menu in “Server Manager.” Select “Local Backup” in the Backup console and click “Backup Schedule” in the Actions pane. Follow the wizard to set up your backup schedule, specifying the items and destination you want to back up.
43. Explain the role of Windows Deployment Services (WDS).
Ans:
WDS is used for deploying Windows operating systems over a network. It allows for automated installations, saving time and ensuring consistent configurations. Windows Deployment Services (WDS) simplifies large-scale Windows installations by enabling network-based deployment, supporting PXE boot for network booting, deploying custom OS images, facilitating unattended installations, and utilizing multicast transmission to efficiently deploy multiple computers simultaneously.
44. What is the purpose of the Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (AD LDS) role?
Ans:
D LDS provides directory services similar to Active Directory but is designed for applications that require a lightweight and separate directory structure. Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (AD LDS) provides a lightweight, directory-based data store for applications that need a directory but don’t require the full capabilities of Active Directory.
45. How can you configure Network Load Balancing (NLB) in Windows Server?
Ans:
Install NLB Feature: Use Server Manager to add the “Network Load Balancing” feature.
Configure NLB: Open NLB Manager and create a new cluster with IP and interfaces.
Set Port Rules: Define rules for traffic handling (Single/Multiple host, affinity).
Cluster Parameters: Choose cluster mode (Unicast/Multicast) and adjust settings.
Add Hosts: Add servers to the cluster with IP, priority, and name.
Testing and Monitoring: Ensure connectivity and monitor cluster performance.
Update DNS: Adjust DNS for NLB cluster’s virtual IP.
Maintenance: Regularly monitor and troubleshoot as needed.
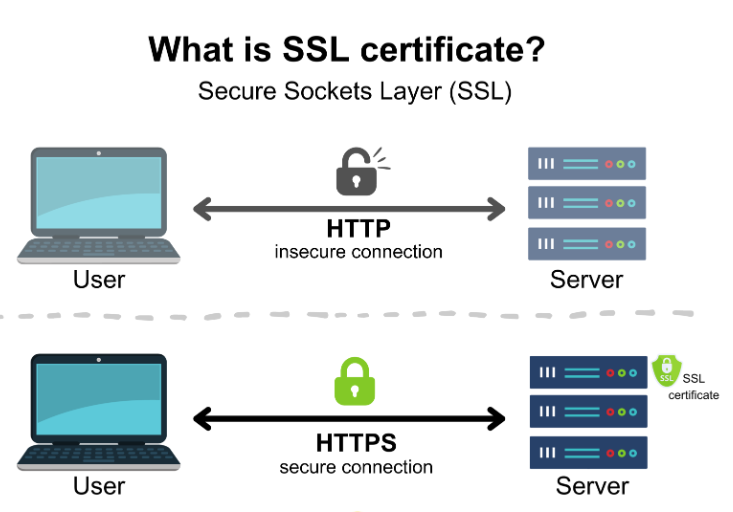
46. Explain the importance of Secure Socket Layer (SSL) certificates in Windows Server.
Ans:
SSL certificates provide secure communication over the internet by encrypting data. In Windows Server, they are essential for securing services like web servers and remote access.SSL certificates are crucial in Windows Server for securing data transmitted between a user’s browser and the server.
47. How do you troubleshoot Active Directory replication issues?
Ans:
Check Event Logs: Examine for replication errors.
Repadmin Tool: Use “repadmin /showrepl” to identify issues.
Network Connectivity: Verify no network problems.
Firewall Settings: Ensure ports aren’t blocked.
DNS Configuration: Confirm the correct DNS setup.
Time Synchronization: Check synchronized time. AD Sites and Services: Verify the proper configuration.
48. What is Windows Server Core, and when might you use it?
Ans:
ows Server Core is a minimal installation option without a graphical user interface. It is suitable for scenarios where a smaller attack surface and reduced resource consumption are priorities. Windows Server Core is a minimal installation option of the Windows Server operating system. It excludes the graphical user interface (GUI) and unnecessary components, reducing the attack surface and resource usage.
49. How can you delegate administrative tasks in Active Directory?
Ans:
Use the Delegation of Control Wizard in Active Directory Users and Computers to grant specific permissions to users or groups for managing specific objects or organizational units. You can use the “Delegation of Control” wizard to delegate administrative tasks in Active Directory. This allows you to assign specific permissions to users or groups for managing certain objects or organizational units within Active Directory.
50. Explain the purpose of the Windows Server Resource Manager (WSRM).
Ans:
WSRM allows administrators to manage system resources, such as CPU and memory, by setting policies and priorities for different applications and processes on a Windows Server. The Windows Server Resource Manager (WSRM) is a feature in Windows Server that helps manage and allocate system resources, particularly CPU and memory, to optimize performance.
51. What is a Network Policy Server (NPS) in Windows Server, and how is it used?
Ans:
NPS is a role that provides network access control and authentication services. It is often used to enforce security policies and authenticate network clients. Network Policy Server (NPS) in Windows Server is a role service providing centralized management and enforcement points for network access policies.
52. Explain the purpose of the Windows Performance Monitor.
Ans:
Performance Monitor allows administrators to monitor and analyze system performance by tracking various performance counters, helping identify bottlenecks and resource usage. The Windows Performance Monitor is a tool designed to monitor and analyze system performance on Windows operating systems.
53. How can you configure a Windows Server as a print server?
Ans:
- Open Server Manager.
- Add the “Print and Document Services” role.
- Access Print Management tool.
- Add your server to Print Management.
- Add printers using the wizard.
- Set up printer security.
- Test with a print job.
54. What is Windows PowerShell Desired State Configuration (DSC)?
Ans:
DSC is a management platform that allows administrators to declare the desired state of a system, automatically configuring and maintaining consistency across servers.PowerShell Desired State Configuration (DSC) is a configuration management platform in Windows PowerShell that enables the declarative specification of the desired state for a system.
55. Explain the purpose of the Windows System Configuration (MSCONFIG) utility.
Ans:
MSCONFIG is a tool used to troubleshoot and configure the startup process in Windows. It allows users to turn startup programs and services on or off. The purpose of the Windows System Configuration (MSCONFIG) utility is to manage system startup services and troubleshoot system configuration issues. It provides a graphical interface to view and modify startup programs, services, boot options, and system.ini files.
56. What is Windows Defender, and how does it contribute to server security?
Ans:
Windows Defender is an antivirus and antimalware solution. On Windows Server, it helps protect against malicious software and enhances overall server security. Windows Defender is Microsoft’s built-in antivirus and antimalware solution for Windows operating systems. It helps protect against various types of malicious software, including viruses, spyware, and ransomware.
57. How can you configure a Windows Server for Remote Desktop Services Licensing?
Ans:
Install Role: Use Server Manager to install the Remote Desktop Licensing role.
Activate Server: Open Remote Desktop Licensing Manager and activate the server.
Install CALs: Add purchased Client Access Licenses.
Configure Licensing Mode: Set mode (Per User/Per Device) in Session Host Configuration.
Specify Server: Enter the licensing server in Session Host Configuration.
Check Diagnoser: Use Remote Desktop Licensing Diagnoser for verification.
Group Policy (Optional): Consider configuring Group Policy for settings.
58. Explain the purpose of the Windows Update Agent.
Ans:
The Windows Update Agent is responsible for managing the installation of updates on Windows-based systems, ensuring the system is up-to-date with the latest security patches and improvements. The Windows Update Agent is responsible for managing and facilitating the installation of updates on a Windows operating system.
59.What is the purpose of Windows Server AppFabric?
Ans:
Windows Server AppFabric is a set of integrated technologies that provide improved hosting, management, and caching capabilities for web applications on Windows Server. Windows Server AppFabric, now deprecated, was a set of integrated technologies in Windows Server aimed at improving the hosting, managing, and scaling of rich, connected applications.
60. How do you perform a server migration in Windows Server?
Ans:
When migrating servers using Windows Server, careful planning is required, starting with recording the present configurations and applications. After verifying compatibility during installation and configuration, move files and apps. Lastly, make sure the transfer goes well by updating DNS records, putting the old server through a thorough testing phase, and decommissioning it only after that.
61. Explain the purpose of the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) in Windows Server.
Ans:
WSL allows the installation and execution of Linux distributions on a Windows Server, enabling developers to run Linux tools and applications natively. The Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) in Windows Server allows Linux applications to be run natively on Windows. It facilitates a seamless integration of Linux and Windows environments, enabling developers and system administrators to leverage both ecosystems for a more versatile and efficient computing experience.
62. What is Hyper-Converged Infrastructure (HCI) in the context of Windows Server?
Ans:
HCI integrates computing, storage, and networking into a single software-defined platform, providing simplified management and scalability in Windows Server environments. Hyper-converged infrastructure (HCI) in the context of Windows Server refers to a software-defined architecture that combines computing, storage, and networking resources into a single, integrated platform.
63. Explain the role of Windows Defender Credential Guard in enhancing security.
Ans:
Credential Guard uses virtualization-based security to protect credentials from theft by isolating them in a secure environment, reducing the risk of credential-based attacks. Windows Defender Credential Guard is a security feature in Windows 10 that helps protect against credential theft attacks. It isolates and secures credentials, such as NTLM password hashes and Kerberos ticket-granting tickets, in a secure, isolated container called the LSASS (Local Security Authority Subsystem Service) process.
64. What is the purpose of the Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) Cleanup Wizard?
Ans:
The WSUS Cleanup Wizard helps maintain the health of the WSUS server by removing obsolete updates, unused computers, and unneeded files and optimizing the update storage. The Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) Cleanup Wizard is designed to help administrators manage and maintain the WSUS server by removing obsolete updates and declining and deleting updates that are no longer needed.
65. How do you implement BitLocker Drive Encryption in Windows Server?
Ans:
Go to “Manage” and select “Add Roles and Features.” Choose BitLocker Drive Encryption during the installation. Enable BitLocker on desired drives using the BitLocker Drive Encryption wizard. Set up recovery options and save the recovery key.
66. Explain the significance of Windows Event Forwarding.
Ans:
Windows Event Forwarding allows centralized collection of event logs from multiple servers, aiding in security monitoring, analysis, and troubleshooting. Windows Event Forwarding allows centralized collection of event logs from multiple machines, enhancing security monitoring and analysis by aggregating logs in a central location for efficient analysis and detection of potential issues or security threats.
67. How can you configure Windows Firewall rules for specific applications?
Ans:
- Open “Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security.”
- Go to “Inbound Rules” or “Outbound Rules.”
- Click “New Rule” on the right-hand side.
- Choose “Program” and click “Next.”
- Specify the path to the program or select from the list.
- Select the action (allow or block) and click “Next.”
- Choose when the rule applies (Domain, Private, Public), then click “Next.”
- Provide a name for the rule and a brief description, then click “Finish” to create the rule.
68. What is the purpose of the Windows Task Manager in server administration?
Ans:
ask Manager provides real-time information about system performance, resource usage, and running processes, aiding administrators in monitoring and managing server health. The Windows Task Manager in server administration monitors and manages system performance, views running processes, analyzes resource usage (CPU, memory, disk, network), identifies and terminates unresponsive applications, and assesses overall system health, aiding administrators in troubleshooting and optimizing server performance.
69. How do you implement Remote Desktop Services Licensing in a Windows Server environment?
Ans:
Navigate to “Manage” > “Add Roles and Features.” Select “Remote Desktop Services Installation” and follow the wizard. Choose “Role-based or feature-based installation” and select the appropriate server. Select “Remote Desktop Licensing” as the role to install.
Complete the wizard, and once installed, open “Remote Desktop Licensing Manager.” Right-click on the server and choose “Install Licenses.” Follow the prompts to enter license information and activate the licenses.
70. Explain the purpose of Windows Defender Application Control (WDAC).
Ans:
DAC helps prevent unauthorized applications from running on a Windows Server by enforcing code integrity policies and enhancing security against malicious software. Windows Defender Application Control (WDAC) enhances system security by allowing administrators to control which applications can run on a Windows system.
71. What is Windows Server Failover Clustering?
Ans:
Failover Clustering provides high availability by grouping servers to work together, ensuring if one fails, another takes over. It’s beneficial for critical applications and services. Windows Server Failover Clustering is a feature that enables the grouping of multiple servers into a single logical unit for high availability and scalability. It ensures continuous availability of services by automatically transferring workloads to another server in the cluster if one fails.
72. How can you configure Windows Server to act as a DNS server for an external domain?
Ans:
Open “Server Manager” on the Windows Server. Go to “Manage” and select “Add Roles and Features.” Choose “DNS Server” during the installation process. After installation, open “DNS Manager” from the Tools menu. Create a new Forward Lookup Zone for the external domain. Add the necessary DNS records for the external domain.
Set up forwarders or root hints for external DNS resolution. Ensure firewall rules allow DNS traffic (port 53) if applicable. Test DNS resolution for the external domain from the server.
73. Explain the purpose of the Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) Content folder.
Ans:
The WSUS Content folder stores update files downloaded by the WSUS server, enabling centralized management and distribution of updates within an organization. The Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) Content folder is a directory where WSUS stores update files locally. It serves the purpose of facilitating centralized management and distribution of Windows updates within an organization. Storing update content locally reduces bandwidth usage and speeds up the update process by allowing client machines to download updates from a local server rather than from Microsoft’s servers over the internet.
74. What is the purpose of the Windows Credential Manager?
Ans:
Credential Manager securely stores credentials such as usernames and passwords, making it convenient for users to access network resources without repeatedly entering login information. The Windows Credential Manager is a feature in Windows that helps users securely store and manage credentials such as usernames and passwords.
75. Explain the concept of Windows Server App-V (Application Virtualization).
Ans:
App-V allows applications to run in isolated environments, reducing conflicts and dependencies and making deploying and managing applications on Windows Server easier. Windows Server App-V, or Application Virtualization, is a technology developed by Microsoft to enable the deployment and execution of applications in a virtualized environment.
76. What is the purpose of the Windows Performance and Reliability Monitor?
Ans:
The Performance and Reliability Monitor provides detailed information about system performance, reliability, and resource usage, aiding in troubleshooting and optimization. The Windows Performance and Reliability Monitor is a tool that provides detailed information about system performance, hardware resource usage, and system stability. It helps users monitor and analyze performance metrics like CPU, memory, disk, and network usage.
77. Explain the purpose of the Windows Deployment Services (WDS) multicast feature.
Ans:
WDS multicast enables efficient deployment of Windows images to multiple clients simultaneously, optimizing network bandwidth during large-scale deployments. The Windows Deployment Services (WDS) multicast feature enables efficient deployment of operating systems to multiple computers simultaneously.
78. What is the purpose of the Windows Hyper-V Replica feature?
Ans:
Hyper-V Replica provides asynchronous replication of virtual machines to a secondary host, ensuring business continuity and disaster recovery in case of a primary host failure. The Windows Hyper-V Replica feature provides a mechanism for replicating virtual machines (VMs) from one Hyper-V host to another.
79. Explain the role of the Windows Task Scheduler in automating administrative tasks.
Ans:
Task Scheduler allows administrators to automate the execution of scripts, tasks, and applications at specified times or in response to specific events. The Windows Task Scheduler automates administrative tasks by enabling users to schedule the execution of programs or scripts at specified times or events.
80. What is the purpose of the Windows Server Backup Command-Line Utility (WBADMIN)?
Ans:
WBADMIN allows administrators to perform backup and recovery operations via the command line, providing scripting capabilities for automated backup tasks. The Windows Server Backup Command-Line Utility (WBADMIN) performs backup and recovery tasks from the command prompt or scripts on Windows Server. It enables administrators to automate backup operations, schedule tasks, and manage backups without using the graphical user interface.
81. How can you enforce strong password policies in Windows Server?
Ans:
Configure Group Policy settings to enforce password complexity, length, and expiration policies, enhancing security for user accounts. To enforce strong password policies in Windows Server, you can use Group Policy. Open the “Group Policy Management Console,” navigate to “Computer Configuration,” “Windows Settings,” “Security Settings,” and then “Account Policies.”
82. Explain the role of Windows Performance Monitor Data Collector Sets.
Ans:
Data Collector Sets allow administrators to collect and analyze performance data over time, aiding in identifying trends and bottlenecks and optimizing system performance. Windows Performance Monitor Data Collector Sets are configurations that allow you to collect and analyze performance data on a Windows system. They act as containers for performance counters, logs, and alerts, providing a convenient way to monitor specific aspects of system performance.
83. Explain the purpose of Windows Server File Classification Infrastructure (FCI).
Ans:
- Classification: Tags files based on content and metadata.
- Automation: Enables automated actions on classified files.
- Policy Enforcement: Enforces data governance policies.
- Search and Retrieval: Facilitates efficient file searching.
- Risk Management: Identifies and manages sensitive data.
- Storage Optimization: Organizes data for efficient storage.
84. What is the significance of Windows Admin Center in server management?
Ans:
- Unified Interface: Centralizes server management in a web-based interface.
- Remote Management: Enables remote administration for servers.
- User-Friendly: Simplifies tasks with an intuitive interface.
- Monitoring: Provides real-time server monitoring and alerts.
- Security: Enhances security with role-based access control.
- Updates: Facilitates Windows Server updates and maintenance.
85. Explain the role of the Windows Security Configuration Wizard (SCW) in server hardening.
Ans:
SCW guides administrators through configuring security settings based on server roles, reducing the attack surface and enhancing overall security. The Windows Security Configuration Wizard (SCW) helps in server hardening by analyzing server roles, creating security policies, and configuring settings to minimize attack surfaces. It restricts unnecessary services and network ports, enhancing the server’s security posture.
86. What is the purpose of the Windows Server Message Block (SMB) protocol?
Ans:
SMB facilitates file and printer sharing and communication between devices on a network. It is integral to accessing shared resources in a Windows environment. The Windows Server Message Block (SMB) protocol facilitates file and printer sharing and communication between devices on a network. It allows for access to shared resources, file operations, and communication between computers running Windows or other operating systems.
87. Explain the role of Windows Server App-V Sequencer.
Ans:
App-V Sequencer packages and prepares applications for virtualization, enabling their deployment on Windows Server without conflicts or compatibility issues. The Windows Server App-V Sequencer is used to package virtualization applications. It captures an application’s installation process, configurations, and dependencies, creating a sequenced package.
88. What is the purpose of the Windows Resource Monitor?
Ans:
Resource Monitor provides real-time information about system resource usage, including CPU, memory, disk, and network, helping administrators identify performance bottlenecks and issues. The Windows Resource Monitor provides real-time information about system resource usage, including CPU, memory, disk, and network. It helps users and administrators identify performance bottlenecks, monitor active processes, and troubleshoot issues by offering detailed insights into resource utilization and system activity.
89. How do you configure a Windows Server to act as a time server in an Active Directory environment?
Ans:
In an Active Directory environment, run PowerShell as Administrator and enter “w32tm /config /manualpeerlist:”time.windows.com” /syncfromflags:manual /reliable:YES” to setup a Windows Server as a time server. Once the Windows Time service has been restarted using “Restart-Service w32time,” be sure that the Windows Firewall is allowing incoming UDP traffic on port 123. By doing this, the server is identified to other devices inside the Active Directory domain as a time source.
90. How can you configure Windows Server to use Network Level Authentication (NLA) for remote desktop connections?
Ans:
Navigate to the “System” control panel, choose “Remote settings,” and turn on the option for “Allow connections only from computers running Remote Desktop with Network Level Authentication” in order to set up Windows Server for Network Level Authentication (NLA) on remote desktop connections. NLA will improve the security of remote desktop connections by demanding user identification prior to initiating a session. Make sure the server has the most recent security upgrades installed.
91. How do you configure Windows Server Active Directory Rights Management Services (AD RMS)?
Ans:
Install the AD RMS role using Server Manager, then follow the wizard to finish the configuration, which includes defining the server certification and license settings, in order to establish AD RMS on Windows Server. Furthermore, set up trust policies and build rights policy templates to enforce data security in the Active Directory system.
92. How can you monitor and optimize Active Directory replication in Windows Server?
Ans:
- Monitor replication status and check Directory Service event logs for problems using tools such as ADREPLSTATUS or Repadmin.
- Create efficient site architectures and modify replication schedules in response to network conditions to optimize replication topology.
- Maintain the general health of Active Directory by fixing performance problems and doing routine health checks to maximize replication effectiveness.
93. What is Windows Storage Spaces Direct, and how does it enhance storage in a cluster?
Ans:
A feature of Windows Server called Windows Storage Spaces Direct makes it possible to use local disks spread across several servers to create a scalable and fault-tolerant storage system. By combining storage resources, offering high availability, and facilitating the effective use of storage capacity through features like tiering and deduplication, it improves storage in a cluster.
94. How do you configure Windows Server Network Load Balancing (NLB) for high availability?
Ans:
Installing the Windows Server Network Load Balancing (NLB) functionality on each server, assigning a virtual IP address, and configuring port rules are the steps involved in configuring NLB for high availability. Modify NLB configurations, including load distribution and affinity, to guarantee fault tolerance and peak performance amongst the clustered servers.
95. How can you monitor and manage disk space usage in Windows Server using PowerShell?
Ans:
- Get Disk Space Information: – To find out how much disk space the server is using, use PowerShell cmdlets like `Get-Volume` or `Get-Partition{. As an illustration, consider the command `Get-Volume | Select-Object DriveLetter, FileSystemLabel, Size, UsedSpace, FileSystemType}.
- Monitor Disk Space Trends: – Set up PowerShell scripts to execute on a regular basis to gather data on disk space and report trends over time. – Use the `Get-Counter` cmdlet or WMI queries to keep an eye on particular disk space-related performance counters.
- Take Action and Cleanup: – Use task scheduler or PowerShell scripts to set up automatic warnings depending on disk space thresholds. To efficiently manage disk space, write scripts to find and delete superfluous files or carry out cleanup operations depending on predetermined parameters.