
As application virtualization is a user centric model, it allows the users to supply the applications wherever they are. It is considered as another deployment application and any organization is a need for this virtualization. So, wisdom jobs provides all the job seekers with advanced Application virtualization interview questions that helps them to acquire knowledge on the questions that are being asked by the company, and also helps in achieving their dream job as an application virtualization developer.
1. What Is Application Packaging?
Ans:
Process of creating installer for application is called application packaging. Usually in it binary files provided by the developers are packaged to form the package. The Main difference between the packaging and re-packaging is that source files does not come in a form of package in packaging where as in re-packaging come in the form of package, which might MSI or legacy package .
2.Mention the Features of the application packaging?
Ans:
Repackaging is a process of capturing the changes that made by the Installation Program (Package) and it is customized to the support company standards and also distribution methods. It is not need to do setup capture to call it repackaging, even creating a must files or is files can be called application repackaging.
3. What Are Steps Of Repackaging?
Ans:
- Review packaging of requirements (User Requirement Review).
- Analyse a vendor package (Tech Review).
- Repackage the application (Setup capture).
- Customize package (Scripting).
- Test package (Testing & UAT).
- Release package to end users (Deployment).
4. Why Repackaging Is Required & What Are Problems In Legacy Installation?
Ans:
The problems with Legacy Installations:
- High Support Costs.
- Fragile Installs & uninstalls.
- A Difficult & labor Intensive to deploy.
5. Name Few Msi Packaging Tools?
Ans:
- Wise for a Windows Installer.
- Wise Package Studio.
- Install Shield.
- SMS Installer.
- Marimba.
- WIX (It cannot be used for re-packaging).
- Sharpdevelop.
- Visual Studio.
6. Name Few Msi Re-packaging Tools?
Ans:
- Wise Package Studio
- Install Shield
- SMS Installer
- Marimba
7. Name Few Deployment Tools?
Ans:
- Radia
- CA DSM
- Altiris Client Management Suite
- Altiris Notification Server Console
- Microsoft Systems Management Server (SMS)
8. What Is Windows Installer?
Ans:
Windows Installer is the built-in Operating System service for Installing and Managing Applications. It provide for standard method for developing, customizing, installing and updating the applications. It is engine for an installation, maintenance, and removal of software on modern Microsoft Windows systems. The installation information, and often files themselves, are packaged in installation packages, loosely relational databases structured as the OLE COM Structured Storages and genarally known as “MSI files”, from default file extension. Windows Installer contains a significant changes from its predecessor, Setup API.
9. What are Benefits Of Windows Installer?
Ans:
- Advertising
- Installation on Demand
- Repair (Self-healing)
- Rollback (Transactional operations)
- Managed Shared Resources
10.What is Msi Installation Mechanism (background Mechanism)?
Ans:
Acquisition : The Installer first installs the feature and then progresses through actions specified in the sequence tables of the installation database. These actions query installation database and generate a script that gives step-by-step procedure for performing the installation.
Execution : The installer passes the information to a process with the elevated privileges and runs the script.
11. What Is A Msi?
Ans:
MSI is “Microsoft Windows Installer”. It is installation, in the form of single file. It is actually the database that contains a several tables (80+). Each of these tables contains the instructions and set-up information.
12. What is Structure Of Msi?
Ans:
- Products(Collection of the Features)
- Features (Collection of the Components)
- Components (Collection of the files and Registries)
13. What Is Product?
Ans:
A single installedworking program is a product. A product is identified by unique GUID (the ProductCode property). A product is not a same as package: a single MSI package might install the multiple various products. For example,an MSI might install French and English versions of a program, each of which is various product.
14. What Is Feature?
Ans:
Features are buckets for Components. Windows Installer configuration commands operate only on the Features (installing, advertising, Uninstalling). Self-healing, installon- demand and the user profile fix-up operate at Feature level.
15. What Is Component?
Ans:
Components are the collections of the resources that are always installed or removed as the unit from user’s system. A resource can be file,registry key, shortcut, or anything else that may be installed. Each component is assigned to the unique component code GUID.
16. What Is Self-healing?
Ans:
When an MSI-based application is to be launched (by clicking on advertised shortcut or file type association), Windows Installer checks an existence of a key path items. If there is a mismatch between current system state and value specified in MSI package (e.g., a key file or registry is missing), then related feature is be reinstalled.
17. Difference Between Self-healing And Repair?
Ans:
Self Heal and Repair are two different concepts in Windows Installer which people more times consider to be the same thing however there is difference in a these two. Self Heal is triggered by the advertised shortcuts, or other advertising information in package which eventually Repairs the application. When application is launched by a advertised shortcut, it checks for all the key paths of Current Feature, if any of key paths is missing it will be launch Repair. If there are more features then it will not to check missing key paths of other features, but only the feature of which can advertised the shortcut is launched.
18. What Is Registry,Tell Structure & Types Of Registry?
Ans:
The Registry is single place for saving data about Windows OS (Hardware & Software):
- Root Keys / Subtrees
- Subkeys
- Hives
- Entries
19. What Are Shortcuts & Types?
Ans:
Shortcuts are entry points to the applications installed on the system which is normally points to be a file:
- Advertised
- Non Advertised
20. What Are Ini File & Its Format?
Ans:
INI files are plain-text files that had configuration information. “INI” stands for:
- initialization.
- [Section]
- Keyname=value.
21. What Are Services & Its Types?
Ans:
- A windows service is background process which is updated by a Service Control Manager of OS.
- Win32 Service (Win32 services are services which is running by an executable file installed by Application).
- System or Kernel Services (Kernel services are services which are used by OS to communicate to hardware devices)
22. Where Is Service Information Stored?
Ans:
Most of the Service information are saved under a windows registry hive “HKLM System Current Control Set Name of the Service”. The location where service information is stored within the application package can vary depending on type of application, programming language, and development framework used.
23. In Msi, Which Tables Contain Information About Service Details?
Ans:
- Service Install (Service Details)
- Service Control (Controlling service during Installation & Un Installation)
24. What Is Odbc & Dsn And Its Types?
Ans:
ODBC means Open Database Connectivity. The purpose of ODBC is to permit the user to access data from any application. The layer between the application and DBMS called DSN.
25. What Is File Association?
Ans:
The Windows operating system find the file types and associates them with programs based on the file extension. A file that have no extension or no associated with the program is called Orphaned.
26. What Is Environment Variable & Its Types?
Ans:
Environment Variables are variables that are set by an Operating System & Application:
- System Variable (Available for all users)
- User Variable (Available for particular user)
27. What Is Property and Types Of Properties, Give Some Examples?
Ans:
Properties are the global variables. Private: The installer can be used only an internally (values can’t be changed during the run time). Manufacture,ProductCode, ProductID, ProductName, ProductVersion Public: The installer can be used both internally & externally (values can be changed during the run time also).INSTALLLEVEL. Restricted Public:The user can’t change value of both internally & externally due to security purposes. ALLUSERS, REBOOT, REINSTALLMODE.
28. What Is Merge Module?
Ans:
Merge modules are the mechanism in the Windows Installer that allows the companies to prepackage and share A standard component definitions.Merge modules are used to delivered the shared code, files,resource.
29. Name Few Merge Module Tables?
Ans:
- ModuleSignature,
- ModuleComponents,
- ModuleDependency,
- ModuleExclusion,
- ModuleIgnore,
- ModuleSubstitution
- ModuleAdminUISequence,
- ModuleAdminExecuteSequence,
- ModuleConfiguration.
30. What Is System Guard?
Ans:
- System Guard tracks and analyses the configuration repositories and sources utilized by application and intercept the usage of those sources, redirecting them to a virtualized times of the sources.
- The Microsoft Soft Grid Application Virtualization (App-V) Platform‘s heart is a System Guard, patented generation which permits applications to run without installing them locally—and without changing a client‘s working system.
31. How To Give Permission to Files, Folders & Registry Keys In a Msi?
Ans:
In the MSI, can give the permissions through the Lock Permission table. But using subinacl exe custom action is the best way to fit the permissions.
32. How To Give Permission to Files, Folders & Registry Keys Through Vb Script ?
Ans:
CACLs should only run on the NTFS partitionsCACLS – Changes Access Control List:
- /T Changes ACLs of a specified files in a current directory and subdirectories
- /E Edit ACL instead of the replacing it
- /C Continue (ignore) access denied errors
- /R user Revoke a specified user access rights (only valid with /E)
33. Detail Background Mechanism Of Merge Module?
Ans:
If there are the number of applications that required a specifically configured component, it would be possible to create a merge module that installs and configures that component. That merge module could then be added to installation packages of each product that required that a specific component. This saves effort of having to individually add important files,registry entries, and the other components to the every installation and installations only need to be rebuilt.
34. How To Disable Arp(add/remove Programs) Details During Insallation?
Ans:
msiexec/iARPSYSTEMCOMPONENT=1
Following entries are the different ARP properties:
- ARPAUTHORIZEDCDFPREFIX
- ARPCOMMENTS
- ARPCONTACT
- ARPINSTALLLOCATION
- ARPNOMODIFY
- ARPNOREMOVE
- ARPNOREPAIR
- ARPPRODUCTICON
- ARPREADME
- ARPSIZE
- ARPSYSTEMCOMPONENT
- ARPURLINFOABOUT
- ARPURLUPDATEINFO
35. What Is Advertisement?
Ans:
It means that, Availability of the application to users or the others with out actually full Installation. There are the two types of Advertising Assigning : An Application appears to the user or the others, when Application is “assigned”. When the user tries to open, it is installed upon a demand. Publishing:No Entry points appear to user or others, when an Application “published” to a group. It is activated only if group Application activates a published Application i.e. Installation on the Demand.
36. What Is Advertised Feature & Component?
Ans:
If Feature or Component is to be advertised, only interfaces required for loading and launching the application are installed to user or others. If a user activates an advertised interface the installer then proceeds to install important Components & Features.
37. What Is Installation On Demand?
Ans:
When the user or application activates the advertised feature or product, The installer proceeds with the installation of the needed components.
38. What Is Transform?
Ans:
A transform is a windows installer file with extension (.MST). It should be used with the MSI to customize or change the installation package without changing a MSI. The installer can only apply transforms during the installation.
39. What Are Types Of a Transform?
Ans:
Embedded transform : Embedded transforms are the saved inside a .msi file of package.
Secured transform : Secured transforms are the stored locally on user’s computer in a location where, on secure file system, the user does not have writeaccess. Such transforms are cached in the location during the installation or advertisement of package. During subsequent installation-on-demand or maintenance installations of package, installer used a cached transforms.
Unsecured transform : Transformsthat have not been secured are called unsecured transforms.To apply unsecured transform, pass the transform file names in the TRANSFORMS property or command line string during the installation.
40. What Are Protocols Supported For Streaming?
Ans:
- RTSP
- RTSPS
- FILE
- HTTP
- HTTPS
41. How Many Transforms Supplied In Command Line?
Ans:
The number of transforms that can be supplied in the command line for application packaging can depend on a specific packaging tool or technology being used. In the context of the software packaging and deployment, a “transform” typically refers to the set of changes applied to the software package during installation. These changes can include the modifications to registry, file system, or other settings to customize installation for a specific scenarios.
42. What Is Custom Action?
Ans:
The Microsoft Windows Installer provides the many built-in actions for performing installation process. For some cases developer writes the action to execute his own installation is called the custom action.
43. What Are Types Of Custom Actions?
Ans:
- DLL file saved in the Binary table stream.
- DLL file that is installed with product.
- EXE file stored in the Binary table stream.
- EXE file that is installed with product.
- Displays the specified error message and returns failure, terminating a installation.
- EXE file having the path specified by property value.
44. What Are Types Of Sequences In Custom Actions?
Ans:
- Normal User Interface.
- Normal Execute a Immediate / Deferred.
- Administrative the User Interface.
- An Administrative Execute Immediate / Deferred.
45. What Are Types Of In Script Options In Custom Actions?
Ans:
- Immediate Execution:
- Deferred an Execution – User Context:
- Rollback only:
- Commit only
- Deferred Execution – System Context
46. Difference Between “immediate Execute / a Deferred Execute”?
Ans:
| Aspect | Immediate Execution | Deferred Execution | |
| Timing of Execution |
Actions are performed immediately during the installation process, often before the installation of files or configuration. |
Actions are scheduled to be executed later, usually after the installation of files or other core components. | |
| Purpose | Typically used for tasks that do not require the presence of installed files or registry entries, such as system checks or property setting. | Used for actions that depend on the installation of files or other components, such as file registration, creating shortcuts, or updating system configurations. | |
| Examples | – Setting properties. – Performing system checks. | – Registering DLLs. – Creating shortcuts. – Updating system configurations. |
47. Difference Between “deferred In System Context / Deferred In User Context”?
Ans:
If Custom action which installs or modify a file under the INSTALLDIR or Installation should be run in the “Deferred in User Context”. If Custom action which installs or edit the system file directly should be run in the “DeferredExecution in System Context”.
48. What Are Types Of Processing Options In Custom Actions And What Is Use?
Ans:
Synchronous : Windows Installer runs the custom action synchronously to major installation. It waits for a custom action to complete successfully before a continuing main installation.
Synchronous,ignore exit code : Windows Installer runs a custom action by synchronously to main installation. It waits for a custom action to finish before continuing the major installation; action can be either success or be fail.
A synch, wait at end of sequence : Windows Installer runs custom action simultaneously with the major installation. At the end it waits for an exit code from custom action before continuing.
49. What Are Types Of Scheduling Options In Custom Actions?
Ans:
Always Execute : This action execute in all the sequences. Run first time: This action execute only for the first time Windows Installer encounters it.
Run once per process : This action execute only a one time either Execute sequence that should not run if installation is running in a silent mode.
Run only if UI sequence was run : This action execute only if either can Execute sequence is run the following User Interface sequence.
50. What Is Launch Condition?
Ans:
A launch condition is the condition or set of conditions that must be met on target system before a software installation or application launch can proceed. Launch conditions are used to check whether a target system meets the certain requirements or has a specific characteristics necessary for successful installation or execution of software.
51. What Is App Search?
Ans:
AppSearch is the feature that involves searching for a specific properties or values on target system during the installation process. This search is typically performed to gather information about system’s configuration, status, or presence of certain components. The results of search can then be used to make decisions or set properties within installation process.
52. What Is Isolated Component, Why Are Using And Its Types?
Ans:
It means to prevent the overwriting of the befoere versions of shared components, and ensures that the other applications do not overwrite the version of shared components.
- Manifest file concept.
- Local file concept.
53. What Is Use Of Msi Assembly Tables?
Ans:
It is used for the registration of the .Net Assembly files. The term “Assembly Tables” in context of MSI (Microsoft Installer) usually refers to the tables related to Windows Assemblies, which are used to manage the shared components and support a side-by-side versioning.
54. What Is Group Policy and How To Set It?
Ans:
Administrators used the Group Policy to explain options for managing, configuration of servers, desktops, and groups of users. It is used to set the policies across a given site, domain, or range of organizational units.Use “gpedit.msc” in the run command to set the policy.
55. What is application package also called?
Ans:
A computer application package, also known as a software suite, is the collection of computer programs that are designed to work together to perform the specific tasks or functions.
56. What Is Conflict Management?
Ans:
When two or more applications can install the same system files (DLLs, .VBXs, and .OCXs), A Windows registry, and the other items. To detect, Conflict Management should used and for resolved a software conflicts, Application Isolation concept should be used.
57. What Are Types Of Deployment (software Distribution)?
Ans:
- Group policy (Active Directory).
- Software Update Services (SUS).
- Windows Update Web site.
- Systems Management service (SMS).
58. What Is Software Distribution?
Ans:
One of the more crucial aspects to managing a Windows environment is the ability to deploying a new applications, updates, upgrades & patches. Distributing the new or updated software is the Software Distribution.
59. Difference between application and application package?
Ans:
An application is the runnable collection of programs. A package is just a collection, not runnable. Also, package may contain a related files and programs. They can be considered as the folder in the computer.
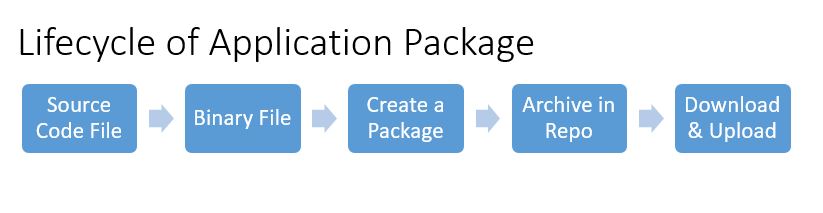
60. What Is Elevated User and How To Create It?
Ans:
If user having a privileges of MSI features (Windows Installer) is called as an Elevated User that can create through the “gpedit.msc” in a run Command or registry keys.
61. What Is Wrapper Msi?
Ans:
A “wrapper MSI” refers to installation package that encapsulates or wraps the another MSI package. This approach is often used in the software distribution and deployment scenarios to provide the additional functionality or customization around installation of primary MSI package.
62. What Is Lock Down Environment?
Ans:
Software restriction policies are provide administrators with a Policy-driven mechanism to identify the software running on computers in the domain, and control its ability to execute. This policy can be used to block the malicious scripts, help lockdown a computer, or prevent unwanted applications from running.
63. What Is Intellimirror?
Ans:
Intelli Mirror management technologies are the set of a powerful features for change and configuration management. It ensures that the users’ data, software, and personal settings are available when they moved from a one computer to the another, and persist when computers are connected to the network.
64. What Is Active Directory?
Ans:
Deploying applications through the Active Directory is done through the use of group policies, and therefore applications are deployed either on per user basis or on per computer basis.
65. What Are Other Tools Used During Testing & Solving problems In Application Packaging?
Ans:
- Picture Taker
- Windows Install Master
- InstallRite
- RegMon
- FileMon
- Procmon
- Process Explorer,/li>
- CsDiff
- Icon Extractor & Icon Builder
66. What Is Orca Tool And Advantages?
Ans:
Orca is the tool provided by Microsoft as part of Windows Installer SDK (Software Development Kit). It is the database table editor for creating and editing Windows Installer packages, particularly for MSI (Microsoft Installer) files.
67. What Is PackageCode?
Ans:
PackageCode is unique identifier assigned to the MSI file. This code is used to differentiate a one version of an MSI package from the another. The PackageCode is crucial for a Windows Installer to determine whether the particular MSI package is update or a completely new installation.
68. What Is Product Code?
Ans:
The ProductCode is the another identifier used in Windows Installer packages (MSI files). Like PackageCode, the ProductCode is a GUID (Globally Unique Identifier), but it serves the different purpose and has a different characteristics. The ProductCode uniquely identifies the particular product as a whole, rather than specific version of a product.
69. What Are Disadvantage/drawbacks Of the Msi?
Ans:
Resiliency : Resiliency can be inconsistent with repackaged applications because repackager utility may not fully understand a component dependencies or what the key paths of application should be. Therefore, an application may be packaged into the one large feature that gets entirely reinstalled if component keypath is missing.
Resiliency : Resiliency can be inconsistent with repackaged applications because repackager utility may not fully understand a component dependencies or what the key paths of application should be. Therefore, an application may be packaged into the one large feature that gets entirely reinstalled if component keypath is missing.
Registration : A Component Object Model (COM) and ActiveX controls not be properly registered. Prior to the Windows Installer, COM and ActiveX registration was black box.
Shortcuts : Shortcuts may not be created as the WindowsInstaller descriptor shortcuts, which enable resiliency. Legacy setup shortcuts were .lnk files that pointed to executable in most cases.
Registration : A Component Object Model (COM) and ActiveX controls not be properly registered. Prior to the Windows Installer, COM and ActiveX registration was black box.
Shortcuts : Shortcuts may not be created as the WindowsInstaller descriptor shortcuts, which enable resiliency. Legacy setup shortcuts were .lnk files that pointed to executable in most cases.
70. What Is Advertisement And Command for Advertisement?
Ans:
It means that, Availability of the application to users or the others with out actually a full Installation.
There are two types of Advertising:
Assigning : An Application are the appears (shortcuts, files & registries) to a user or others, when Application is “assigned”. When user tried to open, it is installed upon demand.
Publishing : No Entry points are the appear to a user or others, when Application “published” to a group. It is activated only if group Application activates a published Application i.e. Installation on Demand.
71. What does Admin Install And Command for It?
Ans:
The Windows Installer can be performed an administrative installation of application or product to a network for used by workgroup. An administrative installation installs a source image of the application onto the network that is similar to the source image on CD-ROM. Users in workgroup who have access to this administrative image can install a product from this source. A user must first install the product from the network to run application.
72. For Which Type Of Packages Admin Install Fail?
Ans:
Any MSI which installs the files based on the selection, be it from a command line. The System Search or a selected options are while installing.
73. What Is a Transaction Processing?
Ans:
One or more operations are the processed together as a single indivisible whole called transaction. All constituent operations must succeed for transaction to succeed, otherwise all operations are rolled back to original state. Windows Installer 4.5 includes support for installing multiple packages using a transaction processing. The packages are the chained together and processed as single transaction. If one or more of packages in a transaction cannot be installed successfully or if end user cancels are the installation, Windows Installer initiates rollback for all of the packages to restore system to earlier state.
74. What Is Dll Cache Folder?
Ans:
The DLL Cache folder, also known as “DLL Cache” or “File Protection” folder, is the system folder in Microsoft Windows that is designed to store backup copies of critical system files. This feature is part of a Windows File Protection (WFP) mechanism, which is designed to prevent overwriting or deletion of essential system files by the unauthorized or incorrect installations.
75. What Are Addlocal And Addsource Properties?
Ans:
ADDLOCAL : It will install the components (file resources) associated with the feature locally on client the package is to be installed on.
ADDSOURCE : The files will “installed” on a source meaning where MSI is to be originally located. There will be actually not be any installation of files into a folder but must exists as “external uncompressed”
76. What is Use Of Installevel Property?
Ans:
The INSTALLLEVEL property is the initial level at which features are selected “ON” for installation by a default. A feature is installed only if value in Level field of a Feature table is less than or equal to the current INSTALLLEVEL value. The installation level for the any installation is specified by a INSTALLLEVEL property, and can be integral from 1 to 32,767.
77. Difference Between Run, Run Once, Active Setup?
Ans:
Active Setup : It is used when application required an installation of the components like files or registry keys on per-user basis, but application has no advertised entry points or other triggers to initiate installation process
Run : The Run key is processed are after every logon, either by Explorer shell, if it is present, or by First Boot Agent (FBA), if a custom shell, Command shell, or Task Manager Shell is to be used. If FBA processes this key, it does so after every log on, not during first boot as it normally would. Typically, this flag is used to load Systray applications, launch services in executables, hide autostart applications, or hide a background processes
Run Once : The RunOnce key is to be processed only a once, by FBA, after Plug and Play device enumeration and DLL registration processing have finished . The values of registry key are deleted from the registry after it is processed, so that it will not run again. Typically, this flag is used to when reboot is required, such as for DLL or OCX registration, or for cleaning up setup or an uninstall.
78. What Is a Logical Structure Of Package?
Ans:
A package explains installation of full product is universally identified by GUID. A product is made up of the components, grouped into the features.
Components : A component is the minimal part of product—every component is treated by Windows Installer as unit: the install developer cannot, for example, use the condition to specify to a install just part of component.
Features : A feature is hierarchical group of components—a feature can contain the any number of be components and the other features.
79. What do with application packaging and virtualisation degree?
Ans:
Application packaging and virtualisation professionals are the find employment as engineers across the different companies in tech industry. They can encounter that test their ability to help the businesses manage digital workplaces and ensure that applications function optimally.
81. What is App Search?
Ans:
- High Support Costs.
- Fragile Installs & uninstalls.
- Difficult & labor a Intensive to deploy.
82. What is Patch?
Ans:
Patching is the streamlined process for updating earlier versions of the Windows Installer setup package i.e. when update only files that already exist in installation package. Only the package code is to changed.
83. What is Upgrade?
Ans:
Upgrade is the process of updating the earlier versions of the Windows Installer setup package . But product code, product version & package code should be changed.
84. What are types of Setup Captures Methods in Wise / Install shield?
Ans:
In Install Shield there are the two types :
Installation Monitor : Repackager watches lower-level system activities and records are related changes made to system by a setup(s) programs.
Snapshot : Scan the computer before and after installation and record differences between the first scan and second.
85. List out benefits of Windows installer?
Ans:
- Advertising
- One of the best feature where can installation be done in demand
- Repair itself
- Rollback option
- Managed shared resources
86. What is file association?
Ans:
Within the Windows operating system, it is the routine that file types are associated with the type of extensions they have. So operating system identifies the file types and links them back to a programs based on file extension they possess. A file that doesn’t have the any file extension nor don’t have any association with the files then they are classified as orphans.
87. What is merge module?
Ans:
A merge module is nothing but the process within the windows installer where it allows the different companies to pre-package certain standard components and definitions into a one single file. A merge module comes into the existence where it needs to deliver the shared code or shared files or shared resources while setup process from single compound file.
88. What Is Difference Between Mnt And Vfs Sequencing?
Ans:
MNT Sequencing : If utility is established to a Mount Drive (the Drive assigned for App V packages) at a time of set up within the process of sequencing (set up monitoring) is known as the MNT Sequencing.
VFS Sequencing : Some of the software does no longer provide a risk to change the installation route other than C: power, for the ones applications App V Sequencer monitors the installation and facts modifications performed to a device drive and creates the parse file machine within Virtual Environment called VFS (Virtual File System) Sequencing.
89. What Is Dsc?
Ans:
DSC is a Dynamic Suite Composition, is the feature presents the ability to have the brand new layer of interoperability, virtualized applications dependencies, in which one App-V bundle depends on and interacts with the every other App-V bundle.
90. What Is App-v Sequencing?
Ans:
The technique of creating the virtualized package deal usage of App-V sequencer is known as the App-V sequencing. The Microsoft Application Virtualization (or App-V) Sequencer is the part of App-V suite used to package deal the programs to be deployed to systems the usage of App-V patron. Properly sequencing programs is a key to a hit App-V implementation.






