
- What is Grey Box Testing?
- Why Grey Box Testing is Important
- Characteristics of Grey Box Testing
- Grey Box vs Black Box vs White Box
- Techniques Used in Grey Box Testing
- Advantages of Grey Box Testing
- Disadvantages and Limitations
- Tools for Grey Box Testing
- Applications in Software Development
- Role of Testers in Grey Box Testing
- Real-world Case Studies
- Future of Grey Box Testing
What is Grey Box Testing?
Software testing is an integral part of the software development lifecycle (SDLC), ensuring that applications perform as expected, meet security requirements, and provide a seamless user experience. Among the various Software testing methodologies, Grey Box Testing stands out as a hybrid approach that combines the techniques of both black box and white box testing. In this model, the tester has partial knowledge of the internal structure or code of the application but still conducts tests from the end user’s perspective. This combination allows testers to design test cases that are more efficient, cover a broader range of scenarios, and identify issues that might not be visible through purely black or white box approaches. Grey Box Testing bridges the gap between functionality testing and structural testing, offering a balance of practicality and thoroughness.
To Earn Your web developer Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Web Developer Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Web developer courses Today!
Why Grey Box Testing is Important
Grey Box Testing plays a critical role in modern software development for several reasons. Firstly, it helps uncover hidden defects that might be missed in black box testing due to limited knowledge of the system’s internal workings. Secondly, it reduces the risk of bias present in white box testing by keeping the tester partially unaware of the full codebase. The method is particularly valuable in scenarios where security vulnerabilities, integration issues, or workflow inconsistencies need to be tested. Since testers understand some internal structures, they can craft more intelligent test cases, thereby improving test coverage. For businesses, Grey Box Testing helps ensure that applications not only function correctly for users but are also structurally sound, enhancing reliability and reducing long-term costs much like how Inheritance in C++ promotes code reusability and structural efficiency in software development.
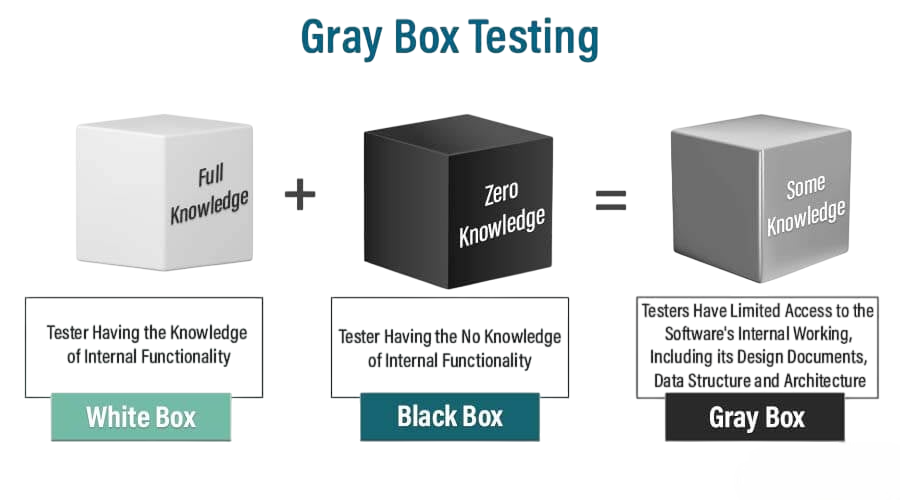
Because it incorporates the advantages of both Black Box and White Box testing methodologies, Grey Box Testing is significant. It enables testers to verify the system’s operation and conduct a cursory analysis of its internal structures or algorithms. This technique assists in locating inefficient code routes, integration problems, and security flaws that conventional testing techniques could miss. Grey Box Testing enhances the overall quality and dependability of software by offering a fair assessment of its internal logic and performance.
Characteristics of Grey Box Testing
Grey Box Testing is defined by several unique characteristics:
- Partial Knowledge – Testers know some of the system’s internal design, architecture, or algorithms but not everything.
- Combination of Methods – It uses a blend of white box (structural) and black box (functional) techniques.
- Focus on End-User Perspective –While testers may know some internal aspects, they often still evaluate from a user’s point of view, a perspective emphasized in many of the Best Software Engineering Courses
- Improved Test Coverage – It bridges the gap between functional and structural testing, covering a wider scope.
- Detects Contextual Issues – Helps uncover problems related to data flow, integration, and improper use of internal components.
- Risk-based Approach – Often applied to high-risk areas like security, middleware, APIs, or critical modules.
These features make Grey Box Testing versatile and adaptable to real-world software testing needs.
Would You Like to Know More About Web developer? Sign Up For Our Web developer course Now!
Grey Box vs Black Box vs White Box
To understand Grey Box Testing, it’s essential to compare it with the other two primary methodologies:
- Balanced Approach: Combines the strengths of both black and white box testing.
- Efficient Test Design: Partial knowledge allows better targeted test cases.
- Improved Coverage: Addresses functional, structural, and integration aspects.
- Early Bug Detection: Identifies hidden issues missed by traditional approaches.
- Cost-Effective: Reduces expensive post-release bug fixes by improving pre-release quality.
- Security Testing: Helps identify vulnerabilities in authentication, data flows, and API endpoints.
- Incomplete Knowledge: Testers still lack full insight into the codebase, which might miss deep structural flaws.
- Time-Consuming: Designing intelligent test cases requires more effort compared to black box testing.
- Limited by Documentation: Quality depends on how much internal knowledge is shared with testers.
- Not Comprehensive: Cannot replace full white box or black box testing in certain critical systems.
- Skill Requirement: Testers must have both programming knowledge and functional understanding.
- Selenium – For functional and UI testing of web applications.
- Postman/SoapUI – For API testing and data flow validation.
- Burp Suite – For penetration and security testing.
- JMeter – For performance and load testing.
- Appium – For mobile application testing.
- Wireshark – For analyzing data packets and network behavior.
- NUnit/JUnit – For unit testing with partial structural awareness.
- Web Applications – To validate business logic, API integration, and workflows.
- Mobile Applications – For functionality, performance, and backend service validation.
- Middleware and APIs – To ensure data flow and protocol handling are correct.
- Security Testing – Detecting vulnerabilities in login systems, access controls, and session handling.
- Cloud Applications – For testing services, configurations, and communication between distributed components.
- E-commerce Platforms – Ensuring checkout flows, payment gateways, and order management are secure and functional.
Black Box Testing: The tester has no knowledge of internal workings and tests purely from the user’s perspective. Focus is on input-output validation.
White Box Testing: The tester has complete knowledge of the source code, algorithms, and architecture, emphasizing structural correctness and code coverage concepts often covered in advanced MTech Courses .
Grey Box Testing: The tester has partial knowledge of the internal system. It combines the functional testing of black box with the structural insights of white box, ensuring better coverage.
In short, black box is “blind,” white box is “transparent,” and grey box is “translucent.”
Techniques Used in Grey Box Testing
To properly do Grey Box Testing, a number of strategies are employed. Matrix testing is a popular technique that aids in determining and evaluating the connections between various variables or system components. Another strategy is pattern testing, which looks for recurring patterns or anomalies to reveal hidden flaws. Regression testing with internal knowledge is another tool that testers employ to evaluate software updates and modifications while comprehending how they affect internal modules. By using statistical methodologies, Orthogonal Array Testing increases process efficiency by achieving maximum test coverage with a small number of test cases. Furthermore, Finite State Machine Testing verifies appropriate behaviour by ensuring that the system moves between states correctly.In order to guarantee seamless communication and data sharing, API testing lastly looks at the integration points between software components, a topic often explored in M.Sc in Computer Science programs. When combined, these methods enable testers to create more intelligent tests, increase productivity, and raise the rate of fault identification.
Advantages of Grey Box Testing
Grey Box Testing provides numerous benefits to organizations and testers:
Are You Interested in Learning More About FullStack With Web developing? Sign Up For Our Web developing Today!
Disadvantages and Limitations
Despite its benefits, Grey Box Testing has limitations:
These limitations highlight that Grey Box Testing should complement, not replace, other Software testing strategies.
Tools for Grey Box Testing
Several tools support Grey Box Testing, depending on the type of testing being performed:

The choice of tool depends on the application type, testing requirements, and industry.
Preparing for Web developer Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on Web developer Training Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Applications in Software Development
Grey Box Testing finds wide application across industries and development environments:
Its versatility makes it particularly useful in Agile and DevOps environments where testing needs to be fast, effective, and iterative, aligning with concepts taught in Latest Technologies in Computer Science .
Role of Testers in Grey Box Testing
In Grey Box Testing, testers are essential and need to have a certain set of hybrid abilities. Strong technical abilities are required, such as a comprehension of APIs, programming, and database query execution. To create relevant test cases based on limited system knowledge and analyse incomplete information, analytical abilities are also crucial. In order to ensure that testing is in line with practical applications, testers who possess a strong foundation in domain knowledge are better able to comprehend business logic and workflows. In order to guarantee comprehensive testing coverage, Grey Box testers collaborate closely with developers, security teams, and product managers.Clear and thorough reporting is also essential; testers need to precisely record errors and offer insights from the viewpoints of the internal system and users, similar to how Sparse Matrix Concepts help efficiently represent and analyze data in computational systems. All things considered, grey box testers play a crucial part in balanced and successful testing by acting as a link between black box testers, who concentrate on the user experience, and white box testers, who focus on internal code and logic.
Real-world Case Studies
E-commerce Platform: A retail company used Grey Box Testing to test its payment gateway. Testers, knowing the encryption method but not the entire code, discovered flaws in token handling that could allow replay attacks.
Banking Application: Testers used Grey Box techniques to check session management. They found vulnerabilities where inactive sessions were not being properly terminated, which could lead to account hijacking an important concept to understand when you Learn Coding Online with Top Programming Courses
Healthcare Application: In an electronic health record system, Grey Box Testing revealed data leakage between user roles by analyzing API calls with partial knowledge of the database schema.
These examples show how Grey Box Testing can detect subtle yet critical flaws.
Future of Grey Box Testing
The future of Grey Box Testing looks promising as systems grow more complex. With the rise of cloud computing, microservices, and APIs, having partial insight into the system while simulating real-world usage becomes increasingly valuable. Automation tools are evolving to better support Grey Box methodologies in Software testing by combining code analysis with user simulation.Additionally, as cybersecurity threats grow, Grey Box Testing will become essential in simulating how attackers with limited knowledge exploit vulnerabilities. Integration with AI and machine learning will further enhance the efficiency of test case design and defect detection. In short, Grey Box Testing is expected to remain a vital approach in ensuring software reliability, security, and quality.



