
- Basics of Cyber Security
- Importance in Today’s Digital World
- Career Opportunities
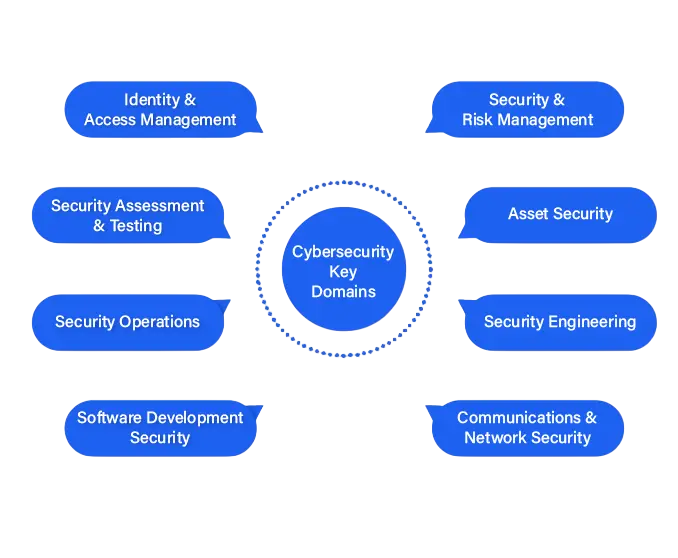
- Domains of Cyber Security
- Cyber Threat Landscape
- Cyber Security in Enterprises
- Role in Government & Defense
- Cyber Laws and Regulations
- Certifications & Courses
- Future of Cyber Security
- Challenges in the Field
- Conclusion
Basics of Cyber Security
In today’s digital-first world, almost every aspect of life is connected to technology be it online banking, e-commerce, cloud storage, social networking, or government services. With this growing dependence on technology comes a parallel rise in cyber threats, making cyber security one of the most critical fields of our time. Cyber security can be defined as the practice of protecting computer systems, networks, and data from theft, damage, and unauthorized access. It is not merely about installing antivirus software or firewalls; instead, it involves a holistic approach that combines technology, processes, Cyber security training , and human awareness. As cybercriminals become more sophisticated, organizations and individuals must adopt robust security measures to prevent financial losses, reputational damage, and disruptions to critical services. Protecting computers, servers, mobile devices, networks, and data from harmful assaults, illegal access, or damage is known as cyber security. The technique of preventing unwanted access, attacks, or damage to computers, networks, and data is known as cyber security. It guarantees the dependability, security, and privacy of digital data. In order to protect digital systems and data, a variety of technologies, procedures, and practices are used.
To become a certified cyber security, have a look at our Cyber Security Online Training right now.
Importance in Today’s Digital World
The importance of cyber security cannot be overstated. Digital transformation has accelerated the shift of businesses, governments, and individuals to online platforms, exposing sensitive data such as personal details, financial records, and intellectual property to cyber threats.
- From ransomware attacks targeting healthcare systems to phishing scams tricking individuals into revealing passwords, cybercrime has become more dangerous than ever.
- The rise of cloud computing, Internet of Things (IoT), and remote work environments further expands the attack surface, giving hackers more entry points.
- Cyber security ensures confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information systems, which are fundamental to trust in the digital ecosystem, and learning How To Become A Penetration Tester is one pathway to contribute to this security.
Without adequate security, innovation and growth in the digital economy would come to a standstill. Because it shields organisational and personal data from online dangers like ransomware, phishing, and hacking, cyber security is essential in today’s digital environment. It ensures that governments and corporations run smoothly, protects privacy, and guards against financial loss. Cybersecurity promotes safe digital growth and innovation by protecting vital systems and fostering confidence in online services. Strong cyber defence is crucial for security, stability, and advancement in today’s interconnected society.
Career Opportunities
One of the biggest attractions of cyber security is its vast career scope. As cyber threats increase, so does the demand for skilled professionals who can prevent, detect, and respond to them. According to industry reports, there are millions of unfilled cyber security jobs worldwide, making it one of the fastest-growing career fields, where understanding threats like What is Spyware is essential for professionals. Roles include security analysts, penetration testers, ethical hackers, security consultants, network security engineers, incident response specialists, cryptographers, and Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs). These jobs are not restricted to the IT sector; industries such as finance, healthcare, retail, energy, and defense all require cyber security expertise. Furthermore, cyber security professionals enjoy high salaries, global opportunities, and the chance to work on cutting-edge technologies like AI and blockchain for security applications.
Domains of Cyber Security
Cyber security is not a single discipline but a collection of interrelated domains. Network security focuses on protecting data as it travels across networks. Application security ensures software and apps are designed securely to prevent exploits. Endpoint security protects devices such as laptops, smartphones, and IoT gadgets from cyber threats. Another crucial domain is identity and access management (IAM), which ensures that only authorized individuals have access to systems and data. Additionally, fields like cryptography, incident response, security operations centers (SOC), and digital forensics are specialized domains that professionals can pursue.
- Cybersecurity encompasses a number of important areas that cooperate to safeguard data and digital infrastructure, including securing communications through a Virtual Private Network.
- Network security protects communication channels and networks against intrusions and assaults.
- Application security guarantees that programmes and software are shielded from flaws both during development and operation.
Data availability, confidentiality, and integrity are the main goals of information security. Data and services housed in cloud environments are protected by cloud security. Endpoint security guards against attacks on end-user devices, such as PCs and smartphones. Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity make ensuring that systems can promptly recover from cyber events, while Operational Security (OpSec) oversees how data is managed and safeguarded within an organisation.
Cyber Threat Landscape
The cyber threat landscape is constantly evolving, driven by technological innovation and the ingenuity of cybercriminals. Common threats include malware, phishing, ransomware, denial-of-service attacks, and zero-day exploits. State-sponsored cyberattacks have also become more frequent, targeting critical infrastructure such as power grids and government databases, highlighting the importance of Ethical Hacking Projects in identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities. The rise of IoT has opened the door to new vulnerabilities, as many connected devices lack strong security mechanisms. Similarly, deepfakes and AI-driven attacks are on the rise, challenging existing defenses. Understanding the cyber threat landscape is crucial for both individuals and organizations to stay proactive in implementing effective defenses. Threat intelligence, which involves gathering data on emerging threats, plays a vital role in predicting and preventing future attacks.
Are you curious to know more about Cybersecurity ? Take advantage of our comprehensive online Cyber Security Online Training
Cyber Security in Enterprises
Enterprises are prime targets for cyberattacks due to the vast amount of sensitive data they handle. A single breach can cost millions of dollars and cause long-term reputational harm. Hence, businesses across industries are investing heavily in cyber security strategies. Enterprise security includes risk assessment, vulnerability management, data protection, compliance with regulations, and employee training. Companies use layered defenses such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, encryption, and advanced endpoint protection. With remote work and hybrid models becoming common, enterprises are also focusing on securing virtual private networks (VPNs) and cloud infrastructure, while taking Deep Dive into Symmetric and Asymmetric Cryptography to strengthen data protection.
- Additionally, many organizations now have dedicated Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) and security teams to manage enterprise-wide security policies and incident response.
- Cyber Security plays a crucial role in enterprises by protecting business data, networks, and systems from cyber threats that can disrupt operations or cause financial and reputational damage.
- Enterprises handle vast amounts of sensitive information such as customer details, financial records, and trade secrets which makes them prime targets for hackers.
Effective enterprise cyber security involves implementing firewalls, encryption, access controls, and regular security audits to detect and prevent attacks. It also includes employee training to reduce risks from phishing and human error. By investing in strong cyber security measures, enterprises ensure business continuity, protect customer trust, and comply with legal and regulatory requirements.
Transform Your Career with Cyber Security Knowledge Enroll in ACTE’s Cyber Security Expert Masters Program Training Course Today!
Role in Government & Defense
Cyber security is equally critical in government and defense sectors. Governments are responsible for protecting sensitive national data, critical infrastructure, and citizens’ personal information. Defense organizations must secure military communication networks, weapons systems, and intelligence operations against cyber espionage and sabotage. Many countries have established dedicated cyber defense agencies, such as the U.S., to enhance Cyber security training and protect critical national infrastructure. Cyber Command and India’s National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC). Cyber warfare, where nations engage in digital attacks against each other, has become a modern reality. As a result, governments are investing in cyber security research, training, and international cooperation. Cyber security is not only a defensive measure but also a strategic tool in modern geopolitics.
Cyber Laws and Regulations
With the rise of cybercrime, laws and regulations have been developed worldwide to ensure accountability and compliance. For example, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union sets strict rules for how organizations handle personal data. In the U.S., laws such as the Cybersecurity Information Sharing Act (CISA) and industry-specific regulations like HIPAA for healthcare ensure compliance with security practices. India has its Information Technology (IT) Act that governs cybercrimes and electronic transactions. Organizations failing to comply with these regulations face heavy penalties and reputational damage.
- Cyber laws and regulations are legislative actions intended to shield people and institutions from online and computer-based criminal activity.
- They cover topics including hacking, data theft, identity fraud, cyberbullying, and online privacy while defining guidelines for the ethical and secure use of digital technologies, including courses like Ethical Hacking With Python .
- These laws aid in the prosecution of cybercriminals and guarantee responsibility.
To protect digital activity, governments all over the world have put in place a number of frameworks, including the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, the Information Technology (IT) Act, 2000 in India, and other national laws. Countries uphold user rights, encourage safe online spaces, and foster confidence in online transactions by implementing these laws.
Certifications & Courses
Cyber security certifications are a vital way for professionals to demonstrate their expertise and gain credibility in the job market. Some of the most recognized certifications include Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH), CompTIA Security+, Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP), Certified Information Security Manager (CISM), and Offensive Security Certified Professional (OSCP). For beginners, courses in network fundamentals, Linux, Python programming, and Enumeration in Ethical Hacking provide a strong foundation. Many universities now offer degree programs in cyber security, while online platforms like Coursera, Udemy, and Cybrary provide flexible learning options. Continuous learning is essential in this field since technologies and threats evolve rapidly. By combining academic knowledge, certifications, and practical experience through labs and projects, professionals can build a strong career in cyber security.
Preparing for a job interview in cybersecurity ? Examine our blog post about Cybersecurity Interview Questions and Answers to get the most of your employment experience!
Future of Cyber Security
The future of cyber security is both exciting and challenging. Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, blockchain, and quantum computing are expected to revolutionize the field. AI can be used to detect anomalies and respond to threats in real-time, while blockchain provides enhanced transparency and security in transactions.
- Cyber security will also expand into new frontiers such as securing autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and space missions.
- The future scope of cyber security thus promises innovation, global demand, enhanced Endpoint Security , and a continuous battle against evolving threats.
- Rapid technological breakthroughs and the growing sophistication of cyber threats will influence the direction of cyber security in the future.
As cloud computing, the Internet of Things, and artificial intelligence (AI) continue to grow, new vulnerabilities will emerge, calling for stronger and more sophisticated countermeasures. The ability of future security systems to recognise and respond to threats instantaneously will be greatly aided by AI and machine learning. Quantum computing has the potential to transform encryption, increasing the complexity and strength of data protection. Additionally, there will be a greater focus on automation, data privacy, and international cooperation to combat cybercrime.
Challenges in the Field
Despite its immense importance, cyber security faces several challenges. One of the most pressing issues is the shortage of skilled professionals, with millions of vacancies globally. Another challenge is the rapid evolution of cyber threats, where attackers often stay a step ahead of defenders. Budget constraints in organizations can limit the adoption of advanced security solutions. Additionally, human error remains a major vulnerability, as many breaches occur due to employees falling victim to phishing or weak password practices, even when organizations implement Ipsec Internet Security . Balancing usability and security is also a persistent challenge, since overly strict measures can hinder productivity. Furthermore, maintaining compliance with multiple regulatory frameworks across regions adds complexity to the field. Addressing these challenges requires collaboration among governments, enterprises, and academia to develop innovative solutions and training programs.
Conclusion
The scope of cyber security is vast and continues to expand as technology evolves. From safeguarding individual users against phishing scams to protecting entire nations from cyber warfare, cyber security plays a crucial role in maintaining trust and stability in the digital age. It offers diverse career opportunities across industries, supported by globally recognized certifications, Cyber security training , and other professional development programs. The field is driven by technological innovation, yet challenged by evolving threats and workforce shortages. In the future, cyber security will intersect with AI, blockchain, and quantum computing, opening new avenues for innovation and defense. For students, professionals, and organizations, investing in cyber security knowledge and infrastructure is no longer optional it is a necessity. As the digital world continues to grow, cyber security will remain one of the most important and rewarding domains of the 21st century.





