
- Introduction
- Why Mobile Security is Important
- Types of Mobile Security Threat
- Key Components of Mobile Security
- Best Practices for Mobile Security
- Mobile Security for Enterprises
- Emerging Trends in Mobile Security
- Conclusion
Mobile security is essential to protect personal information, data, and devices from cyber threats like hacking, malware, and theft. It encompasses various security measures, such as device encryption, secure app management, and safe browsing. Types of mobile security include network security, application security, and data protection, each aimed at safeguarding different aspects of a device’s use. To ensure that employees are well-prepared to handle these security measures effectively, Cyber Security Training Courses can provide essential knowledge and skills to prevent security breaches and protect sensitive information on mobile devices. Best practices for mobile security involve setting strong passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, regularly updating software, using trusted apps, and avoiding unsecured Wi-Fi networks to reduce vulnerabilities and ensure the safety of mobile data.
To Explore Cybersecurity in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Cyber Security Online Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Introduction
In today’s era of digitization, mobiles are used for personal and professional needs. With the increasing dependency of people on smartphones and tablets for communication, banking, shopping, and working purposes, the need for a secure mobile has become vital in this era. According to this, as usage increased, security threats targeting these devices also surged forward and posed threats through data breaches, malware, and unauthorized access. Practicing Cyber Hygiene is essential to mitigate these risks and maintain device security. This blog explores the importance of mobile security, the different forms of security threats, and some best practices to protect mobile devices from cyber attacks. Understanding these things can better help users protect personal and professional data while keeping mobile devices intact.
Why Mobile Security is Important
Mobile security is critical since smartphones and tablets carry enormous amounts of sensitive personal and professional information, making them high-value targets for cybercriminals. The use of mobile devices for banking, shopping, social media, and business communications has exposed users to a wide range of security risks.
A breach can result in identity theft, financial loss, unauthorized access to corporate data, and a compromised personal reputation. Mobile security is essential to prevent data theft, secure transactions, and maintain privacy for both individuals and organizations.
Types of Mobile Security Threat
Malware and Viruses are malicioSoftwareare intended to disrupt, damage, or gain unauthorized access to mobile devices. Some common types include trojans, spyware, and ransomware.
- Phishing Attacks: They are fraudulent attempts to gain access to sensitive information, such as passwords or credit card details, by pretending to be a trusted entity and usually through deceptive emails or messages.
- Network-Based Threats: These attacks take place over insecure networks, including Wi-Fi spoofing or man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks, where data can be intercepted during the transmission process.
- App-Based Threats: Malicious or poorly designed apps that compromise device security by collecting data or spreading malware, often due to inadequate vetting from app stores.
- Physical Device Theft: When a mobile device is stolen or lost, unauthorized individuals may access the data stored on the device, especially if proper security measures, such as encryption or biometric authentication, are not in place.
- SIM Card Swapping: A method by which cybercrooks hijack a victim’s phone number, usually to intercept Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) codes and access accounts.
- Device Security: Encryption, a secure boot process, and biometric authentication, which includes a fingerprint or face recognition facility, ensures that data stored within the device is protected as well as access to only authorized users.
- App Security: Secure mobile applications are ensured using code review, encryption, and download from authenticated sources like official app stores to prevent malware and data leaks.
- Network Security: Protecting mobile devices from insecure networks through tools like Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) and secure Wi-Fi connections is crucial for safeguarding data while in transit.
- Data Protection: Encryption and remote wipe features are crucial for mobile security. Cyber Security Training Courses help employees understand and implement these protections effectively.
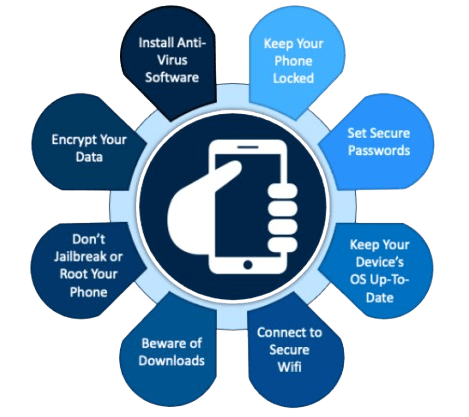
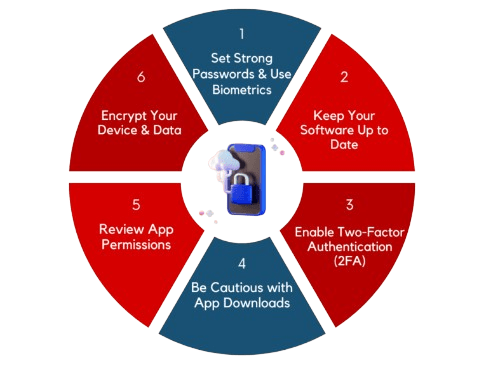
- Keep SoftwSoftwareted: Update mobile operating systems and apps to patch vulnerabilities that attackers might exploit.
- Use Strong Passwords and Authentication: For added security, set strong, unique passwords and enable multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- Install Apps from Trusted Sources: Download apps only from official app stores (Google Play or Apple App Store) to minimize the chances of malware.
- Enable Device Encryption: Ensure that your device has Encryption in Network Security storage to prevent access to sensitive data.
- Enable Remote Lock and Wipe: Be sure to enable remote lock and data wipe for any device that may be lost or stolen to prevent unauthorized data breaches.
- Avoid Performing Sensitive Transactions over Public Wi-Fi: Use a VPN or avoid performing tasks that require sensitive information to access when using unsecured public Wi-Fi.
Interested in Obtaining Your Cyber Security Certificate? View The Cyber Security Online Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Key Components of Mobile Security
Best Practices for Mobile Security
Gain Your Master’s Certification in Cybersecurity by Enrolling in Our Cyber Security Expert Masters Program Training Course.
Mobile Security for Enterprises
Mobile Device Management Companies should adopt MDM solutions to enforce security policies, remotely manage devices, and protect employee mobile devices from accessing company data. Employee training should include best practices related to mobile security, such as avoiding phishing attacks, using secure Wi-Fi, and keeping the device secure. Awareness of threats like a Watering Hole Attack is also essential, as attackers may target specific websites to compromise devices and steal sensitive information. Secure App Development Business houses should develop apps by thinking about security, adhering to secure coding practices, avoiding data leakage, and incorporating robust encryption. Policy enforcement Enforces standards of mobile security company-wide, such as encryption, password protection, and observance of data protection laws.
Emerging Trends in Mobile Security
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are increasingly used in real-time anomaly detection to identify new threats. The Zero Trust Security Model is a new popular approach to mobile security that assumes nobody is trusted by default, even within the network perimeter. With the rise of Malware Attacks, increased encryption techniques are being developed for both stored and transmitted data to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access. Biometric authentication, such as voice and facial recognition, continues to evolve in ways that will provide increased security and convenience to authenticate users.
Are You Preparing for Cyber Security Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Cyber Security Interview Questions and Answers to Boost Your Preparation!
Conclusion
These devices are being increasingly utilized in our personal and professional lives, making securing them a crucial step. To fully protect personal data and maintain privacy, one needs to be aware of mobile security and its various threats while embracing best practices. Mobile security is at the core of the overall Cyber Security Training Courses strategies for enterprises, and recent emerging technologies such as AI, as well as zero-trust models, are going to shape the near future of mobile security; thus, users and organizations remaining informed and proactive will drastically reduce the risk of exposure to mobile security breaches or breaches of data.





