
- What is a DDoS Attack?
- How DDoS Attacks Work
- Common Types DDoS Attacks
- Impact of DDoS Attacks
- Identifying a DDoS Attack
- Mitigating and Preventing DDoS Attacks
- DDoS Attack Trends and Future Threats
- Case Studies: DDoS Attacks in Action
- Conclusion
- The attack on GitHub (2018): At 1.35 Tbps, GitHub was the biggest code hosting platform hit by the record-breaking DDoS. Using Memcached amplification, attackers generated monster volumes of traffic.
- Dyn Attack (2016): Most notable among these is the attack on DNS provider Dyn, which incidentally took down major websites like Twitter, Reddit, and Spotify. The botnet utilized in that attack consisted of connected IoT devices, including webcams and routers.
- Volumetric Attacks cause massive: traffic to a target’s bandwidth. They are usually the most common and depend on very large packets of data to flood the system. Some examples of volumetric attacks include UDP floods and DNS amplification attacks.
- Protocol-Based Attacks: These attacks target flaws in networking protocols with the aim of draining device resources such as routers and Firewall and Antivirus Software. They include Ping of Death assaults and SYN floods.
- Application Layer Attacks: These attacks target the software or application layer. They mainly mimic legitimate traffic coming from legitimate users. They can sometimes be challenging to detect as they seem normal traffic, but they consume a lot of server resources. The best examples of these are HTTP floods and Slowloris attacks.
- UDP Floods: The attackers send many UDP packets to the target server’s random ports. The server responds to all packets, thereby consuming bandwidth and server resources.
- DNS Amplification: An attacker uses misconfigured DNS servers to flood traffic toward the target. The attacker sends minimal DNS queries that eventually trigger responses on the DNS servers. The reactions tend to be voluminous, overwhelming the target.
- SYN Flood: In this form of attack, the number of SYN requests is flooded towards TCP connections that an attacker never completes the handshake, thus leaving the server in a half-open connection that allows no proper processing of subsequent legitimate requests.
- Ping of Death: The attacker sends malformed ping packets that exceed the maximum allowed size and cause a buffer overflow or another system failure on the target.
- HTTP Floods: Attackers send many HTTP requests to a web server to mimic legitimate traffic. It can be programmed to consume resources and slow the server’s response times to real users.
- Slowloris: The attacker keeps many HTTP connections open and sends incomplete requests, waiting indefinitely and taking up all its resources.
- Lost Revenue: The sales or missed opportunities for e-commerce sites and other online services are affected whenever their platforms become unavailable during an attack.
- Recovery Expenses: After an attack has been identified, an organization can be forced to engage security experts, pay protection services against DDoS attacks, and take all necessary measures to restore its services.
- Legal Penalties: Some organizations will also face legal liabilities for not protecting the system to its fullest potential or breaching data protection legislation.
- Slower website performance: a sudden slowdown in site speed or responsiveness.
- Increased Network Traffic: This traffic mostly comes from unexpected or foreign locations.
- Service outages: complaints that users are unable to access services or websites.
- Traffic Monitoring Tools: Utility monitors like Wireshark or Nagios can look for unusual traffic spikes and other anomalies that could indicate a distributed denial of service attack.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): These attacks target the OSI model’s application layer, such as services involved in web servers and databases playing a crucial role in Threat Intelligence by detecting and mitigating potential threats before they cause significant damage to the network.
- Software Upgrades: Software upgrades help prevent the exploitation of known vulnerabilities by closing security gaps. Vulnerability Management ensures systems stay updated, reducing the risk of attacks.
- Redundancy and Load Balancing: Multiplexing traffic or load to various servers or even cloud-based infrastructures may minimize the impact of a distributed denial of service attack.
- Rate Limiting: Activating rate-limiting controls could prevent servers from being overwhelmed with too many requests.
- Cloud-Based DDoS Mitigation: Cloudflare, Akamai, and AWS Shield all offer scalable solutions that absorb the traffic of an impending DDoS attack before it can reach the target server.
- Firewalls and Load Balancers: The rules at the firewall level are specific to DDoS, whereas load balancers help significantly minimize the chances of malicious traffic flooding the system.
What is a DDoS Attack?
A Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attack is maliciously intended to interfere with a website, server, or network’s regular operation by using a flood of traffic to overwhelm it. Unlike a traditional Denial-of-Service (DoS) attack from a single source, in Cyber Security Training Courses, the attack can come from compromised devices worldwide that can create a tremendous amount of traffic, hence way tougher to block. Its primary objective is to drain the target’s resources so the site or service becomes unavailable to legitimate users. The sophistication and frequency of DDoS attack tool are increasing as more business entities and individuals rely on online services. Such attacks can lead to protracted service outages, revenue loss, and harm to an organization’s reputation.
To Earn Your Cyber Security Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Cyber Security Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Cyber Security Online Training Today!
Why Are DDoS Attacks So Seriously?
DDoS service pose a significant risk to enterprises worldwide. These attacks don’t need to breach systems or steal data; instead, they overwhelm services with traffic, causing disruption. DDoS-for-hire services now make it easier for cybercriminals and hacktivists to launch attacks. This underscores the importance of Network Penetration Testing, as organizations must stay vigilant and informed to prevent and mitigate such threats. The impact can be brutal for organizations. They must face extended downtime, a probable violation of customer trust, and all the expenses of recovery and mitigation. As new techniques of DDoS attacks continue to surface, businesses must take preventive measures to win this ongoing battle.
Real-Life Examples of DDoS Attacks
In recent years, the distributed denial of service attack has severely impacted significant organizations. Among the most notable instances are:
How DDoS Attacks Work
DDOS Attacks Mechanism
Flood the target system from different sources with traffic so much that it becomes impossible to differentiate between valid users and invalid requests. DDoS attacks normally occur using botnets, a network system wherein the attackers employ compromised devices. When the target becomes overwhelmed, it eventually cannot process legitimate requests. This may cause either service downtime or performance degradation. Attacks may be carried out on any part of the system’s infrastructure, be it servers, databases, or network equipment.
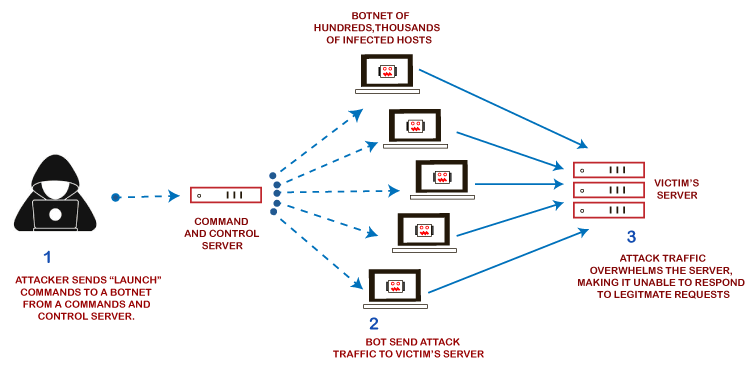
Types of DDoS Attacks
Several types of DDoS attacks differ, and they of a network or server they attack.
Botnets in Distributed Denial of Service Attack
An attacker may remotely control a group of infected devices known as a “botnet.” These devices can include personal computers, smartphones, servers, or IoT devices. Botnets are the core of most large-scale DDoS attacks, allowing attackers to generate massive amounts of traffic from multiple locations. Botnets are created by spreading malware through phishing emails or compromised websites. Infected devices then send traffic to the target site on the attacker’s command, making it difficult to trace the attack’s origin. This highlights the critical importance of Web Security in preventing such infections and protecting against DDoS attacks.
Interested in Obtaining Your Cyber Security Certificate? View The Cyber Security Online Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Common Types of DDoS Attacks
Volumetric Attacks
Volumetric attacks aim to overload the target’s bandwidth with large traffic. It can present itself in any one of the following forms:
Protocol-Based Attacks
The goal of protocol-based DDoS assaults is to deplete network equipment resources, such as firewalls and routers. Some of these cases are:
Application Layer Attacks
These attacks target the OSI model’s application layer, such as services involved in web servers and databases. Examples include Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) that can help detect abnormal traffic patterns indicative of a DDoS attack, enabling quick response to mitigate the impact on the network and systems.
Impact of DDoS Attacks
Financial Expenses and Losses within an enterprise
A Distributed Denial of Service Attack can be financially devastating. The cost of lost time, revenue, and recovery efforts can quickly escalate, particularly for businesses reliant on their online presence. The immediate financial impact of a DDoS attack includes: As noted in Cyber Security Training Courses, these attacks often result in higher operational costs, service disruptions, and potential long-term reputational damage.
Reputation Damage
In the long run, extended downtime or services during an attack can destroy the company’s reputation. Customers expect reliable and constant service; thus, downtime during the distributed denial of service attack can break trust. Negative press and public backlash through social media will also affect the brand image.
Operational Challenges
In addition to financial and reputational harm, a distributed denial of service attack can disrupt the regular functioning of daily life. Critical systems access can be denied to employees, customers cannot utilize services, and IT teams are on an aggressive hot seat for mitigation and the return of normal operations.
Looking to Master Cybersecurity? Discover the Cyber Security Expert Masters Program Training Course Available at ACTE Now!
Identifying a DDoS Attack
Pre-Attack Indicators of DDoS Attack
Some pre-attack symptoms will help identify a distributed denial of service attack well in time before it causes extensive damage:
Tools for DDoS Detection
Sophisticated monitoring and traffic analysis tools can alert one of an attack and mitigate it well before it develops into a more massive attack. Some examples include:
Key Metrics to Monitor
This is mainly based on metrics such as server response times, bandwidth usage, and error rates that may indicate unusual activity; thus, organizations are able to identify in advance any attempt that may portend an attack. Monitoring systems should identify the anomaly in real-time so that the attack does not gain more momentum.
Mitigating and Preventing DDoS Attacks
To protect against or at least reduce the effects of a DDoS attack, here are some best practices that businesses and individuals can make use of:
DDoS Protection Services and Tools
Many companies rely on third-party DDoS protection services to protect websites and applications against attacks. These services often incorporate techniques like Cipher Encryption to secure data transmissions, ensuring that sensitive information remains protected even in the event of a DDoS attack, while also helping to maintain the integrity of communications during an ongoing security breach.
DDoS Resilient Infrastructure
A business should have a multi-layered security infrastructure that prevents or mitigates a distributed denial of service attack. This infrastructure may include a firewall, anti-DDoS software, and traffic analysis tools. All services must be available during an attack and maintain redundancy with fail-over systems.
DDoS Attack Trends and Future Threats
The New Face of DDoS
DDoS attacks are intelligent and targeted. Hackers have become dependent on multi-vector attacks against a system’s traditional defences. The proliferation of IoT devices and AI-powered botnets takes DDoS attacks to a different level that is much more effective and unfilterable. New Techniques and Tactics. The growth in connected devices is extremely fast; therefore, botnets assembled from compromised IoT devices will scale up the attacks initiated by cyber attackers. The future also brings threats based on machine learning.
The Future of DDoS Attacks
DDoS attacks continue to grow, and the future of cybersecurity will depend on how businesses adapt to evolving threats. Advanced detection technology, proactive defense mechanisms, and regular updates to security strategies are essential for staying ahead. Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication(MFA) can further enhance security by adding an extra layer of protection against unauthorized access during such attacks.
Preparing for Cyber Security Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on Cyber Security Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Case Studies: DDoS Attacks in Action
The Most Notorious DDoS Attacks: True Stories
Some of the most significant DDoS attacks, like the Dyn attack or the GitHub attack, give one a sense of the scale of these cyberattacks. These incidents highlight the growing sophistication and potential disruption that large-scale DDoS attacks can cause to online services and infrastructure.
Key Takeaways from High: Profile DDoS Cases
These examples highlighted the role of preparation a good mitigation plan, cooperation with DDoS protection services, and staff education regarding threats. Proactive monitoring and real-time response strategies are also critical in minimizing the impact of such attacks.
Conclusion
DDoS attacks are continuously evolving, so the problem is never-ending. It must be a concern for organizations around the world. Businesses should approach protection that encompasses comprehensive Cyber Security Training Courses, vigilant monitoring of their networks, and DDoS protection services. Such could help in strong defences and proactive planning to mitigate this attack and disrupt the running of services.





