
- Introduction to Endpoint Security
- How Endpoint Security Works
- Types of Endpoint Security Solutions
- Threats Addressed by Endpoint Security
- Key Features of Effective Endpoint Security
- The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Endpoint Security
- Endpoint Security for Remote Workforces
- Conclusion
Understanding Endpoint Security: A Comprehensive Guide explores the critical role endpoint security plays in safeguarding an organization’s network. It focuses on protecting end-user devices such as laptops, smartphones, and desktops from Cyber Security Training Courses, including malware, ransomware, and unauthorized access. The guide covers various security measures, including antivirus software, firewalls, encryption, and multi-factor authentication, to secure endpoints effectively. It also emphasizes the importance of continuous monitoring, updates, and proactive threat detection to ensure comprehensive protection and reduce vulnerabilities in a constantly evolving cyber threat landscape.
Interested in Obtaining Your Cyber Security Certificate? View The Cyber Security Online Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Introduction to Endpoint Security
Endpoint security is the practice of securing end-user devices like computers, smartphones, tablets, and other networked devices from cyber threats. Since most organizations depend on a broad variety of devices to access their corporate networks and data, it is essential to secure those endpoints to avoid data breaches, malware attacks, and other security incidents.
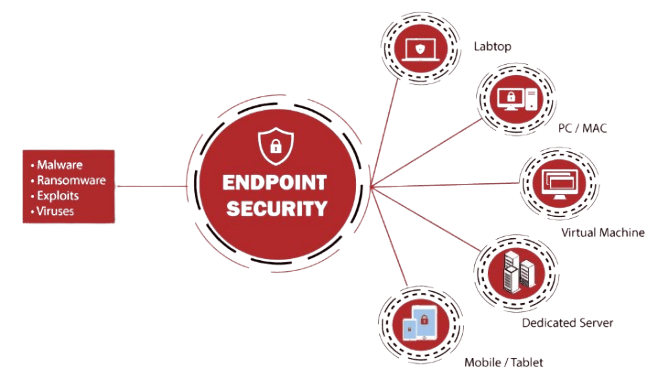
Implementing robust Firewall and Antivirus Software is crucial in providing an additional layer of protection by monitoring and blocking unauthorized access and detecting potential threats before they can compromise the system. Endpoint security solutions monitor and control these devices to ensure they are free from vulnerabilities, detect malicious activity in real time and mitigate them. This is very important because the perimeter of traditional network security has been stretched by the inclusion of different endpoints inside and outside the corporate network in today’s highly interconnected world.
How Endpoint Security Works
The functioning of endpoint security is built through a combination of technologies and policies intended to protect devices from cyber threats. At its core, it is designed to detect, prevent, and respond to security incidents across all endpoints in a network. Here is how it works:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Endpoint security solutions continuously monitor devices for suspicious activity, such as unusual network traffic, unauthorized access attempts, or the presence of Malware Attacks.
- Malware Detection and Prevention: These endpoint security tools use signature-based detection, heuristic analysis, and behavioural monitoring to identify and block known and unknown malware threats before they can cause damage.
- Access Control: These systems enforce policies around who can access devices and what resources they can interact with, thus ensuring that only authorized users or processes can operate on the endpoint.
- Encryption: Many endpoint security solutions use encryption so that even if devices are compromised or stolen, the data remains secure and unreadable without the proper keys.
- Patch and Updates: Endpoint security software might also manage the installation of security patches and software updates to ensure that devices are protected against known vulnerabilities.
- Centralized Management: Endpoint security solutions are generally managed from a central platform, where all security teams can monitor, update, and respond to threats across all devices in real-time.
Types of Endpoint Security Solutions
Antivirus and Anti-MalwareTraditional security solutions detected and removed viruses, worms, and other types of malware. They depended on signature-based detection to identify known threats and prevent devices from infection.
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)EDR solutions offer advanced threat detection, continuous monitoring, and real-time response. They concentrate on identifying suspicious activity, providing deep visibility into endpoints, and enabling security teams to investigate and mitigate threats efficiently.
Mobile Device Management (MDM)MDM solutions manage and secure mobile devices within an organization, such as smartphones and tablets. These solutions enforce security policies, control device configurations, and allow remote data wiping in case of theft or loss.
DLP systems protect sensitive data from unauthorized access, use, or transfer. These systems monitor endpoint activities to prevent data breaches by controlling how data is handled and shared across devices.
Unified Endpoint Management (UEM)UEM integrates multiple endpoint management functions, such as MDM, EDR, and more, into one platform. It allows organizations to centrally manage and secure a variety of devices, including desktops, laptops, smartphones, and IoT devices, through a single console.
Firewall and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS)Endpoint firewalls and Intrusion Prevention System solutions monitor and filter network traffic to and from endpoints, block unauthorized access, and prevent malicious communications from reaching the device.
Encryption SoftwareEncryption solutions ensure that data stored on endpoints is encrypted, making it unreadable to unauthorized users. This helps protect sensitive data in case devices are lost, stolen, or compromised.
Threats Addressed by Endpoint Security
Endpoint security solutions protect devices from various cyber threats, including malware, phishing, insider threats, APTs, spyware, and botnets. Malware, such as viruses, worms, and Trojans, can compromise data, while ransomware encrypts files and demands payment for decryption. Phishing attacks trick users into revealing sensitive information, but security tools prevent this through email filtering and URL analysis. Insider threats arise from trusted individuals misusing access, which is mitigated by monitoring user behaviour. APTs are stealthy, long-term cyberattacks that endpoint security detects through anomaly detection and device isolation. One effective way to combat these threats is by investing in Cyber Security Training Courses, which equip employees with the knowledge to recognize and respond to potential security risks, including insider threats and APTs. Spyware and keyloggers silently steal data, but security software removes these threats. Data breaches, often caused by unauthorized access, are prevented through encryption and access controls. Botnets, which use compromised devices for large-scale attacks like DDoS, are blocked by detecting unusual network activity. Additionally, unpatched vulnerabilities are exploited by hackers, but endpoint security ensures timely software updates, reducing risks.
To Explore Cybersecurity in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Cyber Security Online Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Key Features of Effective Endpoint Security
- Real-Time Threat Detection: Effective endpoint security solutions continuously monitor devices for suspicious behaviour and potential threats. Real-time threat detection allows immediate identification of malicious activity, enabling quick responses to prevent infections.
- Multi-Layered Protection: A strong endpoint security system employs multiple layers of protection, such as antivirus, firewalls, encryption, and behavioural analysis, to safeguard devices from various attack vectors. This approach ensures that if one layer fails, others will provide protection.
- Advanced Malware Protection: State-of-the-art endpoint security employs methods such as signature-based detection, heuristic analysis, and machine learning to identify both known and unknown malware attacks before they can impact endpoints.
- Device Control and Access Management: Ability to ascertain which devices or users ought to have access to the network and implement appropriate policies based on this principle. Include the policy governing external entities, such as USB flash drives, prevent unauthorized attachments from the corporates, etc.
- Endpoint Isolation and Remediation: When a threat is detected, endpoint security solutions can isolate compromised devices from the network to prevent further spread of malware or breaches. Remediation tools help restore infected devices to a secure state.
- Patch Management: Endpoint security systems often include patch management capabilities. These capabilities ensure that devices are updated with the latest security patches and fixes for vulnerabilities, reducing the risk of exploitation through unpatched software.
- Cloud Integration: Most endpoint security solutions have cloud-based features. Such features include enhanced scalability, real-time updates, and even central monitoring. Integration such as this allows security teams to manage endpoints from elsewhere while getting better visibility over the overall security posture.
- Behavioral Analytics and AI Integration: Endpoint Security Solutions that make use of behavioural analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) detect abnormal behaviour patterns that might be leading to a security threat. AI enhances the detection capabilities of emerging threats and zero-day attacks.
Are You Considering Pursuing a Master’s Degree in Cybersecurity? Enroll in the Cyber Security Expert Masters Program Training Course Today!
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Endpoint Security
Threat Detection and PreventionAI-based endpoint security solutions can scan large volumes of data from endpoints to detect patterns and anomalies that could represent potential threats. AI models use machine learning to identify and block known and unknown malware by recognizing behavioural patterns rather than relying on signature-based detection.
Behavioural AnalysisAI-based systems can continuously monitor the behaviour of users and devices to establish a baseline of normal activity. Any deviation from this baseline, such as unusual file access or network traffic, can trigger alerts and automated actions, such as isolating the affected endpoint or initiating a deeper investigation.
Zero-Day Threat DetectionAI is very effective in detecting zero-day attacks, which exploit previously unknown vulnerabilities. Through machine learning, AI systems can identify abnormal behaviours or indicators of compromise (IoC) that may not match known attack signatures, thus detecting new threats in real-time before they cause significant damage.
Automated ResponseAI can auto-report detected threats, so attack mitigation is quicker. For example, AI can cut the offending endpoints from the network connection, block suspicious processes, and initiate automated patches to eliminate vulnerabilities quicker than the manual process.
Predictive Threat IntelligenceAI can analyze historical data on attacks and other intelligence sources of threats to predict future threats. This gives security teams a head start, allowing them to proactively make changes to their defence and thereby lower the chances of being breached. A key component of this proactive approach is Vulnerability Management, which involves identifying, assessing, and addressing potential vulnerabilities within an organization’s systems before they can be exploited by attackers.
Advanced Phishing DetectionAI-driven endpoint security solutions analyze emails, URLs, and other forms of communication to better detect phishing attacks. AI uses NLP and machine learning to identify suspicious messages and block users from clicking on malicious links or downloading malicious attachments.
Fewer False PositivesOne challenge in endpoint security is managing false positives alerts that identify benign activity as a threat. AI helps reduce false positives by continuously learning and refining its detection capabilities, ensuring that security teams focus on genuine threats while minimizing alert fatigue.
Adaptive LearningThe continuously learning nature of AI solutions ensures that the evolving threat landscape can be countered. As threats grow more sophisticated, AI-based endpoint security tools keep up with the change by constantly changing their detection techniques to stay ahead of attackers.
Endpoint Security for Remote Workforces
Securing multiple device types is essential as remote workers use various devices like laptops, smartphones, and tablets to access corporate systems. Endpoint security solutions must support diverse operating systems and platforms, ensuring consistent protection for both company-issued and personal devices (BYOD). VPN integration is crucial for securing remote connections and encrypting communication between remote devices and the corporate network to prevent interception. Cloud-based security solutions provide scalability, real-time updates, and centralized management, allowing IT teams to monitor and protect remote endpoints across different locations. The Zero Trust Security model ensures that no device or user is trusted by default, continuously verifying device health, user identity, and access rights before granting access to sensitive systems. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) further enhances security by requiring multiple forms of verification, preventing unauthorized access even if an endpoint is compromised. Remote Device Management (RDM) enables IT teams to manage endpoints remotely, enforce security policies, update security patches, configure firewalls, and perform remote scans for malware or vulnerabilities. Data Loss Prevention (DLP) tools prevent unauthorized sharing or transfer of sensitive information, safeguarding confidential data from exposure through insecure networks, emails, or unauthorized external devices. Endpoint isolation and remediation automatically isolate compromised devices from the corporate network to prevent further damage, ensuring they are cleaned, updated, and restored to a secure state before reconnecting.
Preparing for a Cyber Security Job Interview? Check Out Our Blog on Cyber Security Interview Questions and Answers
Conclusion
In a more digital and distributed work environment, endpoint security is one of the key components of a strong Cyber Security Training Courses strategy. Since more and more devices are used to access sensitive data and networks, it becomes critical to ensure the security of endpoints to prevent a large array of cyber threats, ranging from malware and phishing to insider attacks and data breaches. Effective endpoint security solutions, therefore, draw on real-time monitoring, multiple layers of defence, AI-driven threat detection, and strong access controls to keep devices and data safe. Additionally, with the growing remote workforces, endpoint security plays an even greater role in ensuring data integrity, privacy, and business continuity regardless of location.





