
- Introduction
- What is Vulnerability Management?
- Why is Vulnerability Management Important?
- The Vulnerability Management Lifecycle
- Best Practices for Effective Vulnerability Management
- Tools and Technologies for Vulnerability Management
- Common Challenges in Vulnerability Management
- Conclusion
- Proactive Threat Mitigation: Since the vulnerabilities are known, identified, and addressed before they are exploited, cyber attacks on an organization can be significantly minimized.
- Regulatory Compliance: Some industries have specific regulatory frameworks, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS. All of these frameworks require robust security practices involving vulnerability management by such organizations.
- Cost Savings: Remediation cost is reduced when weaknesses are addressed before exploitation. A breach can lead to millions in fines, legal fees, and damage control for an organization.
- Reputation Protection: Data breaches or cyberattacks can also impact an organization’s reputation. Vulnerability management enhances customer trust and confidence.
- Operational Continuity: Addressing the vulnerability will guarantee that systems remain secure and prevent costly downtime or disruptions.
- Network Scanning: Scan to determine which are active devices and systems.
- Software Inventory: Extensive list, including version, of the software found in the organization.
- Configuration Audits: Validating configurations with proper security best practices.
- Severity Level: How sensitive is the vulnerability? If it has an RCE or privilege escalation, it has a serious risk and should be fixed as soon as possible.
- Exploitability: How hard or easy can an attacker exploit the vulnerability? The highest priority should go to vulnerabilities with publicly available exploit code.
- Business Impact: If this vulnerability were exploited, what would be the business impact? Consider data loss, service disruption, or sensitive information compromise.
- Patch Management: Application of patches and software updates to close security gaps.
- Configuration Hardening: Harden the configuration of systems to minimize vulnerabilities.
- Network Segmentation: Limit access to sensitive systems or data.
- Access Control: Limit permissions of the user to reduce damage if a vulnerability exists.
- Systems Rescanning: Confirming the resolution of vulnerabilities.
- Continuous Monitoring: Deploying intrusion detection systems (IDS) SIEM (security information and event management) is another technique for real-time monitoring.
- Log Audits: Auditing Security Logs regularly for suspicious activity evidence.
- Establishment of a Vulnerability Management Policy: A formal policy of the process that documents how vulnerabilities are identified, assessed, and mitigated so that they meet organizational goals and regulatory requirements.
- Automate Where Possible: Use automated vulnerability scanning and patch management tools to reduce the gap between discovery and remediation further. Automation reduces the time between detection and fixing, thus minimizing exposure.
- Remediation Prioritization: Remediation should be done based on the severity level of the vulnerabilities. Risk-based models should have mechanisms that ensure critical vulnerabilities receive greater priority for resolution.
- Scheduled Vulnerability Scans and Assessments: New vulnerabilities come with time; therefore, their systems must be scanned and assessed frequently for security.
- Continuous Monitoring: Remediation only happens once. A new vulnerability might soon be discovered after its emergence through constant monitoring.
- Employees Training: Human errors sometimes account for the lion’s share of vulnerabilities. Training employees on best practices, such as how to avoid phishing attacks and use strong passwords, is a good way of reducing exploitation risks.
- Nessus: It scans for known and unknown vulnerabilities. It is also widely used.
- Qualys: This platform gives continuous vulnerability assessment in scanning and remediation mode.
- OpenVAS: Is an open-source vulnerability scanner that finds vulnerabilities in networks and systems.
- Rapid7 Nexpose: It manages vulnerabilities, which helps the organization prioritize vulnerabilities based on risk.
- Tenable.io: It is a cloud-based platform that provides visibility into vulnerabilities across on-premises, cloud, and container environments.
Introduction
With the heightened connectivity of our modern world, cybersecurity threats represent a constant threat looming for every organization and business. This is because they result from increased digital complexities and the increasing prevalence of cyberattacks. For instance, Google Dorking can be used by attackers to exploit poorly secured websites or systems, uncovering sensitive information through advanced search queries. One of the critical elements that bolsters any organization’s cybersecurity strategy relates to Vulnerability Management.
Vulnerability management is a repeated process of identifying, evaluating, and remediating security weaknesses in the IT environment of an organization. Proactively managing vulnerabilities reduces an organization’s attack surface, mitigates cyberattack risks, and ensures organizations are secure with security regulations. In the following blog, we will learn what vulnerability management tools is, why it is critical, and how organizations can develop a successful vulnerability management program.
To Earn Your Vulnerability management Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Cyber Security Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Cyber Security Online Training Today!
What is Vulnerability Management?
Vulnerability management is the process involved in discovering, evaluating, prioritizing, and mitigating vulnerabilities in an organization’s IT systems and networks. These vulnerabilities are weaknesses or flaws in software, hardware, or network configurations that, if exploited, could be used to gain unauthorized access or cause damage to systems and data. Vulnerability management thus aims to reduce an organization’s vulnerability to threats by ensuring that security holes are addressed in a timely manner before they are exploited. This is an ongoing process with varied phases, from discovery to remediation and monitoring. Vulnerability management might overlap with a spectrum of Cyber Security Training Courses practices, including patch management, threat intelligence, and risk management. Still, it mainly focuses on detecting and mitigating vulnerabilities before they become a foundation on which an attack is to be successful.
Why is Vulnerability Management Important?
Vulnerability management cannot be minimized. Today’s Organizations are highly dependent on digital technologies, exposing a larger surface area to potential cyberattacks. Vulnerabilities in operating systems, applications, and devices provide an open door for attackers, often unleashing devastating consequences in the form of data breaches, financial losses, reputational damage, and liabilities in court. To mitigate these risks, Hub and Switch is crucial. Educating employees and users about security best practices, recognizing potential threats, and understanding the importance of keeping systems updated can significantly reduce the likelihood of exploitation, helping organizations prevent costly security breaches.The following are some reasons why vulnerability management is mandatory:
To Earn Your Vulnerability management Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Cyber Security Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Cyber Security Online Training Today!
The Vulnerability Management Lifecycle
A good vulnerability management program should be a single cycle of various stages, encompassing the entire lifecycle from identification through assessment to mitigation. Here is a look at the stages involved:
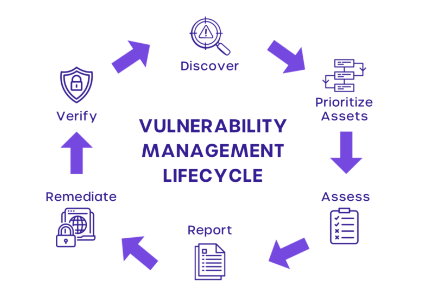
1. Discovery and Identification
The first step to vulnerability management is the discovery and identification of vulnerabilities throughout an organization’s network, systems, and applications. This is mostly done through the use of automated vulnerability scanning tools that scan for known vulnerabilities based on an ever-updated database of threats. These tools help organizations assess Risk Threat and Vulnerability allowing them to identify potential weaknesses in their systems before they can be exploited.
Discovery should identify and discover new assets in the network, as vulnerabilities can emerge in newly introduced or updated systems. This phase involves:
2. Evaluation and Prioritization
Now that all the vulnerabilities have been determined, this is the moment to risk-assess and analyze what impact might take place. Evaluate each vulnerability on any of the following.
Most ratings will use the terms Critical, High, Medium, and Low to represent the risk. This will allow the company to prioritize and remediate the most critical first.
Are You Considering Pursuing a Master’s Degree in Cybersecurity? Enroll in the Cyber Security Expert Masters Program Training Course Today!
3. Remediation and Mitigation
Once vulnerabilities have been identified and prioritized, actions are taken to remediate or mitigate risks. Remediation involves actually resolving the root problem, such as applying a patch to software or updating the system. In cases where remediation cannot be done immediately, mitigation will be used in isolation, network segmentation, or in-depth monitoring to reduce the risk. Remediation may involve:
4. Verification and Monitoring
It should validate the effectiveness of all fixes. It rescans systems for proof that vulnerabilities have been resolved and monitors systems for signs of exploitation. This means it also continues scanning in real-time for new vulnerabilities, ensuring all its systems stay safe. Phases involved:
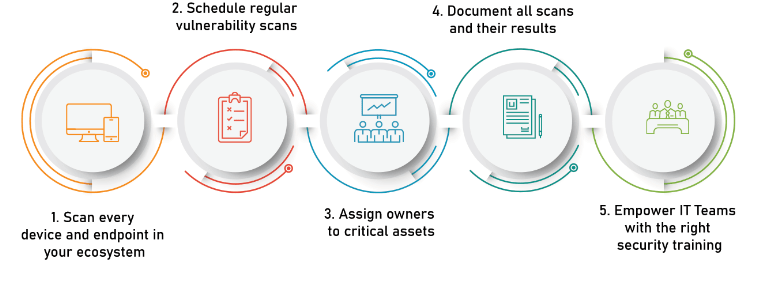
Best Practices for Effective Vulnerability Management
To have effective vulnerability management in Cyber Security Training Courses, the following are the best practices that the organizations must follow:
Tools and Technologies for Vulnerability Management
There are many tools developed which help in managing the vulnerabilities. These tools often include capabilities for testing and simulating attacks, such as delivering Payloads to assess how systems respond to specific types of exploits. These tools give a way to automate the scanning of vulnerabilities, patch management, and reporting. Some of the most popular ones are:
Preparing for a Cyber Security Job Interview? Check Out Our Blog on Cyber Security Interview Questions and Answers
Common Challenges in Vulnerability Management
Though important to an organization’s security posture, vulnerability management has several challenges that make its implementation complex. The most prominent of these is the limitation of resources. Often, organizations need help attaching sufficient numbers of skilled people or time for the vulnerability. It is even worse for large organizations where thousands of potential security flaws may be spread across a complicated IT environment. In such cases, Private key and Public key becomes critical, as vulnerabilities in web applications can be a major target for attackers. It is a very heavy task to identify, scan, prioritize, and remediate such vulnerabilities, overstretching the available resources. Second, the threat environment is constantly in motion, new vulnerabilities arise daily that are critically and promptly requiring attention. And lastly, vulnerability management cannot perform in silos but must be integrated with other security practices, including patch management, incident response, and risk management. This integration will be hard because several departments and processes must be aligned to correctly identify areas with vulnerabilities and then address them appropriately and promptly without falling through various cracks. It takes great tools and methods but requires concerted effort in streamlining workflows to ensure that vulnerability management takes the highest place in the whole organization.
Conclusion
A great aspect of vulnerability management is that it reflects a robust security strategy. Through systematic identification, assessment, and mitigation of vulnerabilities, organizations’ exposure to cyberattacks can be minimized, and damage from security breaches can be proactively reduced. Vulnerability management is a complex exercise, but for organizations with the right tools and resources, the journey to continuous improvement through structured processes and best practices has just begun; such an organization will be ahead of all threats and protect its critical assets. Systematic reviews and improvements in vulnerability management efforts help an organization build a strong defence against new Cyber Security Training Courses risks. Taking proactive and comprehensive approaches will ensure businesses are safe, sound, and secure in hostile digital worlds.





