
- Introduction to Cybersecurity Careers
- Types of Cybersecurity Roles
- Emerging Trends and Future Prospects
- Key Domains in Cybersecurity
- Qualifications and Certifications
- How to Start a Career in Cybersecurity
- Cybersecurity Career Pathways
- Cybersecurity in Different Industries
- Challenges and Rewards in Cybersecurity Careers
- Resources and Tools for Cybersecurity Professionals
- Conclusion
Introduction to Cybersecurity Careers
Cybersecurity is one of the most critical aspects of today’s technology-driven world. With the increase in cyberattacks and data breaches, the demand for skilled cybersecurity professionals has skyrocketed. As companies and governments protect valuable digital assets, the need for cybersecurity experts grows, leading to a wide range of career opportunities in Cybersecurity Training Courses . Whether it’s protecting sensitive data, ensuring compliance with security regulations, or defending against cyberattacks, the role of cybersecurity professionals is essential in safeguarding the digital world. The cybersecurity industry is diverse and offers roles for individuals with various skill sets, ranging from technical to strategic positions. Whether you’re interested in hands-on roles like ethical hacking or prefer strategic roles like cybersecurity consultant, there are abundant opportunities for career growth.
To become a certified cyber security, have a look at our Cyber Security Online Training right now.
Types of Cybersecurity Roles
Cybersecurity offers a wide range of roles that suit different skill sets. Here are some key positions in the field:
- Security Analyst: Security analysts monitor and protect an organization’s computer systems and networks. They detect vulnerabilities, implement security measures, and respond to incidents. The role requires expertise in threat detection, firewall configuration, and the ability to identify potential risks in the system.
- Penetration Tester/Ethical Hacker: Penetration testers simulate cyberattacks to identify security flaws in systems. Their job is to hack into systems (legally) to uncover vulnerabilities. They often use the same tools and techniques as hackers but aim to secure systems rather than exploit them.
- Security Engineer: Security engineers are responsible for designing, implementing, and maintaining secure systems. They focus on both Firewall and Antivirus Software measures to ensure that systems are protected from cyber threats. They often work closely with system administrators to implement security controls at various levels.
- Incident Responder: Incident responders are the first line of defense when a security breach occurs. They identify, contain, and mitigate threats and help recover from cyberattacks. Incident responders work quickly to minimize the impact of a security event and prevent future incidents.
- Security Architect: Security architects are responsible for designing secure infrastructures. They create blueprints for security systems, ensuring they are both robust and scalable. These professionals have deep knowledge of network security and encryption and play a pivotal role in creating secure systems.
- Cryptographer: Cryptographers develop algorithms to protect sensitive data and design encryption protocols to secure data in transit and at rest. They play a crucial role in securing communications and transactions, especially in industries like banking and government.
Emerging Trends and Future Prospects
As technology continues to evolve, new cybersecurity challenges arise. Here are some emerging trends AI and machine learning are being used to detect and respond to threats in real time. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data and identify anomalies faster than traditional methods. The Internet of Things (IoT) introduces numerous security challenges. With billions of connected devices, IoT security is becoming increasingly important to prevent data breaches and unauthorized access. As remote work becomes the norm, cybersecurity experts are needed to secure remote systems, ensure secure connections, and protect against increased cyber threats targeting remote employees. Blockchain technology is used in various industries, and cybersecurity professionals are needed to secure blockchain applications and prevent attacks such as 51% attacks or smart contract vulnerabilities. The CISO is responsible for overseeing an organization’s cybersecurity strategy. They ensure that all cybersecurity efforts align with business objectives and regulatory requirements and work with executive leadership to create long-term security strategies.
To Earn Your Cyber Security Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Cyber Security Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Cyber Security Online Training Today!
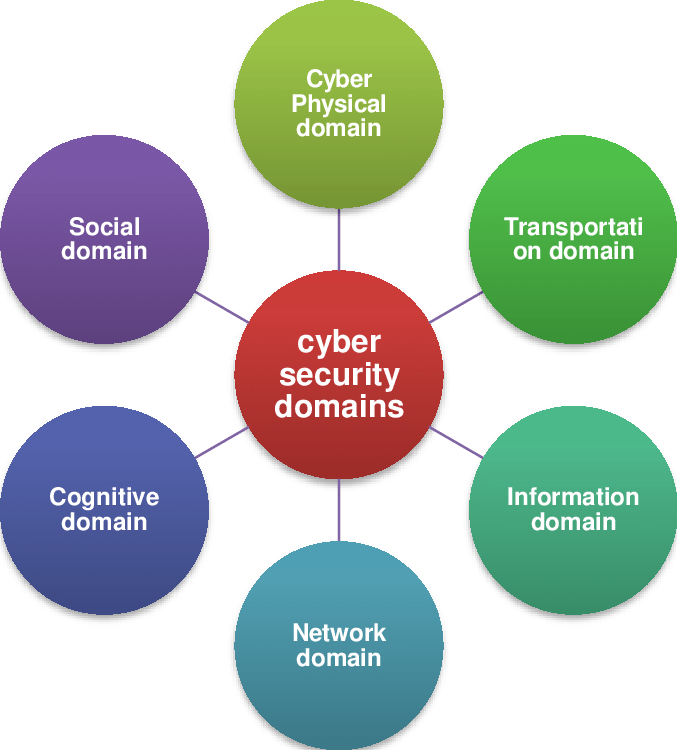
Key Domains in Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity spans several key domains, each with its unique set of challenges and requirements. These domains provide specialization options for individuals looking to focus on a specific area of cybersecurity:
- Network Security: Network security focuses on protecting the integrity of networks and the data transmitted over them. This includes configuring firewalls, detecting network intrusions, and ensuring secure communication protocols.
- Application Security: Application security ensures that software applications are developed with security in mind. Developers and security experts work together to design and test secure applications, addressing issues like cross-site scripting (XSS) and SQL injection.
- Cloud Security: With the rise of cloud computing, Cloud Security Service focuses on safeguarding cloud-based data and applications. This involves securing data storage, preventing data breaches, and ensuring compliance with regulations.
- Endpoint Security: Endpoint security involves protecting devices like laptops, smartphones, and tablets that connect to an organization’s network. Endpoint protection systems, such as antivirus software, detect and prevent threats from these devices.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): IAM focuses on ensuring that only authorized individuals can access specific systems and data. It involves creating user identities, enforcing authentication protocols, and managing user roles and permissions to prevent unauthorized access.
- Security Operations Center (SOC): SOC teams are responsible for monitoring and defending against cyberattacks in real time. They use security information and event management (SIEM) tools to detect, analyze, and respond to security threats quickly.
Qualifications and Certifications
Qualifications and certifications are vital for those pursuing a career in Cybersecurity Training Courses . These credentials help validate your skills and enhance your employability. Some key certifications include:
- CompTIA Security+: This is an entry-level certification that covers basic security concepts like network security, cryptography, and threat management. It is ideal for beginners in cybersecurity.
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP): CISSP is a globally recognized certification that validates your expertise in various domains of cybersecurity. It is ideal for those in managerial or leadership roles in cybersecurity.
- Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH): CEH is for individuals who want to specialize in ethical hacking. It focuses on penetration testing and ethical hacking techniques.
- Certified Information Security Manager (CISM): CISM is for professionals who want to focus on managing and overseeing security in an organization. It is a certification for those looking to become a CISO or security manager.
- Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP): As cloud computing becomes more prevalent, the CCSP is a specialized certification that focuses on securing cloud environments.
How to Start a Career in Cybersecurity
Starting a career in cybersecurity requires a solid foundation in IT. Here are some steps to get started Knowledge of networking, programming, and computer systems is essential. You can start by taking IT courses and learning about operating systems, networking protocols, and database management. Earning certifications like CompTIA Security+ or CEH can provide the necessary skills and industry recognition to start your career. Internships, volunteer work, or personal projects (such as setting up home labs) can help you gain practical experience and demonstrate your capabilities to employers. Joining cybersecurity forums, attending industry conferences, and networking with professionals in the field can help you stay updated and build valuable connections.
Cybersecurity Career Pathways
Cybersecurity offers various career pathways depending on your level of experience and interests. These pathways allow you to start at entry-level positions and move toward more advanced roles:
- Entry-Level Roles: For those just starting in cybersecurity, roles like security analyst, technical support, or network administrator provide hands-on experience. Entry-level certifications, such as CompTIA Security+, can open doors to these positions.
- Mid-Level Opportunities: After gaining experience, professionals can move into roles like penetration tester, security engineer, or incident responder. Certifications like CEH or CISSP may be required to move into these positions.
- Advanced and Leadership Positions: Experienced cybersecurity professionals can progress to roles such as security architect, CISO, or security consultant. These positions typically require significant experience and a combination of technical skills and leadership abilities.
Leverage Cyber Security to Unlock the Future! Enroll in the Cybersecurity Expert Masters Program Training Course Program at ACTE Right Away.
Cybersecurity in Different Industries
Cybersecurity professionals are in demand across various industries. Some of the sectors that particularly require cybersecurity expertise include:
- Financial Services: Banks and financial institutions are prime targets for cybercriminals. Cybersecurity professionals in this sector focus on securing financial data, preventing fraud, and ensuring regulatory compliance.
- Healthcare: The healthcare industry handles sensitive patient Information Security, making it a prime target for cyberattacks. Cybersecurity experts work to protect patient data, secure medical devices, and comply with privacy regulations like HIPAA.
- Government and Defense: Cyberattacks frequently target government organizations. Cybersecurity professionals in this sector focus on protecting national security data, critical infrastructure, and sensitive government communications.
- Technology and Telecommunications: Telecom companies and tech giants require cybersecurity experts to safeguard their networks, protect user data, and secure cloud services. Cybersecurity in this industry focuses on infrastructure protection and ensuring privacy and compliance.
- Retail and E-commerce: With the rise of online shopping, e-commerce websites need cybersecurity professionals to protect customer data and ensure secure payment processing. Retailers also need experts to safeguard against data breaches and fraud.
- SIEM Tools(e.g., Splunk, IBM QRadar)
- Firewalls (e.g., Cisco, Palo Alto)
- Penetration Testing Tools (e.g., Metasploit, Burp Suite)
- Encryption Tools (e.g., OpenSSL)
- Network Monitoring Tools (e.g., Wireshark)
Preparing for a job Interview? Check out our blog on Cybersecurity Interview Questions and Answers !
Challenges and Rewards in Cybersecurity Careers
Cybersecurity careers come with both challenges and rewards. Some challenges include high-stakes pressure, dealing with constantly evolving Overview of Cybersecurity Threats, and long hours during a security breach. However, the rewards are substantial, including job security, high salaries, and the satisfaction of protecting organizations and individuals from cyber threats.
Resources and Tools for Cybersecurity Professionals
To succeed in cybersecurity, professionals use a variety of tools
Conclusion
Cybersecurity Training offers a dynamic and rewarding career path for those interested in protecting digital assets. With a wide range of roles, domains, and industries, there are ample opportunities for growth and specialization. Whether you’re just starting or looking to advance in the field, the cybersecurity industry offers long-term career prospects, job security, and a chance to make a significant impact on the digital world.





