
- Introduction to Confidentiality in Cybersecurity
- Why is Confidentiality Important?
- Threats to Confidentiality
- Best Practice to Protect Confidentiality
- Future of Confidentiality in Cybersecurity
- The Role of Data Encryption and Secure Access Controls
- Conclusion
Confidentiality has become a big brick in the wall of cybersecurity since digital generations face concerns regarding cyber security protection from secrecy. Be it personal information or financial records, intellectual property or another kind of record, non-disclosure isn’t just a matter of compliance but, rather, one that ensures trust, network security, and a long-term existence. For businesses, maintaining confidentiality is particularly crucial in sectors like Cyber Media, where sensitive information such as proprietary technologies, user data, or even industry insights can be targeted by competitors or cybercriminals. This blog explores confidentiality in computer security, explains why it is important, identifies risks that might jeopardize confidentiality, and discusses best practices for protecting such sensitive information.
Interested in Obtaining Your Cyber Security Certificate? View The Cyber Security Online Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Introduction to Confidentiality in Cybersecurity
Confidentiality in Cyber Security Training Courses means that sensitive information is available only to authorized individuals. Integrity (factual accuracy of data) and availability (access to data when needed) also form three core information security practices. These three together make up the CIA Triad, on account of which most security frameworks are considered secure. In other words, confidentiality is managing access to information data, company secrets, or sensitive government files so only authorized people can see or access them. The CIA Triad is the basic model for guidance on security policies and practices. One of the triad’s pillars is confidentiality, which ensures that secret information is held securely and not accessed by unauthorized parties.
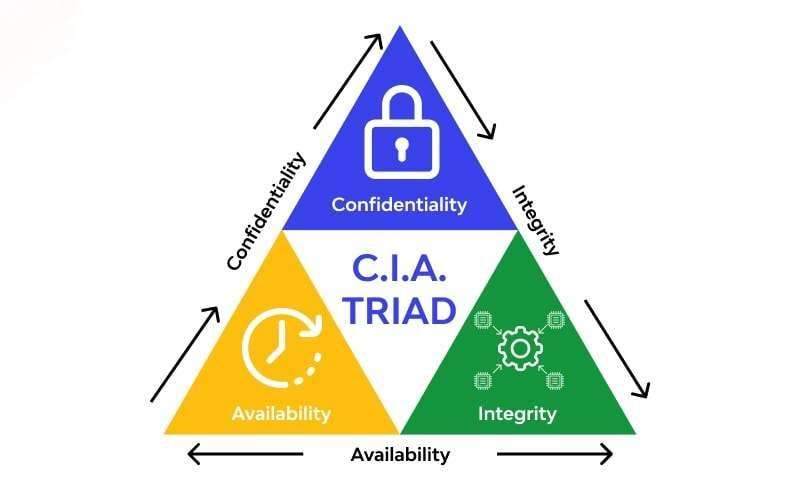
Secure communications encryption and access control accomplish this goal. Data classification plays a critical role in maintaining confidentiality. By categorizing data based on its sensitivity, organizations can implement tailored security measures to protect each type of information. For example, highly sensitive data, such as financial records or personal health information, may require stronger encryption and stricter access policies than less sensitive information. This layered approach ensures that resources are allocated effectively, reducing the risk of unauthorized access while optimizing security efforts. Furthermore, data classification helps organizations comply with regulatory standards, such as GDPR or HIPAA, by ensuring that the appropriate safeguards are applied to different types of data.
Why is Confidentiality Important?
- Every individual has the right to control their information. Data breaches that expose personal details such as Social Security numbers, medical history, or financial information may lead to severe consequences related to identity theft, fraud, and privacy violations. Protecting customer privacy is one of the basic concerns for businesses to acquire customer trust and credibility. Still, a failure to maintain confidentiality may also result in lifelong reputational damage.
- The loss of highly sensitive information due to widespread data breaches makes governments set the course right by enforcing strict privacy laws and regulations for safeguarding personal and corporate data. European Union legislation requires strict protocols for the collection, storage, and processing of individuals’ private information.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act a US law that mandates that healthcare organizations maintain the privacy of patients’ health information. One of the key components of PCI DSS is the implementation of Whitelisting, which allows organizations to control which applications or processes are permitted to run on their systems. Not acting by these regulations attracts severe fines and legal implications.
- Data breaches are costly. In addition to the direct costs of containing and remediating a breach-for example, forensic analysis, notification costs, and technical patches or remediations-organizations will pay fines and suffer loss of business. An example is a breach of financial records or customer data, resulting in lawsuits and loss of customer trust, even a huge market share loss.
- Confidentiality is crucial for intellectual property and trade secrets. Firms spend enormous time, money, and resources on proprietary technologies, processes, or products. A huge financial loss, besides competitive advantage, will result if those assets fall into malicious hands, either by theft or exposure. For industries like the technology sector or pharmaceuticals, confidentiality forms the base of innovation and market position.
- Government institutions and defense agencies handle classified information that, when lost or compromised, can compromise a country’s national security. Classified data, if leaked, can have disastrous implications that expose individuals, assets, and even countries to threats. Therefore, government institutions must use detailed security measures to ensure confidentiality.
To Earn Your Cyber Security Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Cyber Security Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Cyber Security Online Training Today!
Threats to Confidentiality
Insider Threats
This can be considered an insider threat, defined as an organization’s current or former employee, contractor, or trusted individual who misuses access to sensitive information. Insider threats are of two types: intentional, that is, stealing data for personal gain, or accidental, which may involve disclosing confidential information. Insider threats are very dangerous because insiders often have legitimate access to the data and can bypass many security measures.
Cyberattacks
An cyber security threats assumes a trusted identity to steal a person’s login credentials or financial data. Malware is used to steal data or encrypt it by demanding a ransom before releasing it. The attackers intercept any communication between parties without informing them, allowing them to alter or steal Cyber Security Training Courses information.
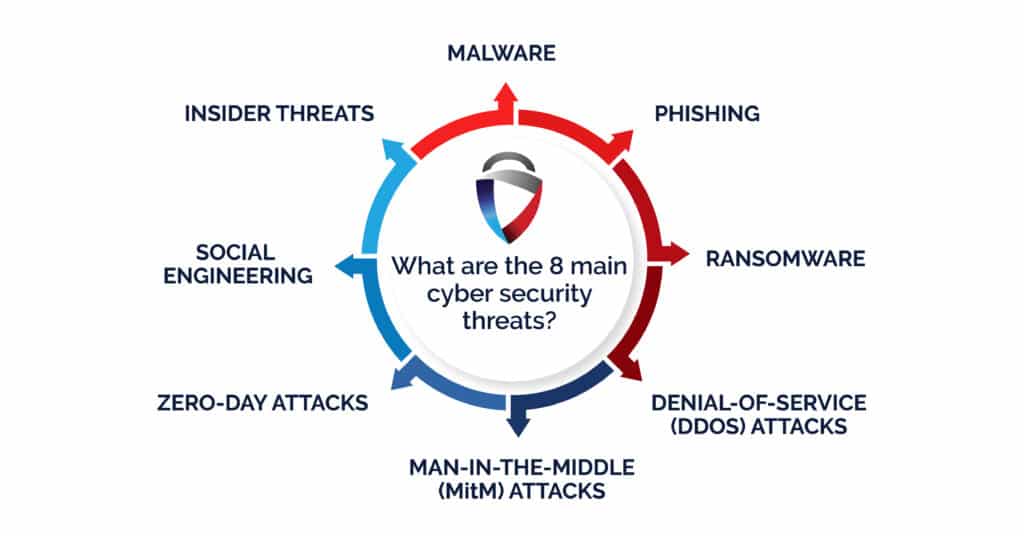
Data Storage Vulnerabilities
Data on servers, databases, or cloud servers is as secure as the systems and processes that protect it. Data revealed to attackers also comes from misconfigured cloud services, unpatched software, or inadequate control over access to data. Proper encryption of data at rest and continuous monitoring of storage systems can keep such access completely unauthorized.
Lack of Authentication
Weak or stolen passwords are the most common form that cybercriminals rely on to sneak into sensitive data. It finds the occasion for vulnerabilities in the security infrastructure by creating weak, reusable, or easily guessed passwords. Two-factor and stronger forms of authentication prevent breaches of weak or compromised credentials.
Best Practice to Protect Confidentiality
Encryption is one of the most effective ways to ensure that data stays confidential, regardless of whether it resides on a device or is transferred over a network. Sensitivity data will remain encrypted if it is intercepted or accessed by other unauthorized parties without any decryption key to decrypt the information. Tight access controls will ensure that only authorized persons can access sensitive data. Cyber Defamation involves the intentional spreading of false or harmful information online, which can severely damage reputations and undermine trust. This includes role-based access controls (RBAC) wherein access is given to an employee based on their role and the principle of least privilege, which denies an individual access to information except for the amount of privilege needed to accomplish the job.
Audits and Monitoring The organization’s status is regularly audited and monitored to ensure that access does not fall into the wrong hands. Continuous system and network monitoring increases the possibility of detecting unauthorized access or suspicious activities. In addition, access log audits should be performed regularly, in combination with periodic and scheduled vulnerability assessments, to confirm that these security controls remain effective and that new vulnerabilities are identified and corrected quickly. Orgminimizens should embrace more robust forms of organisation, such as MFA or biometric verification, to minimize the vulnerability of weak passwords. This method would be much stronger than a password because attackers need more time and energy to break unauthorized access.
Are You Considering Pursuing a Cybersecurity Master’s Degree? Enroll For Cyber Security Expert Masters Program Training Course Today!
Future of Confidentiality in Cybersecurity
Emerging Trends
As cloud computing, IoT devices, and big data analytics grow, so do the opportunities and challenges of ensuring confidentiality. The more information gathered, processed and stored in the cloud or on mobile devices, the more complex it will be to maintain that confidentiality through progressive encryption methods, improvements in access control frameworks, and continually executed security assessments.
AI and ML
AI and machine learning technologies are also being increasingly implemented for anomaly detection, pattern recognition in large data sets, and predicting any possible security breach. Organizations can use them to find vulnerabilities before they are exploited, enhancing the protection of confidential information. Cyber security tools like the Google Hacking Database can be used in conjunction with AI-driven security measures to identify exposed vulnerabilities in public-facing websites or applications.
Privacy Regulations That Matter
Businesses must monitor changing regulations as data privacy laws advance. It is important to maintain compliance with global privacy standards such as GDPR, CCPA, and other regional laws to keep user data confidential and avoid legal violations.
The Role of Data Encryption and Secure Access Controls
Information confidentiality in this modern digital environment is best protected by encryption and access controls. This will ensure sensitive data stored or in transit cannot be accessed by anyone other than the legitimate user using data encryption. Encryption is a process of converting data into an unreadable format by using specific algorithms; even if cybercriminals, for instance, intercept the data, they will not be able to access its content because decryption key is unknown to them. This protects classified data in case of breach and is vital for ensuring compliance with regulations against laws that include GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS. Encryption is not only an imperative way to safeguard data at rest on servers and storage devices but also to protect data in transit as it flows through networks or the internet.
In contrast, secure access controls prevent unauthorized parties from accessing sensitive information, thus significantly reducing the possibility of unauthorized disclosure or break in. However, while access controls are critical, they must be complemented by regular Network Penetration Testing. Basic principles such as role-based access control- restricting access based on job roles assigned to the user- and least privilege principle- allowing users only the minimum amount of access required- are thus considered. Encryption and secure access controls combine together into a sound defense mechanism as they help to counter internal as well as external threats to sensitive data so that organizations have fewer risks of costly breach while ensuring confidentiality and compliance.
Are You Preparing for Cyber Security Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Cyber Security Interview Questions and Answers to Boost Your Preparation!
Conclusion
However, in the world of cybersecurity, only one characteristic is really important Cyber Security Training Courses that data should be protected from unauthorized access and disclosure. This ranges from protecting personal data security to national security. The main point that comes out is maintaining confidentiality at all levels. Knowledge of threats to confidentiality and maintenance of best practice on data encryption, strong access controls, and monitoring can make a breach much less likely to occur. When the digital landscape changes, so must confidentiality protection strategies. Remaining in the vanguard of evolving security practices will be the key to protecting confidence and valuable data in a hyperconnected world. In addition, new technologies that have come into being are more advanced, such as cloud computing and artificial intelligence, which means that approaches to providing confidentiality must be raised in sophistication. Organizations must establish a culture of security, meaning to help employees identify possible threats so that they can prepare to take certain actions about those threats in time before they become major problems.





