
- Introduction to Kali Linux
- Importance in Penetration Testing
- Getting Started with Kali Terminal
- File and Directory Commands
- Network Scanning Commands
- Password Cracking Utilities
- Wireless Hacking Tools
- Exploitation Frameworks
Introduction to Kali Linux
Kali Linux is a specialized, open-source Debian-based operating system developed by Offensive Security for ethical hacking, penetration testing, and cybersecurity research. Packed with a wide range of tools, Kali Linux supports everything from network scanning and wireless testing to reverse engineering and digital forensics. One of the key strengths of Kali lies in its vast library of built-in utilities and command-line tools tailored for real-world cyber operations. Kali Linux commands are essential for navigating the system, automating tasks, and launching sophisticated security assessments. Among the most powerful tools included is Metasploit, a widely used penetration testing framework. Learning Metasploit Kali Linux commands allows security professionals to simulate real attacks and uncover system vulnerabilities with precision. From launching exploits to managing payloads, these commands streamline complex processes and enhance testing efficiency. For aspiring ethical hackers and cybersecurity enthusiasts, understanding Kali Linux commands for ethical hacking is a crucial step toward mastering threat detection and mitigation. Whether you’re learning independently or enrolled in a structured Cyber Security Training program, gaining hands-on experience with these commands builds a strong technical foundation for real-world scenarios and certification readiness. With support for both graphical and terminal-based operations, Kali Linux caters to users at all skill levels. Whether running live from a USB or installed on a virtual machine, it offers unmatched versatility for security auditing and education. In today’s cyber landscape, Kali remains a cornerstone for defensive and offensive security practices.
Interested in Obtaining Your Cybercrime Certificate? View The Cyber Security Online Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Importance in Penetration Testing
- Purpose-Built for Pentesting: Kali Linux is specifically designed for Linux pentesting, making it a top choice among cybersecurity professionals. It includes pre-installed tools for vulnerability assessment, network scanning, and exploitation, reducing the setup time significantly.
- Industry Recognition and Certifications: Many professionals pursuing Linux certification in cybersecurity rely on Kali Linux as part of their training and exam preparation. Its tools align closely with practical testing scenarios found in certifications like CEH and OSCP, where foundational topics such as Exploring Digital Signature in Cryptography also play a vital role in understanding secure communication and data integrity.
- Customizable Command Line with Aliases: Using Alias Kali Linux commands allows users to speed up routine tasks and personalize the terminal, streamlining workflows and improving productivity during complex tests.
Kali Linux plays a vital role in modern penetration testing by offering a stable, secure, and customizable environment packed with industry-standard tools. It empowers ethical hackers and cybersecurity professionals to simulate real-world attacks, identify vulnerabilities, and strengthen system defenses. Here’s why Kali Linux is so important in penetration testing:
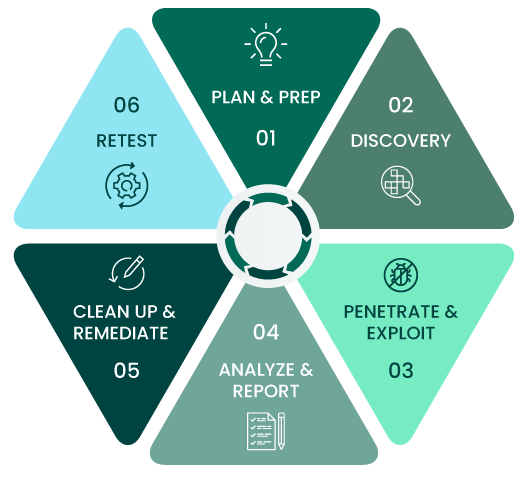
- Mastery of Basic Tools and Commands: Understanding basic Kali commands is essential for performing reconnaissance, privilege escalation, and system exploitation. These commands form the foundation of every penetration tester’s skill set.
- Lightweight Deployment with Docker: With Docker run Kali Linux, testers can quickly spin up isolated environments for secure and scalable testing ideal for CI/CD pipelines or cloud-based assessments.
- Active Community and Updates: Frequent updates and a strong community ensure that Kali Linux stays ahead in the ever-evolving cyber threat landscape, continually adding support for new tools and exploits.
- LS – List Contents: Displays all files and folders in the current directory. A go-to command in any Kali Linux commands for ethical hacking workflow to check for payloads, scripts, or output files.
- CD – Change Directory: Used to navigate between folders. Crucial when switching into tool directories or log folders during active testing, especially during hands-on exercises in Cyber Security Training programs.
- Mkdir – Make Directory: Creates a new folder to store reports, exploit files, or scripts retrieved via Metasploit Kali Linux commands.
- RM – Remove Files or Directories: Deletes unnecessary files or folders. Must be used with caution to avoid losing critical data.
- CP and MV – Copy and Move Files: Used to duplicate or relocate files across directories, especially when organizing test results or exploit data.
- Touch – Create Empty File: Quickly creates a blank file, often used to generate custom scripts or placeholder logs in ethical hacking tasks.
- John the Ripper: A fast and flexible tool used for cracking password hashes. It supports multiple formats and can be automated using various Kali Linux commands for batch testing.
- Hydra: Known for its speed, Hydra performs brute-force attacks on various services like SSH, FTP, and HTTP. It’s a core part of Kali Linux commands for ethical hacking involving network-based logins.
- Hashcat: A GPU-accelerated cracking tool capable of cracking even complex passwords. It’s ideal for offline attacks on leaked hash databases, especially when targeting legacy encryption methods like the Data Encryption Standard Algorithm, which are still encountered in some outdated systems.
- Medusa: Similar to Hydra, Medusa supports parallel login attempts and is often used in scripted attack chains.
- Metasploit’s Auxiliary Modules: Some Metasploit Kali Linux commands allow users to launch brute-force modules directly from the console for password testing.
- Crunch: A wordlist generator that creates custom password dictionaries for targeted brute-force attacks, enhancing control over cracking attempts.
Getting Started with Kali Terminal
Getting started with the Kali terminal is the first step toward unlocking the full potential of this powerful penetration testing platform. The terminal in Kali Linux offers direct access to a wide range of tools and utilities, making it an essential environment for ethical hackers and cybersecurity learners. By mastering Kali Linux commands, users can navigate directories, manage files, control services, and execute complex security assessments with precision and speed. The command-line interface is not just efficient it’s critical for scripting and automation during penetration testing tasks. Among the most important tools accessed via the terminal is Metasploit, one of the industry’s most powerful exploitation frameworks. A solid grasp of networking concepts, such as What is the TCP/IP Model, further enhances your ability to understand how these tools interact with systems and communicate over networks. Knowing how to execute Metasploit Kali Linux commands allows users to launch exploits, manage sessions, and test vulnerabilities in a controlled environment. Whether you’re running scans, cracking passwords, or performing post-exploitation tasks, understanding Kali Linux commands for ethical hacking helps streamline your workflow and ensure repeatable, professional-grade results. For beginners, the terminal may seem intimidating at first, but with practice, it becomes a vital skill that enhances every aspect of a security assessment. With Kali’s documentation and active community, even newcomers can confidently start using the terminal to build real-world hacking and defense skills.
To Explore Cybersecurity in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Cyber Security Online Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
File and Directory Commands
In Kali Linux, managing files and directories through the terminal is essential for both system navigation and efficient penetration testing. Understanding these fundamental Kali Linux commands allows ethical hackers to organize tools, logs, payloads, and scripts effectively. Whether you’re setting up a test environment or handling exploit data from Metasploit Kali Linux commands, these file and directory operations form the foundation of productive workflows. Here are some key commands to know:
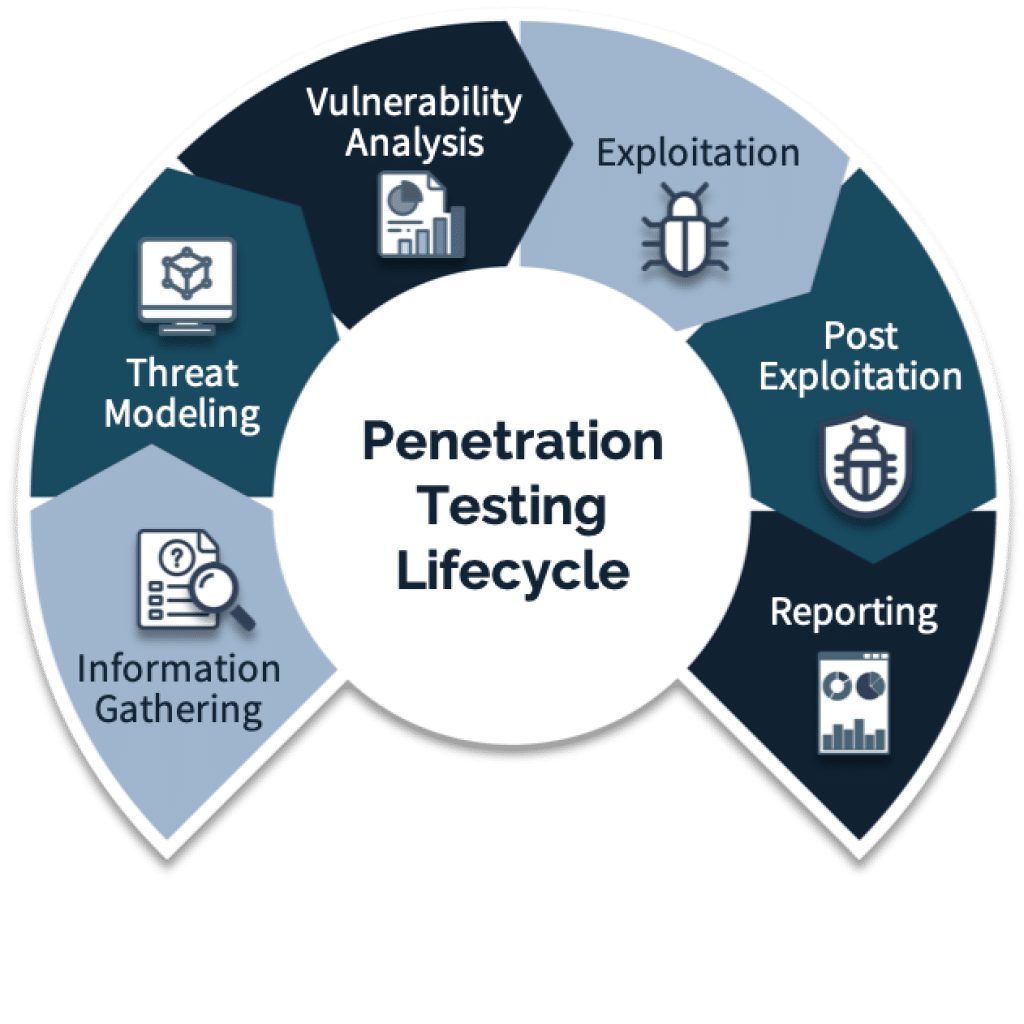
Network Scanning Commands
Network scanning is a critical first step in any Linux pentesting workflow, helping identify active hosts, open ports, and potential vulnerabilities within a target environment. In Kali Linux, mastering network scanning commands is essential for ethical hackers, especially those preparing for Linux certification or pursuing roles in cybersecurity. Tools like nmap, netdiscover, and arp-scan are among the most widely used and can be executed using basic Kali commands through the terminal. These tools enable testers to map out a network’s structure, detect running services, and gather intelligence before launching more detailed assessments. As part of a broader suite of Cyber Security Tools, using Alias Kali Linux settings allows users to customize and shorten frequent scanning commands, streamlining repetitive tasks and improving efficiency. Even when deploying Kali inside containers, using Docker run Kali Linux setups allows network scanning tasks to be isolated and portable, making it ideal for cloud environments or CI/CD pipelines. Whether you are scanning for open ports, detecting operating systems, or identifying firewall rules, Kali Linux offers the flexibility and precision needed for thorough reconnaissance. Understanding and practicing these network scanning techniques not only enhances your technical capabilities but also prepares you for real-world penetration testing challenges and advanced security roles.
Looking to Master Cybersecurity? Discover the Cyber Security Expert Masters Program Training Course Available at ACTE Now!
Password Cracking Utilities
Password cracking is a vital aspect of ethical hacking, used to test the strength of passwords and uncover weak authentication practices. Kali Linux comes equipped with several robust tools designed for this purpose, enabling professionals to simulate real-world attack scenarios. By leveraging Kali Linux commands and integrating them with powerful tools, security testers can perform efficient password audits. Here’s a look at some of the most widely used password-cracking utilities:
Wireless Hacking Tools
Wireless hacking tools are an essential part of any ethical hacker’s toolkit, especially when assessing the security of Wi-Fi networks. Kali Linux offers a comprehensive suite of utilities designed to discover, monitor, and exploit wireless vulnerabilities, making it a key platform for anyone involved in Linux pentesting or pursuing Linux certification. Tools like aircrack-ng, reaver, and wifite enable professionals to capture handshakes, crack encryption keys, and perform brute-force attacks on WPS-enabled routers. With the help of basic Kali commands, users can control wireless interfaces, launch monitor modes, and capture critical packets with precision skills that are highly valuable when getting started with an Introduction to Bug Bounty Programs, where identifying and reporting wireless vulnerabilities can earn real-world rewards. Creating custom Alias Kali Linux shortcuts for repetitive scanning and cracking commands further streamlines the testing workflow, saving time during high-pressure assessments. Even in isolated test environments, using Docker run Kali Linux setups makes it possible to perform wireless testing without affecting the host system ideal for learners and professionals working in virtual labs. Wireless hacking is not just about attacking networks; it’s about understanding how vulnerabilities in configurations, weak passwords, or outdated protocols can be exploited. Mastering these tools and techniques ensures that security professionals can advise organizations on how to strengthen wireless defenses and avoid common pitfalls in their network security infrastructure.
Preparing for Cyber Security Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on Cyber Security Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Exploitation Frameworks
Exploitation frameworks are core components of any advanced Linux pentesting process, allowing ethical hackers to identify, exploit, and validate vulnerabilities in a structured and repeatable way. Kali Linux comes equipped with leading exploitation frameworks like Metasploit, Armitage, and ExploitDB, all of which are widely used by professionals preparing for Linux certification or real-world red team operations. These frameworks streamline post-reconnaissance phases by providing access to thousands of exploits, payloads, and auxiliary modules that can be easily managed using basic Kali commands. For efficient workflows, testers often create custom shortcuts using Alias Kali Linux to simplify frequent tasks such as launching listeners or setting payload options an approach commonly emphasized in hands-on Cyber Security Training programs. Frameworks like Metasploit also integrate well with tools for scanning, brute-forcing, and privilege escalation, creating an end-to-end exploitation pipeline. With the ability to Docker run Kali Linux, security practitioners can even deploy containerized instances of Kali for isolated, repeatable testing environments ideal for classroom labs or CI/CD security testing. Exploitation frameworks not only help uncover critical system flaws but also train professionals to think like attackers, making them invaluable in both proactive defense and certification preparation. Mastery of these tools builds confidence, precision, and real-world readiness in ethical hacking practices.




