
- Introduction to Cryptography in Cybersecurity
- What is Cryptography?
- Key Concepts in Cryptography
- Cryptographic Algorithms
- Cryptographic Protocols in Cybersecurity
- Applications of Cryptography in Cybersecurity
- Cryptography in the Cloud and IoT
- Cryptographic Attacks and Vulnerabilities
- Best Practices for Cryptographic Implementation
- The Future of Cryptography in Cybersecurity
- Conclusion
The digital landscape continues to expand, cybersecurity has become an essential focus for both individuals and organizations. The increasing reliance on digital platforms for communication, transactions, and data storage has significantly heightened the threat of cyberattacks and data breaches. At the heart of modern Cybersecurity Training Courses lies cryptography, a powerful tool designed to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access. By encrypting data, cryptography ensures privacy, integrity, and authentication in everything from online banking to secure messaging and cloud computing. As cyber threats evolve, cryptography remains one of the most effective defenses against data theft, identity fraud, and system manipulation. With its continuous advancements, cryptography plays a crucial role in maintaining trust in the digital world.
Want to learn more about Cybersecurity ? Enroll in our Complete Cyber Security Online Training Online!
Introduction to Cryptography in Cybersecurity
In an increasingly interconnected world, cybersecurity has become a vital concern for individuals and organizations alike. With the rise of digital transactions, data exchanges, and online interactions, the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive information is greater than ever. One of the cornerstones of modern cybersecurity is cryptography, which plays a critical role in safeguarding data, ensuring confidentiality, and maintaining trust between users and systems. Cryptography is more than just an academic concept—it is a key technology that protects information in digital systems, securing everything from online banking and e-commerce to personal communications and critical infrastructure. In this article, we will explore the essentials of cryptography and its pivotal role in cybersecurity. We’ll discuss the key concepts, algorithms, protocols, and best practices used to protect digital data. Moreover, we’ll delve into the challenges posed by emerging technologies such as quantum computing and the ways cryptography is evolving to meet these new threats.
What is Cryptography?
- Encryption and Decryption: Encryption converts plaintext into ciphertext using a cryptographic key, while decryption converts ciphertext back to plaintext. These processes are fundamental to protecting data.
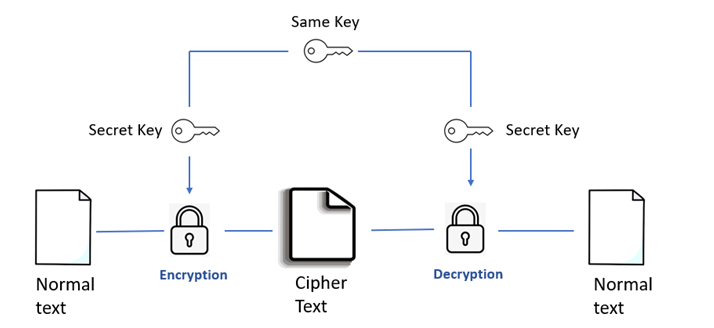
- Cryptographic Keys: Keys are secret pieces of information used to perform encryption and decryption operations. Symmetric encryption uses the same key for both operations, while asymmetric encryption uses a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption.
- Symmetric vs. Asymmetric Cryptography: Symmetric cryptography uses the same key for both encryption and decryption, which makes it faster but less secure if the key is compromised. Asymmetric cryptography uses a pair of keys public and private offering greater security but requiring more computational resources.
- Hash Functions: These are algorithms that take input data (e.g., a file or password) and produce a fixed-size string of characters (hash), which is unique to the input data. Hashing is mainly used for data integrity checks and password storage.
- SSL/TLS: Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS) are protocols used to secure internet communication by encrypting data exchanged between web browsers and servers, ensuring data confidentiality and integrity.
- HTTPS: HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) is the secure version of HTTP, which uses SSL/TLS to encrypt communications between browsers and websites, preventing interception of sensitive information like passwords and credit card numbers.
- IPsec: Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) is a suite of Address Resolution Protocol used to secure IP communications by encrypting and authenticating packets of data exchanged over a network. It is often used in Virtual Private Networks (VPNs).
- Digital Signatures: Digital signatures provide a way to verify the authenticity and integrity of digital messages or documents. They are based on asymmetric cryptography and ensure that a specific sender sent a message and has not been altered.
- Data Encryption: Cryptography secures data both at rest and in transit, making it unreadable to unauthorized users. It protects sensitive information stored on devices or transmitted over networks. Encryption methods like AES ensure data confidentiality and prevent breaches.
- Secure Authentication: Cryptographic techniques, including Password Authentication hashing and digital certificates, verify user identities. These methods ensure that only authorized individuals can access systems or data. Strong authentication, like two-factor authentication (2FA), further enhances security.
- Digital Signatures: Digital signatures authenticate the sender’s identity and ensure the integrity of messages or transactions. They use asymmetric encryption to confirm the legitimacy of data. This prevents tampering, impersonation, and fraud in digital communications.
- Blockchain and Cryptocurrencies: Cryptography secures blockchain networks and digital currencies like Bitcoin. It ensures the integrity and privacy of transactions through hash functions and digital signatures. Blockchain relies on cryptographic methods to maintain decentralized trust and security.
- Brute Force Attacks: In a brute force attack, an attacker attempts to decrypt data by systematically trying every possible key until the correct one is found. The strength of encryption depends on the length and complexity of the key.
- Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) Attacks: In an MITM attack, the attacker intercepts and potentially alters the communication between two parties without their knowledge, often exploiting weaknesses in encryption protocols.
- Side-Channel Attacks: These attacks exploit physical side effects of cryptographic operations, such as timing information or power consumption, to gather information that can be used to break the encryption.
- Weak Algorithms: Older or poorly implemented cryptographic algorithms, such as DES or MD5, are vulnerable to attacks. Using strong, modern algorithms like AES and SHA-256 is essential for security.
- Choosing the Right Algorithm: Select strong, modern cryptographic algorithms like AES, RSA, and SHA-256. These algorithms are widely accepted and have been rigorously tested. Always ensure the chosen algorithm is resistant to emerging threats and computational advancements.
- Key Management and Protection: Securely generate, distribute, and store Quantum Cryptography keys using best practices. Use hardware security modules (HSMs) or key management systems (KMS) to protect keys. Implement regular key rotation and strict access controls to prevent unauthorized access.
- Cryptography Compliance and Standards: Follow industry standards like FIPS 140-2, GDPR, and HIPAA to ensure cryptographic solutions meet legal and security requirements. Compliance helps prevent data breaches and ensures sensitive information is adequately protected. Adhering to these standards strengthens overall cybersecurity.
- Quantum Cryptography: As quantum computing advances, it poses a potential threat to traditional cryptographic systems. Quantum cryptography uses principles of quantum mechanics to secure communication and is a possible solution to quantum computing challenges.
- Post-Quantum Cryptography: Research into post-quantum cryptography is focused on developing new cryptographic algorithms that are secure against quantum computer attacks, ensuring that data remains safe in the quantum era.
- Emerging Trends: Cryptography continues to evolve, with developments in areas like homomorphic encryption (enabling computations on encrypted data) and blockchain-based privacy solutions, aiming to enhance both security and user privacy.
Cryptography is the practice of securing communication and data through advanced mathematical techniques. It involves converting information into a form that is unreadable without the correct decryption key, ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of the data. By utilizing encryption algorithms, cryptography protects sensitive information from unauthorized access, tampering, and fraud. Historically, cryptography was primarily used to safeguard military and governmental secrets, but today, it plays an essential role in securing Digital Forensics communications across various industries. It is fundamental to the operation of online banking, e-commerce transactions, healthcare data management, and cloud services, ensuring that personal and financial information remains safe in an increasingly interconnected world. With the rise of cyber threats, cryptography has become a cornerstone of modern cybersecurity, helping to protect both individual privacy and national security.
Key Concepts in Cryptography
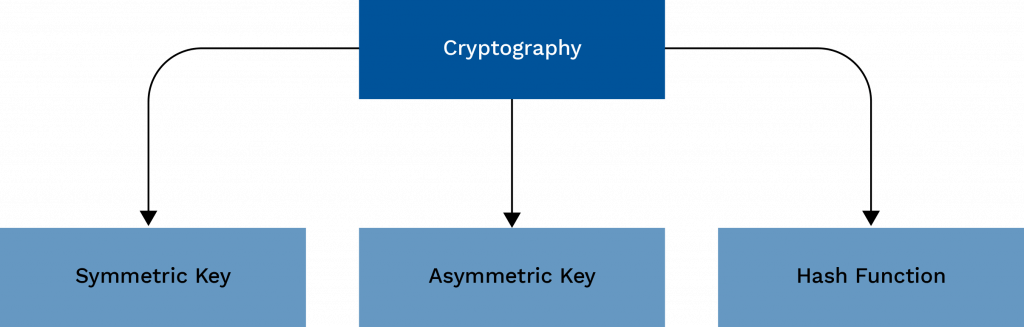
Cryptographic Algorithms
Symmetric Algorithms include the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) and the Data Encryption Standard (DES). These algorithms are efficient for encrypting large amounts of data but rely on keeping the encryption key secret. Public Key Algorithms including RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) and Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) are examples of public key algorithms. Cybersecurity Training Courses use a pair of keys for encryption and decryption, allowing secure communication between parties without sharing a secret key in advance. Cryptographic Hash Functions like SHA (Secure Hash Algorithms), such as SHA-256 and MD5, are popular cryptographic hash functions used for integrity checking and digital signatures. Hybrid cryptography systems combine both symmetric and asymmetric cryptography, leveraging the strengths of each. An example is the use of asymmetric encryption to exchange a symmetric key, which is then used to encrypt the actual data.
Enroll in ACTE’S Cyber Security Online Training if you want to become an expert in cyber security field and have a prosperous career.
Cryptographic Protocols in Cybersecurity
Applications of Cryptography in Cybersecurity
Cryptography in the Cloud and IoT
Securing Cloud Data Cryptography is vital for protecting data stored in the cloud, ensuring its confidentiality and integrity. Cloud service providers use encryption methods for data both at rest (stored data) and in transit (data being transmitted). This encryption prevents unauthorized access and ensures that sensitive information remains private, even if cloud servers are compromised. IoT Cryptography in the Internet of Things (IoT), cryptography safeguards the data exchanged between devices, Network Security Keys, and servers. By encrypting communication, it prevents unauthorized access and protects devices from cyberattacks. Strong cryptographic measures are essential to ensure the secure functioning of IoT devices, such as smart home systems and connected medical devices. Data Privacy Cryptography plays a key role in maintaining data privacy, especially in industries like healthcare and finance. Strong encryption ensures that sensitive personal information, such as medical records or financial transactions, remains protected from unauthorized access. Compliance with data privacy regulations like GDPR and HIPAA requires cryptographic solutions to meet strict security standards and safeguard user information.
Want to Take the Lead in Cyber Security ? Enroll in ACTE’s Cybersecurity Expert Masters Program Training Course Program to Begin Your Adventure Now.
Cryptographic Attacks and Vulnerabilities
Best Practices for Cryptographic Implementation
Preparing for a job interview in cybersecurity ? Examine our blog post about Cybersecurity Interview Questions and Answers to get the most of your employment experience!
The Future of Cryptography in Cybersecurity
Conclusion
Cryptography is the backbone of modern cybersecurity. From encrypting sensitive data to securing online transactions, cryptography plays an essential role in ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of digital communications. However, as cyber threats continue to evolve, Cybersecurity Training must also adapt to stay ahead of malicious actors. By understanding the key concepts, algorithms, protocols, and best practices associated with cryptography, organizations and individuals can better protect themselves against data breaches and cyberattacks. Looking ahead, the future of cryptography will be shaped by advancements in quantum computing, emerging cryptographic techniques, and the continued need to safeguard our digital lives.





