
- Introduction to Data Classification
- Levels of Data Sensitivity
- Types of Classification
- Manual vs Automated Classification
- Classification Tools and Software
- Legal and Compliance Considerations
- Role in Risk Management
- Conclusion
Introduction to Data Classification
Data classification is a fundamental process that helps organizations understand what data they have, where it is stored, and how it should be managed and protected. At its simplest, classification involves categorizing data based on criteria such as content, context, or rules defined by users. This approach is essential for putting in place security controls and policies that match the value and sensitivity of the information. Whether the data consists of emails, documents, databases, or files stored in the cloud, classification helps organizations organize their digital assets in a meaningful way. It separates data into categories like public, internal, confidential, or highly sensitive, allowing security teams to apply the appropriate access controls, encryption, and monitoring in Cyber Security Training. For example, sensitive customer information such as social security numbers or financial data requires more strict handling compared to less sensitive operational information. In addition to security, data classification supports compliance with regulations, risk management, and operational efficiency. Organizations must meet requirements from laws like GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA, and classification provides the visibility needed to protect data and follow these rules. It also helps prevent data sprawl, reduce storage costs, and improve the speed and accuracy of incident response by identifying the affected data during security events. Overall, data classification enables organizations to make informed decisions about how data is accessed, shared, stored, and disposed of. By focusing protection efforts based on the sensitivity of information, businesses can use their resources more effectively, reduce risk, and promote responsible data handling. In today’s data-driven world, classification is a key step toward strong governance, compliance, and security.
Interested in Obtaining Your Cybercrime Certificate? View The Cyber Security Online Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Levels of Data Sensitivity
Data classification typically involves defining different levels of data sensitivity to help organizations manage and protect their information effectively. While the exact categories may vary between organizations, there are common tiers that many follow. The first level is public data, which consists of information that can be freely shared with anyone without any risk. This could include marketing materials, press releases, or general company information meant for wide distribution in What is ECSA. The next level is internal use only, which refers to information that is not intended for public disclosure but is not highly sensitive either. This may include internal policies, meeting notes, or operational details that should be kept within the organization to prevent misunderstandings or misuse. More sensitive is the confidential level, which includes data that, if exposed, could cause moderate harm to the organization or individuals.
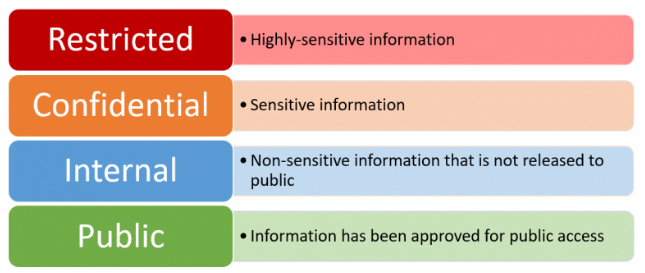
Examples of confidential data include employee records, business plans, or customer contact details. This type of data requires stricter access controls and protection measures to prevent unauthorized disclosure. At the highest sensitivity level, organizations classify data as restricted or highly confidential. Exposure of this data could lead to serious consequences, such as legal action, financial loss, or damage to the company’s reputation. Examples include intellectual property, financial statements, and sensitive personal information protected by laws such as GDPR or HIPAA. By understanding and clearly defining these data sensitivity levels, organizations can implement appropriate security controls and prioritize their efforts where protection is most critical. This structured approach ensures that the most valuable and vulnerable data receives the highest level of security, helping to minimize risks and maintain compliance with legal and regulatory requirements. Ultimately, data classification is a key component of an effective data governance strategy.
Types of Classification
- Public Data: This type of data is intended for general access and can be freely shared without any risk. Examples include marketing materials, press releases, and publicly available reports.
- Internal Use Only: Information in this category is meant for use within the organization but does not contain sensitive details. It may include internal policies, employee directories, or routine operational documents.
- Confidential Data: Confidential data includes information that requires protection because its unauthorized disclosure could cause moderate harm in The Phases of Ethical Hacking.
- Restricted or Highly Confidential Data: This classification applies to data whose exposure could lead to serious consequences such as legal penalties, financial loss, or reputational damage.
- Regulated Data: Certain types of data are governed by laws and regulations that dictate how they must be handled. Examples include personally identifiable information (PII), health records covered by HIPAA, and payment card information regulated under PCI DSS.
- Encrypted Data: While not a classification based on content, encrypted data is information that has been transformed to protect its confidentiality. Encryption is often applied to sensitive or restricted data to enhance security.
- Archived Data: This type refers to data that is no longer actively used but must be retained for legal, compliance, or historical reasons. Archived data typically has different access controls and storage requirements.
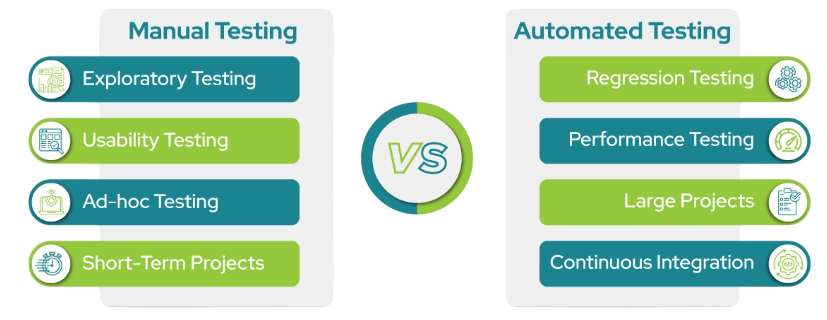
- Manual Classification: In manual classification, human users review data and assign categories based on their understanding and company policies in Cyber Security Training.
- Automated Classification: Automated classification uses software tools to scan data and apply labels based on predefined rules or machine learning algorithms. It can process large volumes of data quickly and consistently.
- Accuracy: Manual classification benefits from human intuition, enabling better handling of context and exceptions. However, it may suffer from errors or inconsistencies due to human fatigue or misunderstanding.
- Scalability: Manual classification is difficult to scale because it requires significant human effort, which may not be practical for large data volumes. Automated classification can handle vast amounts of data efficiently across multiple platforms.
- Flexibility: Manual classification can adapt easily to new data types or unique situations, as humans can interpret nuances that automated tools might miss. Automated classification depends on the quality of its programming and may need regular updates to accommodate changes.
- Cost: Manual classification incurs higher ongoing costs due to labor requirements. Automated classification often requires upfront investment in software but can lower costs over time through efficiency gains.
- Hybrid Approach: Many organizations use a combination of both methods, leveraging automation for bulk classification and manual review for sensitive or complex data. This balances efficiency and accuracy.
- Regulatory Requirements: Laws such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS mandate that organizations identify and protect sensitive data. Proper classification is essential to meeting these legal obligations.
- Identifying Sensitive Data: Classification helps organizations clearly define which data is sensitive and requires special handling, such as personal information, health records, or payment card details.
- Protecting Data: By classifying data correctly, organizations can apply appropriate security controls like encryption, access restrictions, and monitoring to safeguard it from unauthorized access or breaches in Average Annual Salary of a CISSP Certified Professional.
- Avoiding Penalties: Failure to properly classify and protect regulated data can lead to substantial fines, legal penalties, and other financial consequences imposed by regulatory bodies.
- Reputation Management: Data breaches often damage public trust and harm an organization’s reputation. Effective classification helps reduce the risk of such incidents, supporting long-term business success.
- Audit Preparedness: Classification enables organizations to quickly demonstrate compliance during audits by providing clear evidence of data handling practices aligned with legal requirements.
- Retention and Disposal: Classification ensures that data retention and disposal policies comply with laws, helping organizations retain information only as long as legally required and securely delete it when no longer needed.
To Explore Cybersecurity in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Cyber Security Online Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Manual vs Automated Classification
Classification Tools and Software
Numerous tools and platforms are available to support data classification and help organizations manage their information securely. Among the well-known solutions are Microsoft Information Protection, Symantec Data Loss Prevention (DLP), Varonis Data Security Platform, Forcepoint DLP, and McAfee Total Protection for DLP. These tools provide comprehensive capabilities to identify, classify, and protect sensitive data across a variety of environments. They often integrate seamlessly with an organization’s existing IT infrastructure, making it easier to scan data repositories such as file servers, databases, email systems, and cloud storage locations. One of the key features of these platforms is their ability to apply classification labels automatically based on predefined rules, content inspection, or user input in Who is an Ethical Hacker. This helps maintain consistency in how data is categorized and protected throughout its lifecycle. In addition to classification, these tools monitor data usage and user activity to detect unusual or unauthorized access patterns. When a potential data leak or policy violation is detected, they can enforce security controls such as blocking access, alerting administrators, or encrypting the data to prevent exposure. These solutions are designed to work across different environments, including cloud platforms like Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services, and Google Cloud, as well as traditional on-premises systems and mobile devices. This wide coverage ensures that data classification and protection policies remain consistent regardless of where data is stored or accessed. By implementing these tools, organizations can reduce the risk of data breaches, meet regulatory compliance requirements, and improve overall data governance. Ultimately, data classification platforms provide the visibility and control needed to protect valuable information assets in today’s complex and distributed IT landscape.
Looking to Master Cybersecurity? Discover the Cyber Security Expert Masters Program Training Course Available at ACTE Now!
Legal and Compliance Considerations
Role in Risk Management
Effective data classification plays a crucial role in an organization’s overall risk management strategy. By clearly identifying which data is most critical and sensitive, businesses can prioritize their security measures and focus resources where they are needed most. For example, highly sensitive information such as financial records, personal customer data, or intellectual property typically requires strong protections like encryption, strict access controls, and multi-factor authentication. These measures help reduce the risk of unauthorized access or data breaches. In contrast, public data, which poses little or no risk if disclosed, can be managed with minimal security controls. This tiered approach ensures that security efforts are proportional to the sensitivity of the data in How to Become a Cyber Security Engineer, optimizing both protection and operational efficiency. Beyond security, data classification also supports business continuity and disaster recovery planning. By knowing which data is essential for day-to-day operations, organizations can ensure that critical information is backed up regularly and can be restored quickly in the event of a system failure, cyberattack, or natural disaster. This reduces downtime and helps maintain operational resilience. Additionally, clear classification aids in compliance with legal and regulatory requirements, which often mandate specific protections for sensitive data. Data classification aligns with broader enterprise risk management by providing visibility into the organization’s information assets and the potential risks associated with each. This awareness enables leadership to make informed decisions about risk tolerance and mitigation strategies. It also helps minimize the financial, legal, and reputational consequences of data-related incidents by proactively addressing vulnerabilities before they escalate. Overall, effective data classification is a foundational element that strengthens an organization’s security posture, supports regulatory compliance, and enhances its ability to respond swiftly and effectively to incidents.
Preparing for Cyber Security Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on Cyber Security Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Conclusion
Data classification is a vital component of modern information management and cybersecurity strategies. It provides the necessary structure for organizations to handle data responsibly, ensuring that sensitive information is properly identified and protected. By categorizing data based on its value and sensitivity, businesses can implement tailored safeguards that reduce the risk of unauthorized access, data breaches, and misuse. This structured approach not only helps protect organizations from potential legal penalties and financial losses but also guards their reputation, which can be severely damaged by data incidents. Implementing a robust data classification system supports compliance with a growing number of data protection regulations around the world, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA. These laws require organizations to demonstrate that they know what data they hold and that it is adequately protected in Cyber Security Training. Without clear classification, meeting these requirements becomes difficult and can lead to costly penalties. Additionally, classification improves operational efficiency by making it easier to locate, manage, and dispose of data when no longer needed, reducing storage costs and minimizing data sprawl. While setting up an effective classification program can present challenges, including defining consistent criteria and ensuring user adoption, the long-term benefits far outweigh the initial effort. A well-designed system fosters a culture of data stewardship where employees understand the importance of protecting information according to its sensitivity. As organizations face ever-increasing volumes of data and more complex IT environments, the ability to classify and manage data effectively becomes critical to maintaining security and achieving business success. Ultimately, data classification is not just a technical requirement but a strategic enabler for safeguarding information assets and supporting organizational goals.




