
- Introduction to Cyber Law
- Scope and Objectives
- Categories of Cyber Crimes
- Data Protection and Privacy Laws
- Intellectual Property Rights Online
- Electronic Contracts and Signatures
- Jurisdiction and Legal Challenges
- Role of National and International Bodies
Introduction to Cyber Law
Cyber Law refers to the legal measures and frameworks established to regulate activities in the digital space, ensuring ethical and secure usage of technology and the internet. As the world becomes increasingly connected, Cyber Law and Security have emerged as essential components in protecting individuals, organizations, and governments from malicious online activities. These laws address issues such as data protection, privacy breaches, identity theft, hacking, and unauthorized access to sensitive information. With the rising number of cyber security threats, ranging from ransomware attacks to phishing scams and cyber espionage, countries around the globe are focusing on implementing robust legal systems and promoting Cyber Security Training to effectively combat digital crimes. In India, for instance, the Information Technology Act, 2000, serves as the foundational legislation governing cyber activities. Moreover, National Cyber Security initiatives are being developed to strengthen the digital infrastructure, enhance awareness, and coordinate defense mechanisms against large-scale cyberattacks. Cyber law not only enforces legal actions against offenders but also provides guidelines for digital conduct, ensuring a safer and more responsible internet environment. As the digital ecosystem continues to evolve, so must the laws that govern it, making cyber law a dynamic and crucial aspect of modern legal systems.
Interested in Obtaining Your Cybercrime Certificate? View The Cyber Security Online Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Scope and Objectives
- To Regulate Cyber Activities Legally: Establishing clear internet security laws to govern online behavior, transactions, and communication ensures digital accountability and legal clarity.
- To Prevent and Investigate Cybercrimes: Enabling effective cyber investigation mechanisms helps law enforcement agencies trace, analyze, and prosecute cyber offenders efficiently, while initiatives that Explain What Is BOT contribute to identifying and mitigating bot-driven cyber threats.
- To Address Various Cyber Threats: Covering multiple types of cyber security threats such as malware, phishing, and denial-of-service attacks helps in creating comprehensive protective frameworks.
The scope and objectives of Cyber Law revolve around creating a secure and regulated digital environment by addressing cybercrimes, protecting data, and ensuring responsible use of technology. As digital platforms grow, so does the complexity of online threats, making it vital to understand the goals and reach of cyber regulations. The following points outline the key areas covered under this domain:
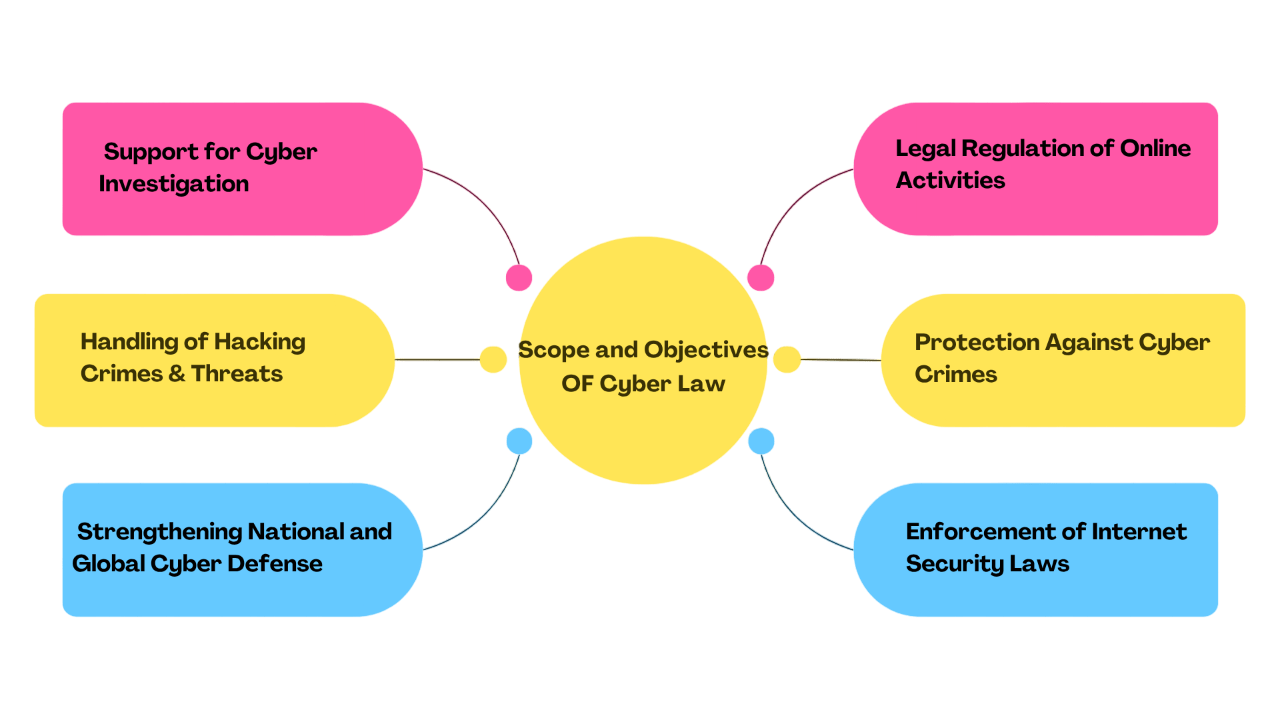
- To Combat Hacking and Unauthorized Access: Tackling hacking crimes through strict laws and penalties discourages unauthorized system intrusions and data theft.
- To Strengthen National and Federal Response: Coordinating with federal cyber crime units ensures a unified national defense against cross-border and high-level cyber threats.
- To Protect User Rights and Privacy: Ensuring online privacy and data protection through well-defined laws enhances trust and safeguards individual rights in the digital realm.
Categories of Cyber Crimes
Cyber crimes are broadly categorized based on the target and nature of the offense, and understanding these categories is crucial to strengthening Cyber Law and Security. The primary types include crimes against individuals, such as cyberstalking, identity theft, and online harassment; crimes against property, which involve hacking, data breaches, and intellectual property theft; and crimes against government or organizations, such as cyberterrorism and cyber espionage. With the rise of sophisticated cyber security threats, these crimes are becoming more frequent and complex, targeting everything from personal data to national defense systems. Financial frauds, ransomware attacks, and phishing scams also fall under common cyber offenses, often resulting in significant economic and reputational damage. Implementing Non-Repudiation in Cyber Security Techniques is crucial to ensure accountability and prevent denial of actions in such malicious activities. In response to this growing threat landscape, nations are increasingly investing in National Cyber Security initiatives to build resilient infrastructures and enhance legal frameworks for cybercrime prevention and prosecution. These efforts include the development of advanced threat detection systems, the implementation of strict data protection regulations, and the promotion of public awareness on digital safety. The categorization of cybercrimes not only helps in better legal classification but also enables the formulation of targeted laws and defense strategies, reinforcing the overall effectiveness of cyber law enforcement.
To Explore Cybersecurity in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Cyber Security Online Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Data Protection and Privacy Laws
- Establishing Internet Security Laws: These laws outline the legal framework for securing online data, ensuring transparency, accountability, and consent in data usage.
- Strengthening Cyber Investigation Capabilities: Modern privacy laws empower law enforcement agencies to conduct cyber investigations into breaches and misuse, while Cyber Security Training ensures these investigations are conducted effectively and ethically, maintaining a balance between security and civil liberties.
- Combating Hacking Crimes: Strong legal provisions are in place to detect, prevent, and penalize hacking crimes, which often lead to major data leaks and identity theft.
Data protection and privacy laws are essential in today’s digital world to safeguard personal and sensitive information from unauthorized access and misuse. These laws not only define how data should be collected, stored, and shared but also establish users’ rights over their own digital information. With increasing online activity, the need for robust privacy legislation has become a priority for governments and organizations alike. Below are six key aspects of data protection and privacy laws:
- Regulating Types of Cyber Security Measures: Laws help define and promote various types of cyber security solutions, such as encryption, access control, and firewalls, to ensure comprehensive data protection.
- Addressing Federal Cyber Crime: National-level legislation plays a critical role in tackling federal cyber crime, particularly those involving interstate or cross-border data breaches.
- Protecting User Rights and Privacy: These laws ensure individuals have the right to know how their data is being used and offer mechanisms to request correction or deletion when necessary.
- Legal Recognition under Internet Security Laws: Most countries have incorporated internet security laws that validate electronic contracts and signatures, giving them the same legal standing as handwritten agreements.
- Preventing Forgery and Hacking Crimes: Robust authentication and encryption methods help prevent hacking crimes, such as unauthorized access or forgery of digital contracts.
- Role in Cyber Investigation: Digital signatures leave electronic trails that are critical for cyber investigation, helping identify parties involved and trace back any tampering attempts. Understanding How Cyber-Physical Systems Work further enhances the ability to secure integrated digital and physical infrastructures involved in such incidents.
- Addressing Types of Cyber Security Risks: Implementing the right types of cyber security measures like digital certificates and multi-factor authentication ensures the integrity of online agreements.
- Federal Cyber Crime Enforcement: Breaches involving forged e-signatures or fraudulent e-contracts can fall under federal cyber crime laws, especially when they cross jurisdictions.
- Boosting Trust in Digital Transactions: Legal frameworks surrounding e-signatures enhance user confidence by ensuring that their data and agreements are handled securely and lawfully.
Intellectual Property Rights Online
Intellectual Property Rights (IPR) online are crucial in protecting the ownership and originality of digital content such as software, music, literature, trademarks, and inventions. In the digital space, where duplication and unauthorized sharing can happen within seconds, the enforcement of IPR ensures that creators and businesses retain control over their innovations. Under Cyber Law and Security, online IPR safeguards help prevent piracy, copyright infringement, and misuse of trade secrets, thereby fostering a secure digital economy. However, the growing wave of cyber security threats, such as data theft and illegal downloads, poses serious challenges to enforcing these rights. Raising awareness through resources like a Quick Guide To Cyber Safety can empower users and organizations to better protect their intellectual property online. Cybercriminals often exploit vulnerabilities in digital platforms to replicate or distribute copyrighted material, leading to financial losses and reputational damage. To combat this, many nations are strengthening National Cyber Security frameworks by incorporating IPR protection into their broader cyber governance policies. These measures include digital watermarking, advanced encryption, and stricter cybercrime laws targeting intellectual property violations. Moreover, international cooperation and treaties play a vital role in ensuring that IPR is respected across borders. As digital content continues to expand, the importance of robust legal protections for intellectual property online becomes even more critical to innovation, economic growth, and creator rights in the cyber world.
Looking to Master Cybersecurity? Discover the Cyber Security Expert Masters Program Training Course Available at ACTE Now!
Electronic Contracts and Signatures
Electronic contracts and digital signatures have become a vital part of today’s digital economy, enabling faster, paperless transactions while maintaining legal validity. These technologies allow individuals and businesses to create, sign, and manage agreements online securely. However, with their growing use, the need for proper legal oversight and protection against cyber misuse is more important than ever. Below are six key aspects of electronic contracts and signatures:
Jurisdiction and Legal Challenges
Jurisdiction and legal challenges in cyberspace present complex issues due to the borderless nature of the internet, making it difficult to determine which country’s laws apply in cases of online misconduct. When cybercrimes such as data breaches, identity theft, or hacking crimes occur across different countries, enforcing laws becomes complicated. Traditional legal systems struggle to keep up with the speed and anonymity of digital offenses. For example, a hacker in one country can target victims in another, raising questions about where the case should be tried and which laws should govern it. This legal ambiguity complicates cyber investigation efforts, as gathering digital evidence and prosecuting offenders often requires international cooperation. A deeper Understanding Cybercrime and its Implications is essential to navigate cross-border legal challenges and strengthen global enforcement strategies. Although efforts are underway to create global agreements, disparities in internet security laws still pose major hurdles. Additionally, the evolving types of cyber security threats demand continuous updates to legal frameworks to ensure relevant protections. In the U.S., for instance, cross-border offenses often escalate into federal cyber crime cases, handled by national agencies like the FBI or DHS. As the digital world expands, addressing these jurisdictional and legal challenges is crucial for effective enforcement, victim protection, and the development of a harmonized global approach to cyber law.
Preparing for Cyber Security Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on Cyber Security Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Role of National and International Bodies
The role of national and international bodies in cyber law enforcement is pivotal in ensuring a secure and well-regulated digital ecosystem. National agencies are responsible for enforcing internet security laws, conducting cyber investigations, and responding to threats that compromise data integrity, critical infrastructure, or public safety. These bodies, such as CERT-In in India or the FBI’s cyber division in the U.S., address everything from routine cyber fraud to large-scale federal cyber crime. Their responsibilities include monitoring hacking crimes, issuing security advisories, and collaborating with law enforcement to identify and prosecute offenders. Simultaneously, international organizations like INTERPOL, the United Nations, and the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) play a key role in establishing global frameworks, facilitating cooperation across borders, and encouraging Cyber Security Training to build a resilient digital ecosystem. They work to standardize legal responses, share threat intelligence, and create common protocols to tackle the growing variety of types of cyber security threats. With cybercriminals often operating beyond national boundaries, these international efforts are essential for ensuring cohesive responses and closing jurisdictional gaps. By aligning laws and improving cross-border collaboration, national and international bodies together help in developing a unified approach to digital law enforcement and global cyber resilience.




