
- Introduction to Cybersecurity in Banking
- Key Cybersecurity Risks Faced by Banks
- Importance of Cybersecurity in Protecting Customer Data
- Cybersecurity Regulations and Compliance in Banking
- The Growing Threats in the Banking Sector
- Best Practices for Cybersecurity in the Banking Sector
- The Role of Encryption in Banking Security
- Emerging Technologies and Cybersecurity in Banking
- The Impact of Cyber Attacks on Banks and Financial Institutions
- Conclusion
Introduction to Cybersecurity in Banking
Cybersecurity for banks is crucial to safeguarding private financial information and ensuring that banking systems remain secure, intact, and accessible. With the rapid expansion of digital banking, online transactions, and mobile banking services, the financial sector faces increasing vulnerabilities to cyber-attacks. Advanced cybersecurity measures are essential to protecting customer data, financial assets, and maintaining trust in banking institutions, which is why Cyber Security Training Courses are crucial for professionals in the industry. Banks must implement multi-layered security strategies, including encryption, biometric authentication, firewalls, and AI-driven threat detection, to mitigate risks. Regular security audits, compliance with industry regulations, and employee training on cybersecurity best practices further strengthen resilience against cyber threats. A proactive approach ensures uninterrupted banking services and long-term financial security.
To Earn Your Cyber Security Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Cyber Security Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Cyber Security Online Training Today!
Key Cybersecurity Risks Faced by Banks
- Data Breaches: The most severe cybersecurity risk for banks is the exposure of sensitive customer data, including personal and financial details. Breaches can occur through weak security measures or vulnerabilities in third-party systems.
- Phishing and Social Engineering: Cybercriminals often trick bank employees or customers into revealing confidential information or granting access to systems through deceptive emails or social engineering techniques.
- Ransomware: Ransomware attacks can disrupt operations by encrypting critical banking systems and demanding payment to restore access, resulting in severe financial losses.
- Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS): DDoS attacks target banking websites and online services, overloading them with traffic that causes outages and service interruptions. Implementing strong security measures like Private key and Public key Cryptography can help protect against these types of threats by ensuring secure communication and data integrity.
- Insider Threats: Employees and third-party contractors with access to sensitive data can commit insider threats by both accidental and intentional means, thus raising a potential security risk.
- Third-Party Risks: Many banks’ services rely on third-party vendors, which leaves open the vulnerability for those external systems to become compromised and steal access to sensitive banking data.
Importance of Cybersecurity in Protecting Customer Data
The protection of customer data is a critical issue in the banking sector. Banks must take strong measures to protect digital financial and personal information. A data breach not only puts customers at risk of identity theft and fraud but also hurts the bank’s reputation and credibility. It is the responsibility of financial institutions to ensure the privacy and security of their customers’ data, and using a Sandbox Environment can help them safely test and analyze potential vulnerabilities without compromising real data or systems. To achieve this, banks must implement robust encryption, multi-factor authentication, and secure transaction protocols. Regular security audits and compliance with industry regulations, such as GDPR and PCI DSS, help strengthen defenses against cyber threats. Employee training on data security best practices is crucial in minimizing risks associated with phishing and social engineering attacks. Additionally, continuous monitoring and advanced threat detection systems allow banks to respond proactively to potential breaches. By prioritizing cybersecurity and investing in advanced protective measures, financial institutions can build customer trust and ensure the long-term security of sensitive financial data in an increasingly digital banking landscape.
Interested in Obtaining Your Cyber Security Certificate? View The Cyber Security Online Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Cybersecurity Regulations and Compliance in Banking
Banks are required to adhere to several cybersecurity regulations that ensure customer data security and compliance with legal obligations. Some of these regulations include;
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): This is a European regulation on the protection and privacy of personal data.
- Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS): This is a set of standards for secure processing and handling of cardholder data.
- Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA): U.S. regulation that governs the protection of financial data in the banking industry.
- Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council (FFIEC): This council provides guidelines on cybersecurity for financial institutions in the U.S.
- Basel III: An international regulatory framework that includes provisions for banking cybersecurity and financial risk management. These regulations are essential, and failing to comply means risking penalties, losing sensitive customer information, and ending up with banks that aren’t secure and trustworthy places.
The Growing Threats in the Banking Sector
The banking industry is an easy target for cybercriminals, as financial data is considered valuable and sensitive. Online banking services, mobile applications, and cloud computing are increasingly used, which opens up more avenues for hackers to get into the system and, therefore, brings new vulnerabilities. Cyber attacks such as hacking, phishing, ransomware, and APTs are also becoming increasingly sophisticated, which is why Cyber Security Training Courses are essential for staying ahead of these evolving threats. Hence, the banks have to remain vigilant and proactive in their security measures. These hackers use increasingly sophisticated approaches, such as AI attacks, to exploit banking systems’ loopholes. As such attacks increase and become more complex, the need for banks to maintain cybersecurity has become an issue of great importance.
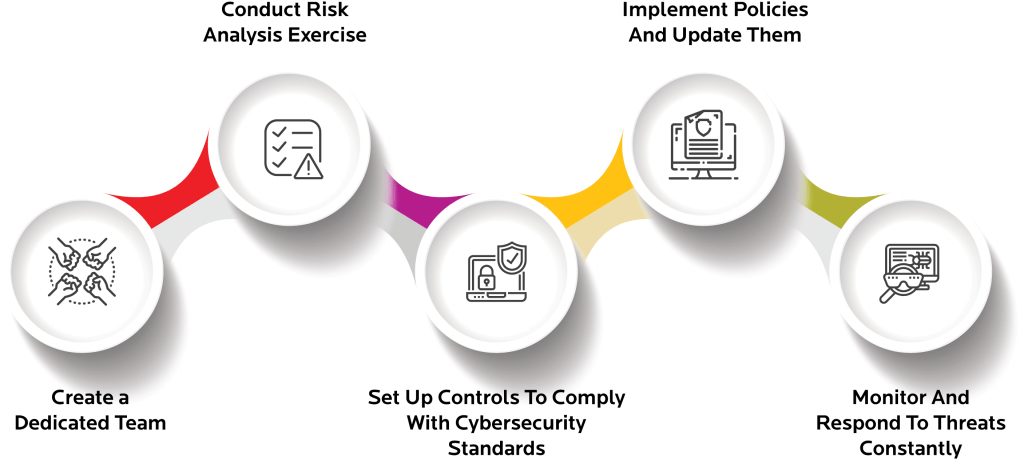
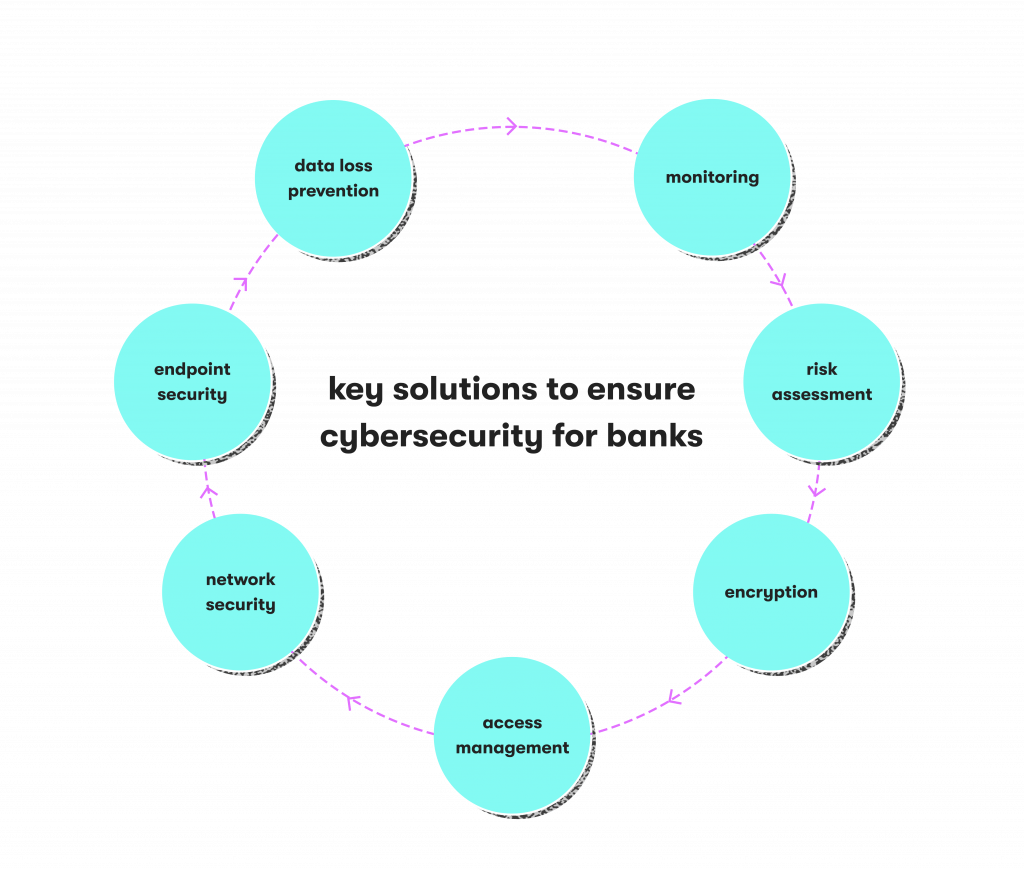
Best Practices for Cybersecurity in the Banking Sector
- Multi-factor Authentication (MFA): This involves using MFA to increase security by requiring more than one form of identification, such as a password and biometric verification, to access sensitive systems.
- Regular Security Audits: Banks should conduct frequent audits to identify system vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with security standards, addressing potential risks proactively.
- Employee Training: Regular training programs help employees recognize cybersecurity threats, such as phishing attacks, and reduce the risk of human error leading to security breaches.
- Data Encryption: Encrypting data in transit and at rest will ensure that even if data is intercepted, it will still be unreadable to third parties. Understanding Network Topology is also crucial, as it helps in identifying the most secure paths for data transmission and minimizing potential vulnerabilities in the network.
- Risk Management and Threat Detection: Advanced monitoring systems will be able to detect unusual behavior and potential threats in real-time and mitigate them before they get out of hand.
- Disaster Recovery and Incident Response Plans: Banks must have well-defined disaster recovery and incident response plans in place to ensure business continuity in the event of a cyber-attack or system failure.
- Third-Party Risk Management: Third-party vendors need to have solid cybersecurity practices in place as well to avoid exposure to vulnerabilities that could allow an intruder to breach the bank’s security.
Looking to Master Cybersecurity? Discover the Cyber Security Expert Masters Program Training Course Available at ACTE Now!
The Role of Encryption in Banking Security
Encryption is essential for the safety of sensitive financial information in banking. It makes data unintelligible so that only the rightful holder can decode it and gain access. End-to-End Encryption (E2EE) ensures that data remains encrypted during transmission, protecting it from interception. Banks also encrypt stored data to safeguard it even in the event of a security breach. Utilizing Command Prompt Commands effectively can help system administrators manage encryption settings and troubleshoot any issues related to data security. Tokenization replaces sensitive data, such as credit card numbers, with unique tokens that cannot be reverse-engineered, minimizing exposure risks. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) further enhances security by requiring multiple verification steps before granting access.
Secure Socket Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocols encrypt communications between clients and banking servers, preventing data interception. Additionally, banks implement Public Key Infrastructure (PKI), which uses digital certificates and cryptographic keys for secure authentication. Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) help monitor and block unauthorized access attempts. Regular security audits and penetration testing ensure vulnerabilities are identified and mitigated. By combining encryption, tokenization, and layered security mechanisms, banks protect financial data, prevent fraud, and maintain customer trust in digital transactions.
Emerging Technologies and Cybersecurity in Banking
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning help detect new threats and respond automatically. They will increase a bank’s capacity to detect and mitigate risks in real time.
- Blockchain: Blockchain is the decentralized and secure way to handle transactions and customer data. This will reduce fraud and ensure data integrity, while also leveraging Internet Protocol Address tracking to enhance security and verify transaction sources.
- Biometric Authentication: The technologies being developed, such as facial recognition and fingerprint scanning, will enhance security and user convenience when accessing banking services.
- Cloud Security: As more banks shift to the cloud, robust cloud security is a prime requirement to safeguard customers’ information and ensure business continuity.
- Behavioral Analytics: By analyzing customers’ and employees’ behavior, suspicious activities can be noticed well in advance, which helps prevent fraud or unauthorized access.
Preparing for Cyber Security Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on Cyber Security Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
The Impact of Cyber Attacks on Banks and Financial Institutions
Cyberattacks on banks can lead to severe financial and operational consequences. These impacts include fraud, theft, and ransom payments, resulting in direct financial losses along with the costs of recovery and mitigation. Non-compliance with data protection regulations or failure to prevent breaches can lead to heavy fines and legal action. Attacks erode customer trust, causing immediate business loss and long-term reputational damage.Ransomware and DDoS attacks can disrupt banking services, reducing customer experience and operational efficiency. Furthermore, banks may face high cybersecurity insurance premiums or difficulties securing coverage after a major cyber incident. Data breaches also expose sensitive customer information, increasing the risk of identity theft and fraud. Cybercriminals often target core banking systems, attempting to manipulate transactions or disrupt financial operations.Additionally, insider threats pose a major risk, where employees or third parties with access to critical systems can intentionally or unintentionally expose vulnerabilities. To counter these threats, banks must implement advanced cybersecurity measures such as real-time monitoring, AI-driven threat detection, multi-factor authentication, and secure encryption protocols. Strengthening cybersecurity resilience is essential to safeguarding financial stability and customer trust.
Conclusion
The banking sector will continue to go digital, and security will stay at the center. As threats in the cyber world become increasingly sophisticated, financial institutions have to keep innovating and strengthening their cybersecurity practices. In this context, there are three important areas that a bank can examine to construct a robust framework of cybersecurity emerging technologies, regulatory compliance, and customer data protection. Cyber Security Training Courses can equip professionals with the knowledge needed to address these critical areas effectively. The future of banking cybersecurity will be proactive and adaptive in safeguarding sensitive financial information and maintaining trust in the digital economic ecosystem.





