
- Overview of Vulnerability Management
- The Vulnerability Management Lifecycle
- Identifying and Classifying Vulnerabilities
- Vulnerability Scanning Tools
- Patch Management Integration
- Risk Prioritization
- Reporting and Analytics
- Conclusion
Overview of Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability management is a critical and foundational component of any organization’s cybersecurity strategy. It involves a continuous process of identifying, assessing, mitigating, and monitoring security weaknesses across all areas of the IT environment. This includes not only hardware and software assets but also cloud infrastructure, network systems, and even human factors such as user behavior and misconfigurations that may unintentionally introduce vulnerabilities. A well-structured vulnerability management program begins with the systematic identification of potential weaknesses using tools such as vulnerability scanners and threat intelligence feeds. Once identified, each vulnerability is assessed for its severity and potential impact in Cyber Security Training, often using frameworks like the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) to help prioritize risks based on their likelihood of exploitation and business impact. Following assessment, appropriate actions are taken to remediate or mitigate the vulnerabilities. This may involve applying software patches, updating configurations, removing unnecessary services, or implementing compensating controls to reduce risk. Importantly, vulnerability management is not a one-time event but a continuous cycle. New vulnerabilities emerge regularly, and previously unknown flaws may be discovered in existing systems, which makes ongoing monitoring and re-evaluation essential. The goal of vulnerability management is to be proactive rather than reactive to detect and address weaknesses before they can be exploited by threat actors. When implemented effectively, it helps organizations reduce their attack surface, improve security posture, and meet regulatory and compliance requirements. In today’s fast-evolving threat landscape, a proactive vulnerability management program serves as a critical defense layer, enabling organizations to stay ahead of threats and maintain resilience against cyberattacks.
Do You Want to Learn More About Cyber Security? Get Info From Our Cyber Security Online Training Today!
The Vulnerability Management Lifecycle
The vulnerability management lifecycle is a structured and continuous process designed to help organizations identify, address, and monitor security weaknesses within their IT environments. It includes several key phases: discovery, assessment, reporting, remediation, and verification. The process begins with the discovery phase in Cyber Security Career Path, where all assets across the organization’s network are identified and cataloged. This includes servers, endpoints, network devices, cloud instances, and any other connected systems. A complete and up-to-date asset inventory is essential, as vulnerabilities cannot be effectively managed if the assets themselves are unknown. Following discovery, the assessment phase involves scanning the identified assets for known vulnerabilities using automated tools. These scans help detect software flaws, misconfigurations, missing patches, and other weaknesses that could be exploited by attackers.
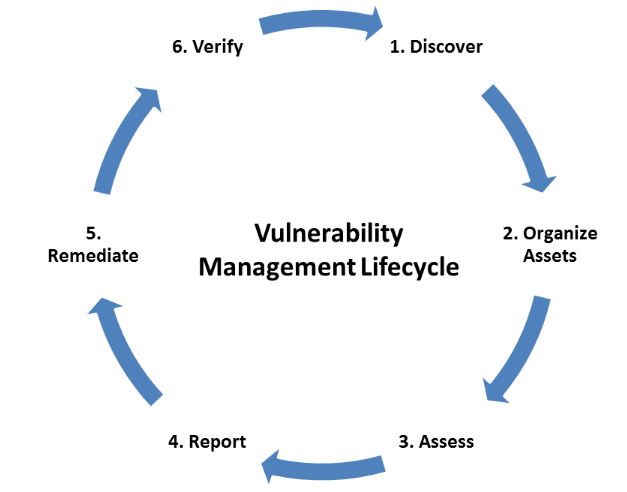
Once vulnerabilities are detected, the reporting phase organizes the findings into actionable intelligence. Reports typically include severity ratings, risk levels, affected systems, and recommendations for remediation, allowing security teams to prioritize their response. The remediation phase focuses on addressing the identified issues. This may include applying software patches, updating system configurations, disabling vulnerable services, or implementing compensating controls to reduce risk. Once remediation actions have been taken, the verification phase confirms whether the fixes have been successfully applied. This step involves rescanning the systems or manually checking the changes to ensure the vulnerabilities have been resolved. Importantly, this lifecycle is not a one-time task. It must be repeated regularly to account for newly discovered vulnerabilities, system changes, and evolving threat landscapes. By maintaining a consistent and proactive vulnerability management lifecycle, organizations can significantly reduce their exposure to cyber threats and enhance their overall security posture.
Identifying and Classifying Vulnerabilities
- System and Network Scanning: Identification begins with scanning IT systems, networks, and applications using automated tools. These tools are designed to detect weaknesses that could be exploited by attackers, helping organizations maintain security visibility.
- Automated Detection Tools: Vulnerability scanners such as Nessus, Qualys, or OpenVAS are commonly used. They identify known vulnerabilities by checking system configurations, installed software versions, and missing updates against vulnerability databases.
- Classification by Type: Once vulnerabilities are detected, they are categorized based on type in Hash in Python. Common types include software bugs, insecure default settings, misconfigurations, outdated software, and missing security patches.
- Severity Assessment: Each vulnerability is assessed for its potential impact and likelihood of exploitation. This helps determine how dangerous it is to the system or network if left unaddressed.
- CVSS Scoring: The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) is a standardized method for rating vulnerabilities. It assigns a numerical score (from 0 to 10) based on factors like exploitability, impact, and complexity, helping teams prioritize fixes.
- Prioritizing Remediation Efforts: By classifying and scoring vulnerabilities accurately, organizations can focus remediation efforts on the most critical threats first, optimizing the use of security resources and minimizing exposure.
- Effective Resource Allocation: Proper classification ensures that limited security resources are directed where they are needed most. High-risk vulnerabilities are addressed promptly, while lower-risk issues are scheduled accordingly, supporting a balanced and effective security strategy.
- Availability of Tools: There are numerous tools available to assist with vulnerability scanning. Well-known options include Nessus, Qualys, Rapid7 Nexpose, and OpenVAS. These tools are widely used in both enterprise and small-to-medium-sized business environments for their reliability and effectiveness.
- Functionality and Purpose: These tools are designed to scan IT systems, networks, applications, and devices to identify known vulnerabilities in Cyber Security Training. They detect weaknesses such as outdated software, open ports, misconfigurations, and missing patches.
- Use of Vulnerability Databases: Vulnerability scanners compare asset configurations against comprehensive databases of known vulnerabilities, such as CVE (Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures). This helps detect whether systems are susceptible to known threats.
- Reporting Capabilities: After scanning, the tools generate detailed reports outlining discovered vulnerabilities. These reports often include descriptions, severity levels, affected systems, and suggested remediation steps, helping security teams take immediate action.
- Remediation Guidance: Many tools offer remediation recommendations or direct links to patches and security advisories. This streamlines the vulnerability management process by helping teams understand and address issues more efficiently.
- Integration with Security Systems: Advanced vulnerability scanners can integrate with asset management, ticketing, and patch management systems. This centralizes control and enables faster response and automation of remediation workflows.
- Importance of Regular Scanning: Conducting regular internal and external scans is critical to maintaining a secure environment. These routine checks help identify emerging vulnerabilities, monitor changes, and reduce the window of exposure to potential threats.
- Understanding Risk Levels: Vulnerabilities vary in terms of the risk they pose. Some have minimal impact, while others can lead to serious security incidents. Prioritization helps organizations decide which issues to address first based on risk.
- Likelihood of Exploitation: One of the main factors in prioritization is how likely a vulnerability is to be exploited. Vulnerabilities with known exploits or that are easy to use are more likely to be targeted and are assigned higher priority.
- Potential Impact on the Organization: The severity of the damage that a vulnerability could cause is also considered in Who is an Ethical Hacker. If a vulnerability could result in data loss, financial damage, or service disruption, it is treated as high risk.
- Use of CVSS Scores: The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) provides a base score that estimates the severity of a vulnerability. This score helps guide decision-making, but it should be balanced with other contextual factors.
- Criticality of Affected Systems: The importance of the affected system plays a major role in prioritization. A vulnerability found on a critical system such as a public-facing server is more urgent than one on a test or development machine.
- Exploit Availability: If a known exploit exists or is actively being used in attacks, the urgency to fix that vulnerability increases significantly due to higher exposure.
- Business Context and Resource Allocation: Prioritizing based on business operations ensures that teams focus on the vulnerabilities that matter most. This helps in using resources effectively and reducing overall security risk.
Would You Like to Know More About Cyber Security? Sign Up For Our Cyber Security Online Training Now!
Vulnerability Scanning Tools
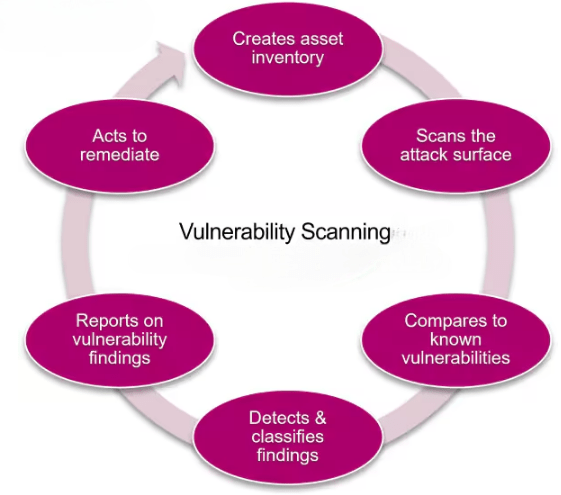
Patch Management Integration
Effective vulnerability management depends heavily on strong integration with patch management processes. Identifying vulnerabilities is only the first step in securing systems; these weaknesses must be promptly addressed to prevent exploitation by attackers. Once vulnerabilities are discovered, deploying patches quickly and efficiently is critical to eliminating risks and protecting organizational assets. The patch management process involves several important steps to ensure successful remediation without disrupting business operations. First, patches are tested in controlled environments to verify that they do not introduce new issues or conflicts. This helps maintain system stability while addressing security flaws in The Phases of Ethical Hacking. Next, deployment schedules are carefully planned to minimize disruption to end users, often occurring during off-peak hours or maintenance windows. After deployment, verification steps confirm that patches have been correctly applied and vulnerabilities resolved. This final stage ensures that the intended protection is in place and functioning as expected. Several patch management tools are available to automate and streamline this complex process. Solutions like Microsoft Windows Server Update Services (WSUS), Ivanti Patch Management, and ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus help organizations efficiently test, deploy, and verify patches across diverse environments. By integrating these tools with vulnerability management systems, organizations create a seamless workflow that connects detection with remediation. This integration allows security teams to prioritize vulnerabilities, trigger patch deployments automatically, and track the status of remediation efforts in real time. The result is a more efficient security operation that reduces the time between vulnerability identification and resolution. In turn, this minimizes the window of exposure during which attackers could exploit unpatched systems. Therefore, the close coordination between vulnerability and patch management is essential to maintaining a strong and resilient cybersecurity posture.
Gain Your Master’s Certification in Cyber Security by Enrolling in Our Cyber Security Expert Master Program Training Course.
Risk Prioritization
Reporting and Analytics
Clear and concise reporting is a crucial aspect of effective vulnerability management because it ensures that all stakeholders, including executives, IT teams, and compliance officers, are well informed about the current security posture. Vulnerability reports should focus on presenting key metrics such as the total number of vulnerabilities detected within the environment, their distribution across different severity levels, and the status of remediation efforts. This helps stakeholders quickly grasp the scope and urgency of the issues that need attention. To make this information more accessible, many organizations utilize dashboards and visual analytics tools that transform raw data into intuitive charts, graphs, and trend lines. These visual representations simplify complex information and make it easier to identify patterns, recurring problems, or areas that require additional focus in Why is Cybersecurity Important. Such clarity enables more informed decision-making and helps prioritize security resources effectively. Beyond internal communication, vulnerability reporting plays a vital role in regulatory compliance. Many data protection laws and security standards, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), and the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS), require organizations to conduct regular vulnerability assessments and maintain documented evidence of corrective actions taken. Proper reporting ensures that organizations can demonstrate due diligence during audits and inspections by providing clear records of how vulnerabilities were identified, assessed, and mitigated. In summary, consistent and transparent reporting supports better security management, helps maintain regulatory compliance, and promotes a culture of accountability and continuous improvement within the organization.
Preparing for a Cyber Security Job? Have a Look at Our Blog on Cyber Security Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Conclusion
Vulnerability management is a vital and ongoing process that plays a key role in protecting organizations from an ever-growing range of cyber threats. This process requires a strategic approach that combines multiple elements to be effective. One important aspect is the use of advanced vulnerability scanning and assessment tools. These tools help detect weaknesses across all parts of an organization’s IT environment, including hardware, software, networks, and cloud infrastructure. Once vulnerabilities are identified, it is essential to prioritize them based on risk, taking into account factors such as the severity of the vulnerability, the likelihood of exploitation, and the criticality of affected systems. Risk-based prioritization ensures that resources are focused on addressing the most urgent and impactful issues first in Cyber Security Training. Effective patching and remediation are also crucial components. Organizations must ensure that fixes are applied promptly and verified to close security gaps before attackers can exploit them. Integrating vulnerability management with other security initiatives, such as patch management, threat intelligence, and incident response, further enhances the overall security posture by creating coordinated defenses. This holistic approach not only reduces exposure to threats but also helps organizations meet industry regulations and compliance requirements, which increasingly demand documented and systematic vulnerability management practices. As cyber threats continue to evolve in complexity and frequency, vulnerability management must evolve as well. Continuous improvement, driven by regular assessments, updated tools, and refined processes, is essential for keeping pace with new challenges. By proactively addressing vulnerabilities through a strategic and adaptive approach, organizations can strengthen their defenses and maintain resilience in a rapidly changing cybersecurity landscape.




