
In modern day business dynamics, there is an application for every need you can imagine. Be it for keeping track of your weekly swimming sessions or to find the best restaurants in town. Python is one language where many of these applications are built as it boasts of a wide range of features it has to offer. This article will unfold one such concept that is Hash In Python.
Following pointers will be covered in this article,
- What Is the Hash Method In Python?
- Sample Program For Hash Method
- Using Hash Method For Immutable Tuple Objects
- Hash Method For Custom Objects
- Sample Program 1
- Sample Program 2
So,let us get started then,
Hash In Python
Python is one of the most popular high level programming languages available in the industry today. Built on the C platform, Python is an Object Oriented Programming language which is not only highly versatile but also a large number of features which enables developers to create high level applications. Python as a programming language comes with a built-in library that has hundreds of modules and functions. One among these is the hash module. In this article we will discuss more about the hash module, its features and how you can make use of the same in your day to day programming.
Before we into the details of this Hash In Python article, let us quickly understand the topic that follows,
What is the Hash Method in Python?
Hash method in Python is a module that is used to return the hash value of an object. In programming, the hash method is used to return integer values that are used to compare dictionary keys using a dictionary look up feature. When used, it calls for the __hash__() of an object which is set by default during the creation of the object by the user.
The syntax for using the hash method is as follows.
- hash(object)
Parameters Of Hash Method
The hash method as a module only takes into a single parameter.
Object: This represents the object whose hash value needs to be returned by the user, be it in the form of an integer, string or float.
Return Value Of Hash Method
When used, the hash method returns the hash value of an object if the same is present. If in a certain situation, the object has a custom hash value, then the method truncates the hash value to the size of Py_ssize_t.
Let us continue with this Hash In Python article and see a sample program, before that a suggestion would to ensure you have all necessary software installed.
Sample Program For Hash Method
To understand the function and uses of the hash method better, let’s take a look at a couple of examples.
- #hash for inter unchanged
- Print(‘Hash for 181 is:’, hash(181))
- # hash for decimal
- Print(‘Hash for 181.23 is:’, hash(181.23))
- #hash for string
- Print(‘Hash for Python is:’, hash(‘Python’))
Output
Hash for 181 is: 181
Hash for 181.23 is: 530343892119126197
Hash for Python is: 3607259692854166150
Moving on with this article, let us see the next method
Using Hash Method For Immutable Tuple Objects
- #tuple of vowels
- vowels= (‘a’,’e’,’i’,’o’,’u’)
- Print(‘The hash is:’, hash(vowels))
When run, the output for the above program will look something like this.
- The hash is: -7033539107181453990
How does hash work for custom objects?
As mentioned in an earlier paragraph, when used the hash method calls for the __hash__() of an object. This means that any object can override the custom hash value for an object.
But in order to get the correct hash value, the method always needs to return an integer and thus one needs to make use of both __eq__() as well as __hash__() to find the same.
Refer to the table below to understand the implementation for custom hash values.
| __eq__() | __hash__() | Description |
|---|---|---|
| (If mutable) Defined | Should not be defined | This requires the key hash value to be immutable. |
| Defined (by default) | Defined (by default) | All objects are compared as unequal. |
| Not defined | Should not be defined | If __eq__() is not defined, then hash also doesn’t need to be defined. |
| Defined | Not defined | __hash__() will be set to None. TypeError is raised. |
| Defined | Retain from Parent | __hash__ = <ParentClass>.__hash__ |
| Defined | Doesn’t want to hash | __hash__ = NoneTypeError is raised. |
Another interesting bit in this article on Hash In Python is implementing Hash Method For Custom Objects,
Hash Method For Custom Objects
Next
- Class person
- def__init__(self,age,name):
- self.age=age
- self.name=name
- def__eq__(self,other):
- return self.age==other.age and self.name==other.name
- def__hash__(self)
- print(‘The hash is:’)
- return hash((self.age,self.name)) person= Person(23, ‘Adam’)
When run, the output of the above program will look like this,
- The hash is: 5445254133660435902
Note: For the above program, the __eq__() method doesn’t need to be implemented as it is created by default for all objects.
Let us see couple of sample programs now,
Sample Program 1
- Python 3 code to demonstrate
- #working of hash()
- # initializing of objects
- int__val=4
- str__val= ‘PythonisBest’
- flt__var==24.56
- #printing the hash values.
- #Notice Integer value doesn’t change
- #you will have an answer later in the article.
- Print(“The integer hash value is : “ + str(hash(int_val)))
- Print(“The string hash value is : “ + str(hash(str_val)))
- Print(“The float hash value is : “ + str(hash(flt_val)))
The output for the above program will be,
- The integer hash value is : 4
- The string hash value is : 2063534490514258345
- The float hash value is : 1291272085159665688
And this brings us to the final bit this article on Hash In Python,
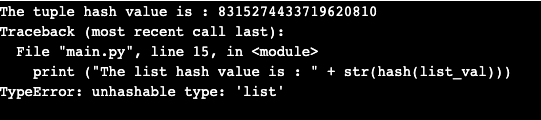
Sample Program 2
- Python 3 code to demonstrate
- #proprty of hash()
- # initializing of objects
- # tuple are immutable
- Tuple__val = (1,2,3,4,5)
- #list are mutable
- List__val = [1,2,3,4,5]
- #printing the hash values.
- #Notice exception when trying to conver to mutable object
- Print(“The tuple hash value is : “ + str(hash(tuple_val)))
- Print(“The string hash value is : “ + str(hash(list_val)))
The output for the above program will be,
Conclusion
The hash method is one of the most useful modules in the Python library. Now that you know its function and uses, we hope that you will use it more often in your day to day coding.





