
- Cyber security is one of the many uses of artificial intelligence. A report by Norton showed that the global cost of typical data breach recovery is $3.86 million. The report also states that companies need an average of 196 days to recover from any data breach. For this reason, organisations should invest more in AI to avoid wastage of time and financial losses.
- AI, machine learning and threat intelligence can recognize patterns in data to enable security systems to learn from past experience. In addition, AI and machine learning enable companies to reduce incident response times and adhere to security best practises.
Introduction to AI and Machine Learning on Cybersecurity:
Experts agree that Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) have both negative and positive effects on cyber security. AI algorithms use training data to learn how to respond to different situations. As they progress, they learn by copying and adding additional information. This article reviews the positive and negative effects of AI on cyber security.
AI and Cyber Security:
Main Challenges Cybersecurity Faces Today:
Despite advances in cyber security, attacks are becoming more and more dangerous. The main challenges of cyber security include:
Geographically distant IT systems— Geographical distance makes manual tracking of incidents more difficult. Cyber security experts need to bridge the gap in infrastructure to successfully monitor incidents across sectors.
Manual Threat Hunting – can be costly and time-consuming, resulting in more going unnoticed.
Reactive nature of cyber security – Companies can solve problems only when they have already happened. Predicting threats before they occur is a major challenge for security experts.
Hackers often hide and change their IP addresses— Hackers use various programs such as Virtual Private Networks (VPNs), proxy servers, the Tor browser, and more. These programs help hackers to remain anonymous and undetected.
- Traditional security techniques use signatures or indicators of compromise to identify threats. This technique may work well for threats already encountered, but they are not effective for threats that have not yet been discovered.
- The signature based technology can detect about 90% of threats. Replacing traditional techniques with AI can increase the detection rate to 95%, but you’ll get an explosion of false positives. The best solution would be to combine both traditional methods and AI. This can result in a 100% detection rate and reduce false positives.
- Companies can also use AI to enhance the threat hunting process by integrating behavioural analysis. For example, you can leverage AI models to develop profiles of each application within an organisation’s network by processing high amounts of endpoint data.
- AI can optimise and monitor many essential data centre processes such as backup power, cooling filters, power consumption, internal temperature and bandwidth usage. AI’s computational powers and continuous monitoring capabilities provide insight into what values will improve the effectiveness and security of hardware and infrastructure.
- In addition, AI can reduce hardware maintenance costs by alerting you to fix equipment. These alerts enable you to repair your equipment before it breaks down in a more serious way. In fact, Google reported a 40 percent reduction in cooling costs and a 15 percent reduction in power consumption at its facility in 2016 after implementing AI technology within data centers.
How AI Improves Cybersecurity:
Threat hunting:
Vulnerability management:
There were 20,362 new vulnerabilities reported in 2019, a 17.8% increase over 2018. Organisations are struggling to prioritise and manage the massive amount of new vulnerabilities they encounter on a daily basis. Traditional vulnerability management methods wait for hackers to exploit high-risk vulnerabilities before deactivating them.
While traditional vulnerability databases are critical to managing and containing known vulnerabilities, AI and machine learning techniques such as User and Event Behavioural Analytics (UEBA) can analyse the baseline behaviour of user accounts, endpoints and servers, and identify anomalous behaviour. Can identify what may indicate a zero-day unknown attack. This can help keep organisations secure even before vulnerabilities are officially reported and patched.
Data centres:
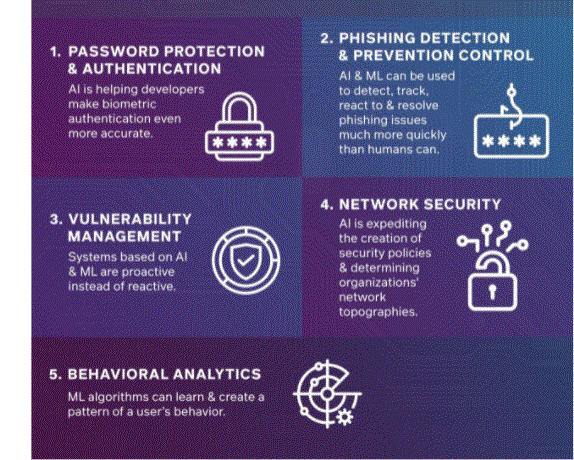
- There are two time-intensive aspects of traditional network security, creating security policies and understanding an organisation’s network topography.
- Policies—Security policies identify which network connections are legitimate and which you should monitor for malicious behaviour. You can use these policies to effectively implement a zero-trust model. The real challenge lies in formulating and maintaining policies in view of the large number of networks.
- Topography—Most organisations do not have precise naming conventions for applications and workloads. As a result, security teams spend a lot of time determining what type of workload a given application is concerned with.
- Companies can leverage AI to improve network security by learning network traffic patterns and recommending a functional set of workloads and security policy.
Network security:
Drawbacks and Limitations of Using AI for Cybersecurity:
There are also some limitations that prevent AI from becoming a mainstream security tool:
Resources— Companies need to invest a lot of time and money into resources such as computing power, memory, and data to build and maintain AI systems.
Data set- AI model is trained with learning data set. Security teams need to get their hands on many different data sets of malicious code, malware code, and anomalies. Some companies do not have the resources and time to obtain all these accurate data sets.
Hackers- also use AI-attackers’ tests and improve their malware to make it resistant to AI-based security tools. Hackers learn from existing AI tools to develop more advanced attacks and attack traditional security systems or even AI-boosted systems.
Neural Fuzzing – Fuzzing is the process of testing large amounts of random input data within software to identify its weaknesses. Neural Fuzzing leverages AI to quickly test large amounts of random input. However, fuzzing has a creative side as well. Hackers can learn about the weaknesses of the target system by gathering information with the power of neural networks. Microsoft developed a method for implementing this approach to improve its software, resulting in more secure code that is harder to use.
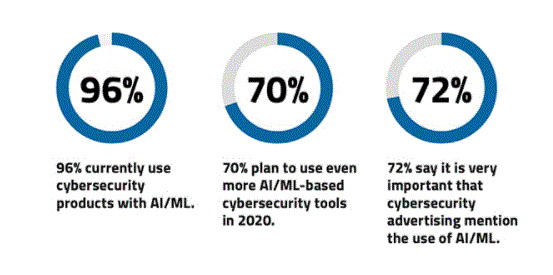
- A huge attack surface
- 10 or 100 thousand devices per organisation
- Hundreds of attack vectors
- Big shortfall in the number of skilled security professionals
- Masses of data that have moved beyond a human-scale problem
- A self-learning, AI-based cybersecurity posture management system should be able to solve many of these challenges. Technologies exist to properly train a self-learning system to collect data continuously and independently from your enterprise information system. That data is then analysed and used to perform the correlation of patterns in the millions to billions of signals belonging to the enterprise attack surface.
Applying AI to cybersecurity:
AI is ideally suited to solving some of our toughest problems, and cyber security certainly falls into that category. With today’s ever-evolving cyber-attacks and the proliferation of tools, machine learning and AI can be used to “keep up with the bad guys,” threat detection and more than traditional software-driven approaches. To react efficiently.
Additionally, cyber security presents some unique challenges:
The result is new levels of intelligence feeding human teams across various categories of cybersecurity, including:
IT Asset Inventory – Obtaining a complete, accurate inventory of all devices, users and applications with any access to the information system. Classification and measurement of business vitality also play a large role in inventory.
Threat Exposure – Hackers follow trends just like everyone else, so what’s fashionable with hackers changes regularly. AI-based cyber security systems can provide updated knowledge of global and industry specific threats to help make critical prioritisation decisions based on what can be used to attack not only your enterprise, but your enterprise. depending on the probability of being used to attack.
Controls Effectiveness – Understanding the impact of the various safety equipment and safety procedures you employ is critical to maintaining a strong security posture. AI can help you understand where your InfoSec program has strengths, and where it lacks.
Breach Risk Prediction – IT asset inventory, accounting for risk exposure and effectiveness control, AI-based systems can predict how and where your breaches are most likely to occur, so you can build resources and tools for vulnerable areas To plan allocation. Instructional insights derived from AI analysis can help you configure and enhance controls and processes to most effectively improve your organisation’s cyber resilience.
Incident Response – AI-powered systems can provide better context for prioritising and responding to security alerts, for faster response to incidents, and surface root causes to reduce vulnerabilities and avoid future issues.
Explainability – The key to using AI to enhance human InfoSec teams is the interpretability of recommendations and analysis. In receiving buy-in from stakeholders across the organisation to understand the impact of various Infosec programmes, and to report relevant information to all involved stakeholders including end users, security operations, CISOs, auditors, CIOs, CEOs and the Board it’s important. director
- Machine learning and artificial intelligence can help protect against cyber attacks, but hackers can thwart security algorithms by targeting the data they train on and looking for warning flags.
- Hackers can also use AI to break through defences and develop mutated malware that alters its structure to evade detection.
- Without large amounts of data and events, AI systems will produce false results and false positives If data manipulation goes undetected, organisations will struggle to recover the correct data feeding their AI systems, with potentially disastrous consequences.
AI Use by Adversaries:
AI and Machine Learning (ML) can be used by IT security professionals to implement good cyber security practises and reduce the attack surface instead of constantly pursuing malicious activity. At the same time, state-sponsored attackers, criminal cyber-gangs and ideological hackers can employ the same AI techniques to defeat defences and evade detection. Here’s the “AI/cyber security puzzle”.
As AI matures and advances rapidly in cybersecurity, companies will need to be mindful of the potential downsides of this exciting new technology:
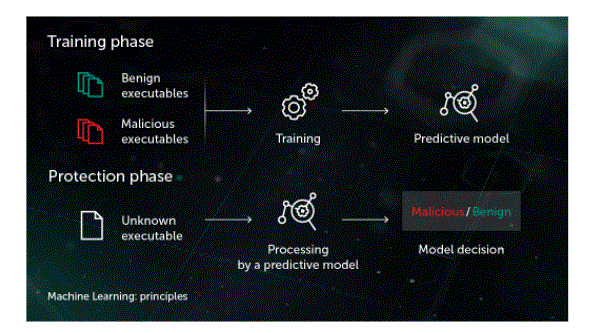
- Analysing and improving the cyber security posture is no longer a human level problem. In response to this unprecedented challenge, Artificial Intelligence (AI) based tools for cyber security have emerged to help information security teams reduce the risk of breaches and improve their security posture efficiently and effectively.
- AI and machine learning (ML) have become important technologies in information security, as they are able to quickly analyse millions of events and identify many different types of threats – from malware exploiting zero-day vulnerabilities. To identify risky behaviour that can lead to phishing. Attack or download of malicious code. These technologies learn over time, drawing from the past to now identify new types of attacks. Behavioural histories create profiles on users, properties and networks, allowing AI to detect and react to deviations from established norms.
Why AI in cybersecurity:
The enterprise attack surface is massive, and is rapidly evolving and evolving. Depending on the size of your enterprise, there are several hundred billion time-varying signals that need to be analysed to accurately calculate risk.
Result?
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning can improve security, as well as make it easier for cybercriminals to systems without any human intervention. This can cause a lot of loss to any company. It is highly recommended to get some sort of protection against cybercriminals if you want to minimise losses and stay in business.
- In recent years, AI has emerged as an essential technology to enhance the efforts of human information security teams. As humans can no longer scale to adequately defend a dynamic enterprise attack surface, AI provides much-needed analysis and threat identification that can be used by cybersecurity professionals to reduce breach risk and improve security posture. can be done for. In security, AI can identify and prioritise risks, quickly spot any malware on the network, guide incident response, and detect intrusions before they begin.
- AI allows cybersecurity teams to form powerful human-machine partnerships that push the boundaries of our knowledge, enrich our lives, and drive cybersecurity in a way that is more than the sum of its parts.
Conclusion:





