
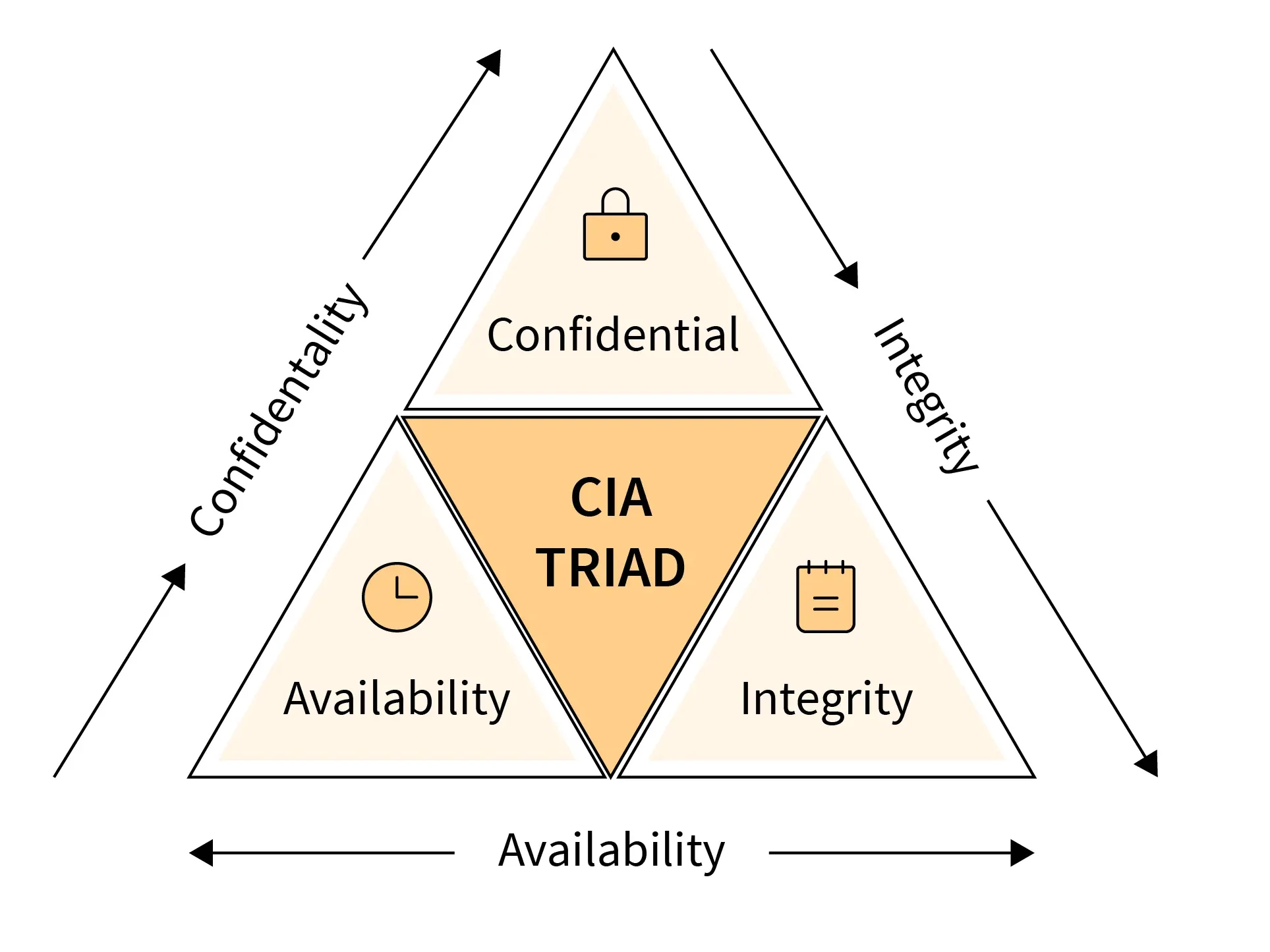
- Introduction to the CIA Triad
- Confidentiality: Protecting Sensitive Information
- Integrity: Ensuring Data Accuracy and Consistency
- Availability: Ensuring System and Data Accessibility
- CIA Triad in Risk Management
- The Interrelationship of the Three Principles
- Real-World Applications of the CIA Triad
- Challenges in Implementing the CIA Triad
- Best Practices for Maintaining the CIA Triad
- Conclusion
CIA Triad Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability is a fundamental framework in cybersecurity that guides organizations in protecting digital assets, sensitive information, and critical systems. These three principles work together to ensure that data is only accessible to authorized individuals, remains accurate and unaltered, and is available whenever needed without disruption. By implementing strong security measures such as encryption, access controls, authentication protocols, and backup strategies, organizations can effectively safeguard their systems from Cybersecurity Training Courses , data breaches, and malicious attacks. In an era of increasing cyber risks and evolving security challenges, understanding and applying the CIA Triad is essential for building a resilient, secure, and trustworthy digital infrastructure that supports business continuity and regulatory compliance.
To learn about different Cybersecurity techniques, sign up for our Cyber Security Online Training.
Introduction
The CIA Triad is a cornerstone concept in the information security discipline that embodies the most important principles of protecting data and systems. There are three primary pillars: Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. These three are the guiding principles behind security policy and practice designed to protect access to sensitive information, ensure that information is correct, and maintain its availability to authorized users when needed. The CIA Triad serves as the foundation for designing robust Data Security frameworks in business, government, healthcare, and personal environments. It helps organizations mitigate risks, prevent cyber threats, and uphold trust in digital transactions and data management. Understanding and implementing the CIA Triad effectively is crucial in maintaining a strong cybersecurity posture against evolving threats.
Confidentiality: Protecting Sensitive Information
- Availability ensures that information and systems remain accessible to authorized users whenever needed, without delays, failures, or disruptions. This principle guarantees uninterrupted access even in cases of hardware failures, cyberattacks, natural disasters, power outages, or unexpected system overloads.
- To maintain availability, organizations implement redundancy, load balancing, failover mechanisms, real-time data replication, regular backups, disaster recovery plans, and high-availability systems to minimize downtime. Security measures like DDOS Mitigation protection, intrusion prevention systems, and real-time monitoring also play a crucial role in preventing service disruptions and mitigating potential threats before they impact accessibility. For example, cloud service providers use multi-region storage, automated failover systems, and scalable infrastructure to ensure continuous data access, even during outages or peak traffic periods.
- In mission-critical industries such as healthcare, banking, telecommunications, and government services, maintaining high availability is essential to ensure seamless operations, prevent costly downtime, and enhance user experience. Any disruption in availability can lead to significant financial losses, operational inefficiencies, and a decline in customer trust, making it a fundamental aspect of cybersecurity and IT infrastructure management.
- The three individual principles that make up the CIA Triad Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability are deeply interconnected and must be carefully balanced to ensure an effective cybersecurity framework. For example, data encryption enhances confidentiality, but if the encryption process is overly complex, it can slow down system performance, affecting availability.
- Likewise, enforcing strict integrity controls, such as digital signatures or multi-step verification processes, may introduce delays or restrictions that impact accessibility. On the other hand, prioritizing availability without proper security measures could expose sensitive data to breaches or unauthorized modifications.
- A well-structured security strategy must account for all three principles, ensuring that neither confidentiality, integrity, nor availability is compromised in favor of the others. Striking the right balance is crucial for organizations to maintain secure, reliable, and efficient systems that protect sensitive information while ensuring smooth operations.
- Health Care: To protect patient medical histories and records, confidentiality must be extremely strong, ensuring only authorized personnel can access sensitive data. Additionally, data integrity must be maintained to prevent errors in diagnoses and treatments, while availability ensures that critical patient Information Security is accessible to healthcare providers whenever needed, especially in emergencies.
- Finance: In banking and financial institutions, customer financial information must remain confidential to prevent fraud, unauthorized transactions, and identity theft. Transaction integrity is crucial to avoid financial discrepancies, manipulation, or corruption of data. Furthermore, online banking services and financial applications should always be available to users, ensuring seamless access to funds and real-time transactions.
- Government: National security data and classified information must be kept confidential to prevent unauthorized disclosures or espionage. Data integrity is essential for accurate decision-making in governance, law enforcement, and defense strategies. Ensuring the availability of critical government systems and infrastructure during emergencies, cyberattacks, or natural disasters helps maintain operational stability and public services.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct periodic audits to identify and address Vulnerability Scanning in systems and data that could affect confidentiality, integrity, or availability.
- Data Encryption: Use encryption technologies to protect sensitive data both at rest and in transit, ensuring confidentiality.
- Access Control: Establish strict access controls so that only authorized personnel may access sensitive data, thereby supporting confidentiality and integrity.
- Backup and Recovery Plans: Regularly back up critical data and make provisions for recovery plans to maintain data availability in the event of system failures or disasters.
- Incident Response Plans: Develop and test incident response plans to handle probable breaches or disruptions with minimal impact on confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
The right to restrict access to only those who should see it is referred to as confidentiality. Protecting confidentiality involves limiting access to sensitive data that may hold personal information, financial records, trade secrets, and even intellectual property. This ensures that unauthorized individuals cannot view, steal, or manipulate critical information. The use of encryption, strong authentication methods, access controls, and secure communication channels guarantees confidentiality by preventing unauthorized access. Encryption ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable without the correct Decryption in Cybersecurity. Additionally, security policies such as role-based access control (RBAC), multi-factor authentication (MFA), and data masking further enhance confidentiality by restricting data exposure to only authorized individuals or systems.
Sign up for ACTE Cyber Security Online Training and get a head start in your career cyber security.
Integrity: Ensuring Data Accuracy and Consistency
Integrity involves ensuring that data is correct, consistent, and trustworthy over its lifetime, preventing unauthorized modifications that could compromise its reliability. It also means protecting against unauthorized changes or data corruption due to intentional or unintentional reasons, such as cyberattacks, system failures, or human errors. The concept applies checksums, hash functions, digital signatures, and audit trails to validate the integrity of data, ensuring it remains unchanged while being stored, processed, or transmitted. Robust access controls and version management further help maintain data accuracy and prevent tampering. In real life, data integrity plays a crucial role in preventing fraud, ensuring accurate financial transactions, maintaining regulatory compliance, and protecting sensitive business information from manipulation.
Availability: Ensuring System and Data Accessibility
Want to Take the Lead in Cyber Security ? Enroll in ACTE’s Cybersecurity Expert Masters Program Training Course Program to Begin Your Adventure Now.
CIA Triad in Risk Management
The CIA Triad is a significant aspect of risk management because it gives a framework for the identification and addressing of potential threats and vulnerabilities to an organization’s information systems. In risk management, the three principles guide the formulation of risk mitigation strategies. For example, Confidentiality risks include the potential for unauthorized access or breaches, which can result in data theft or loss of trust. Cybersecurity Training Courses include data corruption or alteration that might result in poor decisions or financial fraud. Availability risks concern denial-of-service attacks, system outages, and other disruptions that prevent or hinder users from accessing the needed data or services. By analyzing these risks, organizations can prioritize threats, allocate resources effectively, and implement security controls tailored to their specific needs. A balanced approach ensures that strengthening one principle does not compromise the others, maintaining a stable and secure environment. Ultimately, integrating the CIA Triad into risk management helps organizations build resilience against ever-evolving cyber threats.
The Interrelationship of the Three Principles
Real-World Applications of the CIA Triad
The CIA Triad is widely used across various sectors and industries to ensure robust security measures are in place. It can be illustrated with a few examples:
Preparing for Cyber Security job interviews? Check out our Cyber Security Interview Questions and Answers now!
Challenges in Implementing the CIA Triad
Strong security controls can make the systems difficult to access or use, and there will always be a trade-off between confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Cost and Resources Maintaining all three principles requires more financial investment in technologies, personnel, and infrastructure, which is not affordable for some organizations. Evolving Threat Landscape Cybersecurity are constantly changing, and new risks may arise that require updating security policies and practices to ensure the CIA Triad is still effectively maintained. Compliance Organizations must also navigate complex regulatory requirements related to confidentiality and data protection, which can vary by region and industry. This adds another layer of complexity to implementing the CIA Triad.
Best Practices for Maintaining the CIA Triad
To effectively maintain the CIA Triad, organizations can implement several best practices:
Conclusion
The CIA Triad is the foundation of sound cybersecurity, providing a structured approach to safeguarding information assets. Cybersecurity Training ensures that information remains confidential, accurate, true, trustworthy, and readily accessible when needed. By focusing on these three principles Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability organizations can build a robust cybersecurity framework that minimizes risk, prevents data breaches, and protects critical assets from cyber threats. Even though challenges exist in implementing the CIA Triad, such as evolving attack vectors, insider threats, and compliance requirements, its role in maintaining a secure, resilient, and efficient information environment is indispensable in today’s digital world. Businesses, governments, and individuals must continuously adapt and reinforce these principles to stay ahead of cyber risks and ensure long-term data security.





