
What is Decryption?
Decryption converts encrypted data or ciphertext back into its original readable form or plaintext. In cyber security, emsisoft decryptor is critical because crytographic techniques enables authorized users or systems to access and make sense of data previously scrambled for confidentiality purposes. Decryption is the inverse of encryption, which protects information from unwanted access while it’s being transmitted or stored.
Why Decryption is Critical to Cyber Security
There is a huge amount of confidential information that flows encrypt decrypt online. This ranges from personal details, financial transactions, medical records, and even proprietary business data wh, ich have an equal need for protection. Where encryption is generally found in protecting such data, decryption is equally essential since ot security ensures that, wherever required, authorized persons or systems can access and read the encrypt decrypt online information without exposing it to potential threats. Cybersecurity Training Courses is also essential in other network security operations like data recovery, digital forensics, and cybercrime investigations. Sometimes, emsisoft decryptor is required for accessing crucial information during a network security breach or even shortly after an attack in cyberspace.
To learn about different Cybersecurity techniques, sign up for our Cyber Security Online Training at ACTE right now!
Encryption and Decryption: A Symbiotic Relationship
Understanding Encryption
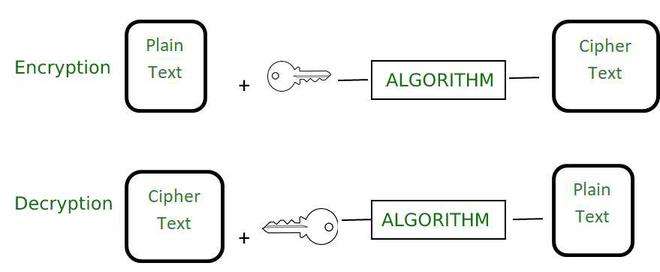
- Encryption is a process where readable data, called plaintext, is changed into an unreadable format, called ciphertext, utilizing an encryption key and a mathematical technique.
- This means that encryption protects data from unauthorized access both in transit and in storage. The only method by which access to original data is possible is when a person uses the corresponding decryption key possessed by them.
- Common encryption algorithms are the much-used AES and RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman), both of which are used to secure data for encrypt decrypt online banking and mail.
- Decryption is essentially the reverse procedure for encryption. It uses a decryption key corresponding to the encryption key to reverse the disordered ciphertext back into its original format of plaintext.
- The keys for encryption and decoding are linked, and the relationship depends on whether the system is symmetric or asymmetric.
- The same key is used for encryption and decryption in symmetrical encryption algorithms. However, an asymmetric encryption algorithm has two different keys provided to it-one public and the other private.
- Decryption in Ransomware in Cybersecurity ensures that it encrypts only the data a person wants to emsisoft decryptor. Thus, it is the basis of secure communication and data storage.
How decryption works
Sign up for ACTE Cyber Security Online Training and get a head start in your career cyber security.
Different Types of Decryption
Symmetric Decryption
Both encryption and decryption employ the same secret key in symmetric encryption. Thus, symmetric encryption is fast but also efficient. However, it also means that both parties must share their secret key in such a way as to be securely shared. The encryption scheme has been compromised if that key is exposed or intercepted. For example, the AES encryption algorithm is one of the most popularly deployed symmetric encryption standards. Asymmetric encryption standards should have access to the same key used since it has been applied for encryption at the point of decryption to extract the data.
Asymmetric decryption
Public-key cryptography, sometimes called asymmetric encryption, uses two different keys. Whereas one key is in the public realm for encryption, the other need not be distributed. The public key is quite liberally dispersed. However, its corresponding private key will not be accessible to anyone. Therefore, one of the merits of using asymmetric encryption is that parties needn’t share the private key, making it a robust protocol to secure internet communications. RSA is one of the most applied asymmetric encryption systems that allow data to be transmitted safely without sharing a secret.
The Decryption Process
Manual Decryption vs. Automated Tools
- Although possible at a theoretical level, this decryption process usually needs to be more practical for mass modern encryption. It would mainly revolve around automated tools that use the right decryption algorithm with a decryption key to restore the same data in a timely and accurate manner.
- These tools can be used on encrypted files, communication methods, or even storage systems, in addition to lost or corrupted data.
- Some tools are specific only to decryption work. Their features include file decryption in batches and supporting different types of encryption standards.
- In more complex situations involving enforcing the law, forensic tools might be used to extract data from devices seized and stored in encrypted form.
- Decryption algorithms are designed to reverse all of the operations performed by encryption algorithms. They usually use the decryption key (or a derived key) to recover the encrypted information into its normal form.
- The length of the key and the algorithm employed significantly impact the strength of the encryption and decryption process.
- AES, RSA, and ECC are very famous decryption algorithms. Each has its merits; however, when the right key is used, all these algorithms provide a secure means of restoring encrypted data to its original state.
- Hence, secure decryption is highly dependent on key management. Lost, compromised, or mismanaged encryption keys could make encrypted data inaccessible or Vulnerability Management to unauthorized access.
- Key management ensures that keys are generated, stored, and protected securely, allowing access only by authorized users when a decryption key is required.
- Implementing good key management practices, HSMs securely hold keys and use role-based access controls to strictly limit who can obtain encryption key access. Additionally, they regularly rotate keys to minimize the risks of key compromise.
Algorithms application in decryption
Key Management in Decryption
Applications of Decryption in CyberSecurity
Protecting Confidential Information
Decrypting is needed to access the secret information when one needs it without breaking its secrecy and confidentiality. Encryption is critical to the banking, health, and government sectors because such information, whether customer data, patient records, or classified government documents, will be very sensitive. For example, secure financial transactions will ensure that confidential banking information is not let out of its way during its transfer. Still, only upon decryption,ot security, at the receiving end, the bank or the customer can view the original transaction details.
Protecting Communication Channels
Another important key to secure communications is decryption, especially for encrypted emails, instant messaging, and encrypt decrypt online transactions. Since encryption is done of a message or file decryption, Cybersecurity Training Courses should only be done at the receiving point. Organizations can keep their communications confidential because decryption is usually done only at the destination. For example, protocols like SSL/TLS (Secure Socket Layer/Transport Layer network security) use decryption to ensure that the data transmission between a web browser and a server goes unobserved.
Encrypted File Storage and Sharing
Decryption remains the primary protection for files stored in encrypted mode or shared. Whether cloud storage, file-sharing services, or an external drive to store those files, encryption shows that the file decryption are safe even when stolen or accessed by the wrong people. Those files can only be accessed by authorized decryption tools.
Leverage Cyber Security to Unlock the Future! Enroll in the Cybersecurity Expert Masters Program Training Course Program at ACTE Right Away.
Decryption and Cyber Attacks
Decryption in Ransomware Attacks
- Most ransomware attacks encrypt the victim’s file decryption and demand a ransom to give back the key. Sometimes, after a ransom is paid, attackers release the key, but more likely, they do not provide it.
- For victims within an organization, decryption is an important step taken not to pay the ransom but to recover the data.
- Network security researchers and cyber defence teams often reverse-engineer ransomware encryption methods to create decryption Hacking Tools And Software that may help victims recover their files without paying the ransom.
- In a brute-force attack, the attackers try all possible combinations of keys, hoping to decrypt the encrypted data. Exponential in dependence on the length of the key, the key becomes too impractically long for modern encryption algorithms such as AES-256.
- However, weak or mismanaged keys can still be vulnerable to brute-force attacks if the encryption is not appropriately carried out or if the key is too small in ot security
- VeraCrypt: is an encryption and password decryptor tool for volumes and files. It’s mostly used to secure one or more drives.
- CyberChef: A tool that handles many cryptographic operations, including decryption, and supports many formats.
- Hashcat: A powerful password decryptor-cracking tool for decrypting password-protected files.
- The keys must be stored within a secure HSM
- Use MFA for the protection of decryption keys
- Rotate encryption keys frequently and check the logs for any access to those keys.
Brute-Force Decryption Attempts
Problems in Decryption of Modern Ciphers
The new encryption strategies are designed to be infeasible to break computationally, even using large computational power. Encryption systems, such as AES-256 or RSA-2048, are highly secure as it would take a significantly large amount of time and computational capabilities to break them, which is mostly not possible with current technology. A growth in encryption methods brings breaking encryption to the limits of cryptography and computational power.
Decryption Tools and Techniques
Recommended Best Decryption Software
Some decryption tools are used to decrypt files by recovering them. Among the most popularly used are:
Best Practices in Key Management and Safe Decryption
To ensure safe decryption practices, it is pretty obvious that strict protocols in key management must be implemented:
Legal and Ethical Issues in Decryption
Legal Aspects of Decryption
The legality of decryption depends on the context, and as in the two preceding examples, it can be serious. For example, decryption may include uninvited access to the encrypted data. In this regard, law enforcement may use decryption while investigating criminal activities. However, the use of decryption tools is heavily regulated. In a few jurisdictions, companies are bound to reveal decryption keys to the authorities in case law enforcement requests it. In other jurisdictions, privacy laws can prohibit unauthorized attempts at decryption.
Ethics of Decryption
Cybersecurity Training is an ethical issue for privacy and data protection. While decryption may guarantee access for the legal parties to their data, unauthorized password decryptor breaches privacy and unethical conduct when personal or confidential data is emsisoft decryptor. An organization must balance its decryption requirement with the burden of protecting user privacy and complying with data protection laws.
Preparing for a job interview in cybersecurity ? Examine our blog post about Cybersecurity Interview Questions and Answers to get the most of your employment experience!
Conclusion
Decryption is the most crucial element of data protection, as it allows authorized recipients to decrypt secret information without necessarily being privy to the content. Advanced threats in the cyber world and more sophisticated encryption algorithms make the art of password decryptor and the tools that can be employed for safe emsisoft decryptor fundamental in protecting sensitive information of ot security. In the future, technology will advance, and encryption and decryption methods will stay at the core of protecting digital assets, ensuring privacy, and making secure communication possible in this increasingly interconnected world.





