
- Introduction
- What is Malware?
- Common Malware Attack Techniques
- Consequences of Malware Attacks
- How to Identify a Malware Infection
- Methods of Precaution against Malware Attacks
- Reaction Against Malware Attacks
- The Future of Malware: Emerging Threats
- Conclusion
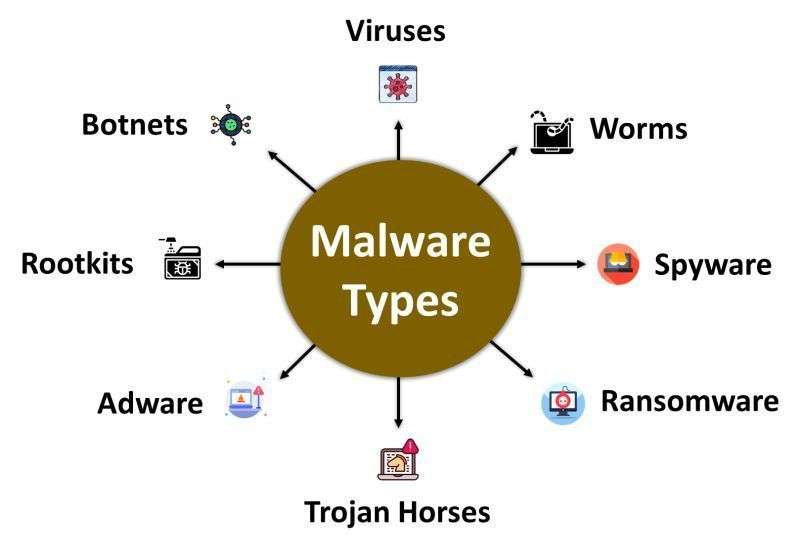
- Virus: A virus attaches itself to legitimate files and moves on to their copies and running. Propagation usually requires user action.
- Worm: This is a self-replicating program that spreads without requiring human intervention. Worms normally exploit network vulnerabilities in propagation.
- Trojan Horse: This is malware that masquerades as a legitimate application or file. During execution, the cybercriminal can access the victim’s system.
- Ransomware: This malware locks the victim’s files or system and requests a ransom to allow access again. It has become one of the most dangerous and widespread kinds of malware.
- Spyware: This software secretly monitors and collects information about the user’s activities, often without their knowledge. Multi Factor Authentication (MFA) provides an extra layer of protection against such threats to enhance security and prevent unauthorized access.
- Adware: Though not all forms of thisware are malicious, adware can display unwanted advertisements. Worse yet, it is often bundled with spyware or malicious application software.
- Rootkits: Malware that hides the existence of its very presence and can alter any of the core functionalities of an OS to completely and partly conceal its presence.
- Slow application: Malware consumes many system resources, slowing down your computer or network.
- Always evident pop-ups: An increase in unsolicited pop-up advertisements or strange messages indicates that you have been infected with adware or other malware
- Your system crashes: Your smooth-running system interferes with malware, making it crash or freeze.
- Network activities look suspicious: Malware might be causing unusual traffic as it communicates with remote servers or spreads to other devices.
- File and settings changes without permission: If your files are deleted or altered without you knowing, or if your settings are changed, it could indicate malware.
- Isolate and Contain the Threat: Immediately pull infected devices off the network to prevent the malware from spreading. If you are working with ransomware, isolating the infected machine will prevent the malware from encrypting more files or systems.
- Removing Malware: Use your antivirus or anti-malware to scan and delete malware on your system. Sometimes, for aggressive and more complex threats, manual removal or professional help may be needed for more extreme measures.
- Recovery of Data and Systems: Malware is removed; restore data from a clean backup that hasn’t been infected. Contact data recovery professionals if no backup is available or it’s compromised. Also, be cautious of Session Hijacking, where attackers steal session tokens to gain unauthorized access.
Introduction
Malware attacks have emerged as one of the most serious and widely spreading threats in the cybersecurity sphere. As technology advances, so does the sophistication of cybercrime. These types of malicious software damage, disrupt, or gain unauthorized access to a system. Ransomware attacks of this kind could run the gamut from system malfunctions to data breaches, financial losses, and a serious erosion of privacy.
Malware virus is evolving into subtler forms and becoming very common, so it’s of great importance to know its form and how to develop strategies to protect your data, devices, and even networks. Here’s a detailed overview of Cyber Security Training Courses, their impact, and the best practices for the prevention and response of such scenarios.
What is Malware?
Malware is “malicious software,” describing a range of malicious or harmful programs designed to damage or exploit systems or steal data, among other malicious actions. Unlike typical software, which uses structures and interfaces with legitimate intentions, the overall point of malware security detection is to take advantage of vulnerabilities and compromise systems. Malware software can be spread through various methods, including email attachments, malicious websites, infected software, or even through vulnerabilities in network protocols, making it a significant threat to both individuals and organizations.
Interested in Obtaining Your Cyber Security Certificate? View The Cyber Security Online Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Types of Malware
There exist many different types of malware, and most use a type of attack and have specific goals; one finds the most common forms of these as:
The Modes of Operations of Malware
Once malware protection seeps into the system, it exploits other available flaws to perform its malicious operation. In some cases, it will even mangle files, probably not only, but also steal sensitive information or even halt the whole system. Malware propagates via email attachments, infected websites, malicious advertisements and downloaded software.
To Earn Your Cyber Security Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Cyber Security Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Cyber Security Online Training Today!
Common Malware Attack Techniques
Malware can be presented in various ways. The following explores the most common methods cybercriminals use which can help prevent such attacks.
1. Phishing
Phishing is the most widely used technique for delivering malware. It describes how people of ill will use a trusted institution, like banks or companies, to send malicious email attachments or links to obtain someone’s attention. Once clicked on, they download malware or prompt the user for sensitive information.
2. Drive-by Downloads
One strategy employed by malware attackers is drive-by download attacks. The virus immediately installs itself on your machine when you visit an infected website. Without your knowledge, it typically takes advantage of flaws in the operating system, plugins, or browser.
3. Malvertising
Malverti ing is an attack in which malicious code is embedded in legitimate online ads. Even reputable sites can serve these ads. When clicked, the mal is installed, often without the user’s knowledge. Implementing Data Classification helps organizations protect sensitive information, minimizing the impact of such attacks.
Consequences of Malware Attacks
The effects of malware attacks are disastrous, depending on the type of malware and the severity level.
1. Financial Losses
FinancialFinancial losses from malware assaults can be enormous. For instance, ransomware prevention encrypts a user’s files and demands money for the decryption keys. Others, like banking Trojans, steal financial data, resulting in financial fraud.
2. Data Theft
Malware data breaches expose financial information, intellectual property, passwords, and personal information. To get money, the data is typically sold on the dark web or utilized for identity fraud. Sometimes, fraudulent acts like creating fictitious accounts or carrying out illegal transactions might be carried out using this stolen data.
3. S stem Damage
Malware, including viruses and worms, can seriously damage computer systems by corrupting files, erasing important data, and bringing down systems entirely, which results in lost productivity and downtime. Furthermore, these infections can spread quickly via networks, impacting numerous devices and increasing the harm. Frequent Network Penetration Testing can assist in locating weaknesses and fortifying defences against malware attacks before they can inflict extensive Damage.
How to Identify a Malware Infection
Understanding a malware infection as early as possible is essential to minimizing Damage. Some warning signs to indicate that there is an infection include:
Are You Considering Pursuing a Master’s Degree in Cybersecurity? Enroll in the Cyber Security Expert Masters Program Training Course Today!
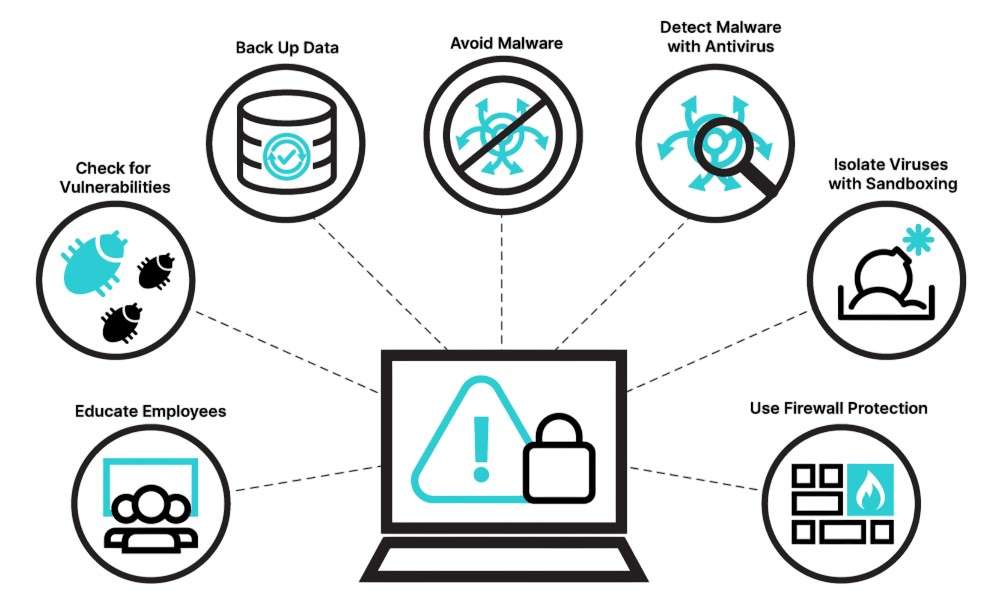
Methods of Precaution against Malware Attacks
No matter how much effort is put into it, the absolute certainty of avoiding malware attacks is impossible. However, several methods of precaution will generally prevent a Cyber Security Training Courses.
Secure Passwords and Multi-factor Authentication
Having different, very strong passwords for all your accounts would be best. MFA (multi-factor authentication) introduces another layer of security to make it more difficult for attackers to jeopardize your accounts. This additional layer typically greatly lowers the possibility of unwanted access by requiring a second form of authentication, like a fingerprint or a code texted to your phone.
Software Updates
Ensure that your OS and applications are updated regularly. The probability that miscreant users will exploit old software to install malware is high; therefore, keeping all your systems up to date is an easy but effective measure. Timely updates patch known vulnerabilities, making it much harder for cybercriminals to gain unauthorized access or deploy malicious software.
Proteting with Antivirus and Anti-malware
Set up a reliable antivirus application. Malware infections can be found and removed with this. Periodically scanning the system and turning on real-time protection for ongoing monitoring is a smart practice. In addition, make sure your antivirus program is updated on a regular basis to recognize and defend against the latest threats and malware variants.
Email Security Practices
Be cautious of unsolicited emails. Avoid opening attachments or clicking links from unidentified senders, and only open emails from senders you have yet to verify after making sure they are legitimate. Because hackers frequently use phoney addresses that seem like real ones, always double-check the email address for minor changes. Cyber Awareness is crucial to identifying these threats and protecting against phishing attacks.
Security Measures for Networks
Employ an intrusion detection system and firewall to keep malware out of your network and devices. Avoid using public Wi-Fi networks without a VPN, as they are vulnerable to virus attacks. Ensure your router is encrypted and locked with a strong password to avoid unwanted access to your home network.
Reaction Against Malware Attacks
Suppose you suspect that your system has been invaded by malware. Reacting in time can help lessen the harm that malware infections create.
Geared Up for an Cyber Security Job Interview? Browse Our Comprehensive Set of Cyber Security Interview Questions to Help You Prepare!
The Future of Malware: Emerging Threats
The future scares and fascinates: malware. Technology advances will obviously advance malware, too. For instance, how much more advanced threats from AI-driven malware will be, altering their modus operandi to evade detection? We will have more targeted malware attacks of a stratagem kind, cyber espionage, perhaps even cyber warfare.
Conclusion
Cyber Security Training Courses are still one of digital security’s most dangerous threats today. From viruses to ransomware, you can imagine the financial, personal, or organizational implications these attacks can cause. Your hances of becoming their next victim will be much decreased if you are aware of the different kinds of malware, how they operate, and how to identify and stop them. Your data and systems can be greatly secured by taking proactive steps like creating strong passwords, updating software, using antivirus software, and using caution when using the internet. This s because a world constantly threatened by changing cyber threats demands that the person be vigilant and prepared.





