
- Introduction to Cybersecurity Careers
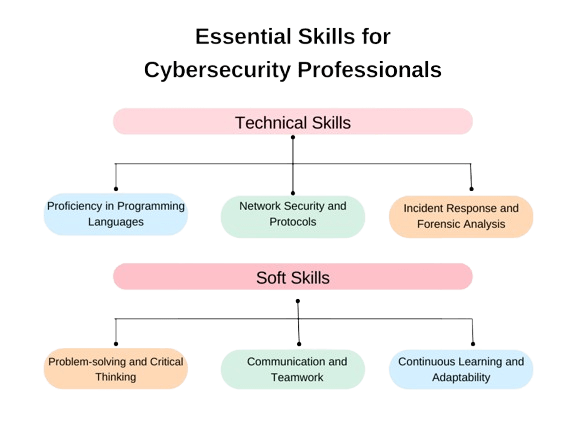
- Technical Skills
- Cybersecurity Frameworks and Standards Knowledge
- Incident Response and Management
- Risk Management and Compliance
- Security Architecture and Design
- Programming and Scripting Skills
- Threat Intelligence and Analysis
- Soft Skills for Cybersecurity Professionals
- Certifications and Education in Cybersecurity
- Conclusion
Introduction to Cybersecurity Careers
Cybersecurity is one of the fastest-growing fields globally, driven by the increasing number of cyber threats and the growing need to protect sensitive data and systems. As organizations and individuals continue to rely heavily on digital technologies, the demand for skilled cybersecurity professionals has skyrocketed. Cyber Security Training Courses are increasingly vital in providing individuals with the necessary skills and knowledge to meet this growing demand and protect against evolving cyber threats. A cybersecurity career can encompass a variety of roles, including security analyst, penetration tester, incident responder, and chief information security officer (CISO). Professionals in this field must be well-versed in both technical and soft skills to address the constantly evolving landscape of cyber threats effectively.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Cybersecurity? Sign Up For Our Cyber Security Online Training Today!
Technical Skills
- Networking Fundamentals: Networking knowledge is essential for understanding how data moves across networks and identifying potential vulnerabilities. Cybersecurity professionals need to be familiar with protocols such as TCP/IP, DNS, HTTP/S, and others. This allows them to monitor traffic, identify malicious activity, and ensure secure communication channels.
- Knowledge of Operating Systems: Cybersecurity professionals must understand various operating systems, such as Windows, Linux, and macOS. This includes knowing how to secure these systems, manage access controls, and troubleshoot vulnerabilities. Many cyberattacks exploit operating system weaknesses, so familiarity with system internals and security configurations is crucial.
- Proficiency in Security Tools and Software: Cybersecurity professionals use a range of tools for threat detection, monitoring, and defense, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), intrusion prevention systems (IPS), and endpoint protection software. Familiarity with these tools is crucial for effectively securing networks and systems. In addition, understanding certifications like OSCP vs CEH Analysis of Two Cybersecurity Certifications can help professionals choose the right training to enhance their expertise and knowledge in cybersecurity.
Technical skills form the foundation of a cybersecurity professional’s expertise. These include a deep understanding of network protocols, operating systems, and security tools used to defend against cyberattacks. Some of the most important technical skills include:
- Understanding Firewalls and VPNs: Firewalls are fundamental in network security, monitoring incoming and outgoing traffic based on predefined security rules. A solid understanding of firewalls and how to configure them is necessary to prevent unauthorized access. Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) are used to secure communications, ensuring data is transmitted safely over potentially insecure networks.
- Cloud Security Expertise: As more organizations migrate to cloud environments, knowledge of cloud security is essential. Understanding how cloud services work, how data is stored, and the specific security risks involved is key to maintaining a secure cloud infrastructure. Key concepts include identity management, encryption, and compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA.
- Penetration Testing and Vulnerability Assessment: Penetration testing, or ethical hacking, involves simulating cyberattacks to identify system vulnerabilities. Proficiency in penetration testing tools (such as Kali Linux or Metasploit) and methodologies is essential. Professionals must also be able to perform vulnerability assessments to find and fix security weaknesses proactively.
Cybersecurity Frameworks and Standards Knowledge
Cybersecurity frameworks and standards help professionals establish best practices for securing systems and data. Familiarity with frameworks like the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, ISO 27001, and CIS Controls can help professionals structure their security strategies. These standards provide guidelines for risk management, incident response, and security operations. Additionally, techniques like Cyclic Redundancy Check are often used to verify data integrity and ensure that transmitted data has not been altered or corrupted, further strengthening security measures.
Incident Response and Management
- Incident response involves detecting, analyzing, and mitigating security incidents such as data breaches, malware infections, and denial-of-service attacks.
- Cybersecurity professionals must be able to identify incidents quickly, contain them, and minimize the damage. This requires knowledge of incident response plans, forensics tools, and communication strategies to inform stakeholders.
- Cybersecurity is not just about protecting against threats; it’s also about understanding and managing risks. Professionals must assess the potential impact of threats and prioritize them based on business value and possible harm.
- Familiarity with compliance regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS is also critical, as organizations must ensure they meet these legal requirements to avoid penalties and maintain trust.
- While not always a core requirement, programming knowledge is increasingly valuable for cybersecurity professionals, especially when it comes to identifying and defending against threats like Vishing Attacks, where attackers use voice communication to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information.
- Skills in languages such as Python, C, and Java and scripting languages like PowerShell or Bash allow professionals to automate security tasks, develop custom security tools, and analyze malware. This ability enhances the efficiency and effectiveness of security operations.
- Threat intelligence involves gathering and analyzing data on potential cyber threats. Professionals need the skills to collect and interpret information from various sources, such as threat feeds, malware samples, and attack trends, to stay ahead of evolving cybercriminal tactics.
- This intelligence is used to predict and prevent attacks, improving an organization’s proactive security posture.
- Analytical Thinking: Cybersecurity professionals must be able to analyze complex problems, assess risks, and develop solutions. Analytical thinking helps them detect patterns, identify vulnerabilities, and respond effectively to incidents.
- Attention to Detail: Cybersecurity involves examining systems and data for minute signs of compromise. Professionals must be detail-oriented to detect the smallest anomalies that could indicate a potential threat, such as a Dictionary Attack, where attackers systematically attempt a large list of possible passwords to gain unauthorized access.
- Communication and Teamwork: Effective communication is essential for cybersecurity professionals to explain technical issues to non-technical stakeholders and collaborate with other teams, including IT, legal, and management. Working well in teams is crucial, especially when responding to incidents or building security strategies.
- Problem-Solving Ability: Cybersecurity professionals are constantly faced with challenges. Solving problems under pressure is vital when dealing with security breaches, system vulnerabilities, and other unexpected issues.
- Continuous Learning and Adaptability: The field of cybersecurity is constantly changing, with new threats, technologies, and regulations emerging regularly. A willingness to keep learning, adapting, and staying updated with the latest trends is essential for long-term success in the field.
- CompTIA Security+ (entry-level)
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP)
- Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH)
- Certified Information Security Manager (CISM)
- Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP)
Interested in Obtaining Your Cyber Security Certificate? View The Cyber Security Online Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Risk Management and Compliance
Security Architecture and Design
Building secure systems requires a deep understanding of security architecture, including the design of secure networks, systems, and applications. Cyber Security Training Courses professionals must know how to create secure infrastructures, implement defense-in-depth strategies, and ensure that security is integrated from the start of system design. This also involves implementing access controls, encryption, and secure authentication.
Programming and Scripting Skills
Threat Intelligence and Analysis
Gain Your Master’s Certification in Cybersecurity by Enrolling in Our Cyber Security Expert Masters Program Training Course.
Soft Skills for Cybersecurity Professionals
In addition to technical expertise, cybersecurity professionals must possess a variety of soft skills to succeed in their roles. These include:
Certifications and Education in Cybersecurity
Certifications and formal education are essential for cybersecurity professionals to validate their skills and knowledge. Some of the most respected certifications include those that focus on areas like Cipher Encryption, which is crucial for securing data through advanced encryption techniques.
Formal education, such as a degree in cybersecurity, computer science, or a related field, can also provide a solid foundation for a career in cybersecurity.
Go Through These Cyber Security Interview Questions and Answers to Excel in Your Upcoming Interview.
Conclusion
To build a successful career in cybersecurity, professionals need to blend technical skills with problem-solving abilities, analytical thinking, and a passion for continuous learning. The evolving nature of cyber threats means that cybersecurity professionals must remain vigilant and adaptable. With the right set of skills, certifications, and experience, cybersecurity professionals can play a crucial role in safeguarding the digital world. In addition to technical expertise, strong communication and collaboration skills are essential for a successful career in Cyber Security Training Courses. Professionals often work in cross-functional teams, where they need to explain complex security concepts to non-technical stakeholders and collaborate with other departments to ensure that security measures align with business goals. Being able to effectively communicate and educate others on security risks and best practices can make a significant impact on an organization’s overall security posture. As cybersecurity threats become more sophisticated, professionals who can adapt, stay informed, and work well with others will be highly valued in the field.





