
- What is Zero Trust Security?
- Core Principles of Zero Trust Security
- How Zero Trust Security Works
- Advantages of Zero Trust Security
- Challenges in Implementing Zero Trust
- Zero Trust Security Frameworks and Tools
- Best Practices for Zero Trust Adoption
- Conclusion
In the rapidly changing space of cybersecurity, network protection methods that were hitherto reliable need to be revised in today’s world. The adage “trust but verify” is no longer a reliable strategy with the increasing complexities of modern enterprise environments. With cloud computing, BYOD policies, and remote work, the security perimeter is no longer confined to a corporate network behind a firewall. This shift means that sensitive Network Penetration Testing, such as company data or communications, are now being transmitted across less secure environments, including personal devices and public networks. This model addresses comprehensive network, application, and data security in ways that the granted trust is continually earned rather than just provided. The blog post will dive into the zero trust architecture model, its core principles, how it works, the benefits it offers, and the challenges associated with its implementation. At the end, you will clearly understand why Zero trust network is emerging as the go-to framework for modern cybersecurity.
To Earn Your Zero Trust Security Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Cyber Security Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Cyber Security Online Training Today!
What is Zero Trust Security?
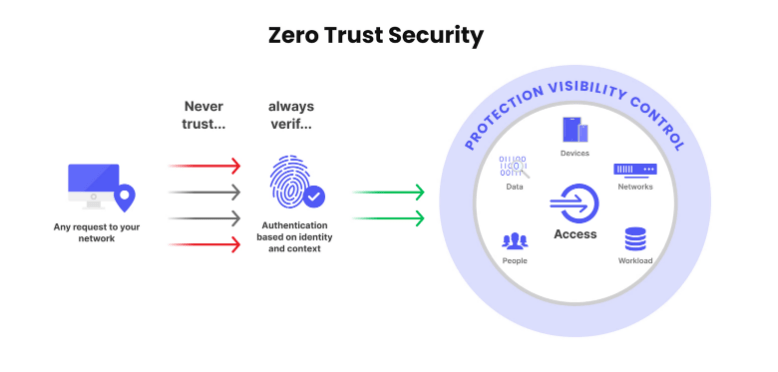
The simplicity of the Zero Trust Security model is summed up in the motto “never trust, always verify.” Traditionally, network security was based on the model of an “inside trusted” and an “outside untrusted” network. Firewalls and VPNs were used mainly to enforce access controls based on the assumption that someone crossing the boundary of a corporate network ought to be trusted automatically. That model will only work for organizations embracing cloud technologies, mobile workforces, and an ever-expanding number of endpoints.
Zero Trust Security flips this model on its head, making Cyber Security Training Courses decisions strictly based on the verification protocols for every device, user, and application accessing a network resource, supplanting Trust based on location or perimeter in light of increasingly sophisticated cyber threats such as insider threats, ransomware, and APTs. Instead, Zero Trust assumes the network is always at risk. He doesn’t rely on the more conventional “castle-and-moat” model, where everything within the network perimeter is trusted by default. It instead ensures access to data and applications through continuous verification of users and devices, regardless of where they are.
Core Principles of Zero Trust Security
Continuous Identity Verification
The very first principle of Zero Trust is continuous identity verification. It is only the requirement of Zero Trust that every access request, however frequent it may be, needs to be continuously verified and not the assumption of giving a wide blanket access to users upon initial authentication. Thus, it would authenticate users, devices, and applications at all access stages and ensure that only the authentic entities could interact with sensitive systems. Verification normally involves MFA, biometrics, device health checks, and behavioural analytics to determine if the user and their device should be allowed in.
Assume Breach
Zero Trust assumes a breach will likely happen sometime, and an attacker could already be in. It shifts the philosophy from one of prevention to containment. Zero Trust is not about blocking the external threat but limiting the damage an attacker can do once accessing a system, assuming a breach. This approach focuses on managing Risk Threat and Vulnerability across the network by continuously verifying and enforcing strict access controls, even for trusted users and devices. This involves micro-segmentation, constant monitoring, and network segmentation to lock down potential threats.
Least Privilege Access
The principle of least privilege indicates granting access to users and devices with the most restrictive level necessary for performing their tasks. Zero Trust uses a concept termed “just-in-time” access, wherein privileges are assigned for only the period needed to accomplish a specific task and then given back. That reduces unnecessary exposure of sensitive resources to users or applications that do not have them. Organizations significantly reduce the risk of insider threats and minimize the impact of compromised credentials by reducing the permissions of every entity in the network.
Micro-Segmentation
Micro-segmentation refers to dividing the network into smaller, isolated segments that prevent lateral movement for attackers inside the network. Access between each segment acts as a separate trust zone with its access being well controlled. In a zero-trust model, micro-segmentation prevents an attacker who gains access to one segment from moving freely to other network parts without further verification. This traffic isolation ensures that critical systems and data remain protected, even in a breach.
To Explore Zero Trust Security in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Cyber Security Online Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
How Zero Trust Security Works
- Authentications of Users and Devices: The user or device accessing network resources should authenticate first. This involves MFA and robust authentication processes. Devices are validated; they should meet the security requirements like updated software and endpoint protection.
- Access control: Users’ and devices’ access is provided once it is verified; access is also given at the minimum required levels to perform their tasks. Examples include preventing certain applications from obtaining a connection to the network or limiting the traffic that may be sent to specific resources.
- Micro-Segmentation and Segregation: The network is split into unique, isolated parts, each with unique access policies, avoiding any damage if an attacker accesses one of the above segments. In an Internet of Things environment, where a large number of connected devices may be spread across various parts of the network, segmentation ensures that a compromised IoT device cannot easily serve as a gateway to the rest of the network.
- Continuous Monitoring and Behavior Analytics: Zero Trust is an always-on activity that necessitates continuous monitoring. Anomalies in behaviour, such as login attempts from unfamiliar locations or unexpected changes in user activity, trigger alerts with corresponding actions in real time.
- Automated Responses: Policies in a Zero Trust environment are normally automated very quickly to isolate the compromised account, devices, or segments with minimum potential damage.
Advantages of Zero Trust Security
Zero trust architecture offers many benefits, especially in today’s dynamic threat landscape. It also minimizes the possible entry points for cyber attackers by implementing the principle of least privilege and restricting access to critical resources. Even if an attacker breaks through one area of the network, the attacker won’t easily get through to other places because of micro-segmentation. That effectively reduces the attack surface. Zero trust monitors and analyzes the behaviour of users and devices in real time. Organizations get better insights into who is accessing their network in Cyber Security Training Courses, when, and from where. Increasing visibility also promotes better control over the network traffic and user activities, thus significantly improving the chances of detecting suspicious actions in time. Since Zero Trust considers all incoming access requests suspect, data protection is ensured through authorization of access only from a valid user and device, thus preventing unauthorized users from accessing sensitive data. Segmentation and continuous monitoring minimize malicious access, keeping the data safe. Zero Trust Security also supports compliance with regulatory standards, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS. Because Zero Trust uses strict access controls combined with a detailed log of every activity performed by the user, it provides a simplified requirement for auditing and reporting that supports compliance with many security regulations.
Are You Considering Pursuing a Cybersecurity Master’s Degree? Enroll For Cyber Security Expert Masters Program Training Course Today!
Challenges in Implementing Zero Trust
Complexity
Implementing Zero Trust in a large organization with legacy systems is complicated and time-consuming because it involves integrating various technologies, tools, and processes into one coherent security model. To ensure robust in Threat Intelligence, organizations may need to invest in advanced firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and secure development practices. In addition, training staff on managing and monitoring the security tools effectively is crucial to maintaining a safe environment. While the initial cost may be significant, these investments are necessary to create a strong security foundation to protect the network from evolving threats.
Culture Change
Zero Trust requires a shift in mindset. People start viewing security no longer as the IT teams’ exclusive duty but as everyone’s shared responsibility in the organization. The employees and departments must understand that security is an ongoing, proactive process that is not once completed. Moving towards an access request model that scrutinizes every request necessitates buy-in from the highest to lowest levels of the organization, coupled with continual education and training so that all understand their roles in maintaining a secure environment.
Zero Trust Security Frameworks and Tools
- The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) published a comprehensive guide to Zero Trust architecture, offering hands-on guidance for organizations to implement this model effectively. Their framework outlines the importance of verifying every request for access, regardless of where it originates, and emphasizes the need for continuous monitoring and adaptive security measures.
- This guide helps organizations transition from a traditional perimeter-based security model to a more dynamic and risk-aware approach, ensuring robust defense mechanisms across their entire IT infrastructure. The initiative redefines security to treat all devices as potentially compromised and requires strict verification of both the user and the device before granting access.
- Google’s BeyondCorp initiative is one of the most notable real-world implementations of a Zero Trust model. Unlike traditional models that rely on perimeter security, BeyondCorp shifts the focus to ensuring that access to internal resources is secure regardless of the user’s location or device.
- By leveraging cloud-based technologies and identity management tools, Google has effectively allowed employees to securely access corporate resources from anywhere in the world, without the need for a traditional VPN.
Best Practices for Zero Trust Adoption
Improving Identity management and MFA will be implemented to limit the availability of network resources only to valid users. Sensitive data must be protected through encryption and access controls. Automating access control decisions and threats could improve efficiency while reducing possible human errors. It will divide your network into secure zones containing all the critical assets to ensure the safety and segregation of those assets. Regular Private key and Public key becomes essential to identify vulnerabilities within each secure zone. Strong Identity and Access Management (IAM) would ensure that only authorized people can access network resources, making it unlikely that unauthorized access or a data breach. Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) adds additional security features to the organization. Even if a password is compromised, extra verification steps will be necessary to allow access. Automation of access control decisions will allow for faster and more uniform security policy enforcement without facilitating the room for potential errors arising during manual processing. Also, micro-segmentation of the network into safe zones is important to separate databases, intellectual property, and financial systems so that lateral movement in the network can be restricted. This will further provide an added layer of defence because, even though one part of the network is compromised, the attackers may easily access sensitive or vital systems.
Preparing for a Cyber Security Job Interview? Check Out Our Blog on Cyber Security Interview Questions and Answers
Conclusion
Zero trust architecture is a new approach in our thinking about network security. Lack of trust assumption and continuous verification ensures full protection of an organization against all those modern Cyber Security Training Courses, including insider threats, ransomware, and data breaches. Zero Trust’s implementation is complex and very resource-intensive. Still, its benefits include a lesser attack surface, improved visibility, and data protection, hence useful in securing today’s highly interconnected and distributed networks. Zero Trust will form the basis for more evolved cyber threats as they build resilient and future-proof security architectures. Zero Trust Security acts as an offence in the traditional models by removing the reliance on Trust and requiring verification for all access requests, regardless of source. This constant scrutiny protects the client from some of the attacks from external sources and greatly minimizes threats from insiders that have recently become common. Zero Trust is difficult and resource intensive, but the benefits the long run provides can supersede all challenges as organizations embrace wider uses of cloud, remote work, and IoT technologies. In an era where threats from the cyber world continue to evolve in complexity, Zero Trust will provide a solid foundation for robust, adaptive security frameworks that build resilience against sophisticated future cyber attacks.





