
- Introduction
- What is Spyware?
- Types of Spyware
- How Spyware Affects Your Device
- Signs Your Device Is Infected with Spyware
- How to Protect Yourself from Spyware
- What to Do if Your Device Gets Infected
- Spyware vs. Other Malware
- Conclusion
Spyware is malicious software designed to secretly monitor and collect information from your device without your knowledge. Cybersecurity Training Courses can come in various types, such as adware, keyloggers, and tracking cookies. Spyware affects your device by slowing performance, compromising personal data, and enabling unauthorized access. Signs of infection include unusual behavior, pop-up ads, and unauthorized changes. To protect yourself, use reliable security software, avoid suspicious downloads, and keep software updated. If infected, run a security scan, remove the malware, and change passwords. Unlike other malware, spyware focuses on data theft, whereas viruses and worms cause more widespread damage. Always stay vigilant to ensure your device’s safety.
To learn about different Cybersecurity techniques, sign up for our Cyber Security Online Training.
Introduction
Spyware has been described as a kind of malicious software that can silently monitor and collect information from your device without your notice or consent. Though the concept of spyware may sound like something out of a spy movie, it’s unfortunately a real threat in today’s digital world. Spyware has ranged from tracking your browsing history and stealing sensitive personal data. This blog will explain what spyware is, how it works, the various types of spyware, its effects on your devices, how to detect it, and how you can protect yourself from falling prey to Database Security. The impact of spyware on your device can range from slow performance and unexpected crashes to severe security breaches. Detecting spyware can be challenging, but common signs include strange pop-up ads, unresponsive behavior, or unexpected changes to your device settings. To protect yourself, it’s essential to use reputable security software, avoid suspicious links or attachments, and regularly update your device and applications. If you suspect your device is infected, running a thorough scan and removing the malware promptly is crucial. Understanding the risks of spyware and staying informed about protective measures can help you safeguard your privacy and prevent data theft.
What is Spyware?
Spyware is a class of malicious software. It secretly tracks information regarding any person or organization without permission from the victim. This kind of software usually finds its place inside other innocent-looking programs or sites and may also run in the background of any computer system undetected. Spyware might be used for tracing your surfing pattern or for pilfering critical personal data, such as Password Authentication, login, credit card details, and others. Spyware works without your permission and is usually downloaded onto your computer while downloading certain applications, clicking malicious links, or visiting compromised websites. Once it is installed, it may start collecting data, logging keystrokes, tracking browsing activity, or accessing private files.
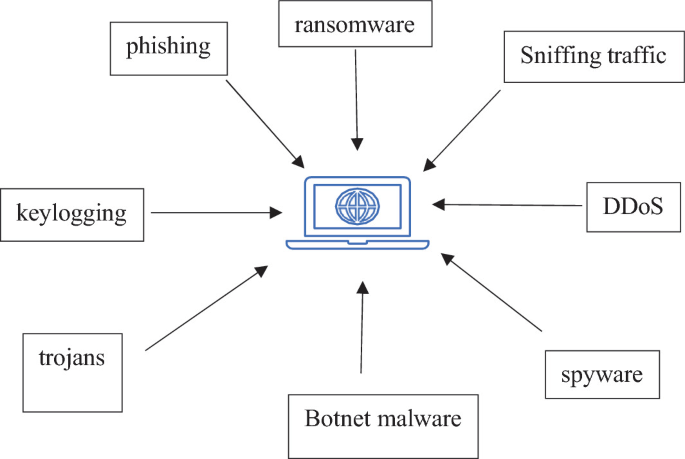
How does spyware work?
Spyware usually runs in the background silently, gathering information about your device and activities. It might record keystrokes, meaning everything you type, such as password inputs, usernames, and more. Informed data then gets sent to the attacker or the one behind the spyware, where it could be used for various things that could be destructive for you. Spyware will also capture things like your browser history, the search queries you entered, and where you visited in Cybersecurity Training Courses . It uses this to generate targeted ads; however, with more serious uses, it might be used in identity theft or financial fraud.
Enroll in ACTE’S Cyber Security Online Training if you want to become an expert in cyber security field and have a prosperous career.
Types of Spyware
There are numerous types of spyware. Depending on how it works and the purpose for doing so, every type has a different methodology.
Here are some of the common types of spyware:- Adware Adware is a type of spyware that mainly shows unwanted advertisements on your computer or device. Although adware itself is not necessarily malicious, it can still track your browsing habits and collect information about your interests, which can be used for targeted advertising. In some cases, adware may redirect your browser to malicious websites or install other forms of malware.
- Trojans Trojans are also known as Trojan horses. They are spyware but come in the form of legitimate software. They can appear in the form of a free download, for instance, an update for software or some free program. Once installed, your data may be stolen or hackers can get unauthorized access to your computer. Keyloggers install other spyware or malware in your computer without your knowledge.
- Keyloggers This category involves spyware with a more serious effect to be placed with hackers as well since they key in your records that include information entered when operating keyboards, whereby your login names, passwords, and other private message keys can find themselves being revealed by such spyware known as a Keylogger.
- Tracking Cookies Tracking cookies are small pieces of data stored on your device while browsing the internet. They track your browsing activity, preferences, and behavior. While cookies are often used by websites for legitimate purposes like remembering your login details or customizing content, they can also be used by third-party advertisers to monitor your activity across different sites, creating a detailed profile of your interests.
Want to Take the Lead in Cyber Security ? Enroll in ACTE’s Cybersecurity Expert Masters Program Training Course Program to Begin Your Adventure Now.
How Spyware Affects Your Device
Spyware can have several negative impacts on your device and online experience. Here are a few of the most common consequences Slower Performance Spyware often runs in the background, using up system resources like memory and processing power. As a result, your device may become sluggish or unresponsive, as the spyware is constantly working to gather and transmit data. Privacy Breaches the most troubling effect of spyware is the likelihood of privacy breaches. Spyware might collect personal details such as log-in credentials, browsing history, and even some financial information. This information could be used to commit identity theft, fraud, or other types of malicious behavior. Data Theft another risk of spyware is direct data theft. In this regard, keyloggers may capture such sensitive information as passwords that help hackers get unauthorized access to your bank accounts or social media accounts. This poses a great danger to your financial security and personal privacy.
Signs Your Device Is Infected with Spyware
Spyware typically runs in stealth mode, which makes it hard to detect. Still, some signs may indicate that your device is infected Increased Pop-ups and Ads If you find that there are too many pop-ups, banners, or advertisements appearing on your screen while browsing the internet, it is probably a sign that adware or spyware is running on your computer. Such unwanted ads may slow down your browsing and redirect you to malicious websites. Slow System Performance If your computer is slowing down, and it only happens when you are running tasks that were smooth before, the culprit could be spyware hogging up the system resources. Spyware can run quietly in the background and can slow up your computer noticeably. Unexplained Changes to Settings Spyware can alter your browser settings, homepage, or default search engine on your computer without asking. If your browser changes that you didn’t make, it’s worthwhile to dig deeper to see if spyware or another type of malware is present.
How to Protect Yourself from Spyware
There are several ways that you can help keep your device safe from spyware and other types of malware
- Use Anti-Spyware Software: Reliable anti-spyware or antivirus software is the best way to prevent spyware from infecting your device. Such tools detect, block, and remove spyware from the system. Remember to update the software regularly to be safe and sound.
- Software Updates: Ensure your operating system, browsers, and other software are always updated with the latest patches, as software developers issue these patches periodically to cover identified security vulnerabilities that spyware may take advantage.
- Avoid downloads and clicking on suspicious links: Avoid downloading any software from dubious websites and clicking on any links within an E-mail Security or SMS because spyware can be installed through this method disguised as a legitimate file or update.
- Firewall protection: A firewall acts as a barrier between your device and the internet, blocking malicious traffic from entering your system. It can help keep spyware out of your system in the first place.
- Use Strong Passwords: Use unique, strong passwords for your accounts to prevent spyware and other malware from getting access to your sensitive information. Consider using a password manager to generate and store complex passwords securely.
Get interview-ready with our collection of Cybersecurity Interview Questions and Answers Questions.
What to Do If Your Device is Infected
If you suspect that your device is infected with spyware, follow these steps Disconnect from the Internet Disconnect your device from the Internet to prevent the spyware from transmitting data. Run a Full System Scan: Use antivirus or anti-spyware software to scan your system and remove any detected spyware. Update Your Software: Ensure your operating system and applications are fully updated to fix any security Vulnerability Management. Change Your Passwords: If spyware has stolen login credentials, change your passwords immediately for all important accounts. Restore Your Device: If necessary, restore your device to a previous backup or perform a factory reset to remove any remaining malware.
Spyware vs. Other Malware
While spyware is often confused with other types of malware, it has its distinct features. Here is a quick comparison
- Spyware vs. Viruses: A virus replicates itself and spreads across devices, while spyware is focused on tracking and stealing data without spreading.
- Spyware vs. Trojans: Trojans are deceptive programs that trick you into downloading them, whereas spyware can often sneak onto your device through other means, such as bundled software.
- Spyware vs. Ransomware: Ransomware locks or encrypts your files and demands payment for their release, while spyware quietly collects data without necessarily causing immediate disruption.
Conclusion
Spyware is a significant security threat that can compromise your privacy and expose your sensitive information without your knowledge. Once installed on a device, Cybersecurity Training can track your online activities, steal personal data such as passwords and financial information, and even monitor communications. In addition to privacy concerns, spyware can slow down your device, affecting its performance and functionality. Being aware of how spyware operates and recognizing its symptoms—such as unusual behavior or increased pop-up ads—can help you stay vigilant and avoid infection. Installing reliable anti-spyware software is one of the most effective ways to prevent spyware from infiltrating your system. Regularly updating your operating system, applications, and security software ensures that you have the latest protections against known vulnerabilities. It’s also essential to be cautious when downloading files or clicking on links, especially from untrusted sources, as these are common ways spyware is introduced. Practicing good cybersecurity habits and adopting preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of a spyware infection. If your device becomes infected, taking immediate action, such as running a full system scan and changing your passwords, is vital. Ultimately, staying informed about cybersecurity threats, maintaining up-to-date defenses, and exercising caution online are key to protecting your digital privacy and security.





