
- Introduction to the Dark Web
- Deep Web vs Dark Web
- Accessing the Dark Web (TOR, I2P)
- Common Activities on the Dark Web
- Legal vs Illegal Uses
- Cryptocurrency and Anonymity
- Risks of Exploring the Dark Web
- Role in Cybercrime and Law Enforcement
Introduction to the Dark Web
The Dark Web is a hidden part of the internet that isn’t indexed by traditional search engines like Google, making it accessible only through specialized tools like the Tor browser. Often misunderstood, the Dark Web offers both legitimate uses and illegal activities. At its core, it provides a platform for anonymity, allowing users to communicate and share information securely without revealing their identities. This level of privacy has attracted whistleblowers, journalists, and individuals living under oppressive regimes. However, the same features also make it a haven for cybercrime, including illegal drug sales, weapons trading, and data breaches. Transactions on the Dark Web are typically carried out using cryptocurrency, such as Bitcoin or Monero, which adds another layer of anonymity and reduces traceability a critical concept often emphasized in Cyber Security Training programs to help professionals understand and counter illicit online financial activities. While navigating the Dark Web, users often rely on Dark Web search engines like Ahmia or Not Evil to locate marketplaces and forums. These search engines function differently from surface web tools, focusing on .onion domains. Due to its illicit activities, the Dark Web is closely monitored by law enforcement agencies around the world, who work tirelessly to infiltrate criminal networks and shut down unlawful marketplaces. Despite its dark reputation, understanding the Dark Web is crucial for cybersecurity awareness and online safety.
Interested in Obtaining Your Cybercrime Certificate? View The Cyber Security Online Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
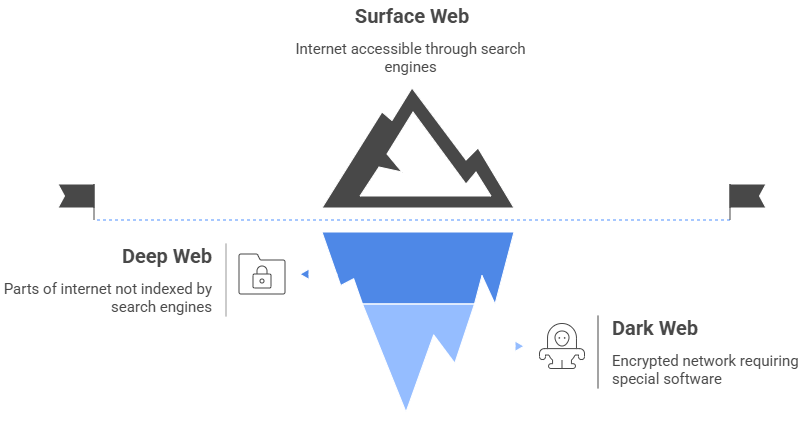
Deep Web vs Dark Web
- Accessibility: The Deep Web can be accessed through normal browsers with proper credentials (e.g., login details), whereas the Dark Web needs a Dark Web browser like Tor.
- Content Type: The Deep Web contains everyday private data like emails or banking info, while the Dark Web often hosts anonymous forums, illegal marketplaces, and whistleblower platforms making it essential to Explain What is Data Classification when determining the sensitivity and handling requirements of such information across different web layers.
- Searchability: You can’t find Deep Web content on Google, but some are accessible through site searches. For the Dark Web, users rely on Darkweb search tools designed to navigate .onion sites.
The internet is divided into several layers, with the Deep Web and Dark Web being two often confused terms. While both exist beyond the reach of traditional search engines, they serve very different purposes. The Deep Web includes content like private databases, academic journals, medical records, and subscription-only sites that are not indexed by standard search tools. In contrast, the Dark Web is a small, intentionally hidden portion of the Deep Web that requires special software like the Darknet Tor browser to access. Here’s a clear breakdown of their differences:
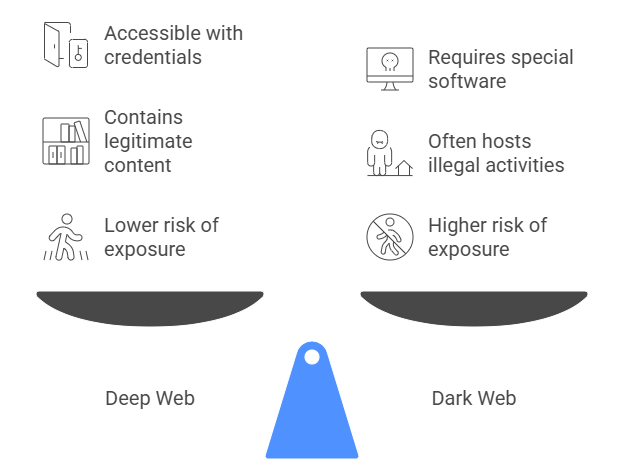
- Purpose: The Deep Web supports privacy for secure services; the Dark Web promotes anonymity but is also linked to illegal activity.
- Applications: Many legitimate organizations offer Deep Dark Web apps for secure data storage, while Dark Web apps often require encryption and anonymity tools.
- Terminology: The Deep Web is often called the Invisible Web, while the Dark Web is part of the darknet, a hidden network only reachable via special tools like the Tor browser.
Accessing the Dark Web (TOR, I2P)
Accessing the Dark Web involves using specialized tools like TOR (The Onion Router) and I2P (Invisible Internet Project), which enable users to browse hidden websites anonymously. These tools mask users’ IP addresses and encrypt traffic, making it difficult for anyone to trace online activity. The TOR network is the most widely used entry point into the Dark Web, allowing access to onion domains that are unreachable through regular browsers. Similarly, I2P offers peer-to-peer communication within an anonymized network, often relying on encryption techniques like the Data Encryption Standard Algorithm to secure data transmission and maintain user privacy. Once inside, users often rely on a Dark Web search engine like Ahmia or Candle to discover hidden forums, marketplaces, and services. These platforms frequently use cryptocurrency, such as Bitcoin or Monero, for transactions, reinforcing a layer of anonymity and making it harder to trace identities. While some people use the Dark Web for privacy-focused reasons such as escaping censorship or conducting secure communications, it’s also home to significant cybercrime, including illegal trade, stolen data, and hacking services. Because of this, global law enforcement agencies actively monitor these networks, often setting up undercover operations to identify and prosecute criminals. Although the Dark Web promises privacy, users must tread carefully, as the line between legal anonymity and illegal activity is thin and constantly monitored.
To Explore Cybersecurity in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Cyber Security Online Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Common Activities on the Dark Web
- Anonymous Communication: Journalists, activists, and whistleblowers use encrypted messaging platforms and Deep Dark Web apps to communicate securely, especially in regions with internet censorship.
- Illegal Marketplaces: Users often engage in buying or selling illicit goods such as drugs, firearms, counterfeit documents, and stolen data, all while using cryptocurrency to remain untraceable a scenario frequently analyzed in Cyber Security Training to help professionals identify and respond to darknet threats effectively.
- Data Breaches and Leaks: Hacked personal information, credit card numbers, and login credentials are frequently traded or sold, making the Dark Web a hub for digital black markets.
The Dark Web is a concealed segment of the Invisible Web, accessible only through tools like a Dark Web browser or the Darknet Tor browser. It offers complete anonymity, which attracts a wide range of users from privacy advocates to cybercriminals. While not everything on the Dark Web is illegal, many activities raise security and ethical concerns. Below are some of the most common activities found on the Dark Web:
- Hacking Services: Cybercriminals offer hacking-for-hire services, malware development, and DDoS attack tools through forums and private listings.
- Darkweb Search and Directories: Since standard search engines don’t index .onion sites, users rely on Darkweb search engines like Ahmia or Not Evil to navigate content.
- Hosting Hidden Services: The Dark Web hosts a variety of services from uncensored news sites to whistleblower portals made accessible via the Darknet Tor browser for users seeking privacy.
- Private Transactions: Cryptocurrencies allow peer-to-peer transactions without revealing personal information, making them ideal for anonymous exchanges on the Dark Web.
- Preferred on Hidden Marketplaces:Most illegal and some legal marketplaces accessed via the Darknet Tor browser or deep dark web apps accept only cryptocurrency, eliminating the need for traceable credit cards or bank accounts an important topic often covered in Learn Cyber Security Books to help readers understand how anonymity and financial privacy are exploited on the Dark Web.
- Difficult to Trace: Unlike traditional banking systems, cryptocurrencies don’t always require identity verification, especially on anonymous platforms found via Darkweb search engines.
- Used for Privacy Tools: Users often donate or subscribe to privacy services on the Invisible Web using cryptocurrency, ensuring both sides remain anonymous.
- Boosts App Security: Many deep dark web apps integrate cryptocurrency payments to maintain user confidentiality and avoid financial tracking.
- Targeted by Law Enforcement: Due to its popularity among criminals, cryptocurrency is closely monitored by law enforcement, especially when linked to activities on the Dark Web.
Legal vs Illegal Uses
The Dark Web is a shadowy section of the internet that is intentionally hidden and can only be accessed using special tools like the Tor browser. One of the primary ways users explore this hidden network is through a Dark Web search engine, which helps them locate .onion sites that are invisible to regular browsers and search platforms. These search engines function within the Tor ecosystem, allowing users to browse content while preserving their anonymity. Cryptocurrency and anonymity go hand in hand on the Dark Web, as digital currencies like Bitcoin and Monero are the preferred payment methods. These currencies enable untraceable transactions, which make them ideal for both privacy-conscious users and those engaging in illegal activities—a concept often explored in any comprehensive Guide To Data Privacy to highlight the importance of secure and anonymous digital exchanges. Unfortunately, the promise of privacy has also made the Dark Web a hotspot for cybercrime, where illegal marketplaces, hacking services, and stolen data are frequently traded. To combat this, law enforcement agencies across the globe have stepped up their monitoring and infiltration efforts, conducting undercover operations to take down criminal networks. While the Dark Web offers tools for secure communication and freedom of expression, its misuse has raised serious concerns, making it a complex environment where the line between privacy and illegality is constantly tested.
Looking to Master Cybersecurity? Discover the Cyber Security Expert Masters Program Training Course Available at ACTE Now!
Cryptocurrency and Anonymity
Cryptocurrency and anonymity are deeply interconnected, especially in the hidden layers of the internet like the Invisible Web and the Dark Web. Digital currencies such as Bitcoin and Monero are widely used on these platforms because they offer a level of privacy that traditional financial systems do not. This anonymity is especially valued by users accessing the Dark Web through tools like a Dark web browser or the Darknet Tor browser, where identities are concealed, and transactions are harder to trace. Here are six key points explaining the relationship between cryptocurrency and anonymity:
Risks of Exploring the Dark Web
Exploring the Dark Web can be tempting for those curious about the hidden corners of the internet, but it comes with significant risks that users must be aware of. While tools like the Darknet Tor browser or any Dark web browser offer anonymity, they also expose users to malicious content and dangerous environments. Simply accessing sites through a Darkweb search engine can lead to illegal marketplaces, phishing pages, or scam services. Many users unknowingly download malicious files or fall victim to ransomware attacks, especially when using unfamiliar deep dark web apps without proper security a risk often highlighted in any Quick Guide To Cyber Safety to educate users on safe browsing practices and threat prevention. The Invisible Web, which includes both the Deep and Dark Web, is not regulated or monitored like the surface internet, making it a breeding ground for cybercrime and exploitation. Identity theft, surveillance, or being flagged by authorities are common consequences if users unintentionally interact with illegal content or marketplaces. Moreover, connecting to the Dark Web without precautions can compromise your system’s security, as hackers and malware distributors often target novice users. While the allure of privacy and secrecy is strong, accessing the Dark Web without understanding its dangers can result in severe digital and legal consequences, making it a high-risk space even with tools like the Tor browser.
Preparing for Cyber Security Job Interviews? Have a Look at Our Blog on Cyber Security Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Role in Cybercrime and Law Enforcement
The Dark Web plays a dual role in the world of cybercrime and law enforcement, acting as both a platform for illegal activities and a target for global investigations. Accessible only through specialized tools like a Dark web browser or the Darknet Tor browser, it provides a high level of anonymity, making it attractive to cybercriminals. These actors use hidden marketplaces, forums, and deep dark web apps to traffic in illegal goods, stolen data, hacking tools, and illicit services. Transactions are typically carried out using cryptocurrency, making it difficult to trace or link to real-world identities. Cybercriminals often rely on Darkweb search engines to locate .onion sites, many of which operate on the fringes of legality. This concealed area of the Invisible Web creates a serious challenge for authorities, as the lack of traditional oversight limits visibility and accountability—an issue thoroughly explored in Cyber Security Training to prepare professionals for detecting and mitigating hidden digital threats. However, law enforcement agencies around the world have adapted by developing advanced digital forensics, undercover operations, and AI-driven tracking systems to infiltrate and dismantle illegal networks. Many high-profile dark web takedowns like Silk Road and AlphaBay have demonstrated that anonymity is not absolute. As cybercrime continues to evolve, so does law enforcement’s strategy in monitoring and responding to threats originating from the Dark Web.




