
- What is vulnerability scanning?
- Why is scanning important?
- Types of Vulnerability
- How this Scanning Works
- Best Practices for Effective Scanning
- Tools for Vulnerability
- Vulnerability trends
- Conclusion
Vulnerability is a core process in cybersecurity whereby systems, networks, and applications are scanned for Identification,vulnerability assessment and mitigation of vulnerabilities in computer systems. This has a significant role in any organization’s Cybersecurity Training Courses strategy as it proactively helps identify weaknesses before harmful actors even exploit them. This process applies automated tools that check a system or security network for known vulnerability scanning, misconfigurations, outdated software, and other security flaws that may expose an organization to risks.
What is vulnerability scanning?
The automatic Identification of potential and actual vulnerabilities in a computer system, network, or application using specifically designed scanning vulnerability tool. They can find nearly all types of problems, from a misconfigured, simple one to a complex security flaw. The basic aim is the detection of weaknesses before these can be exploited by Cyber Insurance ensuring that the security posture of an organization is strong. Unlike penetration testing, which simulates real-world hacking that exploits weaknesses, scanning focuses on detection and reporting. nessus scanner generally look for known vulnerabilities in software, missing patches, weak passwords, improper configurations, and more that might be exploited.
Enroll in ACTE’S Cyber Security Online Training if you want to become an expert in cyber security field and have a prosperous career.
Why is this scanning important?
It is an active defence mechanism whereby organizations can detect security vulnerabilities. Scanning regularly helps identify the vulnerabilities that attackers could exploit, allowing organizations to correct them before they are exploited. Risk prioritization Not all vulnerabilities are equal. Scanning tools assign a risk level to vulnerabilities that help IT teams prioritize remediation efforts based on the severity of the threat.Compliance Most industry standards and regulatory frameworks, such as the PCI DSS, HIPAA, or GDPR, mandate scanning. Regular scanning ensures compliance. Prevention of data breaches: Identifying Vulnerability Management before they are exploited can help prevent cybersecurity and may preclude data breaches, financial loss, or reputational damage.
Want to Take the Lead in Cyber Security ? Enroll in ACTE’s Cybersecurity Expert Masters Program Training Course Program to Begin Your Adventure Now.
Types of Vulnerability
- Network:This method checks for vulnerabilities within an organization’s network, including routers, firewalls, servers, and all other network devices. It often looks for weak configurations, outdated software, and common vulnerabilities like open ports or unsecured communication protocols.
- Web Application: These scan tools particularly test vulnerabilities in Web Security applications and may include SQL injection vulnerabilities, cross-site scripting vulnerabilities, cross-site request forgery, and poorly implemented authentication mechanisms.
- Host-based:This scans individual host systems, such as computers, servers, and virtual machines, for vulnerabilities such as missing patches, outdated software, and weak passwords. It is often used to find vulnerabilities that may not appear at the network level.
- Database:Focused on detecting weaknesses in database systems, such as misconfigurations, weak access controls, unpatched software, and vulnerabilities potentially leading to unauthorized data access.
- Cloud: As companies adopt the cloud, scanning software is being designed to address cloud infrastructure vulnerabilities. Cloud-specific scans include misconfigured cloud storage, access control issues, and insecure APIs.
How this scanning Works
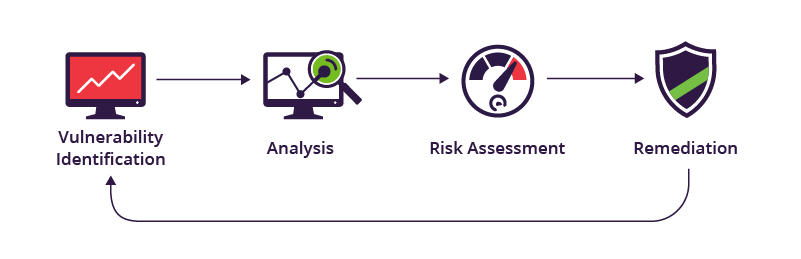
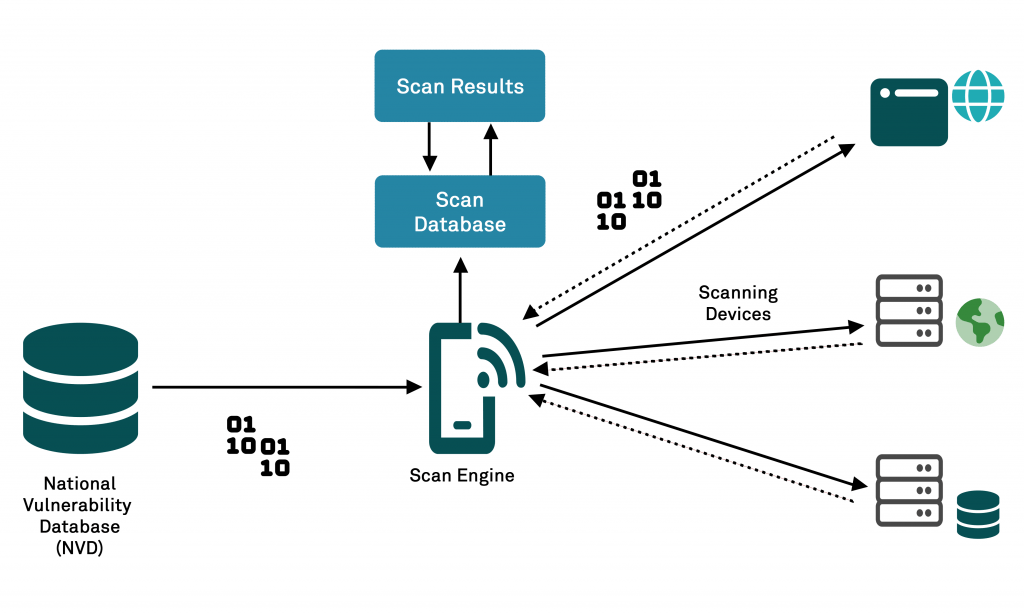
- Fingerprinting and Enumeration: In fingerprinting, systems covered by a scan are recognized. It detects security network devices, installed operating systems, open ports, and services running on a target system.
- Identification of Vulnerability:The scanner scans the target systems and compares them with databases containing known vulnerabilities. Normally, it holds Database Security advisories, CVEs (Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures), and all threat intelligence feeds.nessus scanner identifies weak points due to outdated software, misconfiguring services, weak passwords, or known security flaws.
- Risk assessment: The vulnerability scanners usually assign severity to each finding from the detected vulnerabilities. The reported levels are commonly critical, high, medium, or low risk. More often, nessus scanner can describe the weakness’s significance in terms of what is likely to happen if it were exploited.
- Reporting and Recommendations: The scanner produces a very comprehensive report that includes all the vulnerabilities found along with recommendations on how to address or correct them. Reports usually have links to patching guides, configuration best practices, and other resources.
- Continuous Monitoring:Scanning must not be a one-time exercise but a constant process in which new vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, or patches are addressed as soon as possible. Organizations should include scanning as part of their continuous IOT Security monitoring strategy, allied to others like IDS, firewalls, and penetration testing.
- Nessus is one of the widely used commercial scanners. It can scan from a small server to the largest security network of devices or databases. It is easy to use and has a comprehensive database of vulnerabilities.
- OpenVAS: This is an open-source scanner that is a popular Nessus alternative. It has similar features but requires more configuration and fine-tuning.
- Qualys: Qualys is another cloud-based vulnerability management software. It offers both vulnerability trends and IOT Securitytool services. It is used mainly by enterprises for continuous vulnerability assessments.
- Nmap is mainly a cybersecurity network scanning tool, but it can also be used to detect vulnerabilities by using other tools and scripts, such as the Nmap Scripting Engine.
- Acunetix is a specialized Web Application Security vulnerability scanner that focuses on finding vulnerabilities in web applications, such as SQL injection and XSS.
- Burp Suite: It is a web application security testing platform that includes a vulnerability scanner for identifying issues in web applications.
- Cloud-Native Vulnerability
Organizations moving towards a cloud environment are growing. The necessity of tools for cloud-native infrastructure scanning, which includes vulnerability scanning tools about Kubernetes, Docker, AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, is growing. And now the tool is set up to scan the configuration, misconfigurations and access controls, so there will be no wrong deployment on the cloud. This aspect includes the scanning of Infrastructure as Code or IaC.
- Coverage Across Environments
Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Environments: An organization may operate in a hybrid or multi-cloud environment. Therefore, vulnerability tools should be able to manage these complex infrastructures effectively. Vulnerability scanners adapt to scan different environments, such as on-premise, private cloud, Cybersecurity Training Courses and multiple public cloud services. Endpoint and IoT Security The rise of connected devices has been the need to scan both the endpoints and Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
- Prioritization of Vulnerabilities
Plain vulnerability trends identification is no longer sufficient. Contemporary nessus scanner rely more on contextual data, such as asset criticality, exploitability and exposure, to rank them based on the vulnerability’s potential impact on the organization. This means that the most important problems get addressed in the first instance as remediation activities are effectively managed.
- Integrating with Wider Security Ecosystems
Vulnerability scanners are now being integrated with more general cybersecurity vulnerability tool such as SIEM, SOAR, and TIPs. This enables a holistic IOT Security posture and better detection and response to vulnerabilities. Some scanners have integrated capabilities automatically initiating patching or other remediation activities in the vulnerability management workflow.
- Accelerated Patch Management:
Automated Patch Management More valnerability tools now integrate patch management systems into vulnerability assessment to identify vulnerabilities and apply patches automatically when necessary. This is critical in reducing the time a system is exposed to potential exploitation nessus scanner are also evolving to verify that patches have been properly applied and the vulnerability trends remediated.
Want to Take the Lead in Cyber Security ? Enroll in ACTE’s Cybersecurity Expert Masters Program Training Course Program to Begin Your Adventure Now.
Best Practices for Effective Scanning
To obtain the maximum benefits of scanning, organizations must follow several best practices Regular scans As vulnerabilities change daily, it should scan as frequently as the individual organizational requirement. For example, a weekly, monthly, or quarterly basis can be opted for discovering emerging threats. Patch management scanning needs to be combined with a good patch vulnerability management process. Vulnerabilities should be patched as soon as they are found. Fix critical ones first. All threats are not equal. Prioritize those considered with public exploit codes or those with high impact scores. Careful analysis Reports from vulnerability scans do not necessarily need to be regarded as just a checklist. IOT Security teams must carefully analyze the findings to understand the relevance and context of each identified Vulnerability. Use multiple scanning tools. No scanner can scan all the vulnerabilities. Using a combination of vulnerability tool may ensure higher coverage and minimize the chance of missing critical vulnerabilities. Integrate with other security controls. vulnerability assessment should not be done in isolation but be part of a comprehensive security policy that includes firewall configuration, access control, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and penetration testing regularly.
Tools for Vulnerability
Get interview-ready with our collection of Cybersecurity Interview Questions and Answers Questions. Equip yourself with the knowledge to impress potential employers!
Vulnerability trends
Conclusion
Vulnerability is a crucial part of an organization’s defence and discovers and assists in remediating weaknesses in a timely and cost-effective manner. It cannot replace manual penetration testing or even more sophisticated threat-hunting techniques, but it lays the foundation for a foundational Cybersecurity Training measure to ensure systems can withstand attacks. Organizations will reduce their vulnerability trends to cyber threats and improve their security posture by effectively utilizing Vulnerability scanning, regularly updating their scanning tools, and promptly acting on the findings.





