
- 2-Factor Authentication: What is it?
- Types of Two-Factor Authentication
- 2-Factor Authentication Examples
- Advantages of 2-Factor Authentication (2FA)
- Good Practices for 2-Factor Authentication
- The Two-Factor Authentication Process
- Conclusion
Two-factor authentication adds a layer of security to a user’s account, ensuring that a user goes through two different forms of verification before allowing access. In this case, something one knows is combined with something one has, such as a password with a smartphone or hardware token. The users can minimize the possibility of unauthorized access by protecting accounts with 2FA, even when passwords have been compromised. As Cyber Security Training Courses and malice are evolving, using 2FA is an essential barrier for both phishing and credential thefts. Therefore, this practice is necessary for individual and organizational efforts to keep safe, confidential data.
Interested in Obtaining Your Two-factor Authentication Certificate? View The Cyber Security Online Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
2-Factor Authentication: What is it?
A security procedure called two-factor authentication 2FA, sometimes called two-step verification, requires users to present two forms of identity to access their online accounts or data. In addition to the standard username and password login, 2FA offers an additional security layer. The two elements fall into the following categories:
- Something you are familiar with, like a PIN or password.
- Something you own, like an authentication token or smartphone.
Compared to a simple password, Multi-Factor Authentication is an improved way of protecting critical data. Even if hackers were able to get their hands on your password, they would still require another factor to gain entry to your account. Hackers find obtaining sensitive or confidential data more difficult with this extra degree of protection.
Types of Two-Factor Authentication
- SMS-Based 2FA:Using SMS-Based 2FA, you enter a one-time code sent to your registered phone number and enter it into the login screen. Despite being one of the most popular and straightforward forms of 2FA, it is susceptible to SIM-swapping attacks.
- Time-Based One-Time Password (TOTP):This entails utilizing an authenticator app, such as Authy or Google Authenticator, on your smartphone to generate a unique code. Though it can be inconvenient if your phone is lost or stolen, TOTP is more secure than SMS-based 2FA.
- Universal 2nd Factor (U2F):To gain access to your account, you must physically insert a security key into your device, such as a YubiKey. One of the highest degrees of protection can be achieved by using U2F as a kind of 2FA; however, not every device is compatible with it, and it can be expensive to purchase.
- Biometric 2FA: Biometric 2FA verifies your identity using a biometric factor, like your fingerprint or facial recognition. Although biometric 2FA is safe and practical, not all devices may support it and may be susceptible to spoofing attempts, unlike Password Authentication, which relies solely on a user’s password for verification.
- Push notice 2FA:This entails getting a push notice on the mobile device you registered, asking you to accept or reject the login attempt. Although this kind of 2FA is safe and practical, it requires an internet connection and may not be supported by all apps or services.
- Google Authenticator: This popular authenticator software generates TOTP codes for several services and applications, such as Dropbox, GitHub, and Google accounts.
- YubiKey:To confirm your identity, you can wirelessly use this physical security key or insert it into a USB port. In addition to being interoperable with numerous apps and services, such as those from Google, Microsoft, and LastPass, YubiKey also supports U2F and TOTP.
- Duo Security: Push notifications, SMS-based codes, and phone call verification are just a few of the 2FA techniques supported by Duo Security, a multi-factor authentication service. Duo Cyber Security Training Courses works with various apps and services, including those provided by Amazon Web Services, Cisco, and Microsoft.
- Apple Face ID: This biometric identification method unlocks your iPhone or authenticates you for some apps and services using facial recognition.
- Codes Based on SMS:Numerous apps and businesses offer SMS-based codes as a form of 2FA. When you log in, your registered phone number receives a text message with a code, which you then input into the login screen.
- Security First Use methods offering high degrees of security, including authentication applications like Google Authenticator and Authy and hardware tokens such as YubiKey. Ditch SMS codes since they are susceptible to interception, as Cyber Hygiene Involves Practices for Maintaining Digital Security, which includes using more secure authentication methods.
- Training and Resources Use clear instructions and resources to understand how 2FA works and why that is important. Conduct organized training sessions to increase awareness about security measures and the use of 2FA.
- Flexibility Users should be given a choice as to which method they prefer as their 2FA (app-based, SMS, or biometric). Depending on individual preferences and situations, this can be flexible on the options for the 2FA. That can enhance the adoption and satisfaction of users.
- Redundancy Provide users with other ways into systems, such as backup codes or secondary forms of authentication, to help them regain access if the primary 2FA mechanism is lost (like a lost phone).
- Ongoing Detection At set intervals, scan access logs for suspicious login attempts or patterns and put alerts on any suspicious activity so you can move quickly in case of an actual security event.
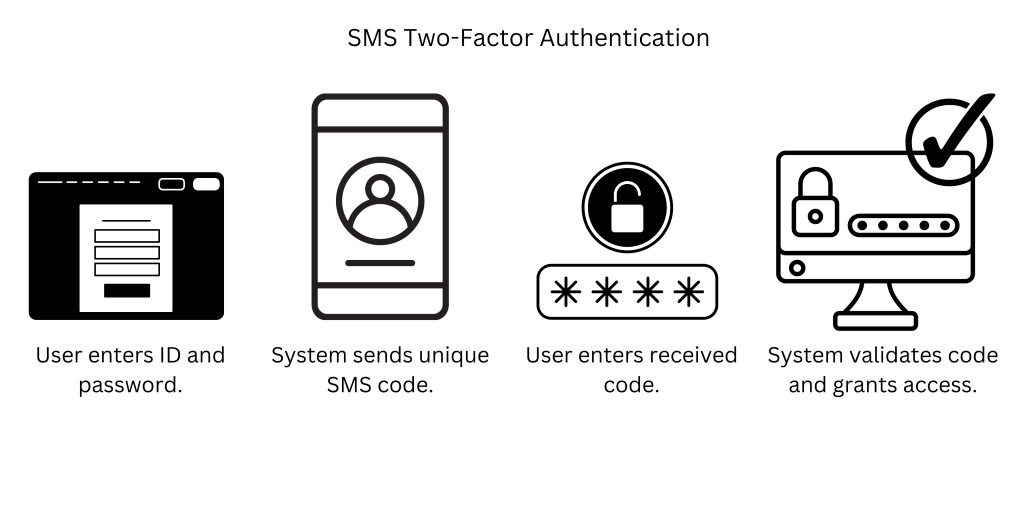
- Username/Password Entry
The user first enters his username and password as something that he knows. Weakness: If someone gets access to the password (phishing, data breaches, etc.), he can easily access the account. That’s why the second factor is desired.
- Request for the Second Factor (Triggering 2FA)
Once the correct username and password are input, the system calls for a second level of authentication. This usually occurs when the system requests one to input a verification or one-time code, highlighting The The Role of Encryption in Network Security to protect the sensitive data during this process.
- The Second Factor
Something You Have Often, this is some tangible item that you possess, such as SMS Code A numeric or alphanumeric code that is sent to a specific phone through the text message; note that this is the most insecure authentication mechanism. Authenticator apps, including Google Authenticator, Authy, and Microsoft Authenticator, perform time-based one-time passwords (TOTPs).
- Verification of the Second Factor
Once the second factor is entered or presented, such as the OTP from the authenticator app or fingerprint scan, it will be compared to a secure database to determine if it is correct. Once verified, access will be granted to the user on the account. If it is incorrect or expired, for example, OTPs that time out will be denied access.
- Access Granted
Having passed both the username/pwd first factor and the second factor, either in the form of OTP, biometric, or another form of authentication, the user then accesses their account or service.
To Explore Two-factor Authentication in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Cyber Security Online Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
2-Factor Authentication Examples
Gain Your Master’s Certification in Cybersecurity by Enrolling in Our Cyber Security Expert Masters Program Training Course.
Advantages of 2-Factor Authentication(2FA)
This is an affirmation of an added layer of security beyond the mere password. It makes it significantly more difficult for other users to have unauthorized access. If one’s password is compromised, the need for the second factor remains very high, such as in a one-time code. Minimized Identity Theft Risks limit the possible attempts of identity theft since two forms of verification would be required. These attackers would need both factors to access sensitive personal information, making it much more cumbersome for them to masquerade as the user, especially after conducting Reconnaissance in Cyber Security to gather information about potential vulnerabilities. Suppose the phishing was successful, and the user inadvertently handed over his password.
In that case, the second authentication factor might have stalled the illegal access because the attacker would have missed one authentication factor. Increased User Trust Implementing 2FA increases a user’s trust and confidence in a service or application. It makes users more willing to interact with platforms that care about protecting their data and provide account protection mechanisms. Most implementations of 2FA include backup methods like backup codes or alternative authentication methods, which can aid users in recovering accounts if they ever lose access to their primary means of 2FA. Protection for Attackers The presence of 2FA deters potential hackers. If a hacker realizes that an account requires several lines of defence to be accessed, they may back off and avoid the target.
Good Practices for2-Factor Authentication
Are You Preparing for Cyber Security Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Cyber Security Interview Questions and Answers to Boost Your Preparation!
The Two-Factor Authentication Process
Conclusion
Two-factor authentication is important security when accessing an account because two verification methods must be used before you can access accounts. This would further protect against unauthorized access even when you are logging on and have compromised your password. Cyber Security Training Courses sensitive information and accounts from phishing and credential stuffing attacks is achieved by combining the know-how, such as a password, with something you have, like a smartphone for a text code or an authentication application. In the end, it is essential for a person and his organization that take on 2FA as a critical step to ensure the safeguarding of his digital assets and the resultant higher security level in such an increasingly vulnerable online environment. It is the easiest measure that makes all the difference to protect personal and sensitive data.





