
In the rapid world of cyber security, the term “reconnaissance” is often heard as one of the first phases in the lifecycle of a cyber attack. So surveillance is vital knowledge whether you are a specialist or just some interested reader who wants to know how cyber Reconnaissance Planned and executed. This is when cyber attacker gather crucial information regarding their target before going live on a full-scale breach. In so many ways, reconnaissance does indeed represent a scouting mission. Like how a military strategist will take time to study the battlefield before going on the offensive, this stage recognizes its importance in defending against cyber security attacks and implementing offensive strategies in the cyber world.
What is Reconnaissance in Cyber Security?
Cybersecurity Training Courses is defined as the act of obtaining information regarding an attack target. An attack target is simply a network, system, or organization. Identify the vulnerabilities or weaknesses at the digital infrastructure front that could later be exploited during an attack. This is very important as planning to breach requires reconnaissance information security specific to your target’s configuration and defences. Information acquired in this reconnaissance step could be:
- Network Infrastructure: What devices, which type of servers, and what services are being used?
- IP Addresses and Domain Names: Configuration of the network and its presence online.
- Employee Details: Who operates the target organization, and what is their job title?
- Open Ports and Services: Which services are open to the exile either by opening or closing the vulnerability.
- Software and Hardware Configurations: Known vulnerabilities in the software, including hardware which the target uses.
- WHOIS Queries: Extracting details from the domain registration would reveal the owner’s name, contact reconnaissance information security, and related infrastructure.
- DNS Enumeration: Discover the hierarchy of a domain and enumerate all valuable subdomains.
- Public Data Sources include companies: social media profiles, blogs, company websites, etc., which can be used to derive reconnaissance information security about employees, technology stacks, and network infrastructure.
- Port Scanning uses: Tools such as Nmap to scan all of the target’s network’s ports.
- OS fingerprinting: Identify the kind of operating system that a target system is running.
- Service Version Detection: Determine which version of services runs on a system to identify known vulnerabilities.
Reconnaissance can take many forms and use both passive and active methods, which we’ll elaborate on in more depth below. Yet, regardless of whether it is passive or active, reconnaissance always precedes most cyber security attacks .
To become a certified cybersecurity, have a look at our Cyber Security Online Training right now.
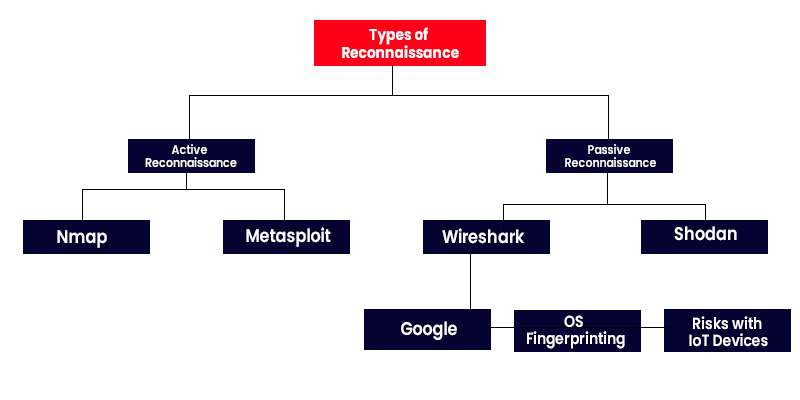
The Two Types of Reconnaissance
Passive Reconnaissance
This is the process of gathering information about a target without directly communicating with the target. This collects reconnaissance information security from public sources such as websites, social media, and open-source data storage repositories. The passive survey Reconnaissance should be done without targeting network engagement. Examples are:
Active Reconnaissance
Active reconnaissance interacts directly with the target’s network or systems. Hackers can scan open ports, perform a Vulnerability Management scan, or search for specific weaknesses in the target configuration. Active surveillance Reconnaissance has more chances of getting noticed by recon in cybersecurity mechanisms such as firewalls or intrusion detection systems. Some examples of this include:
Enroll in ACTE’S Cyber Security Online Training if you want to become an expert in cyber security field and have a prosperous career.
Methods and Tools
The cyber attacker use different methods and tools for conducting surveillance. Some of these are freely accessible information, while others require specialized knowledge.
1. Social Engineering
- Pretexting: This is a process of pretending to be a trusted entity in an organization, such as an IT support staff member, to get employees to divulge confidential information to that person, such as passwords or network configuration information.
- Phishing creates: Fake emails or messages that make someone believe they need to surrender confidential logins, such as logins or access credentials to systems.
- Vishing (Voice Phishing): This is a form of phishing that steals personal or financial information from a person after posing for a while as a particular authority. It could take the form of an impersonation of anybody, such as a government officer or company representative, whereby they pose on the phone.
- DNS Zone Transfer: The attacker may request a Demilitaried Zone transfer to obtain an actual map of the domain of the target, which can include hostnames, subdomains, and related IP addresses.
- DNS Lookup: DNS lookup tools effectively reveal more information about a target’s domain. Information may include associated IP addresses, mail servers, nameservers, etc.
- Port Scanning: An individual can utilize Nmap or Masscan to perform a port scan on all the open ports within the network. This also determines which running services may be susceptible to an attack.
- Service Detection: Once the open ports have been confirmed, the cyber attacker will employ the Nessus or OpenVAS tools to identify services running from the marked ports and determine whether those services have identified security vulnerabilities.
- WHOIS Lookup: Hackers use WHOIS databases to retrieve information relevant to the registration of your domain name, including the contact reconnaissance information recon in cybersecurity of the owner, the hosting provider, and even their server location.
- Google Hacking: Advanced operators in Google can uncover sensitive information that perhaps everyone can access but is not safe enough. For example, “index of” or “password” might reveal files or systems.
- Shodan: Shodan is an indexed search engine for finding internet-based devices, such as cameras, routers, and servers. It allows the attacker to locate devices that are either not configured or have old software packages associated with known exploits.
- Censys: Likewise, Censys is another indexed search engine that indexes internet-based systems of cyber threats, thus letting the attacker discover identities of devices and certificates that might be exploitable.
- Select attack vectors: This allows attackers to choose which ports and services to attack from, knowing that some are closed and others open. This way, attackers can choose the best entry point for their attacks, exploiting a weak service or poor authentication habits.
- Craft Targeted Attacks: Armed with social engineering information, such as employee names and email addresses, phishing emails or spear-phishing campaigns can make attacks more targeted so that suchcyber security attacks might be effective.
- Identify High-Value Assets: Determining important parts, such as servers, databases, or domain controllers, allows attackers to target valuable assets that must be attacked and compromised.
- Minimizing Exposure: Reduce the number of services exposed to the public internet. Allow access only to necessary ports and services while blocking unnecessary ones.
- Utilize Default Configurations: Many devices and services have well-known default configurations that attackers can use. Changing default usernames, IP Subnet , passwords, and configurations reduces the risk.
- Disable Unused Services: Disable unused or unnecessary services, for they broaden the attack surface.
- Implement MFA: This will prevent attackers from gaining entry using only stolen credentials by adding a layer of recon in cybersecurity, like a one-time code sent to a mobile device.
- Privileges: Harden Privileges. Ensure that only those employees and users who need the minimum set of privileges necessary to do their jobs have them, minimizing the impact of any breach.
- Regular Access Reviews: They regularly audit the user access levels to ensure only authorized personnel access sensitive systems.
- Intrusion Detection Systems: They put in IDS solutions that scan for suspicious activities, including port scanning or erratic traffic patterns indicative of cyber reconnaissance efforts.
- Log Analysis: It continuously monitors the system and network logs for recon activities such as failed login attempts or unusual DNS queries.
- Threat Intelligence: Sources providing feeds that bring you emerging Malware Attack techniques, such as reconnaissance activities by actual threat actors.
- Employee Awareness Training: Train your employees to detect phishing, social engineering attacks, and other suspicious practices. People are always the weakest link in a cyber security system.
- Transparent Reporting Channels: Employees must not fear but be at ease when reporting suspicious activities.
- Penetration Testing: Regular penetration testing simulates real-world attacks, including surveillance and exploitation, which helps uncover vulnerabilities before attackers attack.
- Vulnerability Scanning: Regularly scan your network and systems to identify outdated software that is exposed or has configuration errors, which may pose an avenue for a penetration attack.
2. DNS Interrogation
3. Network Scanning
4. Footprinting and Information Gathering
5. Shodan and Other Search Engines
How Attackers Use Reconnaissance to Slec Vulnerability
Once Cybersecurity Training Courses has taken place, attackers obtain very precious information to attack the weaknesses they discovered about their target’s defences. The information compiled gives attackers the capacity to:
For example, suppose a survey finds that a target system is running an obsolete version of some popular software whose vulnerabilities have already been documented. In that case, the attackers are likely to carry out an exploit based on that identified vulnerability. Poor password and credential reuse will allow attackers to identify poor passwords or reused credentials likely to initiate credential stuffing or brute-force cyber security attacks.
Transform Your Career with Cyber Security Knowledge Enroll in ACTE’s Cyber Security Expert Masters Program Training Course Today!
How Organizations Can Protect Against Reconnaissance
While the survey is a large part of the cyberattack lifecycle, there are many things that an organization can do proactively to defend itself. This objective would be to slow or prevent attackers from gathering useful cyber reconnaissance information while detecting and mitigating attempts at surveillance.
1. Protection of External Systems
2. Implementing Strong Access Controls
3. Monitoring and Detection
4. Employee Training
Get interview-ready with our collection of Cybersecurity Interview Questions and Answers Questions. Equip yourself with the knowledge to impress potential employers!
5. Recurring Security Audit
Conclusion
The life cycle of a cyber attack is commonly the least sophisticated and most easily overlooked Cybersecurity Training. People need to understand how attackers gather information about their target to form better defences. Limiting exposure, fortifying controls over access, and looking for suspicious behaviours can reduce overall reconnaissance effectiveness and avoid successful cyber threats. It is as important to be notified on cyber reconnaissance tactics, as it is to counter those efforts in cyber recon in cybersecurity, just as it is for responding to actual breaches. Then, it would be much tougher for the cyber attacker to enter the company’s systems by staying vigilant and improving the security protocols.





