As part of its environmental efforts, Google Cloud aims to run entirely on renewable energy and is carbon neutral. It offers robust security features and tools for identity and access control, compliance, and data protection. Cloud Functions, a serverless computing tool from Google Cloud, enables developers to create apps without worrying about infrastructure management.A diverse spectrum of organisations, spanning many industries, from start-ups to major corporations, comprise GCP’s clientele.Google Cloud is a competitive and forward-thinking option for cloud services due to its ongoing innovation and integration with well-known open-source technology.
1.What exactly is a cloud?
Ans:
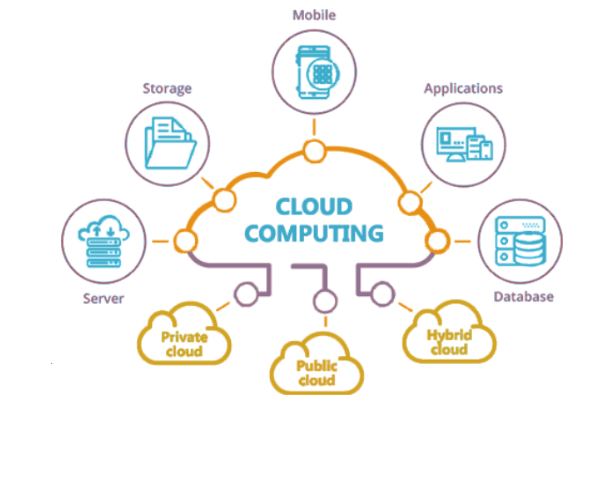
Cloud computing is the term for a network of geographically dispersed servers that store, manage, and provide internet-based access to data and applications. By doing this, computing and storage responsibilities can be transferred to distant data centres.
2.What kind of technology is cloud computing?
Ans:
Cloud computing is a technology that falls under the category of distributed computing and virtualization. It involves the use of a network of remote servers to deliver various computing services over the internet, such as storage, processing, and software applications.
3. Which unique characteristics does cloud computing have?
Ans:
Cloud computing has several unique characteristics that distinguish it from traditional computing models:
- On-Demand Self-Service
- Broad Network Access
- Resource Pooling
- Rapid Elasticity
- Measured Service
- Ubiquitous Access
4. What are the advantages does cloud computing offer?
Ans:
Cloud computing offers numerous advantages, including:
- Cost Efficiency
- Scalability
- Flexibility
- Accessibility
- Automatic Update
- Reliability
5.Exactly how do cloud delivery models work?
Ans:
Cloud delivery models work as follows:
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service): offers virtualized computer resources, including networking, storage, and virtual machines.
PaaS : offers an application development platform complete with tools and runtime environments.
SaaS (Software as a Service): Delivers fully functional software applications over the internet.
6. Identify the key players in the Cloud ecosystem.
Ans:
The cloud ecosystem refers to the interconnected network of individuals, organisations, technologies, and services involved in the deployment, management, and use of cloud computing resources and solutions.
Key players in the cloud ecosystem include:
- Cloud Service Providers (CSPs)
- Software as a Service (SaaS) Providers
- Platform as a Service (PaaS) Providers
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) Providers
- Cloud Consumers
7. Describe the PaaS architecture’s tiers.
Ans:
PaaS makes application development and deployment easier by offering a platform that handles infrastructure management and provides tools for creating and executing software. PaaS (Platform as a Service) architecture typically consists of the following tiers:
- Application Tie
- Middleware Tier
- Infrastructure Tier
- User Interface (UI) Tier
8.What companies offer on cloud services?
Ans:
Numerous companies offer cloud services, with some of the major providers being:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Microsoft Azure
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- IBM Cloud
- Oracle Cloud
- Salesforce
- VMware
9. Describe private cloud?
Ans:
A cloud computing environment designated as private is one that is utilised only by one company. Usually, the organisation’s own data centres or specialised infrastructure are used for hosting.
10. How do hybrid clouds work?
Ans:
Hybrid clouds work by combining private and public cloud infrastructure to create a unified computing environment. Data and applications can move between the private and public segments as needed. Hybrid cloud solutions use technologies like virtualization and orchestration to manage workloads seamlessly between the two environments.
11. Which individual are the cloud users?
Ans:
Cloud users can be individuals, businesses, or organisations that utilise cloud services to store, process, and access data and applications over the internet. They range from individual consumers using cloud storage for personal files to large enterprises employing cloud solutions for their IT infrastructure, software development, and various business operations.
12. Who are the cloud users?
Ans:
People, companies, or organisations who utilise the cloud for computing and data storage are known as cloud consumers. They rely on cloud service providers to administer and supply these services online so that users may access them as needed.
13.Explain the architecture of cloud computing.
Ans:
Cloud computing architecture is a framework that outlines how cloud services are organised and interacted. It typically consists of the following components:
- Front End
- Back End
- Cloud Service Provider
- Middleware
- Data Centers
14. Describe how a service could serve a function.
Ans:
Function as a Service (FaaS) is a cloud computing model where developers can run individual functions or code snippets in response to events. With FaaS, developers don’t need to manage servers or infrastructure; they upload their code, and the cloud provider handles the execution, scaling, and resource allocation automatically.
15. Why are microservices useful on the cloud and what are they?
Ans:
Microservices are a software architectural approach that divides complex applications into small, independent services that communicate with one another via well-defined APIs.
16. Name the top three benefits of using the cloud.
Ans:
The top three benefits of using the cloud are:
Scalability: Easily scale resources up or down to match demand, optimising costs.
Cost Efficiency: Pay for what you use, reducing upfront capital expenses.
Accessibility: Access data and applications from anywhere with an internet connection, promoting flexibility and collaboration.
17. List the Cloud Storage Levels?
Ans:
Three levels are commonly used to classify cloud storage:
Hot Storage: Designed to provide low-latency access to data that is regularly accessed.
Cool Storage: Designed for less frequently accessible data, it has a cheaper cost but significantly longer retrieval times.
Cold Storage: Data that is infrequently accessed but must be kept for compliance or archival purposes is best kept in cold storage.
18. What is the meaning of a cloud usage monitor?
Ans:
A tool or service called a “cloud usage monitor” tracks and examines how cloud resources and services are used in a cloud computing environment. It offers information on resource allocation, consumption patterns, pricing, and performance indicators as well as insights into how cloud resources are used.
19. A polling agent tracks cloud utilisation in what ways?
Ans:
In the context of tracking cloud resource usage, a polling agent is a part or piece of software that continually gathers and keeps track of different data. It records the use of the cloud in a number of ways, including:
- Consumption of resources
- Analysis of network traffic costs
- Measures of performance
- Application Usage Scalability
- Load Security and Compliance
20.What parts make up Windows Azure?
Ans:
Microsoft’s cloud computing platform, Windows Azure, now known as Microsoft Azure, included a number of essential elements and services, such as:
- Azure Compute
- Azure Storage
- Azure Networking
- Azure Databases
21.How do resource agents track and how the cloud is used?
Ans:
To keep track of cloud usage, resource agents employ a number of methods, such as data gathering, polling, event triggers, logging, API integration, and cost analysis. Organisations may better allocate resources and improve security and compliance with this information.
22.What variations may be seen in distributed operations?
Ans:
Variations in distributed operations might take the form of different network setups, data replication techniques, load balancing strategies, fault tolerance systems, and technological stack selections. These variances rely on the precise needs, objectives, and difficulties of the distributed system being used.
23.Mention how dependable and readily available cloud computing is.
Ans:
Depending on the exact cloud service provider and the service level agreements (SLAs) in place, the reliability and availability of cloud computing may differ.
Key factors include:- Redundancy
- Scalability
- Data Replication
- Load Balancing
- Failover and Disaster Recovery
- Geographic Availability
24.What storage classes does Google Cloud Storage provide, and how does it operate?
Ans:
Google Cloud Storage provides a globally distributed storage infrastructure that is scalable. It saves information in the form of objects, which can range in size from a few bytes to several terabytes. Every object has a distinct key that identifies it.
25. Give the top open-source cloud computing example.
Ans:
One of the best open-source cloud computing systems is OpenStack. It is a collection of computer programmes for setting up and running both public and private clouds. The infrastructure as a service (IaaS) offering from OpenStack is used to build and administer virtualized resources such as computing, storage, and networking.
26. What exactly are microservices, and how crucial are they to the cloud?
Ans:
Using the microservices software architecture paradigm, applications are created as a group of compact, loosely linked services. Each service is a separate representation of a particular business function or capacity.
27.What is an AMI? How do we implement it?
Ans:
Amazon Machine Image (AMI) is a pre-configured virtual machine image used in AWS to create Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) instances. AMIs include the operating system, software, and configuration settings needed to launch instances.
28.How an AMI is implemented?
Ans:
- Choose an Existing AMI
- Create Your Own AMI
- Share AMIs
- Launch EC2 Instances
29. What are the Google Cloud APIs? How can you access them?
Ans:
Platforms commonly used for large-scale cloud computing include:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Microsoft Azure
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- IBM Cloud
- Oracle Cloud
- Alibaba Cloud
- VMware Cloud
30. Why are hybrid clouds so crucial?
Ans:
Hybrid clouds are important because they combine the advantages of private and public clouds, providing flexibility, data control, scalability, and cost-efficiency, allowing organisations to optimise their IT infrastructure to meet particular business objectives and regulatory requirements.
31. List the models that are employed for cloud computing implementation.
Ans:
The four types of cloud are:
- public
- private
- hybrid
- community
32.Which are the layers of Cloud Computing?
Ans:
The layers of cloud computing are typically categorised into three service models:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
33. Give an explanation of security management using the cloud.
Ans:
The methods and techniques employed to safeguard information, software, and other resources in the cloud computing environment are referred to as security management. To protect the privacy, availability, and compliance of cloud-based assets, a variety of safeguards must be used.
34. List some prestigious databases and cloud service companies.
Ans:
Large cloud providers:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Microsoft Azure
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- IBM Cloud
- Oracle Cloud
- Alibaba Cloud
35. What are some of the differentiation between mobile and cloud computing?
Ans:
| Aspect | Mobile Computing | Cloud Computing | |
| Definition |
Use of mobile devices for on-the-go computing |
Delivery of computing services over the internet. | |
| Location of Processing | Mainly on the mobile device | On remote servers in data centres. | |
| Device Dependency | Relies on mobile device capabilities. | Reduces device dependency | |
| more scalable |
Multiple inputs and outputs |
Focused on joining data |
36. Which open-source cloud-based database management systems are the most widely used?
Ans:
These are a few of the open-source cloud-based database management systems that are most popular today:
- MySQL
- PostgreSQL
- MongoDB
- Cassandra
- Redis
- Apache CouchDB
- MariaDB
37. What distinguishes scalability from elasticity?
Ans:
The ability of a system to add nodes or resources in order to handle an increasing demand is referred to as “scalability”. Elasticity is a special type of scalability that emphasises dynamically shifting resources up or down based on real-time demand, offering dynamic flexibility to adapt to changing workloads.
38.What exactly does Edge Computing mean?
Ans:
The distributed computing paradigm known as “edge computing” avoids the use of centralised cloud servers by relocating data storage and processing closer to the “edge” of the network, which is where the data is found. Reduced latency, improved real-time processing, and enhanced data security and privacy are its objectives.
39. What functions do APIs provide in cloud services?
Ans:
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) provide essential functions in cloud services:
- Resource Access
- Service Integration
- Data Retrieval
- Authentication and Authorization
40. Distinguish modern cloud architecture from older forms of cloud architecture?
Ans:
Modern cloud: Modern cloud architecture is more agile, adaptable, and focused on optimising performance, security, and cost-efficiency, aligning with the evolving demands of applications and users.
Older forms: These older architectures may still be in use today, especially for established applications and systems.
41. What exactly constitutes the foundation of cloud architecture?
Ans:
Cloud architecture is built on a foundation of virtualization, scalability, service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS), APIs, resource orchestration, data storage, networking infrastructure, strong security measures, monitoring and management tools, geographical regions, availability zones, cost management, and compliance/governance features.
42. Describe AWS.
Ans:
Amazon.com provides Amazon Web Services (AWS), a feature-rich and well-liked cloud computing platform. It offers an extensive array of cloud services and solutions, enabling individuals and businesses to develop and administer applications, store and handle data, and carry out nearly any kind of task in the cloud.
43. Explain the main elements of AWS.
Ans:
- Compute Services
- Storage Services
- Database Services
- Networking
- Security
- Developer Tools
- AI and Machine Learning
The main elements of AWS (Amazon Web Services) include:
44.Explain the process of resource replication in cloud computing?
Ans:
The act of producing duplicate replicas of data, applications, or services across various locations or servers inside a cloud architecture is known as resource replication in cloud computing.
45. Define Containers as a Service (CaaS)?
Ans:
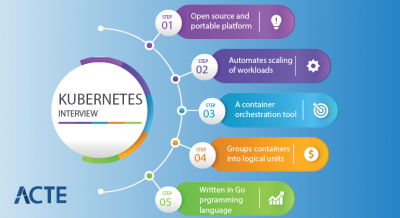
An application deployment and management platform for containerized apps is offered by the cloud computing service known as Containers as a Service (CaaS). By employing container orchestration technologies like Kubernetes, it provides a controlled environment for building, operating, and scaling containers.
46. How are cloud native apps defined by the cloud native foundation?
Ans:
The Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF) defines cloud-native applications as those that are:
- Containerized
- Dynamically Orchestrated
- Microservices-Oriented
- Resilient and Scalable
- Observable Consistently Deployed
- Designed for DevOps
47. Explain API Gateway.
Ans:
An API Gateway is a server or service that functions as an API front-end, receiving API requests, enforcing throttling, security, and access control, forwarding requests to the back-end service, and delivering requests back to the requester after obtaining the response. It serves as a layer for managing APIs and is essential to a microservices design.
48.How does virtualization connect to cloud computing, and what does it mean exactly?
Ans:
A key technology that supports and links cloud computing is virtualization. It is essential to cloud environments’ resource management and infrastructure.
- Server Virtualization
- Network and Storage Virtualization
49. List a few drawbacks of cloud computing.
Ans:
While cloud computing has numerous benefits, it also has some drawbacks, which include:
- Security Concerns
- Downtime
- Limited Contro
- Cost Management
50. Give the names of the many data centres used for cloud computing.
Ans:
Cloud computing providers typically operate multiple data centres across the globe. Here are some major data centre regions of leading cloud providers:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Microsoft Azure
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- IBM Cloud
- Oracle Cloud
- Alibaba Cloud
51. What is Datacenters in Containerization ?
Ans:
Data centres are the actual places or structures where containerized workloads and applications may be housed and managed. The technical foundation for container-based computing is present in these data centres.
52. What specifically does resource replication work in cloud computing?
Ans:
Resource replication in cloud computing involves creating redundant copies of resources, such as data, applications, or virtual machines, in multiple locations or across multiple servers or data centres.
53. How do Low-Density Data Centres work?
Ans:
Low-density data centres are designed to have a lower power and cooling requirement per unit of IT equipment compared to traditional data centres.
54.Define Encapsulation
Ans:
Encapsulation, which refers to the idea of bundling data (attributes), is one of the four core concepts of object-oriented programming (OOP). This unit or class exposes only the interfaces or access points required to interact with the data and methods; it conceals the internal workings of their implementation.
55. Give the names of the many data centres used for cloud computing.
Ans:
Cloud computing providers operate numerous data centres around the world. Here are some of the major data centre regions for leading cloud providers:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Microsoft Azure
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- IBM Cloud
- Oracle Cloud
56. What is the “EUCALYPTUS” of cloud computing?
Ans:
Eucalyptus is a platform that allows businesses to build private and hybrid clouds that are compatible with Amazon Web Services (AWS) APIs. It, like AWS, provides virtualized resource creation and management infrastructure.
57. What actions should you take before employing a cloud computing platform?
Ans:
There are several important steps and considerations to address:
- Assessment of Business Needs
- Data Classification and Compliance
- Cloud Service Selection
- Cost Analysis
- Security Planning
- Data Migration Plan
- Network Connectivity
58.Why would you want to use cloud services?
Ans:
Organisations and individuals choose to use cloud services for a variety of reasons, including the following:
- Scalability
- Cost Efficiency
- Flexibility
- Accessibility
- Reliability and High Availability
- Security
59. What are Cloud-Native Applications?
Ans:
Applications that are specifically created and developed to operate in cloud computing environments are known as cloud-native applications.Key characteristics of cloud-native applications include:
60. What Levels of Cloud Storage Are There?
Ans:
Services for cloud storage provide varying degrees of storage capacity to meet various demands.
- Object Storage
- File Storage
- Block Storage
- Archival Storage
- Cold Storage
61. Describe the cloud computing serverless components.
Ans:
A cloud computing paradigm known as “serverless computing” enables programmers to create and execute programmes without having to worry about maintaining the underlying server infrastructure. Applications automatically scale with demand, and server maintenance is abstracted.
62.Mention the benefits and drawbacks of serverless computing.
Ans:
Benefits of Serverless Computing: Simplified development,auto-Scaling, Cost Efficiency,reduced operational overhead, high availability, event-driven and easy integration.
Drawbacks of Serverless Computing: Vendor lock-in, limited execution time, cold starts,complex debugging,resource constraints,state management,variable performance and security and compliance.
63.What technologies enable the cloud?
Ans:
The cloud relies on several enabling technologies:
Virtualization: permits the operation of numerous virtual machines on a single physical server.
Data Centers: House the infrastructure for cloud services.
APIs: Provide programmatic access to and control of cloud resources.
Hypervisors: Manage resource allocation for virtual machines.
Load Balancers: Distribute network traffic for scalability and availability.
64.Which ways can data security and compliance be guaranteed in the cloud?
Ans:
For organisations, ensuring cloud data security and compliance is of utmost importance. To assist in achieving this, cloud service providers (CSPs) provide a range of products and services. Here are a few strategies to ensure cloud data security and compliance:
- Encryption
- Access Control
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
- Logging and Monitoring
65. How is utility computing applied?
Ans:
By offering computing resources (such processing power, storage, and networking) on a pay-as-you-go basis, utility computing enables businesses to scale resources in response to demand, save expenses, and increase flexibility.
66. Describe the classes Void, Static, and Public.
Ans:
In many settings, mostly in programming, the phrases “Void,” “Static,” and “Public” are employed.
67. Explain how you can vertically scale an Amazon instance.
Ans:
When an Amazon EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) instance is upgraded to a more powerful instance type in order to increase its capacity, this is known as “scaling up,” or vertical scaling.
68.What are the reasons that make Amazon so big?
Ans:
Several important elements have contributed to Amazon’s notable development and success are:
- Diverse Product Offerings
- Customer-Centric Approach
- Innovative Technology
- Global Reach
- Marketplace Model
- Digital Content
69. How can we access control and identification managed in the cloud?
Ans:
Access control and identity management are essential for ensuring the security of cloud resources and data. The tools and services provided by cloud service providers (CSPs) make access and authentication management easier.
70. Describe the advantages of a content delivery network (CDN)?
Ans:
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) offers several key advantages:
- Improved Performance
- Reduced Server Load
- Increased Scalability
- Enhanced Security
- Lower Bandwidth Costs
- Global Reach
71.Give an example of a cloud-related performance issue you encountered and the solution you came up with.
Ans:
Issue:
High latency when accessing a cloud-hosted database. Users were experiencing slow response times when querying the database.
Solution:
- Performance Monitoring
- Database Optimization
- Resource Scaling
- Database Caching
72. Which scripting and automation technologies are frequently used in cloud management?
Ans:
Many scripting and automation tools are widely utilised to increase productivity, manage infrastructure at scale, and streamline operations. Some of the key technologies include:
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
- Shell Scripting
- Python
- Ansible
- Docker and Kubernetes
73. What distinguishes cloud snapshots from backups on the cloud?
Ans:
Cloud snapshots: Snapshots are point-in-time copies of a virtual machine or data volume, capturing the exact state of the system at a specific moment.
Backups: Backups often provide versioning and can be stored in different locations,making them a more robust and flexible solution for data protection and disaster recovery in the cloud.
74. Describe how regional redundancy affects cloud disaster recovery.
Ans:
Regional redundancy ensures that data and services are replicated and dispersed over several geographic locations, which is critical to cloud disaster recovery.
75. What are the steps you may take in a cloud environment to get high availability?
Ans:
In a cloud environment, to get high availability:
- Use Multi-Availability Zones
- Load Balancers
- Auto-Scaling
- Data Replication
- Monitoring & Alert
- Geographic Redundancy
76. What are logging and monitoring services in the cloud, and why are they important?
Ans:
Monitoring services give users immediate access to information on the functionality and condition of cloud resources, while logging services record and preserve information about events and activities in a cloud environment. They are essential for cloud performance optimization, security assurance, cost management, and regulatory compliance.
77. How can one guarantee optimal performance and minimal latency for a cloud application that is spread globally?
Ans:
To ensure that a globally distributed cloud application performs optimally and has the lowest possible latency:
- Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- Regional Data Centers
- Global Load Balancing
- Optimised Content
- Edge Computing
78. Describe the cloud security shared responsibility paradigm.
Ans:
Cloud service providers and customers have different security duties according to the shared responsibility model for cloud security. Although it is the customer’s responsibility to secure their data and apps in the cloud, the provider is in charge of protecting the cloud infrastructure.
79.How do serverless computing services operate, and what are they?
Ans:
Serverless computing services, like AWS Lambda and Azure Functions, operate through the following key principles:
- Event-Driven
- Automatic Scaling
- No Server Management
- Microservices
- Pay-as-You-Go
- Stateless
- Quick Deployment
80. Explain the concept of multi-cloud and its advantages and disadvantages.
Ans:
The process of leveraging many cloud service providers to satisfy an organization’s processing and storage requirements is known as multi-clouding.
Advantages:
- Redundancy
- Vendor Flexibility
- Cost Optimization
Disadvantages:
- Complexity
- Integration Challenge
- Cost Overheads
81.What is a virtual network (V Net) or virtual private cloud (VPC)?
Ans:
An isolated, private network within a cloud computing environment, like Microsoft Azure or Amazon Web Services (AWS), is called a virtual network (VNet) or virtual private cloud (VPC).
82. Describe what a content delivery network (CDN) is.
Ans:
A content delivery network (CDN) uses a geographically distributed network of computers to improve and expedite the delivery of online content to users. CDNs work by caching and storing web content, including images, videos, scripts, and other assets, across multiple servers located in different data centres across the globe.
83.What are the main applications for Azure Blob Storage, and what is it?
Ans:
It is intended to handle and store unstructured data in the shape of blobs or objects. The following are the principal uses of Azure Blob Storage:
- Data Backup and Archiving
- Data Lakes
- Media and Content Delivery
- Log and Telemetry Data
- Backup for Virtual Machines
- Static Website Hosting
84. In a cloud-based network, how can data security and privacy be guaranteed?
Ans:
Data security and privacy in a cloud-based network can be ensured through the following measures:
- Encryption
- Access Control
- Data Classification
- Security Monitoring
- Compliance Standards
- Regular Updates
- Incident Response
85. Describe the main areas of the Oracle Cloud?
Ans:
The following are the primary areas of the Oracle Cloud:
- Compute and Infrastructure
- Storage and Databases
- Networking
- Security and Identity
- Analytics and Big Data
- Application Development
86.Mention a few more noteworthy cloud service providers in addition to the big three (AWS, Azure, GCP).
Ans:
In addition to the three main cloud service providers (AWS, Azure, and GCP), there are a number of other notable cloud providers that target particular market niches and provide specialised services.
- IBM Cloud
- Alibaba Cloud
- Oracle Cloud
- Salesforce
- SAP Cloud Platform
- Rackspace
87. What does the word “elasticity” mean in relation to cloud computing?
Ans:
The context of cloud computing, “elasticity” refers to the ability to dynamically adjust and scale computing resources in response to changing workloads and demands.
88. Why is a load balancer utilised in the cloud, and what does it do?
Ans:
In order to optimise fault tolerance, increase application performance, and guarantee high availability, load balancers are employed in cloud computing to split up incoming network traffic among several servers or resources.
89. Describe the significance of cloud encryption.
Ans:
Cloud encryption is of paramount significance for several reasons:
- Data Privacy
- Compliance
- Data Security
- Multi-Tenancy
- Secure Data Transfer
- Control and Ownership
90.How does the Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE)
Ans:
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) provides Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE), a managed Kubernetes service:
- Cluster Deployment
- Managed Control Plane
- Node Pools
- Container Orchestration
- Automated Updates
- Scaling
- Monitoring and Logging