
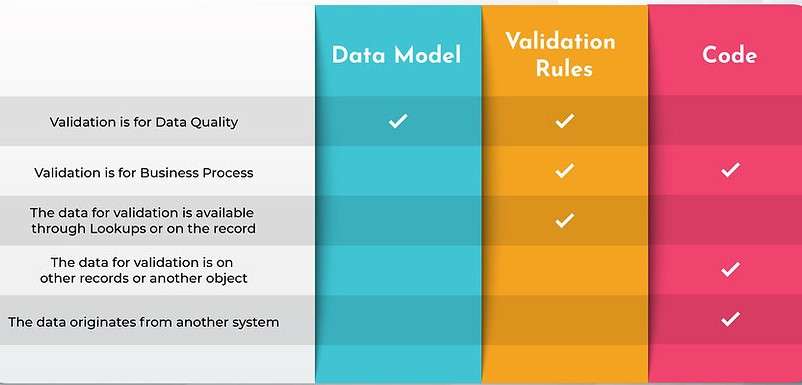
- Introduction to Validation Rules
- Importance of Validation in Salesforce
- Benefits of Using PRINCE2
- Creating Validation Rules
- Syntax and Functions Used in Validation
- Examples of Common Validation Rules
- Error Messages in Validation Rules
- Conclusion
Excited to Obtaining Your Salesforce Certificate? View The Salesforce Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Introduction to Validation Rules
Validation rules in Salesforce are automated processes used to ensure that data entered by users meets specified standards before being saved. These rules help maintain data accuracy, consistency, and integrity. When a user attempts to save a record, Salesforce evaluates the validation rules associated with that object. If the data does not meet the defined criteria, an error message is displayed, preventing the record from being saved until the issue is resolved, ensuring that users are guided through the necessary steps for correction, as emphasized in Salesforce Training. Validation rules are essential in enforcing business policies, preventing incorrect data entry, and ensuring compliance with organizational standards. With Salesforce being a customer relationship management (CRM) platform, data accuracy and reliability are paramount. Validation rules help organizations maintain high-quality data, which is essential for effective decision-making, reporting, and customer engagement.
Importance of Validation in Salesforce
Validation rules play a vital role in maintaining clean and reliable data within Salesforce. Here are some of the key reasons why validation is crucial:
- Data Accuracy and Consistency: Validation rules prevent the entry of incorrect or inconsistent data by enforcing field-level conditions. For example, they can ensure that phone numbers follow a specific format or that mandatory fields are not left empty.
- Compliance with Business Policies: Organizations have specific policies that govern how data should be entered. Validation rules help enforce these policies, such as verifying that discounts do not exceed a predefined limit.
- Improved Reporting and Analytics: Clean data leads to more accurate reports and insights. By preventing invalid data entry, validation rules, as taught in Salesforce Training, enhance the quality of the information used for decision-making.
- Efficiency and Productivity: Validation rules reduce the need for manual data correction by catching errors at the point of entry. This reduces administrative overhead and improves operational efficiency.
- Customer Trust and Satisfaction: Maintaining accurate customer data ensures that communications, orders, and services are accurate and reliable. This leads to better customer experiences and trust.
- Go to Setup → Object Manager.
- Select the object you want to create the validation rule for (e.g., Account, Contact, Opportunity).
- In the Object Manager, select the Validation Rules section.
- Click the “New” button to create a new rule.
- Rule Name: Enter a descriptive name for the validation rule (e.g., PhoneNumberFormat).
- Description: Add a brief explanation of what the rule does.
- The formula defines the condition that triggers the validation. It must evaluate to TRUE to display the error message.
- Example: To ensure phone numbers contain exactly 10 digits:
- LEN(Phone) <> 10
- Enter a clear and specific error message that will display when the rule is triggered.
- Choose where the error message should appear: either at the top of the page or next to the field.
- Click Save and test the rule by attempting to create or update a record that violates the validation criteria.
- = → Equal to
- != → Not equal to
- > → Greater than
- < → Less than
- >= → Greater than or equal to
- <= → Less than or equal to
- AND() → Returns TRUE if all conditions are met.
- OR() → Returns TRUE if at least one condition is met.
- NOT() → Reverses the Boolean value of the condition.
- TODAY() → Returns the current date.
- DATE(year, month, day) → Constructs a date value.
- YEAR() → Extracts the year from a date.
- MONTH() → Extracts the month from a date.
- ISBLANK() → Returns TRUE if the field is empty.
- ISPICKVAL() → Verifies if a picklist field contains a specific value.
- CONTAINS() → Checks if a string contains a specific substring.
- ROUND() → Rounds a number to a specified number of decimal places.
- MOD() → Returns the remainder of a division.
- ABS() → Returns the absolute value of a number.
- NOT(REGEX(Email, “^[A-Za-z0-9._%+-]+@[A-Za-z0-9.-]+\\.[A-Za-z]{2,4}$”)),
- LEN(Phone) <> 10
- CloseDate < TODAY()
- ISBLANK(AccountId)
- Quantity > 0
- Clarity: Use simple, clear language.
- Specificity: Clearly describe the error and the corrective action.
- Action-Oriented: Provide clear instructions on how to fix the error.
- CloseDate < TODAY()
- LEN(Phone) <> 10
Creating Validation Rules
Creating a validation rule in Salesforce is a straightforward process that involves Salesforce Testing. Here’s how to do it:
Navigate to Setup:
Select Validation Rules:
Excited to Obtaining Your Salesforce Certificate? View The Salesforce Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
Define Rule Details:
Write the Formula:
Specify the Error Message:
Save and Test the Rule:
Thinking About Earning a Master’s Degree in Salesforce? Enroll For Salesforce Masters Program by Microsoft Today!
Syntax and Functions Used in Validation
Data Validation Rules use Salesforce’s formula language, which includes functions, operators, and expressions to define the validation criteria. Here are some of the most commonly used functions:
Comparison Operators
Logical Operators
Date and Time Functions
Text Functions
Mathematical Functions
Examples of Common Validation Rules
Salesforce provides several commonly used validation rules that help maintain data quality and enforce business logic. For instance, email format validation can be achieved using the formula, and more complex scenarios can be handled with a Future Method in Salesforce
Preparing for Your Salesforce Interview? Check Out Our Blog on Salesforce Interview Questions & Answer
Error Messages in Validation Rules
Effective error messages help users understand what went wrong and how to correct the issue. When creating error messages, follow these guidelines:
Example:
Validation Rule:
Error Message: “The Close Date cannot be in the past. Please select a future date.”
Validation Rule:
Error Message: “Phone numbers must contain exactly 10 digits.”
Conclusion
Validation rules in Salesforce are essential for maintaining data integrity, enforcing organizational business policies, and ensuring the accuracy, consistency, and reliability of data across the platform. These rules operate by evaluating data entered into fields and returning an error message when the data does not meet predefined criteria. By mastering the creation, logical structure, syntax, and strategic application of validation rules through Salesforce Training, organizations can significantly reduce data entry errors, prevent the storage of incomplete or incorrect records, and streamline workflows across departments. In addition to enhancing the quality of Salesforce data, validation rules support compliance with internal and external standards, improve reporting accuracy, and ensure that only clean and meaningful data enters the system. They also play a critical role in automating quality checks, reducing manual oversight, and enforcing best practices in data management. Well-designed validation rules can guide users through the correct data input process, provide helpful feedback when errors occur, and maintain the integrity of integrations with other systems and applications. By investing time in building robust validation rules, organizations not only safeguard their data but also empower users to work more efficiently and confidently within Salesforce, ultimately driving better decision-making and operational excellence.


