
- Introduction to Bucket Fields
- Purpose and Use Cases of Bucket Fields
- Creating Bucket Fields in Salesforce
- Configuring Buckets with Ranges and Criteria
- Applying Bucket Fields in Reports
- Grouping and Categorizing Data
- Using Bucket Fields for Data Analysis
- Editing and Managing Bucket Fields
Introduction to Bucket Fields
Bucket fields in Salesforce are a valuable reporting feature that enables users to categorize and group data without altering the underlying records or database structure. This functionality is especially useful when users need to segment data quickly for analysis or visualization, but don’t want to create new custom fields or write complex formulas. With bucket fields, users can define ranges or categories known as “buckets” and assign records to these buckets based on the values of a chosen field. Salesforce Training explains that, for example, a sales manager might use a bucket field to group opportunities into revenue ranges like “Low,” “Medium,” and “High” based on their amount. Instead of editing each record or creating a formula field, they can define these buckets directly in the report builder. This makes the report more readable and allows for meaningful comparisons and summaries. Bucket fields support numeric, picklist, and text field types, and are easy to configure using Salesforce’s drag-and-drop interface. Once set up, they appear as new fields in the report, ready for filtering, grouping, or charting. This flexibility allows teams to gain deeper insights quickly, aiding in faster decision-making and reducing reliance on administrative tasks or development support.
To Explore Salesforce in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive Salesforce Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Purpose and Use Cases of Bucket Fields
Bucket fields in Salesforce serve multiple purposes, making them a versatile tool for data analysis and reporting. By allowing users to group values into categories without modifying actual data, bucket fields simplify data categorization and enhance report clarity. This feature is especially beneficial when users need to quickly analyze data trends or segment records without creating custom fields or writing formulas. Salesforce Database Architecture supports common use cases for bucket fields, including sales performance analysis, customer segmentation, revenue categorization, and trend identification. For instance, a sales team might use a bucket field to classify opportunities into revenue bands such as “Under $10K,” “$10K–$50K,” and “Over $50K.” This helps in assessing deal sizes and prioritizing efforts without making changes to the opportunity records themselves. Similarly, support teams can bucket cases by priority such as “High,” “Medium,” and “Low” to allocate resources more effectively and improve service response times.
Bucket fields can be applied to numeric, text, or picklist fields, and are easy to configure using Salesforce’s report builder. They enable users to create clearer, more actionable reports that highlight patterns and insights, all without relying on development or administrative changes. This makes them an essential feature for any team looking to optimize data analysis and reporting within Salesforce.
Creating Bucket Fields in Salesforce
- Access the Report Builder: Start by navigating to the Reports tab in Salesforce. Choose an existing report or create a new one using a report type that includes the field you want to bucket. Open the report in edit mode to begin.
- Select “Add Bucket Field”: In the report outline panel, click on the dropdown next to “Columns” and select “Add Bucket Field.” This opens the Bucket Field editor, where you’ll configure the grouping logic.
- Choose the Source Field: From the available fields, select the one you want to group such as a numeric, text, or picklist field. This is the data that will be categorized into buckets.
- Define Buckets and Assign Values: Understanding OWD in Salesforce for Security involves creating new buckets by naming each category (e.g., “Low,” “Medium,” “High”) and assigning the appropriate values or value ranges. You can manually select values or use ranges for numeric fields.
- Adjust Bucket Settings: Reorder, rename, or delete buckets as needed. Salesforce makes it easy to change configurations, giving you flexibility to match business criteria.
- Review and Preview: As you define your buckets, a preview shows how records are grouped. This helps verify the logic and ensure categories make sense before saving.
- Save and Use in Reports: Once complete, click “Apply” to add the bucket field to your report. You can now use it like any other field for grouping, filtering, or charting to enhance report insights.
- Choose the Field to Bucket: Begin by selecting the field you want to group, such as a numeric field (e.g., Opportunity Amount), a picklist (e.g., Case Priority), or a text field (e.g., Region). This field serves as the basis for creating your bucket categories.
- Define Bucket Type: Salesforce allows you to choose between manual value-based buckets or range-based buckets. For numeric fields, range buckets let you segment values into intervals like “0–10K,” “10K–50K,” and “50K+.”
- Set Bucket Ranges or Values: Salesforce Training teaches that for numeric data, you define start and end points for each range, and for text or picklist fields, you manually assign specific values to buckets.
- Name Each Bucket Clearly: Assign meaningful labels such as “Low,” “Medium,” and “High” to each bucket to ensure clarity in reports. Clear naming improves readability and helps users interpret data quickly.
- Add or Remove Buckets Easily: Salesforce provides the flexibility to add new buckets or remove existing ones as business needs change. This allows reports to stay up-to-date and relevant.
- Preview Bucket Assignments: While configuring, Salesforce shows a preview of how records are distributed across buckets. This helps validate accuracy before finalizing.
- Save and Apply in Reports: Once configured, the bucket field appears as a new column in your report. You can use it for grouping, filtering, or charting to gain actionable insights instantly.
- Versatile Across Business Functions: Bucket fields are useful in various departments. Sales can group deals by size, support can categorize cases by urgency, and marketing can segment leads by behavior or source.
- Enhances Data Visualization: Grouped data is ideal for visual representation in dashboards and charts, helping users compare performance across segments with clarity.
- Flexible and Easily Editable: Bucket definitions can be updated, renamed, or reorganized without altering underlying records, allowing for real-time adaptation to business changes.
- Enables Quick Insights: Salesforce vs. Salesforce Platform shows that categorized data highlights areas of concern or opportunity more clearly, making it easier for teams to take informed, timely actions based on grouped information.
- Simplifies Data Interpretation: Bucket fields allow users to group raw data into meaningful categories, making reports more understandable. Instead of analyzing individual values, users can quickly identify trends and patterns using grouped data like “Low,” “Medium,” and “High.”
- Eliminates Complex Formulas: Bucket fields remove the need for creating formula fields or custom logic. Users can segment data directly in the report builder without writing code, streamlining the reporting process.
- Dynamic Grouping of Values: They support the categorization of numeric, text, and picklist fields. For example, sales opportunities can be grouped into revenue tiers, and customer statuses can be classified as “Active,” “Inactive,” or “Pending.”
Interested in Obtaining Your Salesforce Certificate? View The Salesforce Training Offered By ACTE Right Now!
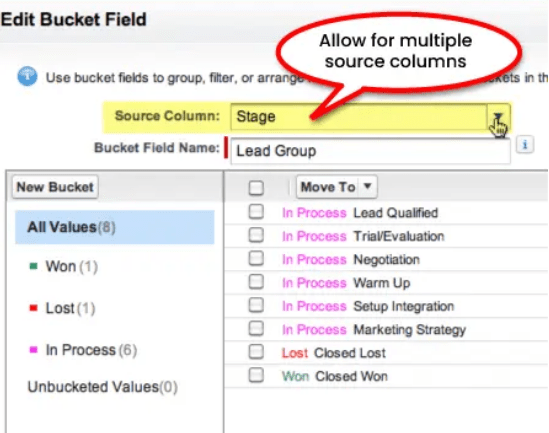
Configuring Buckets with Ranges and Criteria
Applying Bucket Fields in Reports
Applying bucket fields in Salesforce reports is a straightforward yet powerful way to enhance data analysis. Bucket fields allow users to group values from a single field into categories, or “buckets,” directly within the report builder without changing the underlying data or creating custom fields in the object. This functionality is especially useful when dealing with large datasets that require quick segmentation or simplified views. To apply a bucket field in a report, users begin by selecting a field they want to group, such as Opportunity Amount, Case Priority, or Customer Type. Using Salesforce SOQL and the bucket field editor, they can then define custom ranges or categories. For example, in a sales report, opportunities can be bucketed into revenue groups like “Low Value” (under $10,000), “Mid Value” ($10,000–$50,000), and “High Value” (over $50,000). This categorization makes it easier to identify trends, prioritize efforts, or compare performance across different segments. Once created, the bucket field appears as a new column in the report and can be used for grouping, filtering, or charting. This improves readability and helps stakeholders make informed decisions based on clearly segmented data. Ultimately, bucket fields make reports more dynamic and insightful, without requiring complex configurations or development work.
Are You Interested in Learning More About Salesforce? Sign Up For Our Salesforce Training Today!
Grouping and Categorizing Data
Using Bucket Fields for Data Analysis
Bucket fields play a crucial role in data analysis within Salesforce by offering a structured and intuitive way to categorize and interpret information. They allow users to define custom categories known as buckets based on the values of existing fields, without modifying the original data or requiring complex formulas. This makes bucket fields an essential tool for analysts who need to quickly identify patterns, trends, and areas for improvement. By grouping records into meaningful segments, bucket fields help simplify complex datasets and make them easier to analyze. For instance, in a customer service report, case resolution times can be bucketed into categories such as “Fast” (under 2 hours), “Moderate” (2–8 hours), and “Slow” (over 8 hours). Map Methods in Salesforce help with this categorization, allowing service managers to quickly assess team efficiency and pinpoint delays in the resolution process. With these insights, organizations can identify bottlenecks, streamline workflows, and enhance overall customer satisfaction. In sales, bucket fields can be used to classify deals based on value, stage, or probability, providing a high-level view of the sales pipeline. Marketing teams can segment leads based on engagement levels, helping to refine campaign strategies. The flexibility of bucket fields to accommodate numeric, picklist, and text data makes them highly adaptable to various business needs. Overall, bucket fields empower users to uncover actionable insights without relying on technical configurations or database changes. They enhance report clarity, support better decision-making, and enable teams to focus on performance and outcomes rather than data complexity.
Preparing for a Salesforce Job Interview? Check Out Our Blog on Salesforce Interview Questions and Answers
Editing and Managing Bucket Fields
Salesforce provides users with the flexibility to edit and manage bucket fields directly within the report builder, making them highly adaptable to changing business needs. Once a bucket field is created, users can easily modify its definitions, adjust value ranges, or add new categories to reflect updated segmentation strategies. This dynamic capability ensures that reports remain relevant and aligned with current business priorities without requiring changes to the underlying data or object structure. Salesforce Training shows that, for example, if a sales team decides to redefine revenue tiers due to market changes, they can simply update the bucket field in the report, changing the value ranges or labels accordingly. This allows teams to maintain consistent reporting standards while adapting to evolving performance metrics. Moreover, bucket fields are non-destructive. Removing or restructuring a bucket field has no impact on the original data in Salesforce, preserving data integrity. This makes them an excellent tool for experimentation and temporary categorization, especially when testing new reporting approaches or analyzing data from different perspectives. The ability to manage bucket fields easily empowers users to take control of their reporting without needing support from developers or admins. It enhances the self-service nature of Salesforce reporting and supports continuous improvement in data-driven decision-making.





