
Java Web Dynpro, an interface development framework in Java, is a common focus in interviews. Questions often encompass its architecture, features, integration with other technologies, and effective application development practices. Interviewees may be quizzed on aspects like managing user interfaces, data binding, event handling, and utilizing diverse components within the Java Web Dynpro framework. A successful interview performance entails a solid grasp of Java, web development principles, and proficiency in harnessing Java Web Dynpro to craft dynamic and responsive web applications.
1. What Is A View Assembly?
Ans:
The superset of all views that a Web Dynpro application would need to run a particular component are explained in a window. That being said, just a portion of the views embedded in the window will normally be displayed at any given moment.
2. Describe the Faceless component?
Ans:
It is a component that has neither windows nor views. This type of component, referred to as “faceless,” is helpful when encapsulating a complicated functional unit that does not require direct user interaction. The development of a model component is an excellent illustration of a faceless component.
3. What kinds of controllers are there?
Ans:
SAP has provided a general explanation of Web Dynpro controllers in two categories.
The distinction between them is as follows:
- SAP introduced this distinction to maintain a strict division between business application components that process data and those that display it.
- A controller can either have a visual interface or not
4. What Nodes Are There in Recursion?
Ans:
A unique kind of node called a recursion node is employed when a node hierarchy with a recursive structure needs to be established. This is required, for example, if the node hierarchy’s depth is unknown until runtime. It is possible to indicate that a specific node structure gets reproduced as a child of itself by using a recursion node. An excellent illustration of this would be if the context had to store data in a directory-and subdirectory-structured file system..
5. What is an Empty View?
Ans:
An empty view is one particular kind of view. There is no need to manually implement this view, and the only method to interact with it is to use the default inbound plug to show Empty View. If a view set needs a particular area to be vacant, the empty view should be embedded into the view area.
6. How does a Web Dynpro framework choose the specific views that comprise the current view assembly?
Ans:
- Only views with their default flag set to true will be included in the initial view assembly when an application is run for the first time.
- After then, user navigation will take place, and the view assembly will consist of both recently created views and views that have been present in earlier view assemblies.
- Make a WebDynpro Controller defined.
- A Web Dynpro component’s controllers are its working components. SAP has significantly altered the basic MVC controller idea in the creation of Web Dynpro controllers..
7. When a Web Dynpro for ABAP does not implement the view set idea?
Ans:
Web Dynpro for ABAP and Java both have a unique UI element known as the View Container. When added to the view layout, this user interface element serves as a container for any other views. There are many different methods to arrange View Containers such that they provide the required layout on a screen.
8. Describe View Set?
Ans:
A window can be visually divided into predetermined parts using a framework called a view set. A view area is any subset of a view set, and it can contain several views embedded in it.
9. How does a Web Dynpro framework apply model-driven architecture?
Ans:
Developers can concentrate more on the application’s design and less on the coding and technological aspects by using the model-driven approach, which advocates “minimizing coding and also maximizing design.”Business logic should, of course, be the main priority for developers of business applications, and technology implementation should not divert them..
10. How can the lifespan of bespoke controllers be ascertained?
Ans:
A custom controller’s lifetime can be determined by a parameter that is set during the design time declaration. Either “Framework Controlled” or “On-demand” are possible. The Web Dynpro framework will construct a custom controller when the component is instantiated if you select “Framework Controlled.” However, if the user selects “On-demand,” the Web Dynpro developer will have to build the code required to initialize the custom controller.
11. Describe the idea behind lazy data access?
Ans:
Lazy Data Access is a foundational feature of the Web Dynpro architecture. This implies that data generation processes won’t be activated until the data is actually required. When this method is applied to the context’s architecture, it implies that even if the parent node’s lead selection changes, the child node’s supply function will not be triggered until an attempt to access the data in the singleton child node is made.
12. What requirements need to be satisfied before a mapping relationship may be formed?
Ans:
Before a mapping relationship can be established, several requirements must be satisfied.
Firstly, there should be a clear understanding of the entities involved in the mapping, including their attributes and relationships. It is essential to have well-defined source and target entities, each with a set of attributes that need to be mapped.
Secondly, the data types of corresponding attributes in the source and target entities must be compatible to ensure meaningful data transfer
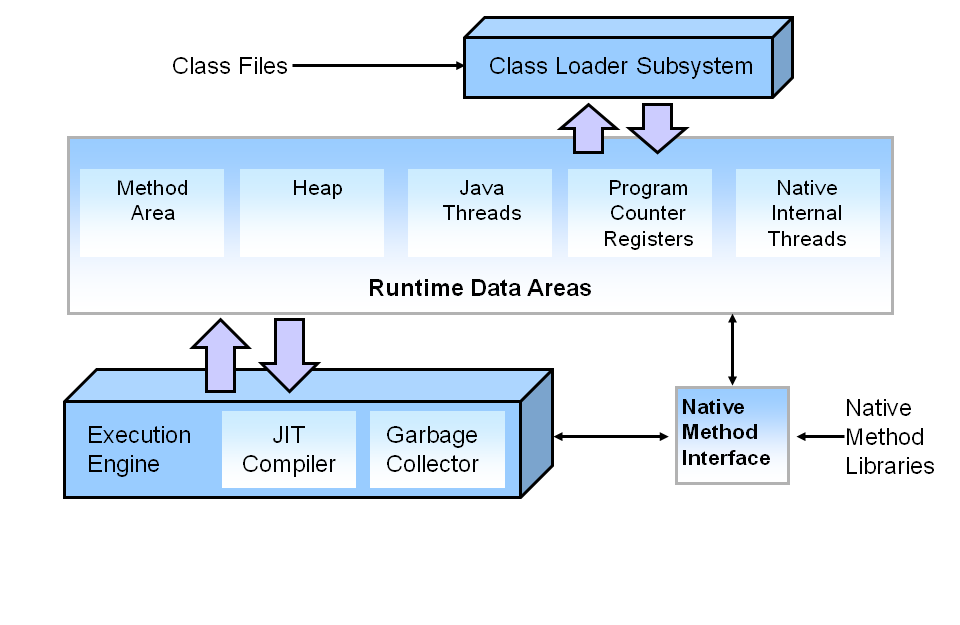
13. What is Garbage Collection In Java, And When Is It Used?
Ans:
The garbage collection is to identify and remove objects that are no longer needed by a program so resources can be reclaimed and reused. A Java object is subject to the garbage collection when it becomes unreachable to a program in which it is used.
14. What Happens If the Primary Approach Is Designated as Private?
Ans:
If the primary approach is designated as private, it means that the method or function can only be accessed within the same class where it is defined. This encapsulation restricts external classes or objects from directly invoking or interacting with the private method. It enhances data encapsulation and security by hiding implementation details. However, it may limit the method’s usability, as only methods within the same class can use it.
15. Consider Writing A Static Public Void Rather Than A Public Static Void?
Ans:
Considering writing a static public void rather than a public static void is a matter of method declaration syntax in programming languages like Java. The order of modifiers doesn’t affect the method’s functionality, so both declarations are equivalent. It’s a stylistic choice, but maintaining a consistent coding style within a project or team is crucial for readability and collaboration.
16. What Would occur If the Method’s Argument Was Not a String Array?
Ans:
If the method’s argument was not a String array, attempting to pass a different data type might result in a compilation error or runtime exception, depending on the programming language. The method expects a specific data type (String array), and passing anything else would violate the method’s signature, leading to a type mismatch error.
17. What Does the Main Method’s String Array’s First Argument Mean?
Ans:
The main method’s String array’s first argument represents the array of command-line arguments passed to a Java program when it is executed. The array’s first member (index 0) includes the first command-line parameter passed to the programme during execution. It allows the program to receive input from the command line, enabling dynamic behavior based on user-provided arguments
18. How to Use One Line of Code to Prove That an Array Is Not Null But Empty?
Ans:
To prove that an array is not null but empty using one line of code, you can check both conditions using the length property. For example, in Java, you can write:
- if
- (array != null && array.length == 0).
This code ensures that the array is not null
first and then checks if its length is zero, confirming that it is an empty
array.
19. What Exemptions Are Checked And Unchecked?
Ans:
With the exception of the class Runtime Exception and its subclasses, a checked exception is any subclass of an Exception (or the Exception itself). Programmers on the client are forced to deal with the potential that an exception may be thrown when an exception is checked. such as an IOException raised by a Java.io.The fileinputstream.read() functionRuntime Exceptions and any of their subclasses are examples of unchecked exceptions. Additionally unchecked are Class Error and its subclasses.
20. What Kinds Of Inner Classes Are There?
Ans:
Local classes, Anonymous classes, Member classes, and nested top-level classes Nested top-level classes
21. How Do An Interface And An Abstract Class Differ From One Another?
Ans:
It is possible for instance methods of an abstract class to implement default behavior. All of the methods on an interface are implicitly abstract, and they can only specify constants and instance methods. Default behavior cannot be implemented. Interface has no implementation and all of its members are public. A class that includes certain abstract methods but some standard class member flavors (private, protected, etc.) is called an abstract class.
22. What Does Synchronization Mean Regarding Multithreading?
Ans:
In terms of multithreading, synchronization refers to the capacity to manage how many threads can access shared resources. A shared variable can be modified by one thread while it is being used or updated by another thread if synchronization is not present. This typically results in serious mistakes.
23. What Does the Pass By Value And Pass By Reference Mean?
Ans:
Pass By Value and Pass By Reference: These are two methods for sending data between functions or procedures in computer languages.
The real value of the variable is supplied to the function in pass by value, and any changes made to the parameter inside the function have no effect on the original variable outside the function. In contrast, pass by reference involves passing a reference (memory address) to the variable, allowing the function to directly manipulate the original data.
24. What Are Map and Hashmap?
Ans:
Computer scientists utilize two types of data structures to hold key-value pairs: hashmaps and maps. More generally, a collection of key-value pairs with distinct keys is referred to as a map. In contrast, a hashmap uses a hash algorithm especially to map keys to array indexes, enabling quick and easy value retrieval.
25. What distinguishes a hashmap from a hashtable?
Ans:
A hashtable and the hashMap class vary primarily in that the former is not synchronized and accepts null data. While a hashmap allows null values as keys or values, a hashtable does not. HashMap does not ensure that the order of the map will remain constant over time. In contrast, a hashtable is synchronized, HashMap is not.
26. How Does a Vector Differ From an Arraylist?
Ans:
Synchronization: The main distinction is that Vector is thread-safe since it is synchronized. In order to prevent data corruption, this makes sure that many threads cannot access and edit the Vector at the same time. However, because ArrayList does not synchronize, it is more effective when used in single-threaded situations.
Performance: Vector operations may be slower than ArrayList operations due to the synchronization overhead. The widespread consensus is that ArrayList performs better if thread safety is not an issue..
27. What Distinguishes an Awt From a Swing?
Ans:
Swing provides a more contemporary and adaptable collection of GUI elements and is an extension of AWT. Because it is fully written in Java and does not depend on the components of the native platform,
Swing applications are the most consistent across various operating systems.
Conversely, AWT makes use of native components, which may lead to variances in behavior and appearance across different platforms.
28. What Distinguishes A Constructor From A Method?
Ans:
A member function called a class’s constructor is utilized to create a class object. It is called with a new operator, shares the same name as the class, and does not have a return type.
A class member function is called a method. It has a return type (void is allowed), is called using a dot operator, and is called after itself.
29. What Are Iterators Like?
Ans:
Exceptions can be used to navigate around the contents of some collection classes.an iterator’s interface.
With this interface, an individual can move through a collection of objects and do actions on every one separately. Iterators represent the collection as of the instant they were collected, so use them with caution.
30. Describe Abstract Class?
Ans:
For an abstract class to be useful, it needs to be expanded or subclassed. It acts as a model. It is possible for an abstract class to have static data even while it is not instantiated. Every class that has an abstract method is inherently abstract and needs to be identified as such. Even if a class doesn’t have any abstract methods, it can nevertheless be declared abstract. As a result, it cannot be instantiated.
31. What Does a Java Static Mean?
Ans:
No matter how many instances of a class there may be, static refers to one per class rather than one for each object. This implies that you can utilize them without having to create a class instance. Because overriding is done based on an object’s type and static methods are associated with classes rather than objects, they are inherently final. If the original static method in a superclass was not marked final, then another static method in a subclass may shadow it. Nevertheless, a non-static method cannot be used to override a static method. Stated otherwise, a static method in the subclass cannot be converted to an instance method.
32.What Constitutes a Final?
Ans:
A final class cannot be subclassed or extended, that is, it cannot be an extended class.
When a final method’s class is inheritable, it cannot be overridden and cannot alter the value of a final variable, which is a constant.
33. Are the imports validated throughout the compilation process?
Ans:
Yes, in Java Web Dynpro, the compilation process validates import statements. The compiler checks the accuracy of import declarations, ensuring the availability and correct usage of referenced classes or packages. This validation is crucial for maintaining code integrity and reliability.
34. Difference Between Declaring A Variable And Defining A Variable?
Ans:
Declaring a Variable:
Definition: Declaring a variable is the process of informing the compiler or interpreter about the data type and the name of the variable without allocating memory.
Defining a Variable:
Definition: Defining a variable is the process of assigning a memory location to the declared variable. It involves allocating space in the computer’s memory to store the actual data.
35. Are Objects Passed Through Reference Or By Value?
Ans:
In programming, objects can be passed by value or by reference depending on the language and its underlying memory management model. When passed by value, a copy of the object is created, and modifications to the copy do not affect the original. In contrast, when passed by reference, the function or method receives a reference to the original object, allowing modifications to directly impact the source.
36. What Is the Meaning of Serialization?
Ans:
The process of serializing an object involves transforming it into a format that is simple to transfer, store, or rebuild. This is crucial when working with intricate data structures or moving things between several environments, like a client and a server.
37. How Does Serialize an Object To A File?
Ans:
To serialize an object to a file, one often utilizes the serialization libraries or frameworks that come with the programming language. The object produces a byte stream that may be written to a file. During the deserialization process, this byte stream is read from a file and reconstructed as an object.
38. Which Techniques for Serializable Interfaces Must Be Applied?
Ans:
It is recommended to utilize the Serializable interface in Java when implementing serialization. The interface is merely a marker interface that indicates that the class is serializable; it has no methods of its own.
However, by implementing certain methods like writeObject and readObject, it’s crucial to handle special issues, including handling temporary fields or offering bespoke serialization methods.
39. How Is Serialization Usually Used?
Ans:
Serialization is commonly used in scenarios involving data persistence, network communication, and inter-process communication.
It allows objects to be saved to disk, transmitted over a network, or sent between different components of an application while maintaining their structure and state. This is particularly valuable in distributed systems and when working with objects that need to be shared across different parts of a program or even different programs altogether.
40. Externalizable Interfaces: What Are They?
Ans:
An interface that can be externalized has two methods: read External and write External. You have control over the serialization mechanism with these methods. Consequently, a class that implements this interface can use these methods to tailor the serialization process.
41. What Must Be Considered When Serializing an Object?
Ans:
Serialization is the process of transforming an object’s state into a format that can be readily stored or conveyed. Several considerations should be made before participating in object serialization to guarantee a seamless and secure operation. To begin, it is critical to deal with any circular references inside the object graph in order to avoid infinite loops during serialization.
42. What Takes Place With The Class’s Static Fields During Serialization?
Ans:
- Static fields are ignored by serialization since they belong to no state.
- Only when a base class can be serialized is it possible to handle its fields.
- Temporary areas.
43. How Can Exceptions Be Handled Differently?
Ans:
- By enclosing desired code in a catch block to catch exceptions, then a try block to execute the desired code.
- In the method’s throws clause, specify the desired exceptions to raise, and then let the method’s caller handle them.
44. Difference Between a Try catch and Throw in Exception Handling?
Ans:
Feature
| ‘try-catch’ Block |
‘throw’ Statement |
| |
| Purpose |
Catches and manages exceptions within a specified code block. |
Explicitly triggers an exception to signify abnormal conditions. | |
| Syntax | ‘java try { // code that may throw an exception } catch (ExceptionType e) { // handle the exception }’ | ‘java throw new ExceptionType(“Error message”);’ | |
| Usage | Employed for handling exceptions within a confined code section. | Used to explicitly raise exceptions, signaling unexpected scenarios. | |
| Multiple Exceptions |
Permits multiple catch blocks for handling various exception types. |
Typically utilized for throwing a specific exception; multiple ‘throw’ statements may be used for different exceptions. | |
| Control Flow |
Facilitates graceful exception handling, allowing the program to continue after addressing exceptions. |
Interrupts the normal program flow, transferring control to an appropriate exception handler. | |
| Handling Unchecked Exceptions |
Can handle both checked and unchecked exceptions. |
Primarily used for throwing checked exceptions, but can also handle unchecked exceptions. | |
| Example |
‘java try { int result = divide(10, 0); } catch (ArithmeticException e) { System.out.println(“Error: ” + e.getMessage()); }’ |
‘java if (input < 0) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Input cannot be negative"); }' |
45.Define a Webdynpro Controller?
Ans:
A Web Dynpro controller is a fundamental component in SAP’s Web Dynpro ABAP framework, serving as the core logic handler for user interface interactions. It acts as a mediator between the user interface and the backend data and business logic. The primary purpose of a Web Dynpro controller is to manage the flow of data and control the behavior of the user interface elements within a Web Dynpro application.
46. Where can locate the Web Dynpro ABAP limitation list?
Ans:
Web Dynpro ABAP, a framework developed by SAP for creating user interfaces in the ABAP environment, comes with certain limitations. One limitation is the restricted support for modern web technologies, as Web Dynpro ABAP is primarily designed for SAP GUI-based applications.
47. In the Web Dynpro application, how is information managed for end users?
Ans:
It is also possible to construct and display messages in an ABAP Workbench that contain information for Dynpro application end users. On a screen, these messages are shown. These are interactive notifications for users that provide crucial details about the Web Dynpro application.
48. Can a Web Dynpro ABAP application have a transaction code created for it?
Ans:
For a web Dynpro application, it is possible to generate a transaction code.
Please take the following actions:
- Proceed to SE93;
- Generate a Code;
Select the final option and preserve values.
49. In a Web Dynpro ABAP, what is a service call? Why is it employed?
Ans:
The Web Dynpro component’s service call is a wizard-based tool that allows you to invoke any function module or class method that is already present. By using a service call, we may automatically generate context nodes and web Dynpro methods based on the parameters of the function module or class method.
50. Difference between a component controller and interface controller?
Ans:
Controller for components: A component controller is a global controller; all views and windows inside that component can access data that is declared in a component controller.
Controller interface: One kind of controller that is in charge of interacting with external web Dynpro components is the interface controller.
51. Difference between node & attribute in Web Dynpro ABAP?
Ans:
Node:
Definition: A node in Web Dynpro ABAP represents a structured data object or a container that holds multiple attributes. It is used to organize and manage complex data structures.
Attribute:
Definition: An attribute in Web Dynpro ABAP represents a single field or property within a node. It holds a specific piece of data.
52. How many different cardinality kinds are there in an ABAP web dynpro?
Ans:
Two varieties of cardinality exist in a web dynpro ABAP matrix.
- Cardinality of collection
- Cardinality of selection
53. How important is the interface controller in an ABAP Web Dynpro?
Ans:
The interface controller in Web Dynpro ABAP plays a crucial role in managing the communication between the interface view and the business logic. It acts as a mediator, handling events triggered by user interactions in the interface view and coordinating the corresponding actions in the backend. This separation of concerns enhances the modularity and maintainability of the code, making it easier to update or extend the application.
54. What is a mapping of context?
Ans:
Context mapping in Web Dynpro ABAP refers to the process of connecting the context nodes and attributes of different controller contexts. It allows data to be shared between different parts of the application, enabling seamless communication between views and controllers. Context mapping is essential for passing information between components and ensuring a consistent flow of data within the Web Dynpro application.
55. What does the interface view property serve as?
Ans:
The purpose of the interface view property in Web Dynpro ABAP is to define the structure and layout of the user interface. It specifies the visual elements, such as input fields, buttons, and tables, that will be displayed to the user. Developers may manage the design and behavior of the user interface by specifying the interface view property, offering a personalized and user-friendly experience.
56. Which upgrade is compatible with the Web Dynpro ABAP?
Ans:
Web Dynpro ABAP is available for upgrades related to the SAP NetWeaver platform. This includes upgrades to the underlying SAP NetWeaver technology stack, as well as updates to the SAP Business Suite, which may impact the Web Dynpro ABAP applications. It’s important to check the compatibility and release notes provided by SAP to ensure a smooth transition during upgrades, preserving the functionality and performance of the Web Dynpro ABAP applications.
57. When using the complex panels, the Web Dynpro program rapidly stops functioning correctly. Why does that issue arise?
Ans:
The reason for this problem is because as UI container elements are nested in Web Dynpro views, the HTML rendering tag’s nesting depth increases. The browser stops because it cannot parse such deep hierarchies due to their approximate depth of 100. As a result, in order to fix this problem, the views’ nesting depth must be reduced. A Web Dynpro does not offer generic simplicity.
58. What Are System Fields?
Ans:
Every ABAP program makes use of the ABAP system fields. A runtime environment fills them, and a program can query their values to determine certain system conditions. Despite the fact that they are variables, you shouldn’t set a value for them as this could replace data that is necessary for the program to function normally. Still, there are a few unique situations where a system variable would need to be overwritten.
59. How will an application be instructed to switch from HTTP to HTTPS?
Ans:
To instruct an application to switch from HTTP to HTTPS in Java Web Dynpro, you need to configure the web server or application server to support SSL (Secure Sockets Layer). This involves obtaining an SSL certificate, configuring the server to use HTTPS, and updating the application’s web.xml deployment descriptor to enforce secure communication.
60. How should the UI element in any layout start with a line break?
Ans:
In Java Web Dynpro, to make a UI element in any layout start with a line break, you can use the New Line property.
Set the “New Line” property of the UI element to “Before” in the property sheet or layout editor. This will ensure that the UI element starts on a new line within its container.
61. How can a Web Dynpro URL’s parameters be read?
Ans:
Web Dynpro URL parameters can be read using the wdThis context node. The wdThis context node provides access to the current
component controller, and you can retrieve URL parameters using the
method. Once obtained, you can access the individual parameters using their names and retrieve their values.
62. In a table or ALV, how will chosen rows be deleted?
Ans:
In a table or ALV (Advanced List Viewer) in Java Web Dynpro, chosen rows can be deleted by implementing a corresponding action in the controller. Define an action for row deletion and associate it with a button or menu item. In the action handler method, retrieve the selected rows using the table’s API and remove them from the underlying data source. Refresh the table to reflect the changes in the user interface.
63. Can an application for WebDynpro be executed in the background?
Ans:
Running a WebDynpro application in the background defeats the point of the MVC controller design for WebDynpro, hence it makes no sense. Nonetheless, a logic to generate background tasks from the Web Dynpro Application can be constructed.
64. How Are Interactive Forms Used?
Ans:
Forms built with Adobe applications can be utilized to develop Web Dynpro user interfaces. moreover capable of integrating ABAP editor and Adobe lifecycle development tools to facilitate user interface creation. Utilizing Adobe tools to construct interactive forms makes it possible to develop UI elements quickly and easily..
65. What are init events in a Web Dynpro, and how are they triggered?
Ans:
- View Controller: WDDOINIT;
- Window Controller: WDDOINIT;
- Component Controller: WDDOINIT
66. Why is garbage collection needed in Java, and how does it work?
Ans:
Garbage collection’s goal is to locate and remove items that the software no longer needs in order to recover and reuse their resources. When a Java object is rendered unusable by a program in which it is utilized, it is susceptible to a garbage collection.
67. What occurs if the primary method is designated as private?
Ans:
In Java Web Dynpro, the main method is typically not explicitly declared by the developer. Instead, the framework automatically generates a main method during compilation. However, if you were to hypothetically declare the main method as private in a Java Web Dynpro application, it would result in a compilation error
68. How does Web Dynpro’s SAP List Viewer work?
Ans:
The SAP List Viewer offers a versatile environment for displaying lists and tabular structures and is used to create ALV components. The output table, header, and toolbar comprise the usual output. Additional dialog boxes allow the user to add columns, aggregations, and sorting choices.
69. Why would a Web Dynpro need a Window Controller?
Ans:
Java Web Dynpro is a framework designed for developing web-based user interfaces in Java. In this context, a Window Controller in Web Dynpro plays a crucial role in managing the flow and behavior of a web application. It acts as a mediator between the user interface and the underlying business logic.
70. Describe the Hook techniques?
Ans:
Hook methods, in the context of Java Web Dynpro, are special methods provided by the framework that developers can override to customize the behavior of their applications. These methods are called at specific points in the lifecycle of a Web Dynpro component, allowing developers to execute custom code at key events.
71. What is a set of views?
Ans:
A view set is a set of visual guidelines that separates a window into predetermined sections. Multiple views can be embedded within a single View Area. A view area is any subdivision of a view set.
The preset view sets listed below are accessible:
- 90-degree T arrangement 180° T layout and 270° T layout Tab strip layout in a grid format.
- A view area is any subdivision that is part of a view set arrangement.
72. What is WebDynpro ABAP’s MVC?
Ans:
The Model-View-Controller (MVC) architecture in WebDynpro ABAP is a design pattern that divides application logic into three interrelated components. The Model represents the data and business logic, the View is in charge of producing the user interface, and the Controller oversees the Model-View communication.
73. In WebDynpro ABAP, what is a selection cardinality?
Ans:
Selection cardinality in WebDynpro ABAP defines the relationship between nodes in the context of a WebDynpro component. It specifies how many elements from one node can be associated with elements in another node. The selection cardinality can be set to values like 0..1 (zero or one), 1 (exactly one), 0..n (zero to many), or 1..n (one to many).
74. Does every controller really have an own Context node?
Ans:
Yes, it is true that each controller in WebDynpro ABAP has its own context node. The context of a WebDynpro component consists of nodes, and each controller within the component has its private context node. This ensures encapsulation of data within the respective controllers, preventing unwanted interference between different controllers.
75. How can a node be declared—in the View Controller or in a Component Controller?
Ans:
Again, this is dependent upon the following: The node should be specified at the Component Controller level if it will be accessible from different views. The View Controller can provide an explanation if the node is unique to a single view, though. The complexity of Webdynpro development increases with its scale, necessitating a greater requirement for explanations at the Component Controller on properties, nodes, methods, etc..
76. Can you use more than one layout in a single view?
Ans:
In Java Web Dynpro, a standard practice is to design a view with a consistent layout. Although it’s technically feasible to incorporate multiple layouts within a view, it’s recommended to uphold a unified layout for improved visual consistency and a user-friendly design, enhancing overall user experience.
77. Is it feasible to call or open a single WebDynpro application from another one?
Ans:
Indeed, it is possible to start one Webdynpro application from another. Obtain the URL of the Web Dynpro component you wish to run first, then open an external window and call that URL. You can use the FM to obtain the URL of any web Dynpro component.
After obtaining the URL in str, you may use ‘str’ and FM to call this web Dynpro, creating_external_window.
78. What is a model of the Web Dynpro Phase?
Ans:
- A series of processing steps are carried out whenever a round trip from a client (browser) to the server takes place. Phase Model is the term for this online Dynpro processing step sequence.
- The Web Dynpro framework bears the obligation of carrying out every task in the phase model.
79. Which ABAP UI technologies are there?
Ans:
Java Web Dynpro is a user interface (UI) technology used in SAP systems for building web-based applications. However, it’s important to note that Web Dynpro is primarily associated with the ABAP (Advanced Business Application Programming) language. ABAP is the proprietary language developed by SAP for building applications within the SAP ecosystem.
80. What Makes Up a Model Class?
Ans:
In webdynpro, the Model class is an assistance class. It has global data, constants in the form of class attributes, and business logic in the form of methods. The attribute wd_assist-> in a webdynpro component provides access to the Model class. Note: When utilizing the object wd_assist to access a class, all of the classes’ visibility properties are applicable.
81. How is an Assistance Class Instantiated in a Webdynpro?
Ans:
In Web Dynpro ABAP, an Assistance Class is a reusable class that contains methods to perform specific tasks and logic related to a particular component or view. To instantiate an Assistance Class in a Web Dynpro application.
- Create an ABAP class that will serve as the Assistance Class. You can do this using the ABAP Class Builder (transaction SE24).
- Define the necessary attributes and methods within the class based on the requirements of your Web Dynpro component or view.
82. What is Webdynpro Design Patterns (GAF, OIF, QAF, Etc.)?
Ans:
Design Patterns in a Web Dynpro, such as GAF (Generic Application Framework), OIF (Object Instance Floorplan),
QAF (Quick Application Floorplan), etc., play a crucial role in enhancing the modularity, maintainability, and scalability of Java web applications.
GAF, for instance, promotes a generic and flexible structure for creating applications, allowing developers to efficiently build various scenarios with consistent design principles.
OIF focuses on managing object instances within the application, ensuring a cohesive and organized approach to data handling.
83. How is a web-based application debugged?
Ans:
Debugging a web-based application necessitates a rigorous approach to finding and correcting code issues. Debugging Java online applications, particularly those built using technologies like as Java online Dynpro, may be done with a number of tools and approaches. Developers frequently use integrated development environments (IDEs) with sophisticated debugging facilities, such as Eclipse or IntelliJ IDEA.
84. How Can You Switch Between Views in WebDynpro?
Ans:
Plugs are used to navigate between views (Inbound and Outbound), How to create F4 Search Assistance in WebDynpro can enable F4 help for an input field by linking the search help to a table field.
Using the WDR_OVR standard assistance component. constructing a help component and adding it as a freely programmed value help to a node element
85. How are the inbound and outbound plugs bound inside a window?
Ans:
Plugs play a crucial role in facilitating communication between different views within a window. Inbound Plugs serve as entry points into a view, allowing data to be passed from the calling view to the current view. Outbound Plugs, on the other hand, enable a view to send data back to the calling view.
86. How Do Anyone Programmatically Control the Visibility of a Webdynpro UI Element?.
Ans:
Controlling the display of Web Dynpro UI components programmatically entails modifying the UI elements’ attributes based on specified situations or user interactions. Developers may utilise the Controller context to dynamically access and alter the attributes of UI components. Developers can use conditional statements or event handlers to set the visibility attribute of a UI element to “visible” or “invisible” based on runtime conditions.
87. Difference between a View and a Window in Web Dynpro?
Ans:
A View in Web Dynpro represents a specific part of the user interface, while a Window is a container that can hold multiple views. Windows are used for navigation between different parts of the application.
88. How can you integrate Web Dynpro with SAP backend systems?
Ans:
Web Dynpro applications can be integrated with SAP backend systems using various technologies, such as RFC (Remote Function Call), BAPI (Business Application Programming Interface), and Web services. These integrations enable seamless communication between the frontend and backend systems.
89. Explain the concept of Cross-Component Context Mapping?
Ans:
Cross-Component Context Mapping in Web Dynpro allows the exchange of data between different components. It enables one component to access and manipulate the context of another component, supporting communication and data sharing in a modular application landscape.
90. How can I implement client-side validations in Web Dynpro?
Ans:
Client-side validations in Web Dynpro can be implemented using JavaScript or the built-in validation features provided by the framework.
Developers can use the onInput processing event to trigger custom validation logic on the client side before submitting data to the server.






