
Product design involves creating and refining products to meet user needs and business goals within technological constraints. It combines user research, design thinking, engineering, and marketing. Designers collaborate with stakeholders to identify pain points and develop solutions using tools like personas, wireframes, prototypes, and usability testing. The goal is to deliver intuitive, attractive, and functional products that drive business success.
1. Describe design process from launch to finish.
Ans:
- Design process begins with understanding the problem through exploration, including request analysis, user interviews, and stakeholder meetings to gather comprehensive perceptivity.
- This is followed by defining the user needs and designing objects easily. Next, move into creativity, where brainstorming and sketching lead to prototype development.
- These prototypes are also tested with the user, incorporating their feedback into iterative design advancements.
- Throughout this process, to ensure nonstop communication with stakeholders and platoon members to align on pretensions and adaptations.
2. How should features be prioritized in a new product?
Ans:
Prioritizing features in a new product involves a structured approach to balance user needs, business pretensions, and specialized feasibility. Start by gathering all possible features through brainstorming sessions with stakeholders and user exploration. Each point is also estimated grounded on its implicit impact on the user experience and its alignment with the design’s pretensions. Use fabrics like MoSCoW( Must have, Should have, Could have, Will not have) or the RICE scoring model( Reach, Impact, Confidence, trouble) to rank features objectively.
3. How is feedback handled when there is disagreement?
Ans:
Addressing feedback with differing viewpoints requires a receptive and constructive mindset. Understanding the feedback thoroughly involves asking clarifying questions and delving into the perspective and rationale behind it. Once the input is acknowledged, it is assessed in the context of user research, design principles, and design goals. This approach ensures that the feedback is meaningfully incorporated into the design process.
4. What is an example of a grueling design project you worked on?
Ans:
By collaborating closely with psychologists, the content was made more impactful. Simultaneously, an iterative design process was employed, incorporating user feedback at each stage to refine the interface for simplicity and accessibility. The app received positive feedback for its user-friendly design and helpful features. This approach significantly enhanced user engagement and contributed to the app’s overall success.
5. How are designs ensured to be accessible to all users?
Ans:
- Ensuring designs are accessible involves adhering to the WCAG( Web Content Availability Guidelines) principles of permeability, exploitability, accessibility, and robustness.
- Use a roster to review designs for color discrepancy, fountain sizes, and button sizes and ensure they are compatible with screen compendiums.
- Also, conduct user testing with individuals who have disabilities to gather direct feedback on availability. Tools like aXe or Wave are also part of my toolkit for automated testing and related issues.
6. Describe a time when a design didn’t go as planned and how it was handled.
Ans:
On a design intended to redesign a web operation, we faced significant detainments due to unlooked-for specialized constraints. Handled this by first reassessing the design timeline and compass with the development platoon to understand what was doable. We also prioritized core functionalities that aligned with user requirements and business pretensions for the original launch, planning to add other features in posterior updates.
7. How does one stay aligned with the latest design trends and technologies?
Ans:
Staying current involves leveraging online resources such as design blogs (e.g., Medium, Smashing Magazine), following industry leaders on social media, and participating in design communities and forums (e.g., Developer Portal, Behance). Attending webinars, workshops, and conferences also helps maintain up-to-date knowledge. Additionally, dedicating time to experimenting with new tools and techniques ensures skills remain sharp and relevant.
8. How does it measure the success of designs?
Ans:
- Depending on the design pretensions, a design’s success can be measured through colorful criteria.
- These might include user engagement criteria ( similar to time spent on the app, conversion rates), usability testing results( error rates, task completion times), and direct user feedback( checks, interviews).
- Also, A/ B testing can give quantitative data on which design variations perform better. Aligning these criteria with the design’s objects from the onset is pivotal for meaningful evaluation.
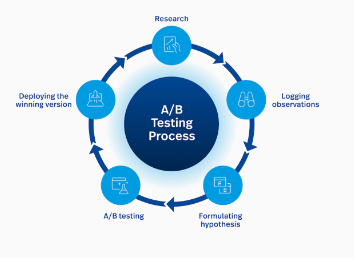
9. Is the product design process the same as the UX design process? Explain the parallels or differences.
Ans:
| Aspect | Product Design | UX Design | |
| Focus and Scope |
Encompasses entire product creation process |
Specifically focuses on enhancing user experience | |
| User-Centric Approach | Balances user needs with business goals and constraints | Prioritizes user needs and goals throughout the process | |
| Phases and Methodologies |
Includes research, ideation, prototyping, testing |
Follows similar phases with emphasis on user research | |
| Roles and Responsibilities |
Broader skill set covering various aspects of design, engineering, and management |
Specializes in creating intuitive user experiences and interfaces |
10. What is the most important skill for a product developer and why?
Ans:
Empathy is the most important skill for a product developer. It allows us to truly understand the user we’re designing for, including their requirements, frustrations, and how they interact with the product. Empathy drives user-centered design, ensuring results aren’t just innovative or visually appealing but authentically solve real user problems in a meaningful way. It’s the foundation of creating products that reverberate with the user and succeed in the request.
11. How is designing approached for a new target followership or demographic?
Ans:
Designing for new target followership begins with thorough exploration to understand their actions, requirements, preferences, and challenges. Use a combination of quantitative data and qualitative perceptivity from interviews or ethnographic studies to make comprehensive user personas. These personas guide the design process, ensuring results are acclimatized to the specific followership.
12. Can a time be discussed when introducing something under tight constraints?
Ans:
- On a design with a veritably limited budget and timeline, we demanded to introduce to meet our pretensions.
- Led a brainstorming session with the platoon to identify the core features that would deliver maximum value to the user.
- We decided to borrow a minimalist design approach, fastening on functionality over aesthetics.
- This not only expedited the development process but also redounded in a user-friendly interface. By embracing constraints as a creative challenge, we launched a product that was well-entered for its simplicity and effectiveness.
13. How is the balance between business objectives and user needs maintained in design?
Ans:
Balancing business pretensions and user needs involves understanding and aligning both aspects from the launch of the design process. Begin by defining clear objects with stakeholders and conducting user exploration to uncover user requirements. Throughout the design phase, to ensure that each design decision supports the user’s pretensions while also contributing to the business objects.
14. How is feedback incorporated into the design process?
Ans:
- Incorporating feedback is a pivotal part of my design process. After presenting designs, and collect feedback from users, stakeholders, and platoon members, precisely considering each piece.
- Classify feedback into themes and prioritize them grounded on their impact on user experience and design pretensions.
- This iterative process involves revising designs grounded on feedback, testing them again, and refining them until the feedback indicates that the design meets the user’s requirements and design objects effectively.
15. How is the decision made regarding which tools to use for a design?
Ans:
Selecting design tools depends on factors such as project scope, team preferences, and specific task requirements. Key considerations include functionality, integration capabilities, and effectiveness for wireframing, prototyping, and collaboration. The choice of tools should streamline the design process, enhance team collaboration, and efficiently meet design objectives. The goal is to use tools that align with the project needs and improve overall design efficiency.
16. Which design trend is causing agitation?
Ans:
A frustrating design trend is excessive minimalism, which, despite its clean aesthetic, can create overly sparse interfaces. This trend often prioritizes looks over usability, leading to a lack of detail and challenging navigation. As a result, users may find the product less functional. Minimalism, when taken too far, can negatively impact the user experience. Balancing simplicity with practicality is crucial to avoid these issues.
17. How is compass creep handled in design systems?
Ans:
- Handling compass creep involves clear communication and setting boundaries from the onset of the design.
- When new requests or features arise, estimate them against the design’s original pretensions and constraints, agitating their impact on the timeline and coffers with stakeholders.
- Prioritize features based on their value to the user and design objectives, and delay unnecessary additions to future updates.
- Regular check-ins with stakeholders help manage prospects and ensure the design remains focused and within the compass.
18. What is the approach to creating a user-centric design?
Ans:
Creating a user-centric design starts with deep user exploration to understand the followership’s requirements, preferences, and pain points. This involves interviews, checks, and assaying user data. Also restate this perceptivity into user personas and trip maps to guide the design process. Prototyping and usability testing are critical, allowing for iterative advancements grounded on real user feedback.
19. How is the specialized feasibility of designs ensured?
Ans:
Ensuring specialized feasibility starts with close collaboration with engineering brigades beforehand in the design process. To maintain open communication channels to discuss constraints and possibilities and explore innovative results together. Knowledge of the technology mound and understanding of introductory coding principles help me produce designs that are both ambitious and attainable.
20. Can a design be described where the design-allowing methodology was applied?
Ans:
- In a design aimed at enhancing the digital experience for a retail app, applied design, allowing methodology to understand user requirements and challenges deeply.
- Empathizing with the user through interviews and observation, we defined crucial pain points in their shopping trip. Creativity sessions generated multitudinous results, which we prototyped and tested with the user, leading to wise feedback.
- This iterative process of testing and refinement, embedded in empathy, allowed us to develop a more intuitive and pleasurable shopping experience, significantly adding user satisfaction and engagement.
21. How are design skills kept sharp?
Ans:
Design skills are honed through continuous learning and practice. Staying current with industry trends ensures relevance. Feedback from peers and mentors provides valuable insights. Active participation in design communities fosters growth. Exploring new tools and techniques keeps the approach fresh. Regularly challenging oneself with new design projects enhances creativity and problem-solving abilities, ensuring continuous improvement.
22. How has data been used to inform design opinions?
Ans:
User data analysis, including heat maps and click-through rates, guided our navigation redesign. The focus was on simplifying user journeys and enhancing accessibility to popular sections. A/B testing validated improved engagement and reduced bounce rates. This data-driven strategy led to a more intuitive user experience. As a result, the redesign effectively met user needs while boosting overall satisfaction.
23. How is a point approached when designing a product?
Ans:
Designing a point for a living product starts with understanding the product’s core value proposition and how this new point will enhance or round it. Conduct user exploration to identify requirements that the end will address, dissect how analogous features work in competitive products, and assess the specialized feasibility with the development platoon. Integrating the point seamlessly into the user experience is pivotal.
24. What role does psychology play in the design process?
Ans:
- Psychology plays an important part in my design process, as understanding mortal geste is crucial to creating intuitive and effective designs.
- Principles from psychology help inform opinions about color, shape, and layout to evoke specific feelings and conduct from users.
- For illustration, understanding cognitive cargo proposition influences how structure information to avoid inviting users.
- Applying cerebral principles about how memory works helps design navigation and interfaces that are easy for users to understand and use.
25. How is design review handled?
Ans:
Design reviews evaluate designs against user needs, project goals, and usability standards. Stakeholders provide feedback on various design elements, identifying areas for improvement. This input is used to make necessary adjustments, refining the design. The review process ensures that the final product aligns with objectives and maintains high-quality standards, ultimately delivering a better user experience.
26. How would a living product be redesigned to enhance its user experience?
Ans:
- Redesigning a living product to facilitate its user experience starts with identifying the areas that need improvement through user feedback, usability testing, and operation data assaying.
- Understanding the user’s pain points, requirements, and actions is pivotal. Would also prioritize the issues grounded on their impact on the user experience and the product’s pretensions.
- Iterative design plays a crucial part, involving creating wireframes and prototypes for the bettered features and testing these with the user.
- This process helps in validating the design changes and ensuring they effectively address the user’s requirements.
27. How is sustainability incorporated into the design process?
Ans:
Incorporating sustainability into the design process involves considering the environmental impact of the product throughout its lifecycle. This can include opting for eco-friendly accouterments, designing for continuity to extend product life, and ensuring the product or its factors can be fluently reclaimed or repurposed at the end of their life. For digital products, sustainability might involve optimizing energy consumption or reducing digital waste.
28. Describe a time when you had to design under significant constraints, similar to time, budget, or coffers.
Ans:
Designing under significant constraints was particularly grueling during a design with a tight deadline and limited budget for a small incipiency. To attack this, I concentrated on espousing a spare design process, prioritizing core functionalities that would deliver the most value to the user. Uniting nearly with the development platoon, we linked features that could be enforced snappily and efficiently. We also employed design patterns and open-source coffers to save time and costs.
29. How are features prioritized for a new product?
Ans:
Prioritizing new product features begins with gathering and analyzing user requirements, aligning them with business objectives, and assessing overall feasibility. Methods like MoSCoW help rank features by importance and impact. Regular adjustments, informed by continuous user feedback and testing, ensure alignment with both user needs and business goals, allowing the product to evolve effectively over time.
30. Describe a challenge faced in a design project and how it was overcome.
Ans:
- In a recent design design, we faced a significant challenge when user feedback indicated that our original design wasn’t as intuitive as we had believed. The challenge was addressing this issue without delaying the design timeline.
- To overcome this, we conducted rapid-fire prototyping sessions, involving users in the co-creation process to snappily conceit and test new results.
- This approach not only helped us identify a further user-friendly design but also fostered a sense of power and satisfaction among the user group. By being flexible and engaging directly with users, we were able to turn a challenge into an occasion for enhancement.
31. How is thickness ensured in designs across different platforms?
Ans:
Ensuring thickness across different platforms requires a strategic approach to design system development and adherence. Start by establishing a comprehensive design system that includes guidelines for design rudiments such as typography, color schemes, and UI factors. This system is participated across brigades to ensure everyone is on the same runner. Tools like Sketch or Figma, which support design libraries and style attendants, help maintain thickness.
32. How is user feedback incorporated into the iterative design process?
Ans:
Incorporating user feedback into iterative design is pivotal for creating user-centered products. Following the creation of original designs, usability testing sessions are conducted to gather feedback through checks or interviews. This feedback is meticulously analyzed to identify common themes and actionable insights. Based on this analysis, designs undergo iterative improvements until they meet the usability norms, ensuring that the final product is both useful and pleasurable for users.
33. What strategies are used to stay aligned with design trends and technologies?
Ans:
- Staying streamlined with design trends and technologies requires a visionary approach to literacy and community engagement.
- Regularly read design blogs, attend webinars, and share in shops and conferences to gain perceptivity into emerging trends.
- Joining design communities on platforms like LinkedIn or Dribbble provides a space for swapping ideas and staying connected with what is passing in the assiduity.
- Experimenting with new tools and methods on specific systems allows for practical application of learned skills, ensuring that expertise remains current and relevant.
34. How are disagreements with stakeholders on design opinions handled?
Ans:
Handling disputes with stakeholders involves open communication, empathy, and evidence-based discussions. Begin by listening to their concerns to understand their perspective and acknowledging the validity of their points. Present design opinions supported by data, such as user research findings, usability test results, and design best practices. Offering alternatives and engaging in negotiations can also be effective.
35. How is designing for availability approached?
Ans:
Designing for availability is an aspect of my design process, ensuring that products are usable by as numerous people as possible, including those with disabilities. This approach starts with understanding the different requirements of the user, including visual, motor, auditory, and cognitive disabilities. Follow established guidelines, similar to the WCAG( Web Content Availability Guidelines), to produce designs that feed these requirements. Ways include:
- Using sufficient color discrepancy.
- Furnishing indispensable textbooks for images.
- Ensuring keyboard navigability.
- Designing screen compendiums.
36. How is the balance between invention and usability maintained in design?
Ans:
- Balancing invention with usability involves creating designs that are both forward-allowing and predicated on user-friendly principles.
- The approach begins with a solid understanding of the user’s requirements and actions, ensuring that innovative features solve real problems or meaningfully enhance the user experience.
- Prototype and test creative ideas beforehand and frequently, gathering user feedback to upgrade and acclimate.
- While exploring new design generalities, I maintain a focus on intuitive navigation and commerce patterns to ensure that users find the product approachable and easy to use.
37. What is the process for testing and validating design opinions?
Ans:
Testing and validating design opinions is a critical part of my design process, ensuring that designs meet user requirements and business pretensions effectively. This process involves several stages, starting with user exploration to inform original design opinions. As designs take shape, use a variety of styles to test and validate these opinions, including usability testing, A/ B testing, and user feedback sessions.
38. How is design approached with scalability in mind?
Ans:
- Designing with scalability in mind means creating designs that can grow and evolve without losing integrity or usability. This involves anticipating unborn requirements and expansion possibilities from the onset.
- Use a modular design approach, creating applicable factors and patterns that can be fluently acclimated or expanded.
- Establishing a strong and flexible design system is pivotal, as it provides a cohesive frame that can accommodate new features or content without taking a complete redesign.
- Regularly reconsidering and streamlining the design system ensures that it remains applicable and probative of the product’s growth.
39. How is user data and sequestration handled in the design process?
Ans:
Handling user data and sequestration is a critical responsibility in the design process, highlighting the importance of designing for trust and transparency. This approach involves being aware of the data collected and ensuring it is necessary for functionality or enhancing the user experience. Incorporating sequestration-by-design principles means considering data protection at every stage of the design and development process.
40. How do you approach designing a product for a global request?
Ans:
Designing for a global request requires a deep understanding of artistic nuances, language differences, and original user actions. My approach involves conducting expansive exploration to understand the specific requirements and preferences of users in different regions. This includes not only verbal restatements but also conforming colors, icons, and imagery to be culturally applicable and reverberative.
41. How do you stay creative and inspired in your work?
Ans:
Staying creative and inspired in my work involves constantly seeking new sources of alleviation and grueling myself to think outside the box. I make it a habit to explore different fields beyond traditional design, such as art, technology, nature, and psychology, to find fresh perspectives and ideas. Sharing in design communities, attending shops, and engaging in creative exercises also stimulates my creativity.
42. Describe your process for uniting with other brigades, similar to engineering or marketing.
Ans:
- Effective collaboration with cross-functional brigades is essential for successful product design. My process starts with clear communication, setting common pretensions, and understanding each platoon’s perspectives and constraints.
- Regular, structured meetings ensure ongoing dialogue while participating tools and documents grease transparent design shadowing. I involve crucial stakeholders beforehand in the design process, soliciting feedback and ensuring alignment.
- This cooperative approach helps identify implicit issues beforehand, allowing for smoother duplications and advances.
- Respect for different moxie and open-mindedness to feedback foster a positive working environment and lead to further holistic and effective design results.
43. How do you approach designing a product from scratch?
Ans:
Designing a product from scratch is an instigative challenge that requires a structured yet flexible approach. Originally, I concentrated on understanding the target user deeply through exploration, interviews, and request analysis, defining the core problem the product aims to break. From there, I develop user personas and scripts to guide the design process. Creativity sessions help in brainstorming implicit results, which are also prototyped and tested with users to gather feedback.
44. How do you ensure your design results are doable and within budget constraints?
Ans:
Ensuring design results are doable and within budget involves close collaboration with the engineering and finance brigades from the onset. Beforehand, in the design process, I discuss specialized constraints and popular limits to understand what’s attainable. Regular check-ins with these brigades as the design evolve help identify implicit issues beforehand, allowing for adaptations before too important time or coffers are invested.
45. How do you measure the success of your design results?
Ans:
- Measuring the success of design results involves setting clear, measurable objects at the launch of the design.
- These might include specific criteria related to user engagement, satisfaction, conversion rates, or usability advancements.
- I use a blend of quantitative data from analytics and qualitative feedback from user interviews and usability testing to assess performance against these objects.
- Reviewing these criteria regularly post-launch provides insight into the design’s impact and areas for enhancement.
46. How are tight deadlines and high-pressure situations handled in systems?
Ans:
Handling tight deadlines and high-pressure situations requires effective time operation, prioritization, and communication chops. Start by breaking down the design into manageable tasks and setting realistic mileposts, fastening on the most critical aspects of the design that will have the biggest impact. Communicating easily with stakeholders about what can be achieved within the given timeframe helps manage prospects.
47. How do you incorporate sustainability into your design process?
Ans:
Incorporating sustainability into the design process involves deliberate efforts to minimize environmental impact while meeting user needs. It starts with choosing eco-friendly or recycled materials whenever possible. The entire product lifecycle is considered during the design phase, focusing on durability and waste reduction. Sustainable practices are integrated at each step, from material selection to final production. The goal is to create designs that are both user-centric and environmentally responsible.
48. How do you approach conflict resolution within a design platoon?
Ans:
- Conflict resolution within a design platoon is vital for maintaining a cooperative and innovative environment.
- My approach is first to understand the perspectives of all parties involved, easing a discussion where each member can express their views without judgment.
- It’s important to concentrate on the problem, not the individualities, relating to the root cause of the conflict.
- Ensuring that all voices are heard and considering concession where necessary helps in chancing a resolution that aligns with the platoon’s pretensions.
49. How do you design for different user personas within the same product?
Ans:
Designing for different user personas within the same product requires a deep understanding of each persona’s requirements, actions, and pretensions. This begins with comprehensive user exploration to produce detailed personas representing the product’s different user base. During the design process, I ensure that features and functionalities feed the specific requirements of these personas, frequently through customizable or adaptive interfaces that allow the user to knitter their experience.
50. How are rapid changes in design tools and technology kept up with?
Ans:
- Keeping up with rapid-fire changes in design tools and technology requires a visionary approach to literacy and rigidity. Allocate time each week to explore new tools, read up on recent tech trends, and experiment with new software.
- Participating in online forums, attending shops, and joining webinars are great ways to learn from peers and experts. Also use social media and professional networks to share knowledge and keenness with the design community.
- Embracing a mindset of nonstop enhancement and being open to change helps me integrate new tools and technologies into my workflow, ensuring that my designs remain innovative and effective.
51. Describe your experience with user testing and feedback collection.
Ans:
- My experience with user testing and feedback collection has taught me the significance of empathy and observation in the design process. I use various styles, including interviews, checks, and usability testing, to gather users’ perceptions.
- Creating a safe and open terrain where the user feels comfortable sharing their honest opinions is crucial. I pay close attention to not only what users say but also their actions and nonverbal cues during testing sessions. This data is also anatomized to identify patterns and practicable perceptivity.
- Incorporating this feedback iteratively into the design process ensures that the final product truly resonates with the user and effectively meets their requirements.
52. How are user requirements balanced with business objectives in designs?
Ans:
Balancing user needs with business objects requires a strategic approach to ensure that designs contribute to both satisfying user gests and achieving business pretensions. Start by easily understanding the business objects and how they align with user requirements. This involves close collaboration with stakeholders to define crucial performance pointers( KPIs) that reflect both user satisfaction and business success.
53. How do you ensure the design aligns with the brand’s identity and values?
Ans:
Ensuring design alignment with a brand’s identity and values starts with a deep dive into the brand itself, understanding its charge, vision, core values, and the emotional connection it seeks to establish with its followership. This foundation informs every design decision, from color schemes and typography to the voice and tone used in UI dupe. I unite nearly with brand brigades to ensure thickness and unity across all touchpoints, creating a flawless brand experience.
54. How do you handle feedback that contradicts your design vision?
Ans:
- Handling antithetical feedback is a delicate balance between defending your design vision and being open to new perspectives. I approach similar feedback as an occasion for growth and literacy.
- Originally, I sought to understand the beginning reasons and enterprises behind the feedback, asking clarifying questions to grasp the complete picture.
- It’s important to assess the feedback objectively, considering the user’s requirements and the design’s pretensions.
- Occasionally, integrating this feedback can lead to innovative results that align with the design vision while also addressing the enterprises raised.
55. What strategies do you use to reduce cognitive cargo in your designs?
Ans:
Reducing cognitive cargo is pivotal for creating user-friendly designs that enhance usability and satisfaction. My strategies include minimizing visual clutter by using clean, simple layouts that concentrate the user’s attention on the most important rudiments. I work on common design patterns and conventions to reduce the literacy wind and make interfaces intuitive. Harmonious use of color, typography, and visual scales helps users navigate and understand content fluently.
56. How do you stay informed about your users’ evolving requirements?
Ans:
Staying informed about users’ evolving requirements requires a visionary and nonstop approach to user exploration and feedback collection. I conduct regular user interviews, checks, and usability testing sessions to gather perceptivity into users’ actions, preferences, and pain points. Keeping an eye on request trends and competitive products also provides an environment on how user prospects are changing.
57. How is error prevention and handling approached in design?
Ans:
- Error prevention and usability are integral to creating flexible and user-friendly designs. The approach focuses on minimizing opportunities for user errors through intuitive design and clear instructions.
- This includes using form attestations and suggestions to help crimes before they are and designing clear paths for users to recover from miscalculations.
- Error dispatches are drafted to be helpful and formative, guiding the user to resolve their issues without frustration. Testing designs with real users help identify common risks and areas for enhancement in error forestallment and running.
- By prioritizing a smooth, forgiving user experience, the design helps make users confidence and satisfaction.
58. How do you ensure availability is integrated into your design process?
Ans:
Integrating availability into the design process is non-negotiable for creating inclusive products. From the onset, I incorporate availability guidelines and principles, similar to the Web Content Availability Guidelines( WCAG), into my design norms. This involves designing for colorful user requirements, including visual, auditory, motor, and cognitive impairments, by enforcing features like keyboard navigation, screen anthology comity, and sufficient color discrepancy.
59. Describe your approach to designing for a global followership.
Ans:
Designing for global followership requires a deep understanding of artistic nuances, language differences, and indigenous user actions. My approach begins with expansive exploration to gather perceptivity into the specific requirements and preferences of users in different regions. This includes considerations for localization, similar to textbook expansion, right-to-left language support, and culturally applicable content.
60. How do you ensure your design opinions are driven by user exploration?
Ans:
Ensuring design opinions are driven by user exploration requires a structured approach to integrating exploration findings into the design process. I start by defining clear exploration objects aligned with the design pretensions and gather perceptivity through colorful styles, similar to interviews, checks, and usability testing. Synthesizing this data into practicable perceptivity, I produce user personas, trip charts, and use cases that guide the design process.
61. How is A/B testing used in the design process?
Ans:
- A/ B testing is a vital tool in my design process for making data-driven opinions and continuously perfecting user experience. This approach involves creating two performances of a design element( A and B) and testing them with parts of the user base to see which performs better against predefined criteria. Start by relating a specific thing or question, similar to perfecting click-through rates or reducing drop-off rates.
- After planting both performances, collect and dissect user commerce data to determine which interpretation more effectively achieves the ideal. This system allows me to reiterate designs grounded in factual user behavior, removing guesswork and enhancing the product’s usability and effectiveness.
62. How do you approach designing for voice interfaces?
Ans:
Designing for voice interfaces involves moving away from visual design principles to emphasize natural language processing, conversation flow, and audible feedback. The process starts with analyzing the environment where the voice interface will be used, including user context, tasks, and goals. Creating personas and scripts is essential to anticipate user needs and ensure that interactions feel natural and intuitive. This approach ensures the design aligns with user expectations and enhances the overall experience.
63. What part does a liar play in your design process?
Ans:
Storytelling plays a critical part in my design process by furnishing a frame that connects the user emotionally and intellectually with the product. It starts with understanding the user’s trip and relating crucial touchpoints where the product can make a significant impact. Through liars, I convey the product’s value proposition in a way that resonates with the user, casting scripts that illustrate how the product solves real problems or enhances their lives.
64. How do you manage clashing feedback from stakeholders?
Ans:
- Managing clashing feedback from stakeholders involves careful concession and agreement- structure. Originally, I ensured that all feedback was heard and conceded, validating the enterprises behind differing shoes.
- By referring back to the design’s pretensions and user exploration, I can give a predicated perspective that aligns feedback with the user’s requirements and design objects.
- Easing shops or conversations where stakeholders can collaboratively review feedback and its counteraccusations helps identify common ground and prioritize conduct.
- Occasionally, it may involve compromising or chancing innovative results that address the enterprises of multiple stakeholders.
65. How do you handle design review?
Ans:
Handling design reviews constructively is crucial for personal and professional design growth. Approaching reviews with an open mind allows for gaining diverse perspectives and improving the work. Listening carefully helps understand core concerns or suggestions fully. It’s important to distinguish between personal preferences and constructive feedback. This thoughtful approach ensures that feedback enhances the design’s overall effectiveness.
66. How do you ensure your designs are both innovative and user-friendly?
Ans:
- Balancing invention with user- benevolence is critical to design success.
- To achieve this, I begin by inventing based on a deep understanding of user requirements and actions, ensuring that any new conception addresses real problems or meaningfully enhances the user experience.
- Inventions are prototyped beforehand and tested with the user to assess their usability and effectiveness.
- Feedback circles are pivotal, allowing for the refinement of innovative ideas to ensure they’re intuitive and accessible. I also consider the literacy wind associated with new features, furnishing guidance, and support to ease relinquishment.
67. How can the challenge of redesigning a well-loved product be navigated?
Ans:
Redesigning a well-loved product presents a unique set of challenges, primarily conserving the substance that users love while streamlining it to meet new requirements or norms. My approach starts with a thorough exploration to understand what users value most about the product. Engaging with the community through checks, interviews, and beta testing helps gather perceptivity into asked advancements without losing core features.
68. What styles do you use for conducting effective user exploration?
Ans:
For effective user exploration, I employ a blend of qualitative and quantitative styles to gain a comprehensive understanding of user actions, requirements, and provocations. Qualitative styles include user interviews, focus groups, and ethnographic studies, which give deep perceptivity into user stations and guests. Quantitative styles, similar to checks, usability tests, and analytics, offer data-driven perceptivity in terms of user actions and patterns at scale.
69. What are crucial performance pointers( KPIs) you consider in product design?
Ans:
In product design, KPIs must reflect both user engagement and business pretensions to measure success effectively. Common KPIs include user satisfaction scores, similar to the Net Protagonist Score( NPS), which gauges the liability of users who recommend the product. Usability criteria, like task success rate and time-on-task, are pivotal for understanding how fluently a user can navigate and use the product. Conversion rates indicate how well the design facilitates user conduct, which is precious to the business.
70. Which design tools are you most complete with, and why do you prefer them?
Ans:
- I am most proficient in Sketch, Adobe XD, and Figma for UI/ UX design due to their cooperative features, effectiveness, and comprehensive design capabilities.
- Sketch is an important tool for high-dedication design and prototyping, with a vast library of plugins that extend its functionality.
- Adobe XD is preferred for its flawless integration with other Adobe Creative Cloud apps, making it ideal for contrivers who also work with plates, videotapes, or vitality.
- Figma stands out for its real-time collaboration features, which allow entire brigades to work on a design contemporaneously. This is invaluable for remote brigades and fast-paced systems.
71. How effective is the navigation flow of a specific app?
Ans:
Assaying an app’s navigation inflow involves assessing its intuitiveness, effectiveness, and alignment with user prospects. An effective navigation inflow should allow the user to achieve their pretensions with minimum trouble and confusion. This involves clear labeling, a logical structure, and thickness across the app. For illustration, if we examine Spotify’s navigation inflow, its effectiveness lies in its simple, intuitive interface that allows user to snappily find new music, pierce their playlists, and explore podcasts with minimum gates.
72. How do you estimate the usability and availability of a product?
Ans:
Assessing the usability and availability of a product involves a combination of user testing, heuristic evaluations, and compliance checks against established guidelines like the Web Content Availability Guidelines( WCAG). Usability testing with a different group of users helps identify specific commerce problems and areas of confusion. Heuristic evaluations by UX experts can uncover usability issues grounded on established principles.
73. What are the strengths and sins of the design in a recent tech product release?
Ans:
- Taking the release of the iPhone 12 as an illustration, a crucial strength in its design is the return to a flat-edge design, which not only differentiates it from former models but also improves grip and aesthetics, listening back to the cherished design of the iPhone 4 and 5.
- The preface of the Ceramic Shield technology significantly enhances continuity, addressing user enterprises about screen damage.
- Still, an implicit weakness lies in the decision no longer to include power appendages and earbuds with the phone.
- While this move is environmentally friendly, consumers have responded with mixed feelings.
74. Describe a product redesign you respect and explain why it was successful.
Ans:
One product redesign I respect is Airbnb’s website and mobile app redesign in 2014, which introduced the” Bélo” symbol, representing belonging. This redesign was successful because it went beyond aesthetic updates; it bettered usability and nautical structure, making it easier for users to discover and bespeak stays. The preface of the symbol unified the brand across different platforms, creating a strong visual identity.
75. What’s your approach to critiquing the work of fellow contrivers?
Ans:
When critiquing the work of fellow contrivers, I approach it with empathy and constructiveness, fastening on specific aspects rather than general prints. I start by pressing strengths to foster a positive atmosphere. Also, I offer formative feedback on areas for enhancement, furnishing concrete exemplifications and suggestions. It’s important to frame reviews in a way that encourages dialogue, asking questions that prompt the developer to reflect on their choices.
76. How do you separate between private opinions and formative review in design?
Ans:
- Separating private opinions from formative review in design involves enforcing the explanation behind feedback and aligning it with design principles and objects.
- Private opinions frequently reflect particular preferences without considering the design’s pretensions or user requirements.
- In discrepancy, formative review is predicated on design fundamentals, user exploration, and specific design conditions. It offers practicable perceptivity that can facilitate the design’s effectiveness.
- To navigate this, I always ask for the logic behind feedback and consider whether it helps achieve the design’s objectives, enhances usability, or addresses user needs.
77. Still, how would you respond, and what would you do?
Ans:
Suppose a customer rejects your design. However, I would first seek to understand their enterprises and specific reasons for rejection if a customer rejects my design. This involves asking questions to clarify their feedback and identify any misalignments between their prospects and the design. I would approach this discussion with openness and without guard, as understanding their perspective is pivotal for moving forward.
78. still, how would you approach it?
Ans:
Suppose you had to tutor an interior designer. Mentoring an inferior developer would involve a balance of guidance, support, and commission. I would start by understanding their strengths, sins, and career bournes to knitter my mentorship approach. Setting clear, attainable pretensions and furnishing regular, formative feedback on their work would be pivotal. I’d encourage them to take on a variety of systems to broaden their chops and experience.
79. Describe a time when you had to balance multiple design systems contemporaneously.
Ans:
- Balancing multiple design systems contemporaneously needed strong organizational and time operation chops. In one particularly busy period, I started by easily outlining the compass, deadlines, and precedences for each design.
- I used design operation tools to keep track of tasks and mileposts, ensuring I allocated my time efficiently.
- Communication with stakeholders was crucial; I handed regular updates and acclimated prospects as demanded. I also abused the strengths of my platoon, delegating tasks where applicable.
- Staying flexible and set to reprioritize grounded on shifting deadlines or critical requests was pivotal. Despite the challenges, this approach helped me maintain the quality of work across systems and meet all deadlines.
80. Describe a time when you had to make a design decision grounded on data rather than suspicion.
Ans:
In a design aimed at adding the conversion rate for an e-commerce point, data analysis revealed that user were abandoning their wagons at the shipping options stage. Despite my suspicion that a redesign of the Wain runner might help, the data refocused on the need for clearer communication of shipping costs and delivery times. Acting on this, I redesigned the shipping options section to include further transparent information and a simplified selection process. This data-driven decision resulted in a significant drop in wain abandonment rates.
81. Mention some of the crucial challenges involved in the work of a product developer.
Ans:
Product contrivers face several crucial challenges, including staying streamlined with evolving design trends and technologies, which is essential for creating innovative and applicable products. Balancing user needs with business objects requires skillful concession and prioritization to ensure a feasible product that satisfies both. Understanding and designing for a different user base presents another challenge: challenging inclusive design practices to feed different capacities, societies, and backgrounds.
82. Explain HCD( Human- Centered Design) approach.
Ans:
- Mortal—Mortal-centered design ( HCD) is an approach to problem-solving that focuses on understanding people’s requirements, actions, and behaviors to produce results that truly meet their conditions.
- This process involves three main phases: alleviation, where contrivers immerse themselves in the user’s terrain to gather perceptivity; creativity, where this perceptivity is converted into innovative ideas and prototypes; and perpetration, where results are meliorated and brought to life.
- HCD prioritizes direct engagement with users through exploration and testing, ensuring that the final product isn’t only usable and accessible but also meaningful and precious to its intended followership.
83. Explain how you make websites and apps accessible to persons with disabilities.
Ans:
Making websites and apps accessible involves clinging to principles and guidelines similar to the Web Content Availability Guidelines( WCAG) to ensure that everyone, including people with disabilities, can use digital products. This includes furnishing textbook druthers for text content, ensuring keyboard navigability for those who can not use a mouse, and creating content that can be presented in different ways without losing information.
84. What are some of the most important rudiments of product design?
Ans:
The most important rudiments of product design include understanding user needs through thorough exploration, which is abecedarian to creating products that give real value. Functionality ensures that the product performs its willed tasks efficiently and effectively. Usability focuses on making products easy and intuitive to use, enhancing the overall user experience. Aesthetics involve the visual, tactile, and overall sensitive design of the product, which significantly affects user perception and product advisability.
85. What’s your process for testing a new product design?
Ans:
- Testing a new product design involves a structured process that begins with defining clear objects grounded in the product’s pretensions and user requirements.
- I then start with usability testing, involving the target user in interacting with prototypes and giving feedback on the design’s intuitiveness and experience.
- Performance testing assesses the product’s functionality and effectiveness under colorful conditions. Availability evaluations ensure the product is usable by people with a wide range of capacities.
- A/ B testing compares different design performances to determine which performs better against specified criteria.
86. Which software programs do you use most frequently in your job?
Ans:
A range of software programs is utilized to address various aspects of the design process. Figma excels with its collaborative features, allowing real-time teamwork on design systems. Adobe Creative Suite, especially Photoshop and Illustrator, is crucial for high-quality illustrations and image manipulation. Sketch is also a key tool for interface design, valued for its simplicity and efficiency. Each tool plays a specific role in enhancing different design facets.
87. How often should product designs be updated to stay fresh?
Ans:
The frequency of streamlining product designs depends on factors such as user feedback, market trends, and technological advancements. Minor updates and optimizations are performed continuously based on user testing and analytics. Major redesigns, however, are less frequent and usually driven by significant changes in user needs, competitive landscape, or brand strategy. These major updates ensure the product remains relevant and aligned with evolving objectives.
88. What’s the difference between UX and product design?
Ans:
- UX( user experience) design and product design are closely affiliated fields, but they concentrate on different aspects of the product development process.
- UX design is primarily concerned with the overall experience of a user when interacting with a product.
- It focuses on usability, availability, and the trip users go through, aiming to produce flawless and satisfying commerce.
- Product design, on the other hand, encompasses the broader compass of bringing a product from idea to vend, which includes UX but also involves considering business pretensions, request exploration, product strategy, branding, and functionality.
89. What’s the thing about product design?
Ans:
The goal of product design is to deliver solutions that address user needs and solve specific problems effectively, efficiently, and aesthetically, while aligning with business objectives. This process involves understanding user behaviors, preferences, and challenges through exploration and testing. Insights gained are translated into tangible products that meet user expectations and business goals. The design must balance functionality, user experience, and visual appeal to create impactful solutions.
90. Is Figma used for product design?
Ans:
Yes, Figma is widely used for product design due to its powerful and flexible toolset that supports the entire design process, from ideation to prototyping. Its cloud-based platform enables real-time collaboration among team members, making it ideal for teams working remotely or across different locations. Figma offers a comprehensive range of features, including vector graphic editing, prototyping capabilities, and design systems management. This versatility and collaborative functionality make it a top choice for modern design teams.






