
A software architect is a senior-level professional who plays a pivotal role in the design and development of software systems. They are responsible for creating high-level architectural designs that guide the implementation of complex software solutions, ensuring that they meet business requirements, technical specifications, and industry standards. Software architects leverage their expertise in programming languages, frameworks, and system architectures to make informed decisions on technology, design, and development methodologies.
1. What experience exists in designing software systems for scalability?
Ans:
When designing software systems for scalability, aspects including load balancing, distributed computing, horizontal and vertical scaling, caching techniques, and data partitioning are frequently taken into account. Choosing suitable technologies and architectural patterns, weighing the trade-offs between these variables, and creating systems that can withstand growing loads without sacrificing availability and performance are all part of my experience.
2. What is the role of a software architect throughout the software development lifecycle?
Ans:
During the planning stage, architects work with stakeholders to establish the goals, constraints, and scope of the project. Subsequently, they steer the process of design and development by converting functional requirements into appropriate technologies and architectural frameworks. Architects oversee development projects to guarantee that standards, best practices, and architectural principles are followed.
3. How is alignment with business requirements ensured in architectural proposals?
Ans:
- Criteria analysis: To make sure that the suggested architecture successfully satisfies these criteria, architects work closely with stakeholders to comprehend corporate objectives, user demands, and functional requirements.
- Alignment with Strategic Objectives: Architects consider aspects like time to market, cost-effectiveness, adaptability, and scalability to match the architecture with the organization’s strategic objectives.
- Constant Communication: Throughout the development process, architects keep the lines of communication open with stakeholders, asking for input, verifying presumptions, and making necessary adjustments to the design to guarantee alignment with changing business priorities.
- Business Value Assessment: To efficiently prioritize projects and distribute resources, architects evaluate the business value of architectural decisions by taking into account variables including ROI, TCO, risk reduction, and competitive advantage.
4. What methods are used to identify and evaluate system requirements?
Ans:
- Stakeholder analysis: Identify and interact with important parties, such as business users, subject matter experts, and technical teams, to determine their needs and priorities.
- Requirement Gathering: To ensure thorough coverage of functional, non-functional, and technical requirements, conduct workshops, interviews, surveys, and observations to gather requirements from stakeholders.
- Prioritization and Validation: Set requirements in order of significance for business objectives, practicality, and system impact.
- Documentation: To aid in communication, traceability, and management throughout the development lifecycle, document requirements methodically using defined forms, such as user stories, use cases, or requirement specifications.
5. What is different between ensuring architectural integrity and selecting technologies.
Ans:
| Aspect | Ensuring Architectural Integrity | Selecting Technologies |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Ensures that the architectural design follows best practices, industry standards, and organizational guidelines, promoting consistency, modularity, and flexibility. | Focuses on evaluating and choosing appropriate technologies, frameworks, and tools to implement various aspects of the software solution, considering factors such as scalability, performance, and security. |
| Concerns | Emphasizes the overall structure and organization of the software system, including components, modules, interfaces, and interactions, to meet project requirements and goals. | Primarily addresses the technical aspects of the implementation, including programming languages, databases, development frameworks, and third-party libraries, to support the architectural design. |
| Involves | Involves reviewing architectural diagrams, design documents, and codebase to ensure adherence to architectural principles and identifying any deviations or inconsistencies. | Involves researching, evaluating, and comparing different technologies, conducting proof-of-concepts, and analyzing trade-offs to make informed decisions about technology selection. |
| Long-term Implications | Affects the overall maintainability, scalability, and extensibility of the software system by establishing a solid foundation for future development and evolution. | Affects the immediate implementation and deployment of the software solution, influencing factors such as development time, performance, and compatibility with existing systems. |
6. How are technical necessities balanced with business constraints in architecture decisions?
Ans:
Gain a solid awareness of the requirements, limitations, and objectives of the business. Examine different technical strategies that might satisfy these requirements and weigh the risks of each option. To balance the benefits and drawbacks against the constraints of your firm, do a cost-benefit analysis. Throughout the process, keep lines of communication open between technical teams and stakeholders.
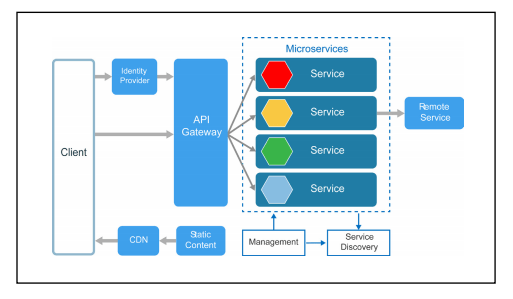
7. What involvement is there with designing microservices architectures?
Ans:
Gathering involves understanding domain boundaries, scalability, and system needs with stakeholders. Decomposition identifies components for microservices, ensuring clear boundaries and choosing appropriate communication protocols like message queues, gRPC, or REST. Designing for resilience includes circuit breakers and retries, while logging and monitoring ensure visibility. Planning deployment strategies such as canary releases or blue-green deployments helps minimize downtime and risk.
8. How are security and compliance prioritized in software architectures?
Ans:
- Risk Assessment: Carry out a comprehensive risk assessment to determine any security risks and compliance needs pertinent to the application domain.
- Security by Design: Rather than approaching security as an afterthought, incorporate it into the architecture from the beginning. This covers ideas such as data encryption, defense in depth, and least privilege.
- Compliance Frameworks: Make sure that the design complies with all applicable regulatory standards by adhering to pertinent compliance frameworks like GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS.
- Data protection: To safeguard data while it’s in transit and at rest, use techniques like tokenization, encryption, or anonymization.
9. What process is followed for evaluating and selecting technology stacks for projects?
Ans:
- Evaluating Needs: Recognize the particular needs of the project for compatibility, security, scalability, performance, and functionality.
- Research: Look into the frameworks and technologies that are out there and match the needs of the project in detail. Think about elements like documentation, ecosystem, maturity, and community support.
- Proof of Concept (PoC): Create a prototype or proof of concept utilizing a few chosen technologies to assess each one’s feasibility for the project. This enables practical testing and the verification of important presumptions.
- Flexibility and Scalability: Evaluate how well the technological stack can grow and adapt to meet changing business requirements in the future.
- Vendor Lock-in: Take vendor lock-in into account and choose technologies that provide portability and interoperability.
- Team Expertise: Assess the development team’s proficiency and knowledge of the selected
10. How is familiarity with cloud-native architecture and deployment strategies demonstrated?
Ans:
- Containerization: Utilize technologies like Docker to bundle dependencies and applications into portable, lightweight containers.
- Orchestration: To automate the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications, make use of container orchestration systems such as Kubernetes.
- Microservices: To encourage scalability, flexibility, and resilience, design applications as a group of loosely linked microservices, each operating in a separate container.
- Immutable Infrastructure: Replace rather than alter infrastructure components, seeing them as disposable, by adopting an immutable infrastructure strategy.
- DevOps Practices: Use DevOps techniques to improve communication between the development and operations teams, facilitating automated testing, continuous integration, and continuous delivery (CI/CD).
- Serverless Computing: To abstract away infrastructure management and grow automatically based on demand, investigate serverless computing technologies like AWS Lambda or Azure Functions.
11. What measures ensure high availability and fault tolerance in distributed systems?
Ans:
Enhance system reliability by deploying redundant components across multiple servers or data centers. Use load balancing to distribute traffic evenly and prevent overloading. Implement failover mechanisms to redirect traffic during failures and replicate data across nodes for availability and recovery. Design with isolation to prevent failures from affecting other components.
12. How is RESTful API design approached?
Ans:
Design APIs with resource-based endpoints using nouns, adhere to a uniform interface with standard HTTP methods and status codes, and ensure statelessness by including all necessary request information. Implement HATEOAS for client resource discovery, use versioning to manage API evolution, and ensure backward compatibility to support existing users effectively. Additionally, prioritize security and performance to optimize the API’s reliability and user experience.
13. Explain the importance of loose coupling in software architecture and how you implement it.
Ans:
- Abstraction: To enable interchangeable or pluggable implementations, isolate components from concrete implementations using interfaces, abstract classes, and dependency injection.
- Event-Based Communication: Use event-driven designs to reduce direct dependencies between components and to promote flexibility and scalability.
- Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA): This design approach views systems as a group of loosely connected services that interact with one another using standard interfaces.
- Dependency Inversion Principle (DIP): which permits high-level modules to stay independent of low-level details by relying on abstractions rather than specific implementations.
- Componentization: To reduce inter-component dependencies and enable independent development and testing, the system should be broken down into smaller, modular components with clearly defined interfaces and responsibilities.
14. How are data consistency and synchronization challenges addressed in distributed systems?
Ans:
- Replication and Consensus: To guarantee data consistency across replicas, use replication strategies like leader election, consensus algorithms (like Paxos and Raft), and distributed databases with robust consistency models.
- Eventual Consistency: Adopt eventual consistency models, which sacrifice instantaneous consistency in favor of asynchronous data consistency that is attained over time. This approach increases availability and partition tolerance.
- Conflict Resolution: Use techniques like version vectors, last-writer-wins, or application-specific resolution procedures to manage conflicting updates to the same data.
- Transaction Management: To coordinate and synchronize distributed transactions across several data stores or services, use compensation-based techniques or distributed transaction protocols (e.g., 2PC, 3PC).
15. What insights can be shared about event-driven architecture and message queuing systems?
Ans:
To sum up, I have worked with message queuing systems and event-driven architecture (EDA) and have used decoupled communication, message brokers for scalability, microservices integration, asynchronous processing, reliability, fault tolerance, and a variety of EDA patterns. These methods have been crucial in creating loosely linked, scalable, and robust systems that can manage distributed computing issues in the real world.
16. What strategies are employed for optimizing performance in software architecture?
Ans:
- Performance Profiling: Use tools and techniques to identify performance bottlenecks in areas including CPU usage, memory consumption, disk I/O, and network latency.
- Caching: Use caching techniques to increase response times and lower latency by storing computed values, query results, and frequently requested data in distributed caches or memory.
- Optimized Data Structures and Algorithms: Select effective data structures and algorithms suited to certain use cases to reduce memory usage and computational overhead.
- Concurrency and Parallelism: Make use of methods like thread pooling, asynchronous processing, and parallel execution to take advantage of multi-core computers and increase throughput.
- Database optimization: Optimize database queries, indexes, and schema designs to enhance query performance, lower database load, and reduce delay in data retrieval and manipulation processes.
17. How is containerization and orchestration technology utilized?
Ans:
- Containerization: I have packaged apps and their dependencies into small, portable containers using containerization platforms like Docker. Containerization makes consistent development, testing, and deployment across various infrastructure environments possible.
- Orchestration: I have worked with orchestration tools like Kubernetes to automate the deployment, scaling, and administration of containerized apps.
- Microservices Implementation: Technologies such as Containerization and orchestration are excellent for implementing microservices-based architectures.
18. Explain the principles of domain-driven design (DDD) and its application in software architecture
Ans:
To align business needs with software implementation, teams should use a common language. Complex domains should be divided into manageable bounded contexts with unique models. Aggregates and entities ensure consistency and data integrity, while immutable value objects enhance reuse and maintainability. Domain events capture significant changes to support loose coupling and event-driven systems.
19. What process is followed for creating and documenting software architectures?
Ans:
Software architecture involves compiling and analyzing requirements, creating a high-level conceptual design, and refining it into a detailed layout with deployment, data flows, and protocols. Design choices are documented with diagrams and formats, followed by validation through reviews and feedback. The architecture is then continuously evolved and maintained.
20. How are scalability considerations incorporated into architectural designs?
Ans:
- Componentization and Modularity: Divide the system into separate, scalable parts according to workload demands by breaking it down into modular parts with clearly defined interfaces.
- Horizontal Scaling: To accommodate the increasing load, design systems for horizontal scalability. Divide the workload among several instances or nodes and utilize strategies like load balancing, sharding, and partitioning.
- Elasticity: Implement auto-scaling systems that dynamically scale up or down to maintain optimal performance and resource usage. These mechanisms automatically alter resource allocation based on demand.
- Statelessness: To promote horizontal scaling and resilience, design stateless components whenever feasible. Reliance on server-side state can impede scalability and introduce single points of failure.
21. What strategies ensure systems are easily testable and maintainable?
Ans:
First and foremost, I stress the division of responsibilities, guaranteeing that every part serves a specific function and facilitating the isolation and testing of individual parts. Second, because dependency injection makes it simple to swap out components for mocks or stubs, I support its use in managing dependencies and facilitating unit testing. To ensure system functionality and catch regressions early, I recommend implementing automated testing techniques such as unit, integration, and end-to-end tests.
22. How do design patterns impact software architecture?
Ans:
- Design patterns are essential to software architecture because they offer reusable fixes for frequent design issues.
- Architects can enhance the flexibility, scalability, and maintainability of software systems by utilizing design patterns.
- To enable centralized access to common resources, the Singleton design, for instance, makes sure that a class has just one example.
- Because it allows for components to subscribe to and receive notifications about state changes, the Observer pattern facilitates loose coupling between components.
- Additionally, design patterns facilitate cooperation and understanding within development teams by providing a standard language for developers to communicate.
23. How are data privacy and protection concerns addressed in architectural designs?
Ans:
A number of crucial tactics are needed to address data privacy and security issues in architectural designs. To start, I make sure that private information is encrypted while it’s in use and while it’s being sent to avoid unwanted access. I also utilize role-based permissions and access controls to limit authorized users’ access to data. In order to confirm user identities and stop illegal access to private information, I also support the usage of secure authentication methods like OAuth and multi-factor authentication.
24. What experience is there with designing for extensibility and modifiability in software systems?
Ans:
- Anticipating future changes and smoothly adapting to them are key components of software system design for extensibility and modifiability.
- I use a few different approaches to accomplish this. First off, I support the adoption of modular designs, in which pieces are highly cohesive and loosely connected, making it easy to grow or replace them without compromising other system components.
- In addition, I advocate for encapsulating behavioral variants and facilitating dynamic runtime adjustments through the use of design patterns like Strategy and Decorator patterns.
25. How are architectural reviews and validations conducted?
Ans:
First and foremost, I work closely with stakeholders—business users, developers, and operations teams—to get their input and make sure that the technical specifications and business objectives are met. In addition, I compare the suggested design to accepted standards, including scalability, dependability, and security, using best practices and architectural principles. To find potential architectural faults, performance snags, and inconsistent design, I also run in-depth code reviews and inspections.
26. Explain the concept of service-oriented architecture (SOA) and its advantages.
Ans:
- An architectural methodology known as Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) emphasizes the division of software systems into loosely linked, interoperable services.
- Services in Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) are self-contained, modular functional units that interact with one another over common protocols like SOAP or HTTP.
- Better flexibility and agility are two benefits of service-oriented architecture (SOA) since services may be designed, deployed, and scaled independently of other system components.
- Furthermore, because services are easily exchanged and linked across various platforms and applications, SOA encourages reuse and interoperability.
- Because services are meant to encapsulate business logic and expose it as reusable components, SOA also makes it possible to achieve greater alignment with business processes.
27. How is technical debt managed within architecture designs?
Ans:
In architecture designs, managing technical debt requires a number of critical approaches. First off, in order to find and fix technical debt early in the development process, I support proactive debt management techniques like automated testing, code reviews, and frequent refactoring. In addition, I focus on high-priority debt items that present the most danger to the project’s success by ranking technical debt items according to their effect on system quality, stability, and maintainability.
28. What experience is there with cloud migration and hybrid cloud architectures?
Ans:
- There are a number of important factors to take into account while designing for cloud migration and hybrid cloud architecture.
- Taking availability, scalability, and compliance needs into account, I first evaluate the current system’s suitability for cloud deployment.
- Along with that, I identify workloads and services that may be migrated to the cloud, giving priority to those that have the greatest potential to save money and perform better.
- Additionally, in order to properly take advantage of the scalability and agility of cloud platforms, I design for cloud-native concepts like serverless computing, microservices, and containers.
- Utilizing established protocols and APIs to facilitate communication between cloud-based and on-premises components is another way I handle data integration and interoperability issues.
29. How are system integration and interoperability challenges approached?
Ans:
Careful thought and preparation are necessary to overcome system integration and interoperability issues and guarantee smooth communication and cooperation amongst heterogeneous systems. My strategy for overcoming these obstacles consists of multiple crucial actions. First, I determine the needs for system integration and its dependencies, taking into account both functional and non-functional elements such as data formats, protocols, and performance standards.
30. Explain the concept of polyglot persistence and its relevance in modern architecture.
Ans:
- A design strategy known as polyglot persistence promotes the use of several database technologies in a single application to store various kinds of data based on their unique needs.
- Polyglot persistence has multiple benefits in modern architectures, where programs frequently have to handle a variety of data types and access methods.
- First of all, it gives developers the ability to choose the best database technology for any use case, maximizing data consistency, scalability, and performance.
- Furthermore, polyglot persistence encourages agility and adaptability, releasing programs from the confines of a single database technology to develop and adjust to changing needs.
31. How is compliance with industry standards and regulations ensured in architectural designs?
Ans:
To ensure architectural designs comply with industry standards and regulations, I first review relevant guidelines and laws, such as GDPR and ISO/IEC 27001. I then incorporate compliance needs like auditability, data management, and encryption into the design. Collaboration with legal and compliance teams ensures alignment with regulatory requirements. Compliance decisions and justifications are documented to facilitate audits.
32. What methodology is used for identifying and mitigating architecture risks?
Ans:
- Thorough risk assessment, detecting possible risks and weaknesses associated with the architecture design, including tech dependencies, security flaws, scalability constraints, and problems with regulatory compliance.
- Furthermore, I rank hazards according to their significance and probability, giving special attention to high-risk areas that represent the biggest danger to the project’s success.
- Thirdly, I create strategies and backup plans for risk mitigation, picking different technologies, transferring or avoiding hazards, and adjusting architectural designs.
- As a project progresses, I also keep an eye on potential risks and track them.
- When conditions change, I review and update my risk management plans.
- In conclusion, I foster an environment of risk consciousness and proactive risk handling among the project team members, urging candid dialogue, teamwork, and collective accountability for minimizing risks.
33. What experience is there with designing scalable and elastic systems?
Ans:
- Design systems to grow horizontally by dynamically adding or deleting instances or nodes in response to shifting demand. This is known as horizontal scaling.
- Put in place auto-scaling systems that, in response to predetermined criteria, including CPU usage, memory consumption, or request rates, automatically modify resource allocation. Systems can now dynamically scale up or down to meet variations in demand.
- Microservices architecture breaks down large, cohesive applications into smaller, autonomously deployable microservices, each handling a distinct business function.
- These architectures facilitate the use of containerization and orchestration technologies while allowing services to grow independently, thus promoting scalability and elasticity.
- Make use of cloud-based storage options that may scale according to demand.
34. Explain the role of continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) in architecture design.
Ans:
- Architecture design heavily relies on Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Deployment (CD).
- Regular code integration into a shared repository is a key component of continuous integration (CI), and automated testing and validation procedures guarantee code quality.
- CD improves on Continuous Integration (CI) by automating deployment and facilitating the smooth release of tested code updates into production settings. CI/CD work together to expedite software delivery, promote teamwork, and streamline development—all essential for building scalable, robust systems with shorter release cycles.
35. How is versioning and backward compatibility handled in architecture designs?
Ans:
- I use a versioning technique, like a calendar or semantic versioning, that fits the project’s needs and lifecycle.
- To ensure smooth software interactions between newer and older versions, I also build APIs and interfaces with backward compatibility in mind.
- In order to convey expectations to stakeholders and architecture users, I document versioning policies and compatibility guarantees.
- In order to properly manage the evolution of APIs and interfaces, I also put versioning controls and governance procedures into place, including version deprecation and sunset regulations.
36. What approach is used for designing fault isolation and recovery mechanisms?
Ans:
My top priority while creating fault isolation and recovery procedures is locating possible spots of failure in the system architecture. To guarantee fault isolation, I then incorporate redundancy and failover techniques at crucial points, such as load balancers and database clusters. A further measure to prevent failures from spreading throughout the system is the use of circuit breakers and graceful degradation techniques. Automated monitoring systems are essential for quickly identifying abnormalities and taking appropriate action.
37. How is disaster recovery and business continuity designed for?
Ans:
- Identifying potential hazards through risk assessments is a common practice in disaster recovery and business continuity planning.
- I create detailed strategies that specify how to respond in different situations.
- I ensure high availability by implementing failover and redundancy techniques across various cloud regions or data centers.
- I also ensure coordination during catastrophes via efficient communication protocols and regular drills and exercises to validate disaster recovery strategies.
38. Explain the role of caching in optimizing performance within architectural designs.
Ans:
Caching enhances performance by lowering latency for frequently accessed data. This entails using techniques like time-based expiration and cache warming, as well as caching data in memory or distributed caches. Traffic from origin servers is offloaded by using edge caching and CDNs, and efficiency is ensured by tracking cache metrics. Data integrity and performance are guaranteed by carefully focusing on cache invalidation and consistency.
39. How is traceability and monitoring ensured in architectural designs?
Ans:
- Integrating instrumentation and logging to record pertinent system events is necessary to ensure traceability and monitoring.
- Monitoring tools such as APM systems and log management platforms gather and analyze system telemetry data.
- Establishing KPIs and SLOs, together with proactive alerting and notification systems for anomaly identification, facilitates measuring system performance versus goals.
- Regular reviews and audits ensure that traceability systems continue to be efficient and in line with corporate goals.
40. What experience exists with designing for internationalization and localization?
Ans:
Software must be modified to accommodate various language and cultural norms when designing for internationalization and localization. Internationalization frameworks and libraries facilitate the critical task of developing user interfaces and content that are both translatable and culturally appropriate. To guarantee linguistic accuracy and cultural relevance, localization protocols for translation management should be established, and extensive testing should be done.
41. How is user experience and accessibility incorporated into architectural design?
Ans:
- In order to ensure equitable access to digital products and services, it is important to prioritize the requirements and preferences of diverse user groups while designing for user experience (UX) and accessibility.
- This strategy incorporates a number of fundamental ideas, such as carrying out user research to comprehend user requirements and behaviors, designing intuitive and user-friendly interfaces, maximizing responsiveness and performance across devices, and conforming to accessibility guidelines like WCAG.
- Refine the user experience and remove barriers to accessibility, such as making sure the website is compatible with screen readers and offering alternative language for images, depending on incorporating user feedback through usability testing and iteration.
- I work to make inclusive and interesting experiences for all users by using a user-centered design approach and including accessibility best practices all along the way.
42. Explain the concept of event sourcing and its benefits in architecture design.
Ans:
According to the event sourcing design pattern, a series of immutable events that are recorded in a log establish the state of a system. Every event is a representation of a change in the system’s state and includes all the data required to rebuild the system’s state at any given time. Since each system change is documented as an event, this architecture design method has many advantages, including enhanced auditability and traceability.
43. What methods ensure compliance with privacy regulations such as GDPR or HIPAA in architecture?
Ans:
- Implementing strong security and data protection mechanisms is necessary to ensure architecture designs comply with privacy standards like GDPR or HIP
- AA. In order to limit access to authorized users, sensitive data must be encrypted both in transit and at rest. Access controls and authentication procedures must also be put in place, and sensitive data access must be audited in order to identify and handle unlawful access attempts.
- Furthermore, I design with data reduction and anonymization in mind, making sure that only pertinent data is gathered and processed and that personally identifiable information (PII) is, whenever feasible, anonymized or pseudonymized.
- Architecture designs are kept compliant with privacy rules and industry standards by regular risk assessments and compliance audits.
44. What experience exists in designing for real-time analytics and big data processing?
Ans:
- Implementing strong security and data protection mechanisms is necessary to ensure architecture designs comply with privacy standards like GDPR or HIP
- AA. In order to limit access to authorized users, sensitive data must be encrypted both in transit and at rest. Access controls and authentication procedures must also be put in place, and sensitive data access must be audited in order to identify and handle unlawful access attempts.
- Furthermore, I design with data reduction and anonymization in mind, making sure that only pertinent data is gathered and processed and that personally identifiable information (PII) is, whenever feasible, anonymized or pseudonymized.
- Architecture designs are kept compliant with privacy rules and industry standards by regular risk assessments and compliance audits.
45. How is multi-tenancy and scalability addressed in architectural design?
Ans:
- Architecting systems that can effectively service numerous tenants while supporting growth and unpredictable demand is known as “multi-tenancy and scalability design.
- Using methods like virtualization and Containerization entails planning for resource isolation and tenant segregation to stop one tenant from affecting others.
- In order to ensure optimal resource use and performance, I additionally integrate dynamic scaling methods that dynamically supply and de-provision resources based on workload indicators.
- I also design with tenant customization and setup in mind, giving tenants the freedom to personalize their spaces without compromising their privacy.
- Through the prioritization of scalability and multi-tenancy in architecture designs, I facilitate the effective service of different user bases and enable enterprises to adjust to evolving business requirements.
46. Explain the principles of evolutionary architecture and its relevance in modern systems.
Ans:
Evolutionary design places a strong emphasis on flexibility and gradual modification over time to meet the changing requirements of the system and its users. Modifiability, testability, simplicity, and evolvability are some of its guiding principles. With constant feedback and iteration, this method allows structures to adapt to changing needs, commercial goals, and technological advancements. Enabling systems to change in response to new possibilities and challenges promotes sustainability and resilience and ensures long-term viability in dynamic situations.
47. How are cross-cutting concerns like logging and auditing managed in architecture?
Ans:
- Architecture designs handle overarching issues such as auditing and logging by taking a systematic approach that encourages maintainability, modularity, and reusability.
- Generally, I use aspect-oriented programming (AOP) approaches or design patterns like decorators and interceptors to implement cross-cutting concerns.
- By enclosing the functionality for logging and auditing into distinct modules or components, I guarantee concern separation and reduce code duplication.
- To help with analysis and compliance management, I also use centralized logging and auditing systems to combine logs and audit trails.
48. What experience is there with designing for high-performance computing and scientific applications?
Ans:
This involves using parallel computing strategies, such as multithreading, distributed computing, and GPU acceleration, to take advantage of concurrency and increase computational throughput. I create scalable and fault-tolerant architectures using scientific libraries like NumPy or SciPy for numerical computation and distributed computing frameworks like MPI (Message Passing Interface) or OpenMP.
49. How is edge computing and IoT addressed in architectural design?
Ans:
- Developing distributed systems that can effectively handle and analyze data at the network edge, nearer to the data source or end-user device, is a key component in designing edge computing and Internet of Things architectures.
- This necessitates the use of IoT protocols and communication technologies in addition to edge computing infrastructure, which includes edge devices, gateways, and edge servers.
- In order to reduce latency and bandwidth needs, I create architectures that take advantage of edge computing capabilities to execute data preprocessing, filtering, and aggregation at the edge.
- Additionally, I use scalable and decentralized communication protocols like MQTT or CoAP to provide effective data transfer between edge devices and cloud services.
50. Explain the concept of reactive architecture and its benefits in building responsive systems.
Ans:
In distributed systems, responsiveness, resilience, and elasticity are prioritized in reactive architecture. In order to create systems that can manage fluctuating workloads and gracefully handle faults, it embraces concepts like responsiveness, message-driven communication, and elasticity. To achieve high throughput and low latency, reactive architectures make use of event-driven processing models and asynchronous, non-blocking communication patterns.
51. What approaches ensure compliance with security standards such as OWASP Top 10?
Ans:
- There are various essential elements involved in ensuring architecture designs comply with security standards like OWASP Top 10.
- I start by thoroughly assessing the risks in order to find any potential weak points or dangers in the security.
- Second, I include security best practices and controls—like output encoding, authentication, authorization, and encryption—into the architecture design.
- Thirdly, I use libraries and security frameworks to apply security policies uniformly throughout the system.
- Fourth, in order to confirm adherence to OWASP Top 10 and other security requirements, I regularly perform security reviews and assessments.
- In order to foster a culture of security and guarantee adherence to security procedures throughout the development lifecycle, I also offer security awareness and training sessions for development teams.
52. How is compliance with GDPR or CCPA regulations ensured in architecture?
Ans:
To identify and mitigate risks related to personal data, conducting data privacy impact assessments is essential. Implementing privacy-enhancing technologies, such as encryption, anonymization, and pseudonymization, helps protect personal data. Establishing data retention and deletion policies in compliance with regulations like CCPA and GDPR is crucial. Setting up systems for managing user consent and implementing procedures for handling data access requests, breaches, and regulatory inquiries ensures robust data privacy management.
53. What methods are used to design for privacy by design and default?
Ans:
- We are integrating privacy guidelines and specifications, like purpose-limited architecture, data minimization, and data protection by design, into the architectural design process.
- protecting personal data by implementing privacy-enhancing tools and methods such as data anonymization, access limits, and encryption.
- We are identifying and reducing privacy risks throughout the system’s lifetime by conducting privacy impact assessments.
- We supply development teams with privacy awareness and training programs to foster a culture of privacy consciousness and guarantee adherence to privacy best practices.
54. Explain the principles of chaos engineering and its role in architecture resilience testing.
Ans:
Embracing failure as a natural part of system behavior, the focus is on proactively testing resilience through chaos experiments. This involves applying the scientific method—creating theories, planning experiments, and evaluating results—to identify weaknesses. Automation of these experiments ensures continuous testing of system responsiveness and resilience. Gradually expanding the scope and complexity of experiments helps uncover hidden failure mechanisms.
55. How is data encryption and key management handled in architecture?
Ans:
- Data encryption and key management are essential parts of my architectural designs that guarantee sensitive data security and confidentiality.
- Encryption is used both in transit and at rest, using strong encryption techniques and protocols chosen in accordance with the sensitivity of the data.
- To create, store, distribute, rotate, and revoke encryption keys, secure key management procedures must be followed.
- Secure key management and storage are guaranteed when hardware security modules (HSMs) or cloud key management services (KMS) are used.
- End-to-end data protection procedures are established by integrating encryption and key management into data operations, which reduces the possibility of unwanted access or data breaches.
56. What experience exists with designing for HIPAA compliance in healthcare systems?
Ans:
Strict security, privacy, and data protection measures must be put in place while designing for HIPAA compliance in order to secure protected health information (PHI). Vulnerabilities and compliance gaps are found through risk assessments, which are then followed by the implementation of technical security measures like encryption and access controls. Administrative measures, including as guidelines, protocols, and educational initiatives, guarantee adherence to HIPAA regulations.
57. How is PCI DSS compliance addressed in payment systems architecture?
Ans:
- Strict security measures are required for payment systems to comply with PCI DSS in order to safeguard cardholder data and guarantee safe transactions.
- Encryption techniques protect cardholder data during transmission and storage, and segmenting the cardholder data environment minimizes the scope of compliance.
- Access rules restrict cardholder data, and security incidents are quickly detected and addressed through routine monitoring and audits.
- Implementing strong security controls and adhering to PCI DSS rules assure compliance.
58. Explain the concept of zero-trust architecture and its relevance in security design.
Ans:
The “never trust, always verify” philosophy is adopted by zero-trust architecture, in which access is expressly allowed depending on risk factors, identity, and context. Before allowing access, identity and access control systems confirm the legitimacy of the device and the identities of the users. Network perimeters are established by micro-segmentation, and security issues are immediately detected and addressed by ongoing monitoring and logging.
59. What approaches ensure compliance with ISO 27001 for information security management?
Ans:
- Establishing a thorough information security management system (ISMS) is necessary to comply with ISO 27001 criteria.
- A methodical approach starts with risk assessment and gap analysis to detect security risks and compliance gaps.
- Risks are reduced, and ISO 27001 standards are met by developing and implementing security policies, procedures, and controls.
- Implementing an ISMS and keeping track of security controls and metrics will guarantee their efficacy, and including stakeholders will help foster an organizational culture of security and compliance.
60. How is GDPR compliance achieved in data processing systems?
Ans:
Using privacy by design and default principles to safeguard personal data and adhere to GDPR is part of designing for compliance. This entails carrying out impact analyses on data protection, putting in place organizational and technical safeguards to guarantee data security and confidentiality, creating procedures for data subject rights, and putting in place retention and deletion guidelines. Regular audits ensure compliance, address privacy concerns, and improve data protection, preserving privacy and transparency.
61. What approach is used for designing to meet NIST cybersecurity framework requirements?
Ans:
- My strategy for building compliance with the NIST cybersecurity framework is to match architecture designs to the five main purposes of the framework (Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover).
- This entails carrying out risk analyses, putting security measures in place, continuously monitoring, organizing for incident response, and developing recovery plans.
- Through the incorporation of NIST principles into architectural designs, I guarantee a comprehensive and proactive strategy toward cybersecurity.
62. Explain the principles of secure software development lifecycle (SDLC) and its importance.
Ans:
The principles of a secure software development lifecycle (SDLC) emphasize integrating security measures at every stage of software development, including requirements, design, coding, testing, deployment, and maintenance. By ensuring that security is incorporated into the software from the beginning, this method reduces weaknesses and boosts resistance to online attacks.
63. How are secure authentication and authorization mechanisms incorporated into architecture?
Ans:
Architecture designers utilize secure authentication and authorization methods such as role-based access controls, strict password policies, and multi-factor authentication. To protect critical resources, fine-grained authorization techniques and protocols like OAuth and OpenID Connect are employed. Sensitive data is encrypted, and regular security audits are conducted to mitigate potential risks. Logging and monitoring tools are also implemented to quickly identify and respond to unauthorized access attempts.
64. Discuss designing for secure API gateways and access controls.
Ans:
- Strong access restrictions must be implemented when designing secure API gateways to prevent unauthorized users from accessing critical information or features.
- Authentication techniques like OAuth, JWT, or API keys can be used to do this.
- Furthermore, throttle, rate limitation, and IP allowlisting can be used to reduce the risk of assaults such as DDoS or brute force efforts.
- Frequent security audits and monitoring assist in locating and resolving gateway issues.
65. How are secure communication channels and encryption designed?
Ans:
Encryption methods such as TLS/SSL must be used when designing secure communication channels to safeguard data sent between the client and server. Strong key management procedures and cipher suites guarantee the integrity and secrecy of data while it is in transit. The security posture of the communication channels is strengthened by using secure communication libraries and frameworks, as well as appropriate configuration and certificate management.
66. Explain the concept of threat modeling and its role in architecture security analysis.
Ans:
- Identifying possible threats to a system, evaluating their impact and likelihood, and developing remedies to reduce risks are all part of the threat modeling process.
- Assisting architects in foreseeing and addressing security risks early in the design phase plays a critical role in architecture security analysis.
- Threat modeling aids in the construction of robust and safe architectures by taking into account a variety of attack vectors and giving security controls priority.
67. How is secure logging and auditing practiced in architectural designs?
Ans:
In order to assist forensic analysis and compliance needs, secure logging and auditing techniques entail collecting and preserving pertinent system activity in a tamper-evident way. The confidentiality and integrity of log data are guaranteed by putting in place the appropriate access controls, encryption, and integrity checks. Logs should be regularly reviewed and analyzed in order to identify security events and unauthorized access attempts quickly.
68. Describe designing for secure identity management and federated authentication.
Ans:
- Centralized identity providers, such as Active Directory or LDAP, must be implemented as part of secure identity management and federated authentication design to identify and authorize users across numerous systems.
- Safe and easy resource access is made possible by using federated authentication protocols such as OAuth or SAML.
- Role-based access controls and multi-factor authentication improve security posture and reduce the possibility of unwanted access.
69. What methods are used for secure data storage and encryption at rest?
Ans:
Sensitive data must be encrypted before being stored in databases or file systems to ensure secure data storage and encryption at rest. Data confidentiality is ensured by using robust encryption algorithms and key management procedures, even if storage media are hacked. Frequent security audits and evaluations aid in locating and fixing holes in data storage systems, guaranteeing that data is safe for its whole life.
70. Explain the principles of secure coding practices and security testing in architecture design.
Ans:
- Adhering to best practices and guidelines is part of secure coding techniques, which help create software that is resistant to security breaches.
- Input validation, appropriate error management, and secure API design are all part of this to guard against frequent flaws like XSS or injection attacks.
- Static and dynamic code analysis, penetration testing, and fuzz testing are examples of security testing techniques that assist in locating and addressing software vulnerabilities during the development and deployment stages, guaranteeing a solid and safe architecture.
71. How is secure error handling and exception management addressed in architecture?
Ans:
- Exception management and secure error handling are essential elements of architecture desiAdhering to best practices and guidelines is part of secure coding techniques, which help create software that is resistant to security breaches.
- Input validation, appropriate error management, and secure API design are all part of this to guard against frequent flaws like XSS or injection attacks.
- Static and dynamic code analysis, penetration testing, and fuzz testing are examples of security testing techniques that assist in locating and addressing software vulnerabilities during the development and deployment stages, guaranteeing a solid and safe architecture.
- They entail safeguards to graciously handle errors and keep private data safe from prying eyes. This entails cleaning up error messages, safely tracking errors, and giving users only the information they require.
72. What experience exists with designing secure cloud environments and network segmentation?
Ans:
- When designing secure cloud environments, a deep awareness of the security features and best practices offered by cloud service providers is necessary.
- This entails using virtual private clouds (VPCs), network access restrictions, and network segmentation to isolate critical resources and prevent unwanted access.
- Additionally, implementing encryption for data at rest and in transit further enhances the security of sensitive information.
73. How are secure API endpoints and rate limiting incorporated into architectural design?
Ans:
Authentication technologies like OAuth, JWT, or API keys are implemented to validate customers’ identities while designing secure API endpoints. Rate-limiting limits the quantity of queries a client may submit in a given amount of time, preventing abuse or misuse of APIs. API security can be managed centrally, with access limits, rate limitations, and suspicious activity monitoring made easier with the use of gateway solutions and management platforms.
74. Explain the concept of threat intelligence and its role in proactive security measures.
Ans:
- Information regarding possible threats and vulnerabilities is gathered, analyzed, and applied to improve security posture through the use of threat intelligence.
- Staying updated about new threats and attack methods involves keeping an eye on a variety of sources, including threat feeds, security advisories, and incident reports.
75. What strategies ensure secure configuration and patch management?
Ans:
Establishing and implementing secure configuration guidelines for every element of the architecture—including network devices, operating systems, and applications—is known as secure configuration management. This entails restricting access using the least privilege principle, turning off pointless services, and hardening configurations. Patch management is the process of deploying security patches on time to reduce potential risks and updating software and firmware on a regular basis to address known vulnerabilities.
76. Describe designing for secure logging and monitoring in compliance audits.
Ans:
- Developing strong logging systems to record pertinent security events and activities inside the architecture is a necessary part of designing for secure logging and monitoring in compliance audits.
- This includes tamper-evidently logging essential system actions, changes in access control, and authentication attempts.
- It is crucial to make sure logs are encrypted, kept in a safe location, and shielded from unwanted access.
- The prompt discovery and handling of security issues is made possible by the use of real-time monitoring and alerting technologies.
- Giving auditors access to thorough and accurate log data during compliance audits aids in proving compliance with legal standards and security guidelines.
77. How is secure supply chain management and third-party integration handled?
Ans:
The careful screening and validation of suppliers and partners in the supply chain is necessary when designing for secure third-party integrations and supply chain management. This entails evaluating their security procedures, investigating their security posture, and creating legal contracts to uphold security standards. By putting in place safe lines of communication and data-sharing procedures, third-party integration risks can be reduced. Ongoing compliance with security standards is maintained through regular audits and third-party inspections.
78. Explain the principles of secure incident response and incident management in architecture design.
Ans:
- In order to properly respond to security issues and minimize their impact, predefined procedures and protocols must be established.
- This is the foundation of incident management and secure incident response concepts.
- Assisting responders in the containment, eradication, and recovery processes entails creating roles and duties, establishing communication channels, and putting incident response playbooks into practice.
- Resilience against future threats is increased, and incident response capabilities are improved by incorporating lessons learned from previous incidents and performing post-incident reviews.
79. What methods are used for secure software updates and version control?
Ans:
Managing software patches and updates requires putting in place a systematic methodology in order to handle secure software upgrades and version control inside architecture designs. Establishing a safe update procedure that confirms the legitimacy and integrity of software updates prior to deployment is part of this. Software versions and configurations can be managed while speeding up the updating process with the use of automated deployment pipelines and version control systems.
80. Describe designing for secure DevOps practices and automation.
Ans:
- Every phase of the DevOps lifecycle, from development and testing to deployment and operations, must incorporate security as part of the design for secure DevOps processes and automation.
- This entails putting in place security measures, including automated configuration management tools, vulnerability detection, and code analysis.
- Security flaws can be found and fixed early in the development process by integrating security tests into automated build pipelines.
- Rapid reactions to security events and proactive security posture management are made possible by the use of continuous monitoring tools and infrastructure as code (IaC) implementation.
- Fostering a collaborative culture amongst the development, operations, and security teams also helps to advance continuous security practice improvement inside the DevOps environment and creates a shared responsibility for security.
81. How do you guarantee that the architecture you propose effectively aligns with business requirements?
Ans:
Ensuring congruence with business requirements necessitates careful study and stakeholder involvement. This entails comprehending the aims, limitations, and goals of the business, converting them into technical specifications, and regularly assessing the architecture against changing business requirements. Frequent feedback loops and engagement with stakeholders guarantee that the suggested architecture effectively satisfies their needs and complements the overarching business plan.
82. How are system requirements identified and assessed in architecture design?
Ans:
- Stakeholder interviews, user story collection, and documentation analysis are standard steps in my process for determining and evaluating system requirements.
- This aids in comprehending the system’s functional and non-functional requirements.
- Methods such as use case analysis, requirement prioritization, and prototyping further aid in refining and validating requirements to ensure they are thorough, understandable, and practical.
83. What strategies manage challenges related to data consistency and synchronization in distributed systems?
Ans:
Using distributed transaction management techniques, data replication and synchronization mechanisms, and distributed consensus protocols such as Paxos or Raft are some strategies for maintaining data consistency and synchronization in distributed systems. Furthermore, despite reducing synchronization issues, using message queues and event-driven architectures can assist in guaranteeing eventual consistency among dispersed components.
84. Discuss the concept of service-oriented architecture (SOA) and its advantages.
Ans:
- Software components are built as reusable services that can be accessed and coordinated over a network in a technique known as service-oriented architecture (SOA).
- Because SOA encourages loose coupling between services, it allows for autonomous development and deployment and provides benefits, including increased agility, scalability, and interoperability.
- It also helps dispersed computing settings, improves maintainability, and allows service reuse.
85.How is compliance with industry standards and regulations ensured in architectural designs?
Ans:
To ensure compliance with industry norms and rules, it is necessary to keep up with pertinent laws, regulations, and industry best practices. To guarantee compliance with standards like PCI DSS, GDPR, HIPAA, or ISO 27001, routine audits, risk assessments, and compliance checks are required. Using privacy-by-design guidelines, incorporating security frameworks, and incorporating compliance needs into architecture design procedures all contribute to making sure that architectures adhere to pertinent rules.
86. How is internationalization and localization approached in architectural design?
Ans:
- Software must be designed to accommodate a variety of languages, cultures, and regional preferences in order to be considered locally and internationally.
- This includes providing dynamic content adaption, utilizing locale-specific formatting, and separating text from code.
- Software that is linguistically and culturally appropriate for a variety of user bases can be made using localization libraries, testing the language, and working with localization specialists.
87. How is user experience and accessibility integrated into architectural design?
Ans:
It is important to take into account the needs of users with a range of abilities and preferences when designing for accessibility and user experience. This entails carrying out usability tests, user research, and integrating WCAG and other accessibility guidelines into design procedures. Accessible content formats, keyboard accessibility, screen reader compatibility, and the application of responsive design principles all contribute to inclusive user experiences that serve a diverse user base.
88. Explain the concept of event sourcing and the benefits it brings to architecture design.
Ans:
- Changes to the application state are recorded as a sequence of immutable events in the event sourcing pattern.
- This method supports event-driven architectures, allows temporal queries, and provides a complete historical record of state changes, among other advantages like auditability, scalability, and flexibility.
- Event sourcing makes building systems that are traceable, durable, and flexible to changing business needs easier.
89. How is traceability and monitoring incorporated into architectural designs?
Ans:
Architectural designs must incorporate logging, instrumentation, and observability techniques to collect and analyze real-time system behavior in order to provide traceability and monitoring. Monitoring system interactions, identifying problems, and calculating performance metrics entails using tools for distributed tracing, centralized logging, and performance monitoring. Creating thorough monitoring dashboards and alerts promotes proactive problem response and helps guarantee visibility into system health.
90. What experience exists in designing for real-time analytics and large dataset processing?
Ans:
- Using distributed computing frameworks such as Apache Spark or Apache Flink, stream processing architectures such as Apache Kafka or AWS Kinesis, and putting in place data ingestion pipelines and data lakes are all part of designing for real-time analytics and processing of massive datasets.
- This makes it possible to process, analyze, and draw conclusions from huge amounts of data in real-time, which helps businesses make decisions quickly and gain useful insights.






