
You’ve arrived to the right site if you’re looking for SAP ABAP on HANA Interview Questions for Experienced or Newcomers. There are several instances worldwide from numerous purported businesses. Research indicates that the market share of SAP ABAP on HANA is approximately 0.9%. Thus, you are still able to advance in your SAP ABAP on HANA Developer profession. In order to help you ace your interview and land the perfect job as a SAP ABAP on HANA Expert, ACTE offers Advanced SAP ABAP on HANA Interview Questions.
1. What is SAP ABAP on HANA?
Ans:
SAP ABAP on HANA combines SAP’s Advanced Business Application Programming (ABAP) language with the SAP HANA in-memory database platform. It enables developers to leverage the power of SAP HANA for faster and more efficient data processing in SAP applications. SAP ABAP on HANA represents the synergy between the ABAP programming language and the SAP HANA in-memory database platform.
2. Explain the key features of SAP HANA.
Ans:
- In-Memory Computing: Processes data in-memory, leading to faster data retrieval and analytics.
- Columnar Storage: Stores data in columns rather than rows for improved compression and query performance.
- Advanced Analytics: Supports advanced analytics, including predictive analytics and machine learning.
- Real-Time Data Processing: Enables real-time data processing and analytics for instant insights.
3. What is the significance of SAP HANA in the context of ABAP development?
Ans:
SAP HANA significantly enhances the performance and capabilities of ABAP development by leveraging its in-memory computing, advanced analytics, and real-time processing features. It allows developers to perform code pushdown, shifting data-intensive operations from the application to the database layer, leading to improved performance and reduced latency.
4. Differentiate between SAP HANA and traditional databases.
Ans:
| Aspect | SAP HANA | Traditional databases |
|---|---|---|
| In-Memory Processing: | SAP HANA stores and processes data in memory | Traditional databases typically use disk-based storage. |
| Columnar Storage: | HANA employs columnar storage for better compression and query performance | Traditional databases often use row-based storage. |
| Advanced Analytics: | SAP HANA supports advanced analytics natively | Traditional databases may require additional tools for such capabilities. |
5. What is CDS (Core Data Services) in SAP HANA?
Ans:
Core Data Services (CDS) in SAP HANA is a data modeling technique that allows developers to create and use data models with rich semantics in the database layer. CDS creates database views, which ABAP programs, UIs, and other applications can consume. It simplifies data modeling and ensures consistency between the database and application layers.
6. Explain the importance of AMDP (ABAP Managed Database Procedure) in SAP HANA.
Ans:
AMDP allows developers to write database procedures in the database layer using SQLScript, executed in the SAP HANA database. This brings the power of SAP HANA’s processing capabilities directly into the ABAP environment, enhancing performance by reducing data transfer between the application and database layers. By enabling the pushdown of logic to the database layer, AMDP contributes to the overall optimization of SAP applications in HANA environments.
7. What are the performance benefits of using SAP HANA for ABAP development?
Ans:
- Faster Data Access: In-memory processing accelerates data retrieval and manipulation.
- Real-time Analytics: Enables real-time analysis of data for instant insights.
- Code Pushdown: Moves data-intensive operations to the database layer for improved performance.
- Parallel Processing: Supports parallel processing, optimizing the use of multiple processors.
8. Describe the role of SAP HANA Studio in ABAP development.
Ans:
- An integrated development environment (IDE) called SAP HANA Studio is used for SAP HANA development tasks.
- In the context of ABAP development, it provides tools for creating and managing database artifacts, analyzing performance, and optimizing SQL queries.
- Developers can use SAP HANA Studio to work on ABAP on HANA projects efficiently.
- While SAP HANA Studio is more commonly associated with native HANA development, it does play a role in ABAP development in the context of SAP HANA.
9. How do you activate the SAP HANA database for an existing ABAP system?
Ans:
The activation process involves configuring the SAP system to use the SAP HANA database. It includes installing the SAP HANA database software, performing system copies, and adjusting system parameters. Activation is a complex process that must be well organized to guarantee a seamless transition from a traditional database to SAP HANA.
10. What is the significance of code pushdown in SAP HANA?
Ans:
Code pushdown refers to the optimization technique of moving data-intensive operations from the application layer (ABAP) to the database layer (SAP HANA).
This is significant in the context of SAP HANA as it leverages the in-memory processing capabilities of the database, resulting in improved performance and reduced data transfer between the application and database layers. It helps better use the advanced features provided by SAP HANA.
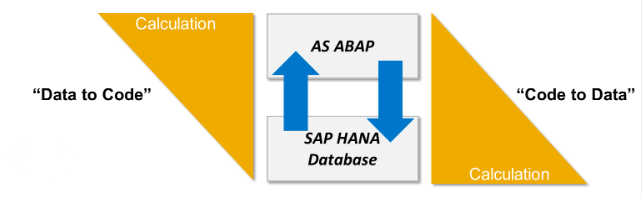
11. Explain the concept of SAP HANA SQLScript.
Ans:
SAP HANA SQLScript is a procedural language for developing stored procedures and functions in the SAP HANA database. It extends SQL by providing additional programming constructs such as loops, conditional statements, and exception handling. SQLScript allows for the efficient execution of complex logic directly within the database, maximizing the performance benefits of SAP HANA’s in-memory processing.
12. How do you handle database procedures in SAP ABAP on HANA?
Ans:
In SAP ABAP on HANA, database procedures can be handled using ABAP Managed Database Procedures (AMDP). AMDP allows developers to define and implement database procedures directly in the ABAP class using SQLScript. This facilitates code pushdown, enabling the execution of data-intensive operations in the SAP HANA database and improving performance.
13. What is the purpose of the ABAP Dictionary in SAP HANA?
Ans:
- The ABAP Dictionary in SAP HANA is a central repository for data definitions and metadata.
- It allows developers to define and manage database objects such as tables, views, and indexes.
- In the context of SAP HANA, the ABAP Dictionary plays a crucial role in defining HANA-specific artifacts and optimizing data models for better performance.
- It supports data modeling and metadata management and ensures consistency and reusability of data structures, contributing to efficient and well-organized development practices on the SAP HANA platform.
14. Explain the concept of SQL optimization in SAP HANA.
Ans:
SQL optimization in SAP HANA involves optimizing SQL queries to enhance database performance. This includes using features such as indexes, proper data modeling, and efficient SQLScript coding. The goal is to minimize resource consumption and execution time, leveraging SAP HANA’s capabilities for parallel processing and in-memory data access.
15. How do you use ABAP to create views in SAP HANA?
Ans:
In SAP ABAP on HANA, developers can create views using Core Data Services (CDS). CDS allows the definition of semantically rich data models in the ABAP layer, which can be exposed as views in the SAP HANA database. Other ABAP programs, UIs, or external data retrieval and manipulation applications can consume these views. Refer to the latest SAP documentation for the most accurate and up-to-date information on creating views in SAP HANA using ABAP.
16. What is SAP Fiori, and how does it relate to SAP ABAP on HANA?
Ans:
SAP Fiori is a design principle and user experience (UX) approach that strives to give SAP applications a standardized, user-friendly interface. In the context of SAP ABAP on HANA, Fiori is often used to design modern, responsive, and user-friendly interfaces for applications running on SAP HANA. ABAP developers can use Fiori elements to create Fiori apps that leverage the capabilities of SAP HANA.
17. Explain the Smart Data Access (SDA) concept in SAP HANA.
Ans:
- Smart Data Access in SAP HANA allows users to access and integrate data from remote sources seamlessly.
- It enables data virtualization, allowing SAP HANA to retrieve and combine data from various sources, including other databases or external systems.
- This integration is done without physically replicating the data into the SAP HANA database.
18. How do you integrate SAP HANA with SAP Business Suite applications using ABAP?
Ans:
Integration of SAP HANA with SAP Business Suite applications involves various steps:
- Activating SAP HANA database for the existing system.
- Adjusting application-specific coding for code pushdown.
- Enhancing data models using HANA-specific features.
- Utilizing CDS views and AMDP for optimized database procedures.
19. What is the role of the HANA Deployment Infrastructure (HDI) in ABAP development?
Ans:
HANA Deployment Infrastructure (HDI) is a feature in SAP HANA that allows developers to manage and deploy database artifacts such as tables, views, and procedures in a more modular and transportable way. In ABAP development, HDI can be used to package and transport HANA-specific artifacts efficiently, improving the lifecycle management of database objects.
20. What are the different types of indexes in SAP HANA?
Ans:
SAP HANA supports various indexes for optimizing data retrieval and query performance. Some common types of indexes in SAP HANA include:
- Column Store Index: Optimized for columnar storage.
- Bitmap Index: Used for columns with low cardinality.
- Spatial Index: Used for spatial data types.
- Full-Text Index: Enables efficient text search.
- Hash Index: Used for hash partitioning.
21. Explain the concept of delta merge in SAP HANA.
Ans:
- Delta merge is a process in SAP HANA that consolidates and optimizes data storage.
- In HANA’s columnar storage, data is stored in memory in delta storage and then periodically consolidated into central storage through a delta merge process.
- This optimization reduces the storage footprint and improves query performance by eliminating redundant or obsolete data.
22. What are the different types of replication methods in SAP HANA?
Ans:
There are several replication methods in SAP HANA, including:
- SAP Landscape Transformation (SLT): Real-time data replication from SAP and non-SAP source systems.
- SAP HANA Direct Extractor Connection (DXC): Real-time replication from SAP ERP using SAP extractors.
- SAP HANA Smart Data Integration (SDI): Provides real-time and batch data integration from various sources.
- SAP HANA Smart Data Access (SDA): Virtualization of data from remote sources without physical replication.
23. How do you handle currency conversion in SAP HANA?
Ans:
Currency conversion in SAP HANA is a common requirement in financial and reporting scenarios where data from multiple currencies needs to be aggregated or presented in a consistent currency. Currency conversion may be handled in a few different ways. in SAP HANA, and the choice depends on factors such as the complexity of your scenario, the version of SAP HANA, and your specific business requirements.
24. Explain SLT’s (SAP Landscape Transformation) purpose in SAP HANA.
Ans:
- SAP Landscape Transformation (SLT) is a technology developed by SAP that provides real-time data replication and transformation capabilities for SAP HANA and other SAP databases.
- SLT is primarily used for data replication from source systems, such as SAP ERP, non-SAP databases, or other third-party systems, to SAP HANA.
- Its primary purpose is to enable real-time or near-real-time access to operational data for analytics and reporting in the SAP HANA environment.
25. What are the best practices for optimizing ABAP code for SAP HANA?
Ans:
- Use Open SQL statements with HANA-specific optimizations.
- Leverage code pushdown techniques, such as AMDP (ABAP Managed Database Procedures).
- Optimize data models using Core Data Services (CDS).
- Minimize data transfer between the application and database layers.
- Use HANA-specific features like secondary indexes and partitioning.
26. How does ABAP for SAP HANA improve the performance of reports?
Ans:
ABAP for SAP HANA improves report performance through code pushdown, where data-intensive operations are moved to the SAP HANA database. This reduces data transfer between the application server and the database, leverages in-memory processing, and allows for parallel processing. Additionally, using HANA-specific features like CDS views and AMDP enhances report performance.
27. What is the use of the SAP HANA Transport Container (HTC)?
Ans:
The SAP HANA Transport Container (HTC) is used to bundle and transport SAP HANA artifacts, such as packages, content, and configurations, from one system to another. It provides a consistent and organized way to transport HANA-related objects between different environments in the system landscape. Tools like SAP HANA Transport for ABAP (HTA) are also used to transport ABAP artefacts between SAP HANA systems.
28. How do you use SAP HANA Live with ABAP?
Ans:
SAP HANA Live is a set of pre-built views and analytics capabilities designed to provide real-time operational reporting and analytics on top of SAP HANA. These views expose business data directly from the SAP Business Suite and other data sources in SAP HANA, allowing quick and easy reporting without complex data extraction and transformation.
29. Explain the concept of SQLScript procedures in SAP HANA.
Ans:
- SQLScript procedures in SAP HANA are reusable units of SQL code that encapsulate business logic and can be executed in the SAP HANA database.
- They are written in the SQLScript language and can include SQL queries, control-flow logic, and exception handling. SQLScript procedures are beneficial for code modularization and performance optimization.
30. What is the role of the ABAP Development Tools (ADT) in SAP HANA development?
Ans:
The ABAP Development Tools (ADT) is an Eclipse-based integrated development environment (IDE) used for SAP HANA development. In SAP HANA development, ADT provides tools for creating, editing and managing HANA artifacts such as database procedures, views, and CDS views. It facilitates a unified development experience for ABAP and SAP HANA development within the Eclipse IDE.
31. How do you use SQLScript to manipulate data in SAP HANA?
Ans:
- SQLScript is used in SAP HANA to manipulate data using SQL-like syntax.
- You can use SQLScript in stored procedures, functions, and anonymous blocks to perform SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, and more operations.
- SQLScript also supports control-flow statements, variables, and exception handling to build complex logic for data manipulation directly within the SAP HANA database.
32. What is the purpose of the SAP HANA database client?
Ans:
The SAP HANA database client allows users to connect to the SAP HANA database server from various client applications, tools, and programming languages. It serves as an interface for executing SQL queries, managing database objects, and performing administrative tasks. The database client facilitates communication between client applications and the SAP HANA database.
33. How do you transport ABAP objects between SAP systems in SAP HANA?
Ans:
- ABAP objects, including programs, function modules, and other development objects, can be transported between SAP systems using the Transport Management System (TMS).
- Transport requests are created in the development system and moved through different landscapes (quality, production, etc.) using TMS.
- In SAP HANA, additional considerations may be needed for transporting HANA-specific objects like CDS views or procedures.
34. Explain the concept of runtime objects in SAP HANA.
Ans:
Runtime objects in SAP HANA refer to artifacts created and executed during runtime rather than predefined during design time. Examples include dynamic views and temporary tables created and used for specific runtime scenarios. Runtime objects provide flexibility and efficiency in handling data while executing specific tasks.
35. What is the role of the ABAP SQL Monitor in SAP HANA?
Ans:
The ABAP SQL Monitor in SAP HANA analyses and optimizes SQL statements executed in ABAP programs. It provides information about the performance and execution details of SQL queries, helping developers identify areas for improvement. The SQL Monitor assists in optimizing database access and achieving better performance in ABAP programs using SAP HANA.
36. How do you use SAP HANA data types in ABAP programs?
Ans:
- SAP HANA data types can be used in ABAP programs when dealing with HANA database artifacts such as CDS views or AMDP methods.
- Developers can leverage HANA-specific data types, like HANA Date or HANA Time when defining variables or parameters in ABAP programs that interact with HANA databases.
- When working with SAP HANA in ABAP programs, you can leverage these data types to interact with the database efficiently.
37. What is the significance of the ABAP RESTful programming model in SAP HANA?
Ans:
The ABAP RESTful programming model allows developers to build modern, state-of-the-art applications in ABAP by adhering to RESTful principles. It enables the development of OData services and Fiori applications in an efficient and standardized way. The RESTful programming model simplifies the creation of ABAP applications that seamlessly integrate with SAP Fiori and other web-based technologies
38. Explain the concept of AMDP method calls in SAP HANA.
Ans:
AMDP (ABAP Managed Database Procedure) method calls in SAP HANA involve executing database procedures written in SQLScript directly from ABAP programs. Developers can call AMDP methods in their ABAP code, which then triggers the execution of corresponding database procedures in the SAP HANA database. This approach optimizes performance by pushing data-intensive operations to the database layer.
39. How do you use the ALV (ABAP List Viewer) with SAP HANA?
Ans:
- ALV can be used with SAP HANA in ABAP programs to display data in a tabular format.
- Developers can leverage HANA-specific features like CDS views or AMDP to fetch data efficiently and then use ALV to present the data in various formats (grid, list, or tree).
- ALV with SAP HANA allows for a user-friendly display of large datasets with enhanced performance.
40. What are the critical considerations for designing ABAP programs for SAP HANA?
Ans:
- Leverage code pushdown techniques like AMDP for improved performance.
- Utilize HANA-specific features such as CDS views and HANA SQLScript.
- Minimize data transfer between the application server and the database.
- Optimize data models for SAP HANA’s in-memory processing capabilities.
- Consider the use of parallel processing for data-intensive operations.
- Regularly monitor and analyze SQL statements for performance optimization.
41. How do you optimize ABAP code for parallel processing in SAP HANA?
Ans:
To optimize ABAP code for parallel processing in SAP HANA, you can:
- Utilize parallel Open SQL statements.
- Use parallel cursor techniques to fetch data concurrently.
- Leverage parallel processing options in ABAP programs (e.g., PARALLEL keyword in SELECT statements).
- Take advantage of HANA-specific features for parallel execution.
42. Explain the SAP HANA extended application services (XS) concept.
Ans:
SAP HANA extended application services (XS) is a set of application services embedded in the SAP HANA platform. It includes SAP HANA XS Classic and SAP HANA XS Advanced. XS Classic is a lightweight application server, while XS Advanced is a more powerful and flexible platform, providing application development, runtime, and deployment services.
43. What is the role of the SAP Fiori elements in ABAP on HANA development?
Ans:
SAP Fiori elements are UI design patterns and templates that provide a consistent and responsive user experience across SAP applications. In ABAP on HANA development, Fiori elements simplify the creation of Fiori apps by providing predefined templates for common application scenarios, reducing the need for extensive manual UI coding.
44. How do you handle buffering in SAP HANA?
Ans:
- SAP HANA handles buffering differently compared to traditional databases.
- In HANA, data is primarily stored in memory, reducing the need for extensive buffering mechanisms.
- Developers can leverage SAP HANA’s efficient in-memory processing and columnar storage to access data quickly without relying heavily on traditional buffering technique
45. What is the purpose of the SAP HANA-specific ABAP statements?
Ans:
SAP HANA-specific ABAP statements provide a way to leverage HANA-specific features directly in ABAP programs. Examples include:
- EXEC SQL for executing SQLScript procedures.
- SELECT…INTO CORRESPONDING FIELDS OF TABLE for optimized data retrieval.
- FOR expressions for optimized looping over internal tables.
46. Explain the role of the ABAP on HANA-specific tools in SAP HANA development.
Ans:
- ABAP on HANA-specific tools, such as the ABAP Development Tools (ADT) in Eclipse, provide an integrated environment for developers to design, implement, and optimize ABAP programs that interact with SAP HANA databases.
- These tools offer features like code pushdown analysis, performance monitoring, and support for HANA-specific artifacts.
47. How do you use AMDP with Open SQL in SAP HANA?
Ans:
- ABAP Managed Database Procedures (AMDP) can be used with Open SQL in SAP HANA to execute database procedures written in SQLScript.
- Developers can define AMDP methods within ABAP classes containing Open SQL statements and then call these methods from ABAP programs.
- This enables code pushdown and optimized data processing in the SAP HANA database.
48. What are the fundamental principles of SAP HANA multi-tenancy?
Ans:
Fundamental principles of SAP HANA multi-tenancy include:
- Isolation: Each tenant has an isolated schema, data, and runtime environment.
- Shared Resources: Tenants share common resources like hardware and software.
- Customization: Tenants can customize their schemas and configurations.
- Efficiency: Multitenancy optimizes resource utilization by serving multiple tenants on a shared infrastructure.
49. How do you use SAP HANA-specific views in ABAP programs?
Ans:
- SAP HANA-specific views, such as Calculation Views or Analytical Views, can be used in ABAP programs through Open SQL statements or CDS views.
- Developers can create and define these views in SAP HANA and then consume them in ABAP programs to retrieve and manipulate data efficiently.
- Always refer to the documentation for accurate and up-to-date information for your specific SAP HANA and ABAP versions.
50. Explain the concept of virtual data models in SAP HANA.
Ans:
Virtual data models in SAP HANA refer to creating models without physically storing the data. This can be achieved using views like Calculation Views or CDS views, which make it possible to define intricate data structures and relationships. Virtual data models provide flexibility and efficiency without physical data replication.
51. What is the role of the ABAP Development Workbench in SAP HANA development?
Ans:
- The ABAP Development Workbench in SAP HANA development is used for creating and managing ABAP-based applications that leverage the capabilities of the SAP HANA database.
- Developers use this workbench to write ABAP code, define data models, and design user interfaces for programs that utilize the SAP HANA system.
- It provides tools and features that enable the seamless integration of ABAP applications with the powerful capabilities of the SAP HANA database.
52. How do you use SAP HANA annotations in ABAP programs?
Ans:
SAP HANA annotations in ABAP programs provide additional metadata and instructions to the SAP HANA database about optimizing the processing of ABAP programs. Annotations are typically added to the data definition and database access statements to influence the behavior of the SAP HANA database during runtime.
53. What is the purpose of the SAP Fiori launchpad in ABAP on HANA applications?
Ans:
The point of entry is the SAP Fiori Launchpad for SAP Fiori applications and provides a single point of access to various applications and analytical tools. In ABAP on HANA applications, the Fiori Launchpad hosts and launches Fiori apps, providing a modern and user-friendly interface for end-users to interact with applications running on the SAP HANA platform.
54. Explain the SAP HANA Live Cache concept in ABAP on HANA.
Ans:
SAP HANA Live Cache in ABAP on HANA is a feature that enables the efficient management and storage of frequently accessed data. It acts as an in-memory cache for frequently used data to improve performance and reduce latency in ABAP applications running on the SAP HANA platform.SAP HANA-specific views can be utilized in applications to view and work with data kept in SAP HANA databases.
55. How do you handle security in SAP HANA-enabled ABAP applications?
Ans:
- Security in SAP HANA-enabled ABAP applications is managed through various mechanisms, including user roles, authorizations, and secure coding practices.
- Access controls, encryption, and secure communication protocols are implemented to protect sensitive data.
- SAP HANA’s role-based security model is often leveraged to control access to different HANA database objects.
56. What is the significance of the ABAP Managed Database Procedures (AMDP) framework in SAP HANA development?
Ans:
AMDP is a framework in SAP HANA development that allows developers to define and execute database procedures directly in the ABAP code. This enables the seamless integration of ABAP and SQL script, allowing developers to leverage the power of SAP HANA for data processing within ABAP programs. It enables developers to harness the power of SAP HANA for data-intensive operations while maintaining a unified and familiar ABAP development environment.
57. How do you use ABAP CDS (Core Data Services) in SAP HANA?
Ans:
- ABAP CDS defines and consumes data models in ABAP applications. It allows developers to define data structures, associations, and annotations declaratively.
- ABAP CDS is tightly integrated with SAP HANA, and its data definitions can be translated into SAP HANA-optimized structures.
- It is mighty when used with SAP HANA as it allows for creating database views, enabling better performance and optimization.
58. Explain the concept of SAP HANA dynamic tiering.
Ans:
SAP HANA Dynamic Tiering is an extension of the SAP HANA database that enables the management of warm data (less frequently accessed data) in more cost-effective storage solutions, such as disk-based storage. It allows organizations to balance performance and storage costs by moving data between in-memory and extended storage based on access patterns.
59. What is the role of the SAP HANA Development perspective in ABAP development?
Ans:
- The SAP HANA Development perspective in the ABAP Workbench provides tools and editors specifically designed for developing applications that leverage SAP HANA capabilities.
- It includes features for defining HANA database artifacts, writing SQLScript procedures, and optimizing ABAP code for execution on the SAP HANA platform.
- SAP Business Application Studio (BAS) is gaining popularity as an alternative to SAP HANA Studio for cloud-based development.
60. How do you use SAP Fiori Elements in ABAP on HANA applications?
Ans:
- SAP Fiori Elements is a design approach that allows developers to create SAP Fiori applications using predefined templates and annotations.
- In ABAP on HANA applications, Fiori Elements simplifies the development process by providing a consistent and responsive user interface.
- Developers can leverage Fiori Elements to create applications seamlessly integrating with the SAP Fiori Launchpad.
61. What is the significance of the SAP HANA data lifecycle manager?
Ans:
- The SAP HANA Data Lifecycle Manager (DLM) manages the data lifecycle in SAP HANA. It helps automate tasks related to data aging, archiving, and partitioning.
- Using DLM, organizations can optimize storage and improve performance by transferring data that is not used as often to lower-cost storage solutions.
62. How do you use the HANA-specific SELECT options in ABAP?
Ans:
- HANA-specific SELECT options in ABAP allow developers to use SAP HANA’s advanced querying capabilities.
- Examples include “FOR UPDATE,” which enables optimistic locking, and “HINT,” which allows developers to provide hints to the HANA database optimizer for query optimization.
- These options allow you to take advantage of SAP HANA’s advanced capabilities for processing data efficiently.
63. Explain the concept of SAP HANA transport groups in ABAP development.
Ans:
SAP HANA Transport Groups bundle and transport HANA database artifacts with ABAP development objects. This ensures that changes to the database structure and associated ABAP code are transported together, maintaining consistency between the ABAP and HANA layers.
64. What is the role of the HANA Rules Framework in ABAP on HANA applications?
Ans:
- The HANA Rules Framework defines and executes business rules directly within the SAP HANA database.
- In ABAP on HANA applications, this framework allows developers to implement and manage complex business rules at the database level, improving performance and maintaining data integrity.
- BRFplus is often used in ABAP on HANA applications and can be integrated with SAP HANA to handle complex decision logic.
65. How do you handle currency conversion in SAP HANA using ABAP?
Ans:
- Currency conversion in SAP HANA using ABAP is typically done through built-in functions and expressions in SQLScript.
- Developers can leverage functions like “CONVERT_CURRENCY” to handle currency conversion directly within the HANA database when querying or manipulating data.
- This may involve calling AMDP methods from ABAP programs and handling the results accordingly.
66. What is the purpose of the SAP Fiori launchpad designer in ABAP on HANA?
Ans:
The SAP Fiori Launchpad Designer in ABAP on HANA is a tool for designing and configuring the SAP Fiori Launchpad. The Fiori launchpad is a central entry point for users to access SAP Fiori applications and other content in a user-friendly and role-based manner. The Launchpad Designer allows administrators and designers to tailor the launchpad to meet an organization’s specific needs.
67. Explain the concept of SAP HANA XS Advanced.
Ans:
SAP HANA XS Advanced is an extended application server environment for SAP HANA. It provides capabilities for developing and deploying applications, services, and extensions on the SAP HANA platform. XS Advanced supports a microservices architecture and enables the development of applications using various programming languages.XS Advanced introduces enhancements and additional capabilities compared to the original XS.
68. How do you handle data persistence in SAP HANA using ABAP?
Ans:
Data persistence in SAP HANA using ABAP involves storing and retrieving data efficiently. Developers use optimized SQLScript for data manipulation and leverage HANA-specific features like column-store tables and in-memory processing to ensure fast and efficient data access. Using SAP HANA-specific features, such as CDS views and AMDP, can provide better integration with the SAP HANA database and leverage its advanced capabilities.
69. What is the role of the ABAP Restful Application Programming Model (RAP) in SAP HANA development?
Ans:
- ABAP RAP is a programming model that allows developers to build RESTful applications on top of the SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP), including SAP HANA.
- It simplifies development by providing conventions and effective practices for creating maintainable and scalable applications that expose and consume data via RESTful APIs.
70. How do you use the SAP HANA-specific data types in ABAP programs?
Ans:
- SAP HANA-specific data types in ABAP programs define variables, fields, and optimized parameters for SAP HANA processing.
- Examples include HANA-specific numeric types like DECIMAL and INTEGER, which take advantage of the high-performance processing capabilities of the SAP HANA database.
- These data types are designed to enhance performance and support features specific to the HANA database.
71. Explain the concept of SAP HANA data aging.
Ans:
- SAP HANA Data Aging is a feature that allows organizations to manage the volume of data stored in the SAP HANA database over time.
- It involves moving older, less frequently accessed data to a lower-cost storage solution while keeping a reference to the data in the central database.
- This helps optimize storage costs and improve overall system performance.
72. What is the significance of the ABAP for SAP HANA data modeling tools?
Ans:
- ABAP for SAP HANA Data Modeling Tools allows programmers to make and manage data models directly in the ABAP Development Workbench.
- These significant tools enable developers to leverage SAP HANA’s advanced data processing capabilities and create efficient data models for ABAP applications.
- These tools enable developers to design, create, and manage database artifacts optimized for SAP HANA.
73. How do you use SAP Fiori Elements with analytical apps in ABAP on HANA?
Ans:
SAP Fiori Elements with Analytical Apps in ABAP on HANA allows developers to install analytical applications with minimal email coding. Fiori Elements generates the user interface based on metadata annotations, providing a consistent and responsive design for analytical apps. Analytical apps built with Fiori Elements provide a consistent and responsive user experience for analytical tasks.
74. What is the purpose of the ABAP on HANA code inspector?
Ans:
- The ABAP on HANA Code Inspector is a tool for performing static code checks and analyzing ABAP programs in the context of SAP HANA development.
- It helps identify potential performance issues, coding inefficiencies, and adherence to best practices for ABAP programming in the context of SAP HANA. Using the ABAP on HANA Code Inspector is a proactive approach to ensure the quality, performance, and consistency of ABAP code in the context of SAP HANA databases.
75. Explain the concept of ABAP on HANA performance analysis tools.
Ans:
ABAP on HANA performance analysis tools are tools SAP provides to analyze and optimize the performance of ABAP programs running on SAP HANA databases. These tools help developers and administrators identify performance bottlenecks, analyze runtime behavior, and implement optimizations to ensure efficient execution on the in-memory SAP HANA platform.
76. How do you handle authorization in SAP HANA-enabled ABAP programs?
Ans:
Authorization in SAP HANA-enabled ABAP programs is managed through roles and privileges. Developers assign the necessary roles to users, and the SAP HANA database checks for the required privileges during runtime. This ensures that users have the appropriate permissions to access and manipulate data. SAP HANA uses a role-based authorization model, where users are assigned roles that grant specific privileges to database objects.
77. How do you use SAP Fiori Elements for worklist pages in ABAP on HANA?
Ans:
- SAP Fiori Elements for Worklist Pages in ABAP on HANA enables developers to create worklist pages with a consistent and responsive design.
- Fiori Elements automatically generates the user interface based on metadata annotations, simplifying the development process for worklist pages.
- Worklist pages are commonly used to display a list of items or tasks that require user action.
78. How do you use the SAP Fiori Elements for transactional apps in ABAP on HANA?
Ans:
SAP Fiori Elements is a framework that simplifies the development of SAP Fiori apps by generating user interfaces based on metadata annotations and OData services. For transactional apps in ABAP on HANA, Fiori Elements can be used to create apps that provide a consistent and responsive user experience for transactional tasks.
79. Explain the concept of ABAP for SAP HANA data models.
Ans:
ABAP for SAP HANA data models refer to the design and representation of data structures and relationships in the context of ABAP programming when utilizing the in-memory SAP HANA capabilities database. These data models are optimized to use SAP HANA’s advanced features, such as in-memory processing, parallelization, and optimized data storage.
80. What is the role of the ABAP on HANA-specific runtime object editors?
Ans:
ABAP on HANA-specific runtime object editors plays a crucial role in developing and maintaining ABAP programs and objects when working with SAP HANA as the underlying database. These editors are specialized tools within the ABAP Development Workbench that allow developers to interact with and modify runtime objects directly during the execution of ABAP programs.
81. How do you use SAP HANA-specific features in ABAP programs?
Ans:
- Developers can use SAP HANA-specific features in ABAP programs by incorporating optimized SQLScript, leveraging HANA-specific data types, and utilizing advanced database operations for better performance.
- This includes using features like table partitioning, parallel processing, and advanced analytics functions.
- By incorporating these practices into your ABAP programming, You may utilize SAP to its fullest extent. HANA-specific features improve your ABAP programs’ performance, scalability, and efficiency within the SAP HANA landscape.
82. What is the purpose of the SAP Fiori launchpad content manager in ABAP on HANA?
Ans:
Developers can use SAP HANA-specific features in ABAP programs by incorporating optimized SQLScript, leveraging HANA-specific data types, and utilizing advanced database operations for better performance. This includes using features like table partitioning, parallel processing, and advanced analytics functions. The Fiori Launchpad in ABAP on HANA is a dynamic environment, and new features or tools may be introduced in subsequent releases.
83. Explain the concept of ABAP for SAP HANA-managed database procedures.
Ans:
- ABAP Managed Database Procedures (AMDP) is a framework introduced by SAP to allow developers to write database procedures using SQLScript directly within ABAP programs.
- AMDP enables seamless integration of ABAP and SAP HANA native SQLScript, allowing developers to push down computation-intensive logic to the SAP HANA database.
- This helps in leveraging the in-memory processing capabilities of SAP HANA and optimizing the performance of ABAP programs.
84. How do you use the SAP Fiori Elements for analytical apps in ABAP on HANA?
Ans:
SAP Fiori Elements for Analytical Apps in ABAP on HANA enables developers to create analytical applications with a consistent and responsive design. Fiori Elements automatically generates the user interface based on metadata annotations, simplifying the development process for analytical apps. Fiori Elements simplifies the development process and ensures a consistent and responsive user experience for analytical scenarios
85. What is the significance of the SAP Fiori launchpad in the context of ABAP on HANA applications?
Ans:
The SAP Fiori Launchpad is significant in the context of ABAP on HANA applications as it provides a unified and user-friendly entry point for Fiori apps. It enhances the user experience by offering a centralized hub for accessing various applications and analytical tools running on the SAP HANA platform. It enhances user productivity, simplifies navigation, and contributes to an integrated and streamlined user experience within the SAP landscape.
86. How do you use the SAP Fiori Elements for overview pages in ABAP on HANA?
Ans:
SAP Fiori Elements for Overview Pages in ABAP on HANA allows developers to create overview pages with aggregated information and key performance indicators (KPIs). Fiori Elements handles the generation of the user interface based on metadata annotations, simplifying the development process. Fiori Elements simplifies the development process and ensures a consistent and responsive user experience for analytical scenarios.
87. Explain the concept of ABAP for SAP HANA analytical privilege.
Ans:
- Analytical privileges in the context of SAP HANA refer to a security mechanism that controls access to data at a granular level within analytical scenarios.
- Analytical privileges are designed to restrict users’ access to specific data based on predefined rules, allowing organizations to enforce data-level security in analytical applications.
- In the context of ABAP for SAP HANA, analytical privileges are used to control access to data when working with CDS views, especially for analytical scenarios.
88. What is the role of the ABAP on a HANA-specific object navigator?
Ans:
The ABAP on HANA-Specific Object Navigator is a tool in the ABAP Development Workbench that allows developers to navigate and explore HANA-specific objects. It provides an organized view of objects related to SAP HANA development, facilitating efficient development and troubleshooting. These tools provide a navigation and development environment for ABAP on HANA applications.
89. How do you use the SAP Fiori Elements for fact sheets in ABAP on HANA?
Ans:
- SAP Fiori Elements for Fact Sheets in ABAP on HANA enables developers to create fact sheets with detailed information about specific business objects.
- Fiori Elements handles the generation of the user interface based on metadata annotations, streamlining the development process for fact sheets.
- Fiori Elements simplifies the development process and ensures a consistent and responsive user experience for fact sheet scenarios.
90. What is the purpose of the ABAP for the SAP HANA SQL console?
Ans:
- The ABAP for SAP HANA SQL Console is a tool in the ABAP Development Workbench that allows developers to execute SQL statements directly against the SAP HANA database.
- It is helpful for testing and optimizing SQL queries and performing ad-hoc data analysis.
- It’s important to note that features and tools in the SAP ecosystem are subject to updates and changes.
91. Explain the concept of ABAP for SAP HANA ABAP Development Tools (ADT).
Ans:
- ABAP Development Tools (ADT) for SAP HANA is an integrated development environment provided by SAP for ABAP developers working on SAP HANA projects.
- ADT enhances the development experience by providing a collection of resources and attributes designed expressly for ABAP developers who are leveraging the capabilities of the SAP HANA in-memory database.
- It integrates seamlessly with the Eclipse IDE (Integrated Development Environment) and is designed to efficiently support ABAP development for SAP HANA.
92. What is the role of the ABAP in HANA-specific transport organizer?
Ans:
The ABAP on HANA-Specific Transport Organizer is a tool in the ABAP Development Workbench that allows developers to organize and transport HANA-specific and ABAP development objects. It ensures consistent and synchronized deployment of both ABAP and HANA artifacts. The transport organizer is not specific to ABAP on HANA but is a fundamental part of the SAP development and deployment process.
93. What is the significance of the ABAP on HANA-specific search?
Ans:
- ABAP on HANA-Specific Search Helps enhance search functionality in ABAP applications by leveraging SAP HANA’s search capabilities.
- They provide efficient and optimized search results, improving the overall performance of search functionalities.
- While the term “ABAP on HANA-specific search” may not represent a standalone feature, the search capabilities within ABAP development tools, SAP HANA Studio, and related environments play a crucial role in improving developer productivity, code quality, and overall development efficiency on the SAP HANA platform.
94. How do you use SAP Fiori Elements for object pages in ABAP on HANA?
Ans:
SAP Fiori Elements for Object Pages in ABAP on HANA allows developers to create object pages with detailed information about specific business objects. Fiori Elements handles the generation of the user interface based on metadata annotations, simplifying the development process for object pages. Fiori Elements simplifies the development process and ensures a consistent and responsive user experience for detail-based scenarios.
95. Explain the concept of ABAP for SAP HANA calculation views.
Ans:
- ABAP for SAP HANA Calculation Views involves designing and using calculation views in ABAP applications to perform complex calculations and aggregations on data stored in the SAP HANA database.
- Calculation views are vital for analytical processing in ABAP on HANA.
- They can be used for different purposes, such as aggregating data, joining tables, applying filters, and performing complex calculations.






