
- Introduction
- Definition and Theories
- Types of Leadership Styles
- Characteristics of a Good Leader
- Importance in Organizations
- Transformational vs. Transactional
- Leadership vs. Management
- Ethical Leadership
- Leadership Development
- Case Studies
- Common Challenges
- Conclusion
Introduction
What Is leadership in organization is one of the most studied and vital aspects of any organization. It plays a crucial role in shaping organizational culture, influencing team dynamics, and driving business success. Leadership is not merely about holding a position of authority; it is about inspiring, guiding, and influencing others toward a shared vision or goal, a quality that can be cultivated through PMP Training. Effective Leadership becomes even more essential in a world characterized by constant change and growing complexity. Organizations rely on leaders to innovate, respond to challenges, manage teams, and uphold values. Leadership effectiveness can often determine the difference between organizational success and failure.
To Explore PMP in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive PMP Certification Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Definition and Theories
Leadership in organization can be defined as the process of influencing and guiding individuals or groups to achieve common goals, a process that is often strengthened by adopting Effective Methods of Recruitment. Unlike management, which focuses on planning and controlling, Leadership is about motivating and aligning people. Over the decades, several leadership theories have been developed to understand how effective leaders behave and why people follow them.
Major Theories of Leadership:
- Trait Theory – Suggests that great leaders are born with certain traits like intelligence, confidence, and charisma.
- Behavioral Theory – Focuses on what leaders do, not who they are. It classifies
- Leadership into task-oriented and people-oriented behaviors.
- Contingency Theory – This theory argues that leadership effectiveness depends on the situation and context.
- Situational Leadership leadership in organization Theory – Leaders adapt their style based on the maturity of their followers.
- Transformational Leadership Theory – Emphasizes vision, inspiration, and change.
- Transactional Leadership Theory – Based on structured tasks, rewards, and punishments.
Each theory provides unique insights and contributes to a better understanding of what makes a leader effective in varying contexts.
Types of Leadership Styles
Leadership styles refer to the behavior patterns a leader exhibits in directing, motivating, and managing teams. These styles vary based on personality, organizational culture, and the nature of tasks, and are often influenced by principles of Corporate Social Responsibility.
Common Leadership Styles:
- Autocratic Leadership – The leader makes decisions unilaterally. Efficient but can demotivate teams.
- Democratic Leadership – Involves team members in decision-making. Encourages creativity and engagement.
- Laissez-Faire Leadership – Gives employees the freedom to make decisions. Effective with highly skilled teams.
- Transformational Leadership – Inspires and motivates employees to exceed expectations.
- Transactional Leadership – Focuses on structure, rewards, and supervision.
- Servant Leadership – Prioritizes serving others before self-interest. Builds trust and loyalty.
- Charismatic Leadership – Relies on charm and persuasion to influence others.
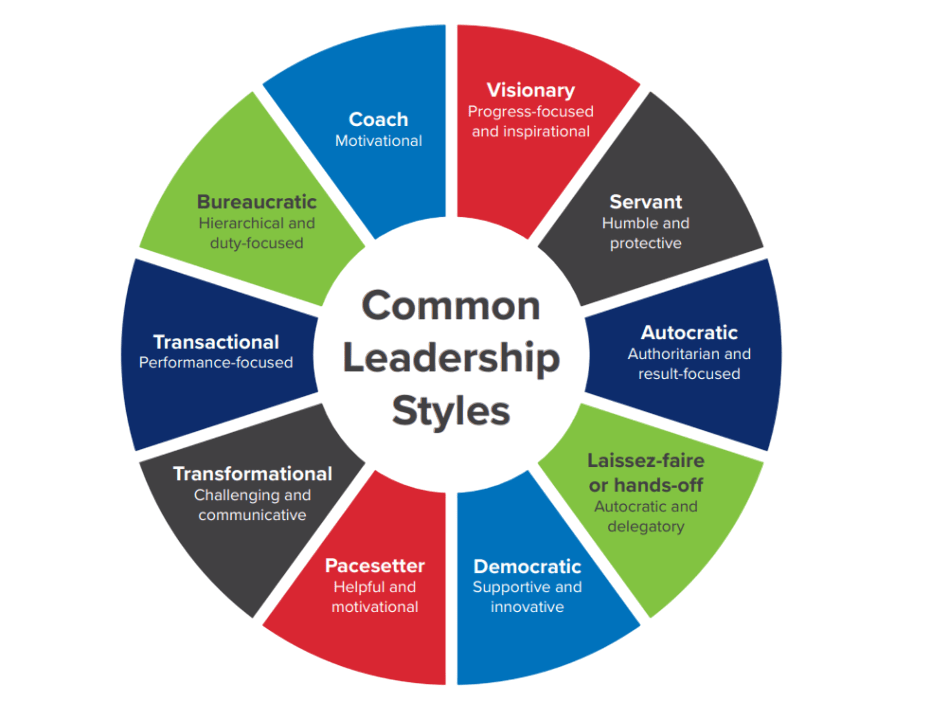
Choosing the right style depends on the leader’s personality, team maturity, and organizational needs.
Are You Interested in Learning More About PMP? Sign Up For Our PMP Certification Training Today!
Characteristics of a Good Leader
Effective professional development leadership training relies on a set of qualities that help individuals motivate, influence, and guide others. These traits are important for handling complex issues, building trust, and forming strong relationships within a team or organization. One crucial quality is having a visionary mindset. This trait allows leaders to see the bigger picture and set a clear path ahead, a skill that can be nurtured through PMP Training. Integrity ensures that they act with honesty, ethics, and transparency, earning the respect of those around them. Emotional intelligence helps leaders recognize and manage feelings both their own and those of their team members. Strong communication skills let them express goals, expectations, and constructive feedback clearly.
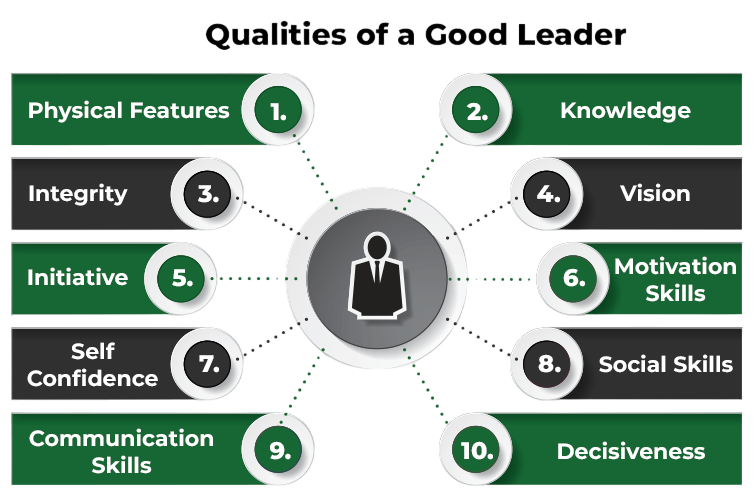
Equally important are empathy, which builds connection and support, and decisiveness, which enables leaders to make quick and confident decisions. Adaptability keeps them resilient and flexible in the face of change, while confidence inspires others and provides a sense of direction. While some people may naturally have these qualities, great leaders develop them through experience, education, and self-reflection. Developing these traits is vital for becoming a strong and effective leader.
Are You Preparing for PMP Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Project Management Interview Questions & Answer to Boost Your Preparation!
Importance in Organizations
Leadership significantly affects all levels of an organization. It impacts areas like employee morale, productivity, innovation, and customer satisfaction. One main role of leadership is to provide vision and direction. This helps the team understand the organization’s overall purpose and goals. Leaders also play a vital part in managing change, a process that can be better aligned with the principles of What is Service Marketing. They assist teams in navigating transitions and new developments effectively. Good leaders inspire their teams. They motivate employees to perform their best and stay engaged. They help create a positive work environment by settling conflicts and encouraging collaboration among team members. Moreover, leaders shape the organizational culture by setting standards for values, behaviors, and work ethics. Another important role of leadership is to develop talent. Leaders guide employees and prepare future leaders within the organization. Without strong leadership, even the best strategies may fail. Leadership keeps the organization focused, motivated, and ready to meet its goals.
Transformational vs Transactional Leadership
These two styles are among the most researched professional leadership training and practiced in modern organizations, reflecting principles closely tied to What is Human Resource Management. Understanding their differences helps identify which style suits which context.
Transformational Leadership:
- Focuses on inspiration, motivation, and change.
- Leaders are visionaries who challenge the status quo.
- Encourages innovation and creativity.
- Builds emotional commitment among followers.
Transactional Leadership:
- Based on structure, rules, and supervision.
- Leaders use rewards and penalties to drive performance.
- Emphasizes short-term goals and efficiency.
- Works well in routine or structured environments.
Both styles have their place. Often, the best leaders combine elements of both depending on situational needs.
Leadership vs Management
| Aspect | Leadership | Management |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Vision and strategy | Planning and execution |
| Approach | Inspires and motivates | Organizes and coordinates |
| Goal | Change and innovation | Stability and efficiency |
| Relationship | Builds trust | Maintains authority |
| Decision-making | Risk-taking | Risk-averse |
An organization needs both strong Leadership and efficient management. Leadership sets direction, while management ensures smooth operations.
Are You Considering Pursuing a Master’s Degree in PMP? Enroll in the PMP Masters Program Training Course Today!
Ethical Leadership
Ethical Leadership is rooted in respect, honesty, fairness, and accountability. Ethical leaders comply with laws and standards and uphold moral principles in decision-making.
Features of Ethical Leadership:
- Acts with transparency and fairness.
- Encourages ethical behavior in others.
- Builds a culture of trust.
- Promotes social responsibility and sustainability.
Ethical leaders create workplaces where employees feel safe, respected, and valued. This, in turn, enhances organizational reputation and long-term success.
Leadership Development
Developing leadership skills is important for everyone in an organization, not just those at the top. Investing in leadership professional leadership training is vital for nurturing future leaders and ensuring stability as the company grows. Businesses often use various effective strategies to build leadership abilities. Mentoring and coaching provide personalized guidance from experienced leaders, while workshops and professional leadership training sessions offer structured education on key leadership concepts, which align closely with the principles of Managerial Economics in Business Decision-Making. Job rotation and cross-functional projects expose individuals to different roles and challenges, helping them gain a broader perspective. Feedback systems, including performance reviews and 360-degree assessments, allow individuals to identify their strengths and areas for improvement. For higher-level positions, executive education programs offer in-depth training to improve strategic thinking. Organizations that focus on professional development leadership training often see higher employee engagement, lower turnover, and a strong internal talent pool, all of which support long-term success.
Case Studies
- Satya Nadella – Microsoft When Nadella became CEO in 2014, he transformed Microsoft’s culture from internal competition to collaboration. Through empathetic Leadership, he revived the company’s innovation and employee morale.
- Indra Nooyi – PepsiCo Known for her transformational Leadership, Nooyi led PepsiCo, which focused on health-conscious products and sustainable business practices. She fostered a people-first culture and invested in leadership development.
- Elon Musk – Tesla and SpaceX Musk exhibits charismatic and transformational traits. He sets ambitious goals and challenges norms. While controversial in his style, his Leadership has pushed technological boundaries and created new industries.
These examples show that leadership styles can vary, but the impact of strong Leadership is universally significant.
Common Challenges
Typical professional development leadership training Challenges are often linked to mastering Core Operations Manager Responsibilities.- Managing Change – Resistance from employees or stakeholders.
- Diverse Teams – Navigating cultural, generational, or functional differences.
- Conflict Management – Handling interpersonal tensions and disputes.
- Decision Fatigue – Making continuous critical decisions.
- Maintaining Morale – Keeping teams motivated during downturns.
- Delegation – Struggling to let go and empower others.
Overcoming these challenges requires emotional intelligence, resilience, and a commitment to continuous improvement.
Conclusion
What Is leadership in organization is both an art and a science. It involves inspiring others, making tough decisions, upholding values, and driving positive change. Effective Leadership goes beyond positional power; it is about influence, vision, empathy, and action, qualities that can be strengthened through PMP Training. Every leadership in organization style offers value in different contexts, from transformational to transactional and ethical to charismatic. The best leaders are adaptable, lifelong learners who evolve with their teams and environments. The demand for effective, ethical, and innovative leaders will only grow as the world changes. Organizations that invest in cultivating Leadership at all levels are more likely to thrive, overcome challenges, and achieve lasting success.





