
Welcome! In this session, we’ll look at fundamental BOXI ideas using a series of basic interview questions. Whether you’re preparing for an interview or brushing up on BOXI fundamentals, these questions cover everything from Universes to Web Intelligence. Let’s go into the fundamentals of SAP BusinessObjects.
1. What is Business Objects (BO) SAP?
Ans:
The business intelligence suite SAP BusinessObjects XI (BOXI) includes tools for dashboards (Xcelsius), data integration (Data Services), data exploration (Explorer), and reporting (Web Intelligence, Crystal Reports). It offers a complete solution that supports ad hoc queries, analytics, and visualization while converting data into insightful understandings.
2. What kinds of products fall under the category of Business Objects?
Ans:
- Web Intelligence (WebI): Web-based ad hoc reporting tool: .
- Crystal Reports: A powerful web and print reporting tool.
- Interactive dashboards : It made with SAP BO Dashboards (Xcelsius).
- Explorer: A self-serve tool for exploring data.
- Universes: Semantic layer for easier access to data.
3. In SAP BO, what is a Universe?
Ans:
In SAP BusinessObjects (BO), a Universe serves as a semantic layer that simplifies the interaction with databases. It acts as an intermediary, offering a streamlined view of data by defining relationships, structures, and business logic. Universes enable users to create reports without needing in-depth knowledge of underlying database complexities.SAP BusinessObjects offers a streamlined, user-friendly layer called A Universe that abstracts the intricacies of databases. It lets users to produce
4. In SAP BO, what is a dashboard?
Ans:
A dashboard in SAP BusinessObjects is a graphic depiction of important performance metrics and business data. Dashboards, which are made with software like as Xcelsius or Lumira, facilitate rapid decision-making by providing interactive, real-time information via graphs and charts.
5. In SAP BO, what is a Crystal Report?
Ans:
A Crystal Report in SAP BusinessObjects is a tool for creating highly structured reports from various data sources. It allows parameterized reporting, has a wide range of formatting options, and can be distributed both online and offline.
A Crystal Report in SAP BusinessObjects serves as a robust reporting tool designed for creating, formatting, and generating customizable reports from diverse data sources. It empowers users to craft visually appealing and interactive reports, incorporating elements like charts and graphs.
6. What is a key for a domain?
Ans:
Generally speaking, “domain.key” refers to a key file connected to domains in settings such as encryption, SSL/TLS security, or particular software setups. Within SAP BO, a key for a domain functions as a unique identifier linked to a set of values in that domain. This key is essential for efficient data retrieval and plays a crucial role in establishing relationships between different datasets. The precise meaning varies based on the technology or domain in question.
7. For what purposes are Business Objects Data Services utilized?
Ans:
- Data integration, transformation, and quality control are among the ETL operations for which BusinessObjects Data Services (BODS) is utilized.
- With seamless interface into both SAP and non-SAP systems, it facilitates real-time processing, data movement, and replication.
- By streamlining the ETL procedure, BODS promotes effective data flow and supports data-driven decision-making.
8. What is the difference between a slice and a dice in SAP BO?
Ans:
| Operation | Slice | Dice | |
| Definition |
Selecting a single dimension to view a specific subset of data. |
Selecting multiple dimensions to view specific intersections of data. | |
| Purpose | Focus on a specific dimension to analyze data along one axis. | Analyze data across multiple dimensions, drilling down into specific intersections. | |
| Result | Reduces data to a two-dimensional view, eliminating other dimensions. | Creates a subcube, providing a more detailed view of the data. | |
9. Could you describe a report’s lifetime in SAP BusinessObjects XI?
Ans:
To create a report, a data source must be specified, the report layout must be created, the report must be scheduled or run, and finally it must be distributed to end users. In SAP BusinessObjects XI, a report undergoes stages such as creation, modification, and distribution throughout its lifetime. Reports are crafted using tools like Crystal Reports or Web Intelligence, saved, and scheduled for distribution. Throughout their existence, reports may be updated, shared with users or groups, and refreshed as necessary.
10. What distinguishes Crystal Reports from Web Intelligence?
Ans:
Crystal Reports is a strong tool for producing finely structured and interactive reports, whereas Web Intelligence is a web-based ad hoc reporting tool. Crystal Reports is tailored for creating pixel-perfect, highly formatted, and print-ready reports. Conversely, Web Intelligence is designed for ad-hoc querying and analysis, enabling users to interactively explore and visualize data. Crystal Reports excels in structured and static reporting, while Web Intelligence thrives in dynamic and user-driven scenarios.
11. .How is data security managed in SAP BusinessObjects?
Ans:
The management of data security is achieved by means of user authentication, access controls, and the assignment of privileges to individuals and groups.Data security in SAP BusinessObjects is administered through user authentication, authorization, and access controls. Users are authenticated based on their credentials, and authorization is defined through roles and privileges, restricting access to specific data and functionalities.
12. Describe drill-down and drill-up as they relate to reporting.
Ans:
Drill-up is the opposite of drill-down, involving accessing more in-depth data from a higher-level summary. Drill-down and drill-up refer to the capacity to navigate through different levels of detail in a report. Drill-down involves transitioning from a summarised view to a more detailed one, while drill-up is the reverse, moving from detailed information to a higher-level summary. These features enhance the interactive and exploratory aspects of reporting.
13. How does SAP BusinessObjects support mobile reporting?
Ans:
SAP BusinessObjects provides mobile solutions, allowing users to access reports and dashboards on mobile devices through applications or responsive web interfaces. SAP BusinessObjects facilitates mobile reporting through its mobile application, enabling users to access and interact with reports on various mobile devices. Reports are optimised for mobile viewing, ensuring a responsive and user-friendly experience.
14. What is the role of a key performance indicator (KPI) in BusinessObjects reporting?
Ans:
KPIs are measurable values representing key business metrics, providing a quick overview of business performance in reports and dashboards. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) in BusinessObjects reporting are metrics that gauge an organisation’s performance against strategic goals. KPIs aid in monitoring and analysing business performance, providing stakeholders with valuable insights for decision-making.
15. How does SAP BusinessObjects support multi-language reporting?
Ans:
SAP BusinessObjects allows for the creation of reports in multiple languages, supporting globalization and localization requirements.SAP BusinessObjects supports multi-language reporting by allowing the creation of reports in different languages. This is achieved through localization features, enabling the translation of text elements like labels and descriptions to cater to users with diverse language preferences.
16. Explain the concept of bursting in SAP BusinessObjects reporting.
Ans:
Bursting involves the automated distribution of a report to multiple recipients based on specified criteria, such as department or region. Bursting in SAP BusinessObjects reporting involves automatically delivering a single report to multiple recipients. Each recipient receives a personalised subset of the data based on predefined criteria, allowing for targeted distribution to different stakeholders.
17. How many Domains are present in Business Objects?
Ans:
- “Domains” in SAP BusinessObjects generally relate to universes, which are semantic layers that make data access easier for reporting.
- Depending on the demands of the business, there are different numbers of domains. Domains in Web Intelligence (WebI) refer to data collections used to create reports.
- The precise meaning varies according to the particular BusinessObjects environment.
18. How can you optimize the performance of reports in SAP BusinessObjects?
Ans:
Performance optimization involves using efficient queries, indexing, and limiting the amount of data retrieved in reports. To optimise performance in SAP BusinessObjects reports, minimise unnecessary data retrieval, optimise queries, use caching mechanisms, and establish efficient database connections. Additionally, proper indexing and partitioning of data sources contribute to enhancing report execution speed. Caching and aggregation strategies can also be employed.
19. What is the objective of SAP BusinessObjects’ Query as a Web Service (QaaWS)?
Ans:
QAAWS enables third-party applications to use web services to access and retrieve data from SAP BusinessObjects reports. The goal of Query as a Web Service (QaaWS) in SAP BusinessObjects is to provide a web service interface for queries. This allows external applications to consume BusinessObjects queries as web services, promoting integration with other systems and ensuring interoperability.
20. What distinguishes a SAP BusinessObjects universe from a report?
Ans:
A report is a document generated by Web Intelligence or Crystal Reports that uses the definitions from the universe as a semantic layer to define data structures. A SAP BusinessObjects universe acts as a semantic layer, simplifying database complexities for end-users and facilitating report creation. In contrast, a report is a document generated using tools like Crystal Reports or Web Intelligence, presenting data derived from a universe. The universe serves as an intermediary layer, defining data relationships and structures.
21. Describe the SAP BusinessObjects notion of dynamic cascading prompts.
Ans:
Users can choose values in a single prompt using dynamic cascading prompts, which increase involvement by dynamically adjusting the subsequent prompts based on the values selected.Dynamic cascading prompts in SAP BusinessObjects create a hierarchical relationship where the values in one prompt dynamically control the values displayed in another. This feature allows for interactive and personalised reporting experiences, refining the dataset based on user selections.
22. How are report and universe versioning and promotion managed in SAP BusinessObjects?
Ans:
In order to monitor modifications in reports and universes and enable regulated promotion between development, testing, and production environments, SAP BusinessObjects offers versioning and promotion management capabilities
23. In SAP BusinessObjects Data Services (BODS), what is a Derived Table?
Ans:
- In BODS, a derived table is one that is produced during the data extraction and transformation process.
- These tables are frequently generated through a variety of procedures from pre-existing tables.
- In SAP BusinessObjects Data Services, a Derived Table is a table created during the data transformation process.
- It is not directly sourced from input data but is derived through calculations, expressions, or joins, enabling the creation of custom tables tailored to specific reporting requirements.
24. Could you describe a Data Federator’s function in SAP BusinessObjects?
Ans:
In response, Data Federator enables users to bring together data from various sources—including SAP and non-SAP systems—into a single, unified view without the need for data relocation. A Data Federator in SAP BusinessObjects enables the virtualization of data by combining and presenting information from various heterogeneous sources in real-time. It allows users to access and analyze data seamlessly, providing a unified view for reporting and analysis.
25. What factors should be taken into account when creating effective universes in SAP BusinessObjects?
Ans:
A few things to think about are choosing the right data sources, refining queries, creating effective joins, and making sure that indexing is done correctly for better performance. When creating effective universes in SAP BusinessObjects, consider factors such as clear business requirements, optimal data modeling, proper joins, minimizing cardinality issues, and meeting end-user needs for reporting and analysis.
26. In what ways does SAP BusinessObjects facilitate user cooperation and report sharing?
Ans:
Collaboration tools from SAP BusinessObjects include annotating and commenting on reports and dashboards, as well as securely sharing them with other users. SAP BusinessObjects promotes user cooperation and report sharing through features like user permissions, scheduling options, and distribution channels. Users can collaborate by sharing reports, scheduling automatic report delivery, and implementing user-specific access controls, fostering effective collaboration and information sharing within the organization.
27. Describe SAP Lumira’s function within SAP BusinessObjects.
Ans:
With the help of SAP Lumira, users can produce engaging and dynamic data visualizations for improved data display and analysis. Within SAP BusinessObjects, SAP Lumira serves as a self-service data visualization and exploration tool. It enables users to import, prepare, and visualize data in a user-friendly interface, creating interactive dashboards and reports for enhanced data analysis and decision-making.
28. In SAP BusinessObjects, how may report execution be scheduled and automated?
Ans:
SAP BusinessObjects scheduling tools can be used to schedule reports, enabling automated delivery and execution at certain times. Report execution in SAP BusinessObjects can be scheduled and automated using the scheduling feature. Users can set specific time intervals for report execution, ensuring that reports are generated and delivered automatically. This reduces manual intervention and improves operational efficiency.
29. Describe SAP BusinessObjects’ aggregate awareness concept.
Ans:
By identifying and making use of pre-aggregated data when necessary, aggregate awareness enables the universe to leverage aggregate tables for enhanced query performance.
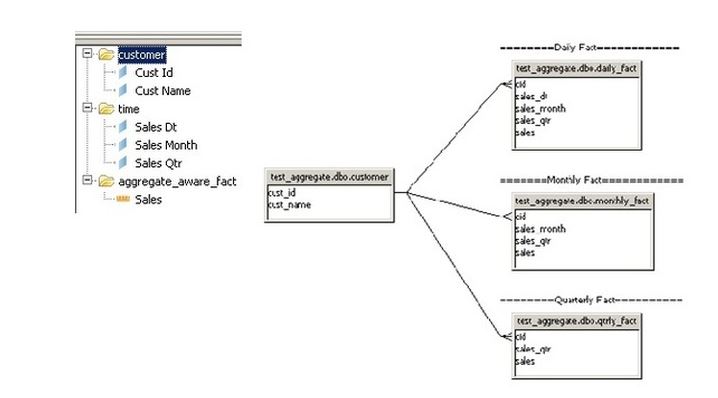
30. What does SAP BusinessObjects’ Audit Database serve as?
Ans:
The Audit Database facilitates administrators’ ability to track and evaluate system performance by storing data regarding user actions, report executions, and system utilization. The Audit Database of SAP BusinessObjects serves as a place to log and store data on system events, user activity, and report execution specifics. For the purpose of logging modifications, keeping an eye on user interactions, and guaranteeing adherence to security and legal standards, it offers an audit trail.
31. In SAP BusinessObjects, how may row-level security be implemented?
Ans:
Security profiles and filters can be used to establish row-level security, limiting user access to particular data according to predetermined criteria. Row-level security in SAP BusinessObjects can be established by applying user and group access restrictions. Administrators assign specific filters or conditions to user roles, controlling access to individual rows of data and maintaining data security and confidentiality.
32. Describe the SAP BusinessObjects Universe Design idea of context
Ans:
When it comes to joins and relationships, contexts in universe design assist clear up any confusion and give guidance on how tables should be linked in response to user queries. In SAP BusinessObjects Universe Design, a context represents a specific resolution path for ambiguous joins within a universe. It defines how tables are joined based on query requirements, ensuring accurate and unambiguous data retrieval.
33. Can you explain the function of SAP BusinessObjects’ Adaptive Processing Server?
Ans:
Background processing activities in SAP BusinessObjects, such as scheduled report execution, are managed by the Adaptive Processing Server. The Adaptive Processing Server in SAP BusinessObjects is responsible for overseeing various background processing tasks. It dynamically allocates resources based on system demands, optimizing server performance by adapting to changing workloads
34. For real-time data integration and reporting, how is SAP BusinessObjects supported?
Ans:
For reporting purposes, real-time data sources can be connected to by technologies like Web Intelligence and Dashboards, which are supported by SAP BusinessObjects Data Services (BODS). SAP BusinessObjects supports real-time data integration and reporting through technologies like SAP HANA and SAP BW (Business Warehouse). These solutions enable organisations to access and analyse real-time data, facilitating timely and informed decision-making.
35. Describe the function of SAP BusinessObjects Web Intelligence’s Query Panel.
Ans:
- In Web Intelligence, the Query Panel is a user interface used to define report elements, choose data, and create queries.
- To develop queries for data analysis and retrieval, users can utilise SAP BusinessObjects Web Intelligence’s Query Panel.
- Building complex reports is made possible by its user-friendly interface, which offers a means of choosing data, setting filters, and arranging data items.
36. How are ad hoc reporting and analysis supported by SAP BusinessObjects?
Ans:
Tools such as Web Intelligence facilitate ad-hoc reporting, enabling users to generate reports and queries without prearranged frameworks. Tools that are easy to use, such as Web Intelligence and Crystal Reports, provide ad hoc reporting and analysis within SAP BusinessObjects. Without requiring in-depth technical knowledge, users may create reports instantly and perform ad hoc analysis with the help of these tools’ user-friendly interfaces, drag-and-drop functionality, and interactive capabilities.
37. Describe the function of SAP BusinessObjects Web Intelligence’s Query Panel.
Ans:
In Web Intelligence, the Query Panel is a user interface used to define report elements, choose data, and create queries. In SAP BusinessObjects Web Intelligence, the Query Panel is a functionality.offering flexibility and ease of use for users with varying levels of technical expertise.
38. How are ad hoc reporting and analysis supported by SAP BusinessObjects?
Ans:
Tools such as Web Intelligence facilitate ad-hoc reporting, enabling users to generate reports and queries without prearranged frameworks. SAP BusinessObjects facilitates ad hoc reporting and analysis through its user-friendly tools, such as Web Intelligence and Crystal Reports. These tools feature intuitive interfaces and interactive functionalities, allowing users to create spontaneous reports and perform ad hoc analysis without requiring advanced technical skills. With drag-and-drop capabilities, users can easily select data elements, apply filters, and dynamically explore data, enabling the generation of customised reports. This accessibility empowers non-technical users to independently explore and gain insights from the data, fostering a responsive and collaborative decision-making environment.
39. Describe the various parts of the SAP BusinessObjects architecture.
Ans:
Web intelligence, Crystal Reports, Universe Designer, Central Management Server (CMS), and other components are part of the SAP BO architecture. The SAP BusinessObjects architecture includes components such as the Central Management Server (CMS), Adaptive Processing Server, Web Application Servers, Report Servers, and Data Servers. These components collaborate to manage user access, process reports, and retrieve and store data.
40. In SAP BO, what is a universe, and how is it distinct from a report?
Ans:
Between the database and the end user, a universe serves as a semantic layer that offers a perspective that is suitable for business purposes. Documents called reports are produced by retrieving and presenting data from these universes. In SAP BusinessObjects, a universe is a semantic layer that simplifies database complexities, offering a user-friendly view for end-users to create reports. A universe defines data structures and relationships. In contrast, a report is a document generated using tools like Crystal Reports or Web Intelligence, presenting data derived from a universe.
41. How are various degrees of security handled by SAP BO?
Ans:
SAP BO has multiple tiers of security, including data-level, application-level, and object-level security. By doing this, it is made sure that users can only access the resources for which they are authorized. SAP BusinessObjects manages various levels of security through features like user authentication, authorization, and access controls. Security levels are maintained by defining user roles, privileges, and restrictions, ensuring that users access only relevant data and functionalities based on their roles and responsibilities. Row-level security and folder-level security contribute to precise control over data access.
42. Describe the distinctions between Crystal Reports and Web Intelligence (WebI).
Ans:
- Crystal Reports and Web Intelligence (WebI), integral components of the SAP BusinessObjects (BO) suite, manifest notable distinctions in their design and functionality. Crystal Reports, with its heritage as a pixel-perfect reporting tool, excels in delivering highly formatted and printable reports.
- Suited for static and structured reporting needs, Crystal Reports is often the preferred choice when precise formatting is paramount. Conversely, Web Intelligence is a dynamic and web-based reporting tool that empowers users with interactive and ad-hoc reporting capabilities.
- It serves as a self-service reporting platform, fostering exploratory and flexible reporting experiences. The key differentiator lies in Crystal Reports’ strength in producing traditional, formatted reports, while WebI excels in providing real-time, interactive, and web-based reporting solutions.
43. Explain the steps involved in planning and releasing reports in SAP BO.
Ans:
The process of planning and releasing reports within SAP BusinessObjects encompasses a series of meticulous steps aimed at ensuring the seamless creation, testing, and deployment of reports. Commencing with the planning phase, where comprehensive requirements are gathered and analyzed, the subsequent steps involve the actual design of the report utilizing the chosen reporting tool, be it Web Intelligence or Crystal Reports.
Following the design phase, critical tasks such as establishing data connections, formulating queries, and exhaustive testing to guarantee report accuracy are undertaken. Upon successful validation, reports are released or published to the SAP BusinessObjects repository or a designated platform, considering factors like user access rights, scheduling preferences, and delivery mechanisms. This holistic process ensures the strategic and effective deployment of reports within the SAP BO environment.
44. What are SAP BO prompts, and what performance tuning options are available for them?
Ans:
Prompts from SAP BusinessObjects, which are essential components for improving report interactivity, let users submit data dynamically. Prompt performance adjustment options are centered on maximizing their use to reduce the effect on report execution times. Techniques include limiting prompt values to appropriate subsets, wisely using default values to expedite user interactions, and reducing the total number of prompts in a report. Furthermore, pre-fetching prompt values, where appropriate, shows up as a useful strategy to preventatively improve performance by reducing possible delays related to prompt value queries during report execution.
45. Describe the idea of SAP BO contexts and their application.
Ans:
Contexts are essential to the SAP BusinessObjects universe design because they help solve loop problems and complex interactions that might occur when tables have several paths connecting them. In essence, a context guarantees precision and clarity in data retrieval by defining a certain set of joins or a path across tables for a given query. Contexts, which are produced with the aid of tools like the Universe Design Tool (UDT) and Information Design Tool (IDT), remove uncertainty from query processing and offer a well-organized framework for precise outcomes. Their usage is especially important in situations where complex data structures require exact path definitions in order to preserve the integrity of the data model.
46. When working with enormous datasets, how can the performance of SAP BO reports be improved?
Ans:
Addressing performance challenges in SAP BusinessObjects reports when dealing with extensive datasets necessitates a multi-faceted approach to optimization. Strategies include aggregating data at the database level to reduce the volume of records fetched, optimizing queries to ensure efficiency, leveraging indexed fields for expedited data retrieval, and implementing data pruning techniques to eliminate unnecessary data. Additionally, server-level caching, adoption of efficient data retrieval methodologies, and meticulous optimization of report design elements contribute collectively to a significant enhancement in report performance, particularly when grappling with large and complex datasets.
47. Give an example of a situation in which you had to diagnose and fix performance problems in a SAP BO environment.
Ans:
An illustrative example of diagnosing and rectifying performance issues within a SAP BusinessObjects environment involves a systematic analysis of query execution times, identification of sluggish database queries, and subsequent optimization measures. This may encompass fine-tuning universe structures, ensuring appropriate indexing within the underlying database, and leveraging performance monitoring tools to pinpoint specific bottlenecks. Adjustments to caching mechanisms, strategic deployment of query parallelization, and careful allocation of resources emerge as key considerations in the diagnostic and remedial process, ensuring optimal performance and responsiveness within the SAP BO ecosystem.
48. Could you describe an instance in which you used SAP BO to implement sophisticated security requirements like row-level security?
Ans:
The implementation of row-level security within SAP BusinessObjects is a critical endeavor, particularly when dealing with sensitive or confidential data. This involves the establishment of security profiles and constraints based on user roles and privileges. Filters or security constraints are integrated into the universe or report design, restricting data access based on predefined criteria. For instance, filters tied to LDAP or Active Directory attributes can be employed to dynamically control data visibility based on user roles. This ensures that each user is presented with a tailored dataset, adhering to specific security requirements and granting access only to the data they are authorized to view.
49. Give an explanation of the slice and dice idea in relation to SAP BO analysis.
Ans:
- In the realm of SAP BusinessObjects analysis, the concept of “slice and dice” introduces an interactive and dynamic approach to exploring multidimensional data.
- This methodology enables users to selectively “slice” the data by choosing a subset along one dimension and “dice” it by selecting another subset along a different dimension.
- This interactive analysis empowers users to drill down into specific areas of interest within the dataset, facilitating a granular understanding of data patterns and relationships.
- The ability to dynamically navigate through dimensions enhances the user experience, enabling nuanced exploration and analysis of multidimensional data within the SAP BO environment.
50. In SAP BO reports, how can dynamic hierarchies be implemented?
Ans:
- Dynamic hierarchies within SAP BusinessObjects reports contribute to a more interactive and flexible user experience by allowing users to dynamically navigate through hierarchical levels of data.
- This can be achieved through features such as “drill down” or “drill up” options within the report interface.
- By interacting with these dynamic hierarchy controls, users can seamlessly explore different levels of granularity within the data, adapting the report view to their analytical needs.
- This dynamic hierarchy implementation not only enhances user engagement but also provides a versatile approach to data analysis within the SAP BO reporting environment.
51. Explain the ways in which SAP BO can be integrated with other SAP products.
Ans:
SAP BusinessObjects (SAP BO) boasts versatile integration capabilities with various SAP products, fostering a cohesive enterprise ecosystem. For instance, seamless integration with SAP Business Warehouse (BW) facilitates robust reporting and dashboard creation by tapping into BW data. Similarly, integration with SAP ERP systems empowers users to generate in-depth analytics by accessing pertinent data. The native support for SAP HANA leverages its high-performance in-memory capabilities, while integration with SAP Analytics Cloud completes the comprehensive analytics landscape.
52. How can reports from SAP BO be integrated into third-party programs, like online portals?
Ans:
The incorporation of SAP BO reports into third-party programs, such as online portals, is facilitated through multiple avenues. Leveraging web services enables external applications to access and consume BusinessObjects reports and data. Additionally, embedding reports into third-party applications using iframes ensures a seamless and integrated user experience. The export functionality, supporting various formats, coupled with APIs, allows for automated retrieval of report data, enhancing integration capabilities.nt.
53. Describe the best techniques and factors to take into account while creating SAP BO reports for mobile devices.
Ans:
Techniques for Creating SAP BO Reports for Mobile Devices:Creating SAP BO reports optimized for mobile devices requires a strategic approach. Implementing responsive design ensures adaptability to diverse screen sizes, providing an optimal viewing experience. Employing mobile application design, such as utilizing the SAP BO Mobile App, enhances user accessibility and interaction. Performance optimization becomes crucial, involving the streamlining of queries to facilitate faster loading, particularly in environments with limited bandwidth.
54. What benefits and drawbacks come with adopting SAP BO multisource universes?
Ans:
The adoption of multisource universes in SAP BO yields several benefits. It facilitates a unified view by amalgamating data from multiple sources, fostering a comprehensive reporting environment. Additionally, it mitigates data redundancy by creating a shared semantic layer for reporting purposes. However, challenges arise in managing the complexity associated with multisource universes, and performance concerns may surface when dealing with substantial datasets from diverse sources.
55. Describe the steps involved in auditing and keeping an eye on SAP BO system activity
Ans:
Ensuring transparency and compliance in SAP BO involves a meticulous auditing process. Initially, administrators enable auditing through the Central Management Console (CMC), configuring settings to capture relevant events. Defining auditing options becomes pivotal, specifying the activities to be audited, including login/logout, report access, and modifications. Regularly reviewing audit logs becomes an ongoing practice to monitor user activities, identify potential issues, and maintain a secure and compliant system.
56. Have you ever used Software Development Kits (SDKs) to customize SAP BO?
Ans:
The utilization of Software Development Kits (SDKs) in customizing SAP BO is a common practice among developers. SDKs empower developers to extend and enhance BO’s functionality, creating tailored applications, and seamlessly integrating with other systems. This flexibility allows organizations to adapt SAP BO to their specific requirements, ensuring a more personalized and efficient user experience.
57. What steps would you take to upgrade or migrate a sizable SAP BO setup to a new version?
Ans:
The process of upgrading or migrating a substantial SAP BO setup involves several meticulous steps. Commencing with a comprehensive backup of the existing system, an assessment of the new version’s features, compatibility, and potential impacts follows. Setting up a dedicated test environment is crucial for simulating the migration and identifying potential issues.
A detailed migration plan is then developed, encompassing considerations for downtime, data migration, and user training. The actual migration process involves executing the plan, migrating servers, content, and configurations to the new version. Post-migration, a thorough testing phase is imperative to validate both functionality and performanc
58. Is it possible to use SAP BO for predictive analytics? If so, describe the accessible features and tools.
Ans:
- Indeed, SAP BO supports predictive analytics through tools like SAP Predictive Analytics.
- This capability empowers users to construct and deploy predictive models, seamlessly integrating them into BO reports and dashboards.
- The integration of predictive analytics enhances the decision-making process by providing insights into future trends and patterns, contributing to a more informed and data-driven approach to business strategies.
59. How may location-based analysis and geospatial data be included in SAP BO reports?
Ans:
SAP BO facilitates location-based analysis by seamlessly integrating with mapping tools. Geospatial data, essential for geographic insights, can be effortlessly included in reports using specialized components. This integration enables the creation of visually impactful reports and dashboards that leverage geographic information, providing a deeper understanding of data patterns based on location.
60. Describe the SAP BO notion of data federation and how it varies from conventional ETL procedures.
Ans:
In the context of SAP BO, the concept of data federation stands out as a dynamic approach to accessing and amalgamating data from diverse sources in real-time, eliminating the need for physical data movement. This stands in contrast to traditional Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) procedures, where data is extracted, transformed, and loaded into a central repository before analysis. The advantages of data federation include real-time access to distributed data, a reduction in data redundancy, and minimized storage requirements.
61. In what ways have you enhanced or modified SAP BO’s capabilities in the past projects using SAP BO SDKs?
Ans:
In the course of previous projects, SAP BO’s capabilities were extended and tailored through the strategic utilization of SAP BO SDKs. These software development kits served as a cornerstone for enhancing functionality, enabling the creation of custom applications, seamless integration with external systems, and the automation of specific processes.
This approach allowed for a more personalized adaptation of SAP BO to the unique requirements of each project, contributing to the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the business intelligence solutions implemented.
62. Which techniques and strategies do you employ, especially when dealing with large datasets, to maximize SAP BO performance?
Ans:
When faced with the challenge of handling large datasets within SAP BO, a set of proven techniques and strategies comes into play. Optimizing queries, leveraging indexes, and implementing efficient join operations are integral parts of the approach.
Additionally, employing data pruning methods, such as data aggregation and partitioning, becomes crucial. These strategies, combined with caching mechanisms, aim to minimize the impact on system resources, ensuring optimal performance and responsiveness when dealing with substantial datasets.
63. Discuss the advanced features, such as input controls, custom computations, and hyperlinks, that may be found in SAP BO Web Intelligence reports.
Ans:
In the course of previous projects, SAP BO’s capabilities were extended and tailored through the strategic utilization of SAP BO SDKs. These software development kits served as a cornerstone for enhancing functionality, enabling the creation of custom applications, seamless integration with external systems, and the automation of specific processes.
This approach allowed for a more personalized adaptation of SAP BO to the unique requirements of each project, contributing to the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the business intelligence solutions implemented.
64. Describe how to utilize SAP BO Analysis for Office and how data exploration is improved by using it.
Ans:
- SAP BO Analysis for Office stands as a powerful tool that revolutionizes data exploration within the SAP BO ecosystem.
- This tool seamlessly integrates with Microsoft Excel, offering users a familiar interface for multidimensional analysis.
- By connecting directly to SAP BO data sources, Analysis for Office enables the creation of pivot tables, charts, and interactive dashboards within the Excel environment.
- This not only streamlines the analytical process but also significantly improves data exploration by providing users with a user-friendly and intuitive interface, resulting in more efficient and insightful decision-making processes.
65. What is the process for adding cascading prompts to reports in SAP BO Web Intelligence?
Ans:
The implementation of cascading prompts in SAP BO Web Intelligence involves a systematic process. Firstly, a series of prompts is created, where the values in one prompt dynamically influence the values available in subsequent prompts. This is achieved through the establishment of links between the prompts using predefined queries.
As users make selections in one prompt, the values cascade down to the linked prompts, refining the available options and providing a more targeted and interactive filtering experience. This enhances the flexibility and precision of data retrieval in SAP BO Web Intelligence reports.
66. What are the best practices for creating interactive, user-friendly SAP BO dashboards in terms of layout, data visualization, and interactivity?
Ans:
Creating interactive and user-friendly SAP BO dashboards involves adhering to several best practices. In terms of layout, maintaining a clean and organized design with consistent formatting enhances visual appeal.
Optimal data visualization is achieved by choosing appropriate chart types, effectively using color coding, and ensuring that data density does not compromise comprehension. Interactivity is enhanced by incorporating drill-down features, filters, and tooltips, fostering user engagement.
67. What is SAP BusinessObjects, and how does it fit into the larger picture of business intelligence?
Ans:
SAP BusinessObjects (SAP BO) is a comprehensive suite of business intelligence (BI) tools designed to empower organizations in transforming raw data into meaningful insights. Positioned within the larger landscape of business intelligence, SAP BO plays a pivotal role by offering tools for reporting, analytics, dashboards, and data exploration.
By providing a unified and cohesive solution, SAP BO facilitates informed decision-making across the organization, ensuring that data-driven insights contribute to strategic and operational excellence.
68. Describe the function of a SAP BusinessObjects universe.
Ans:
- At the heart of SAP BusinessObjects lies the concept of a universe, serving as a crucial intermediary between the underlying data sources and the reporting tools.
- The universe acts as a semantic layer, abstracting the complexities of the database structure and providing a business-friendly representation of data elements.
- By simplifying data access, universes streamline the report creation process, enhance consistency across reports, and ultimately improve the efficiency with which users interact with and derive insights from their data.
69. What distinguishes SAP BO’s Web Intelligence from Crystal Reports?
Ans:
In the realm of SAP BusinessObjects, Web Intelligence and Crystal Reports serve distinct purposes, each distinguished by its unique characteristics. Web Intelligence is tailored for ad-hoc reporting, emphasizing real-time data exploration and interactivity.
It supports features such as input controls, custom computations, and web-based interaction. In contrast, Crystal Reports excels in the creation of highly formatted, pixel-perfect reports, often used for predefined and static reporting needs. The differentiation lies in their respective strengths, with Web Intelligence focusing on dynamic, user-driven reporting, and Crystal Reports excelling in meticulous, formatted outputs.
70. What is a SAP BO report’s essential elements?
Ans:
A SAP BusinessObjects (SAP BO) report comprises several essential elements that collectively contribute to its functionality and structure. These elements include data elements, representing fields sourced from the underlying data; report elements, such as tables or charts visualizing the data; filters for refining data display; formatting options for aesthetics; and additional components like input controls and hyperlinks for enhanced interactivity. Together, these elements form a comprehensive report within the SAP BO environment.
71. What are the various security levels you can apply and how does SAP BO’s security function?
Ans:
SAP BO incorporates a multifaceted security model encompassing various levels to safeguard data and ensure controlled access:
- User Security: Involves assigning specific privileges to users based on their roles and responsibilities.
- Object Security: Controls access to specific reports, folders, or universes, ensuring a fine-grained level of authorization.
- Data Security: Restricts access to certain data based on user roles, safeguarding sensitive information.
- System Security: Manages overall system access and permissions, regulating who can administer the system.
72. Is it possible for SAP BO to connect to several data sources at once?
Ans:
SAP BusinessObjects (SAP BO) exhibits the remarkable capability of seamlessly connecting to multiple data sources concurrently. This robust feature empowers organizations with the versatility to aggregate and analyze data derived from diverse databases, applications, and systems within a unified and cohesive reporting environment. The ability to integrate information from various sources enhances the comprehensiveness and depth of analytical insights, contributing significantly to the effectiveness of business intelligence processes.
73. What is an Input Control for Web Intelligence?
Ans:
- An Input Control within the context of Web Intelligence represents a sophisticated feature designed to provide users with a dynamic and interactive means of manipulating and filtering data within a given report.
- This powerful functionality encompasses various user-friendly elements such as drop-down lists, date pickers, and sliders. Through these input controls, users can actively engage with the report content, dynamically adjusting parameters and customizing their viewing experience to meet specific analytical requirements.
- This feature significantly enhances the flexibility and user-driven nature of data exploration within Web Intelligence.
74. For what purpose does SAP BO’s Central Management Console (CMC) exist?
Ans:
The Central Management Console (CMC) in SAP BO serves a pivotal role as the central hub for administering, configuring, and managing various aspects of the SAP BO environment. This comprehensive tool is tailored for system administrators, providing them with a centralized platform to oversee and control user access, configure server settings, establish security permissions, schedule and monitor reports, and execute a myriad of administrative tasks essential for ensuring the seamless and efficient operation of the entire SAP BO ecosystem.
75. Describe how to set up a report in SAP BO.
Ans:
- The process of setting up a report in SAP BO involves a systematic and user-friendly approach. Commencing within the Web Intelligence application, users initiate the creation of a report by selecting a relevant data source.
- Subsequently, a query is formulated to retrieve the desired dataset. The design phase ensues, wherein users can intuitively drag and drop data elements onto the report canvas, crafting the report structure.
- Further customization is achieved through formatting options, the application of filters, and the inclusion of necessary calculations.
- The completed report is then saved, and upon execution, users can view and analyze the results. For added convenience, reports can be scheduled for automatic generation and distribution according to organizational needs.
76. What does SAP BO Explorer aim to achieve?
Ans:
SAP BO Explorer is strategically designed to revolutionize the process of data exploration within the SAP BO ecosystem. Functioning as a self-service, search-based interface, its primary goal is to provide users with an intuitive and simplified means of navigating and visualizing data. Unlike traditional reporting tools that may necessitate complex query creation, BO Explorer offers a more accessible approach. By enabling users to quickly search, retrieve, and analyze data without the need for extensive technical expertise, it aims to broaden the user base within an organization, fostering a culture of data-driven decision-making.
77. Could you elaborate on what a “dimension” in SAP BO reporting means?
Ans:
In the realm of SAP BO reporting, a dimension assumes the role of a critical attribute or characteristic of data that serves to provide context and categorization. Dimensions typically encompass descriptive fields, such as product names, geographic locations, or time periods.
These attributes are fundamental in organizing and analyzing data within reports. Essentially, dimensions define the structure of the data, adding granularity to analytical insights and facilitating a more nuanced understanding of the information being presented.
78. How can a basic table be created in SAP BO’s Web Intelligence?
Ans:
Creating a basic table in SAP BO’s Web Intelligence involves a user-friendly and iterative process. Users initiate the creation by dragging and dropping desired dimensions and measures onto the report canvas. These elements are then arranged in rows and columns to form the fundamental structure of the table.
Further customization is achieved through the application of formatting options, such as cell borders, font styles, and color coding. Additionally, users can introduce any necessary calculations or aggregations to enhance the depth of the tabular representation. Upon completion, the report is saved and executed to display the table with the specified data, offering a clear and organized presentation of the analytical insights.
79. What does SAP BO mean by a prompt, and how does it apply to reporting?
Ans:
In the context of SAP BO, a prompt serves as a dynamic and interactive user interface element that facilitates personalized data retrieval within a report. By incorporating prompts, users are empowered to enter specific values or make selections that directly influence the content of the report.
This dynamic functionality allows users to actively engage with the data, tailoring the report to meet specific criteria or preferences. Essentially, prompts provide a mechanism for user-driven customization, enhancing the adaptability and relevance of the reported information.
80. How may information be filtered in a SAP BO report according to particular criteria?
Ans:
- Filtering information in a SAP BO report based on specific criteria is a fundamental aspect of data refinement and customization.
- Users can apply filters to dimensions or measures within the report, defining conditions that data must meet to be included in the presentation.
- This can be accomplished during the initial creation of the report or interactively while viewing the report.
- By employing filters, users can focus on subsets of data that meet predefined conditions, allowing for a more targeted and insightful analysis aligned with specific criteria or parameters.
81. In a SAP BO universe, what does a join do?
Ans:
Within the SAP BO universe, a join assumes a crucial role in defining the relationships between tables or queries within a given data source. A join specifies how data from different tables is intricately linked and combined to retrieve coherent and meaningful information.
By establishing these connections, SAP BO ensures the seamless integration of data from diverse sources, laying the foundation for the creation of comprehensive reports that draw on multiple data sets to provide a holistic and unified view of organizational data.
82. Could you list a few typical elements or widgets seen in SAP BO dashboards?
Ans:
SAP BO dashboards feature a diverse array of elements and widgets that collectively contribute to a rich and interactive user experience. These include various types of charts such as bar charts, pie charts, and line charts, each offering unique insights into different aspects of the data.
Gauges and meters provide a visually impactful representation of key performance indicators (KPIs). Tables and crosstabs facilitate the display of tabular data, while interactive filters and input controls empower users to customize their viewing experience. Images and logos can be incorporated for branding purposes, and scorecards offer a concise presentation of metrics and organizational goals.
83. How does drill-down in SAP BO reporting improve user interaction, and what does it mean?
Ans:
- Drill-down functionality in SAP BO reporting significantly enhances user interaction by providing a hierarchical and detailed exploration of data.
- It allows users to transition from summarized or aggregated data to more granular levels, gaining deeper insights into specific dimensions or categories.
- By drilling down, users can uncover hidden patterns, anomalies, or trends within the data.
- This interactive capability fosters a more dynamic and iterative analytical process, empowering users to navigate through data hierarchies and make informed decisions based on a comprehensive understanding of the information presented.
84. What distinguishes SAP BO Explorer from Web Intelligence and other conventional reporting tools?
Ans:
SAP BO Explorer stands out from Web Intelligence and other conventional reporting tools through its distinctive approach to data exploration. Unlike traditional tools that often require predefined queries and structured reports, BO Explorer introduces a search-based and intuitive interface. This interface enables
85. What function does SAP BO’s Central Management Server (CMS) serve?
Ans:
The Central Management Server (CMS) within the SAP BusinessObjects (SAP BO) ecosystem is a cornerstone component that fulfills a pivotal role in orchestrating and managing the entire infrastructure. Functioning as a centralized repository, the CMS stores vital information related to system configurations, user details, and metadata.
It serves as the linchpin for coordinating communication among the diverse components of the SAP BO environment, ensuring seamless integration and efficient functioning. By housing critical data pertaining to user identities, security settings, and system configurations, the CMS facilitates streamlined administration, contributing significantly to the overall governance and robustness of the SAP BO landscape.
86. How are scheduled report instances handled by SAP BO?
Ans:
- SAP BO introduces a powerful feature in the form of scheduled report instances, offering a mechanism for users to capture snapshots or versions of reports at predefined intervals.
- These instances serve as static representations of the report content at the time of scheduling, providing users with the ability to access historical or point-in-time data without the need to regenerate the entire report.
- The handling of scheduled report instances involves the storage of these snapshots within the system, often distributed through various channels such as email or document repositories.
- This ensures that users can conveniently access and review specific instances of reports, enhancing the efficiency of information retrieval and historical analysis.
87. Which user roles are common in SAP BO, and what kind of permissions do they typically have?
SAP BO encompasses a diverse array of user roles, each designed to cater to specific functions within the business intelligence landscape. Common user roles include the Administrator, who holds comprehensive control over system configurations and security settings. Designers possess the capability to create, modify, and manage various reporting artifacts such as reports, universes, and dashboards. Explorer roles are tailored for users engaging in intuitive data exploration, while Viewers and Consumers have the ability to interact with reports and dashboards, albeit with limited or no design privileges.
88. Describe the SAP BO “Read” and “View” permissions.
Ans:
The “Read” permission provides users with access to retrieve data from the system. While users with “Read” permission can view report content and explore data, certain interactive functions may be restricted. On the other hand, the “View” permission extends beyond mere access and retrieval, empowering users to actively engage with reports. With “View” permission, users can leverage features like drill-downs, apply filters, and dynamically interact with the content within the report, facilitating a more immersive and participatory analytical experience.
89. Is it possible to link to flat files and relational databases with SAP BO?
Ans:
SAP BO offers a robust and versatile connectivity framework that enables seamless integration with various data sources. Whether dealing with flat files such as Excel spreadsheets or CSV files or relational databases like Oracle or SQL Server, SAP BO provides dedicated connectors and tools to establish connections. This inclusive approach allows users to effortlessly link to and integrate data from diverse sources, fostering a holistic and comprehensive approach to data analysis and reporting within the SAP BO environment.
90. In SAP BO, how may users share reports with others?
Ans:
The collaborative nature of SAP BO is underscored by its multifaceted approach to report sharing. Users can disseminate reports through several channels, including exporting reports to different formats (such as PDF or Excel) for sharing via email or file-sharing platforms.
Additionally, users can schedule report instances to be automatically generated and distributed at predetermined intervals. Publishing reports to the BI Launchpad provides a centralized platform where other users, possessing the requisite permissions, can access and view shared reports.
91. In a Web Intelligence report, how can cells be formatted conditionally?
Ans:
- Web Intelligence, a powerful reporting tool within SAP BO, empowers users to enhance the visual appeal and interpretability of their reports through conditional formatting.
- To achieve this, users can follow a systematic process. Firstly, they select the target cells for conditional formatting.
- Navigating to the Format tab, users access the “Format Cells” option, where they define specific conditions based on values or comparisons.
- Subsequently, users articulate the desired formatting rules, encompassing aspects such as color, font styles, and other visual attributes.






