
If you are preparing for Hyperion Planning Interview, then you are at the right place. Today, we will cover some mostly asked Hyperion Planning Interview Questions, which will boost your confidence. Oracle Hyperion Planning is centralized planning, budgeting, and forecasting solution that integrates financial and operational planning processes. Therefore, Hyperion Planning professionals need to encounter interview questions on Hyperion Planning for different enterprise Hyperion Planning job roles. The following discussion offers an overview of different categories of interview questions related to Hyperion Planning to help aspiring enterprise Hyperion Planning Professionals.
1. What is Hyperion Planning?
Ans:
Hyperion Planning is an enterprise-wide planning, budgeting, and forecasting solution. It is a part of the Oracle Hyperion EPM suite, designed to help organizations streamline their planning processes, improve accuracy, and ensure alignment with business goals. It provides a collaborative environment for creating and managing budgets, forecasts, and financial plans.
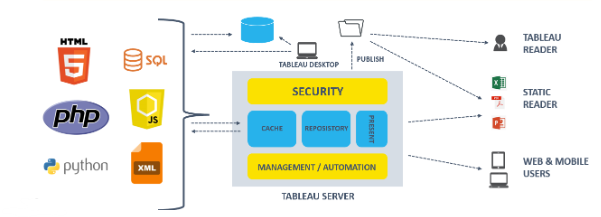
2. Describe the essential elements of Hyperion Planning.
Ans:
- There are several components that make up Hyperion Planning, including:
- Web-based Interface: A web interface allows users to access and enter data.
- Planning Server: Oversees the planning program and synchronizes data across many users.
- Calculation Manager: Enables business rules for data computations to be created and managed.
- Essbase Database: Offers a quick and scalable platform for analysis by storing multidimensional data.
3. What is the role of Essbase in Hyperion Planning?
Ans:
Essbase is the underlying multidimensional database in Hyperion Planning. It stores and manages data in a format that facilitates complex analysis. Essbase enables fast retrieval of data, supports complex calculations, and allows for the creation of sophisticated models. It forms the backbone for efficient budgeting, forecasting, and reporting within Hyperion Planning.
4. How does Hyperion Planning support the planning process?
Ans:
- Hyperion Planning supports the planning process by:
- Enabling Collaboration: Multiple users can contribute to plans simultaneously, fostering collaboration.
- Data Entry and Validation: Users can input and validate data through a user-friendly web interface.
- Workflow Management: It streamlines the approval process, ensuring that plans are reviewed and approved systematically.
- What-If Analysis: Users can perform scenario planning and analyze the impact of different assumptions on plans.
5. What are the key benefits of using Hyperion Planning for financial planning?
Ans:
- Hyperion Planning offers several benefits, including:
- Improved Accuracy: Centralized data ensures consistency and accuracy in financial plans.
- Efficient Collaboration: Multiple stakeholders can contribute to the planning process in real-time.
- Scenario Planning: Users can model different scenarios to assess the impact on financial outcomes.
- Streamlined Workflow: It automates the approval process, reducing the time required for plan approval.
6. Explain the concept of Business Rules in Hyperion Planning.
Ans:
Business Rules in Hyperion Planning are sets of instructions that define how data is calculated and aggregated. These rules determine the logic for consolidating, aggregating, and calculating data in the planning application. They are created using the Calculation Manager and can be customized based on the organization’s specific requirements. Business Rules play a crucial role in automating the planning and forecasting process, ensuring consistency and accuracy in calculations.
7. How does Hyperion Planning handle security for sensitive financial data?
Ans:
- Hyperion Planning employs a robust security model that allows administrators to define access controls at various levels:
- Application Security: Controls access to the entire Hyperion Planning application.
- Dimension Security: Specifies access to specific dimensions within the application.
- Member Security: Provides granular control over access to individual members within dimensions.
- Data Security: Allows administrators to restrict access to specific data based on user roles.
8. What are the main dimensions in Hyperion Planning?
Ans:
- Account dimension defines financial categories (revenue, expenses, etc.).
- Entity dimension defines organizational units (companies, departments, etc.).
- Time dimension defines periods (years, quarters, months, etc.).
- Optional dimensions like product, customer, or geography can be added for richer analysis.
9. Explain the difference between Essbase and Planning.
Ans:
| Essbase: | Planning: |
|---|---|
| Multidimensional Database Management | Financial Planning Application |
| Powerful Calculation Engine | Business Rules and Workflow for Planning |
| Supports both Read and Write Operations | Primarily Designed for Data Input and Validation |
10. How does Hyperion Planning handle multi-dimensional reporting and analysis through Smart View?
Ans:
Hyperion Planning seamlessly integrates with Smart View, an Excel add-in, to facilitate multi-dimensional reporting and analysis. Users can harness the power of Smart View to connect directly to Hyperion Planning, enabling them to create sophisticated reports and conduct ad-hoc analysis within the familiar Excel interface. Smart View allows users to drag and drop dimensions, dynamically slice and dice data, and create complex financial models, enhancing the depth and flexibility of reporting. This integration provides a seamless experience for finance professionals who prefer working in Excel while leveraging the multidimensional capabilities of Hyperion Planning.
11. Can you explain the integration capabilities of Hyperion Planning with other Oracle EPM tools?
Ans:
- Hyperion Planning integrates seamlessly with other Oracle EPM tools, facilitating end-to-end financial processes:
- Data Integration: Hyperion Planning can pull data from various sources, ensuring a unified view of financial information.
- Reporting Integration: It integrates with tools like Hyperion Financial Reporting for creating comprehensive financial reports.
- Data Synchronization: Hyperion Planning can synchronize data with Essbase databases for consistent analysis.
- Workflow Integration: Integrates with Oracle Workflow to automate approval processes.
12. How does Hyperion Planning handle intercompany eliminations in the consolidation process?
Ans:
Intercompany eliminations in Hyperion Planning are crucial for ensuring accurate financial reporting and consolidations. The system allows administrators to define specific intercompany relationships and establish rules for eliminations. During the consolidation process, intercompany transactions are identified and eliminated to avoid double-counting and present a consolidated, accurate view of financial data. Hyperion Planning’s capabilities include automating the intercompany elimination process, ensuring that it aligns with accounting standards and organizational policies. This feature contributes to the integrity of financial statements, particularly in organizations with complex structures involving intercompany transactions.
13. What are the different data loading methods in Hyperion Planning?
Ans:
- Manual entry: Directly inputting data through grids or forms.
- Rules files: Automated data population based on defined formulas and calculations.
- Integrations: Importing data from external sources like ERP systems.
14. How does Hyperion Planning support driver-based planning for organizations focused on key performance indicators (KPIs)?
Ans:
Hyperion Planning supports driver-based planning, a methodology where financial plans are linked directly to operational drivers and key performance indicators (KPIs). Users can define drivers, such as sales volume or headcount, and link them to financial outcomes. Changes in drivers automatically update the financial plan, allowing for real-time adjustments based on operational performance. This approach enhances the accuracy and responsiveness of financial plans, aligning them closely with the operational realities of the organization. Driver-based planning in Hyperion Planning is particularly beneficial for organizations seeking a more dynamic and data-driven approach to financial forecasting and analysis.
15. What are some basic calculations you can perform in Hyperion Planning?
Ans:
- Simple arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, and multiplication.
- Ratio calculations like percentages and growth rates.
- Logical functions like IF statements and conditional formatting.
16. What role does “Approval Workflow” play in the planning process within Hyperion Planning?
Ans:
Approval Workflow in Hyperion Planning streamlines and automates the approval process, ensuring that plans progress through defined stages efficiently. Users can configure workflow rules, specifying the sequence of approvals and the individuals responsible at each stage. The workflow ensures that plans undergo systematic review and approval, reducing manual intervention and potential errors. Notifications are sent to relevant stakeholders upon completion of each stage, providing transparency and accountability. The Approval Workflow feature contributes to a well-controlled planning environment, where plans are methodically reviewed and approved, aligning with organizational governance and compliance requirements.
17. Explain the different types of hierarchies in Hyperion Planning.
Ans:
- Parent-child hierarchies establish clear relationships between members (e.g., departments reporting to a division).
- Level-based hierarchies group members based on defined levels (e.g., product categories on different levels).
- User-defined hierarchies allow for custom groupings and aggregations for specific analysis needs.
18. What are attributes and how are they used?
Ans:
Attributes provide additional data tags to members (e.g., product size, customer segment). Used for filtering, grouping, and creating attribute-based calculations for deeper insights.
19. Explain the concept of data aggregation in Hyperion Planning.
Ans:
Rolling up data from lower levels (accounts, periods) to higher levels (categories, totals). Aggregation rules can be defined to handle specific scenarios like weighted averages or minimum values.
20. What is the role of “Calculation Manager” in Hyperion Planning?
Ans:
Calculation Manager in Hyperion Planning is a powerful tool that allows users to create and manage business rules for data calculations. These rules define the logic for consolidating, aggregating, and calculating data within the planning application. With a Calculation Manager, administrators can design sophisticated business rules tailored to the organization’s specific requirements. This includes defining complex allocation methods, performing currency translations, and executing other calculations critical for accurate financial planning. The intuitive interface of the Calculation Manager streamlines the rule creation process, ensuring that data calculations align with business objectives and contribute to the overall accuracy of the planning process.
21. What are Smart Cubes and what are their benefits?
Ans:
Pre-calculated aggregations of large datasets stored in Essbase for faster retrieval and analysis. Improve performance and efficiency, especially for complex models and frequent reporting.
22. Can you elaborate on the integration capabilities of Hyperion Planning with Data Relationship Management (DRM)?
Ans:
Hyperion Planning seamlessly integrates with Data Relationship Management (DRM), enhancing metadata management and hierarchy control. The integration enables a centralized approach to managing hierarchies, relationships, and metadata across various dimensions. Changes made in DRM are reflected in Hyperion Planning, ensuring consistency and accuracy in metadata. Administrators can leverage DRM’s versioning and approval workflows for metadata changes, contributing to a well-controlled and documented metadata management process. The integration of Hyperion Planning with DRM supports organizations in maintaining a synchronized and organized approach to managing metadata across the entire EPM ecosystem.
23. How can Hyperion Planning facilitate the integration of non-financial data in the planning process?
Ans:
- Hyperion Planning is not limited to financial data; it can integrate non-financial data as well:
- Custom Dimensions: Users can create custom dimensions to represent non-financial aspects, such as units, quantities, or headcount.
- Data Relationship Management (DRM): Integrates with DRM to manage hierarchies and relationships for both financial and non-financial data.
- Metadata Management: Enables the incorporation of non-financial metadata for comprehensive planning.
24. Describe some security features in Hyperion Planning.
Ans:
User groups and roles control access to specific dimensions, data, and functions. Data encryption and audit trails ensure data integrity and track user actions.
25. How does Hyperion Planning handle dynamic security through “Security Filters”?
Ans:
Hyperion Planning incorporates dynamic security through the use of “Security Filters,” offering administrators granular control over data access. Security Filters can be applied at different levels, including row-level and member-level security. Row-level security filters data based on user-specific criteria, limiting access to specific rows of data. Member-level security ensures restricted access to specific members within dimensions. The dynamic nature of these security filters allows for adjustments based on user attributes or changing conditions, contributing to a more adaptive and responsive security infrastructure. This ensures that users have access only to the data relevant to their roles and responsibilities, enhancing data confidentiality and security.
26. Explain the different types of Essbase storage options (AO, Dense, Sparse) and their trade-offs.
Ans:
AO (aggregation-only) prioritizes quick aggregations but sacrifices write performance. Dense stores all data values, optimizing writes but slower for aggregations. Sparse stores only non-zero values, balancing performance for both writes and reads.
27. Can you elaborate on the role of “Security Filters” in Hyperion Planning?
Ans:
Security Filters in Hyperion Planning allow administrators to define security based on specific criteria:
- Row Level Security: Filters data based on user-specific criteria, limiting access to certain rows of data.
- Member Level Security: Restricts access to specific members within dimensions, ensuring data confidentiality.
- Dynamic Security: Security filters can be dynamic, adjusting based on user attributes or changing conditions.
- Enhanced Data Confidentiality: Ensures that users only have access to the data relevant to their roles and responsibilities.
28. Can you explain the role of “Data Forms” and “Data Grids” in Hyperion Planning?
Ans:
Data Forms and Data Grids in Hyperion Planning serve as essential interfaces for users to input, review, and manipulate planning data. Data Forms provide customizable templates for structured data input, validation, and submission. Users can interact with these forms to input or review data in a user-friendly environment. On the other hand, Data Grids offer grid-based views of data, allowing for more flexible and dynamic data manipulation. Users can slice and dice data within forms and grids interactively, focusing on specific subsets for analysis. Additionally, users can add cell text and annotations, providing context and explanations for data entries, contributing to a more comprehensive and collaborative planning process.
29. How can you optimize a Hyperion Planning application for better performance?
Ans:
- Utilizing Smart Cubes, partitioning large dimensions, and minimizing complex calculations in forms.
- Regular database maintenance and tuning Essbase storage options based on data access patterns.
30. What is the significance of the “Plan Type” in Hyperion Planning?
Ans:
The “Plan Type” in Hyperion Planning refers to different versions or scenarios of the financial plan. It allows organizations to manage multiple planning scenarios concurrently, such as budget, forecast, and actuals. Each Plan Type can have its own set of dimensions, data, and business rules, providing flexibility for scenario planning and analysis.
31. How does Hyperion Planning handle currency conversion for global organizations?
Ans:
Hyperion Planning supports multi-currency environments through its currency conversion functionality:
- Exchange Rates: Administrators can define exchange rates for different currencies.
- Local Currency: Data can be stored in local currencies, and Hyperion Planning automatically converts it to a reporting currency.
- Consolidation: The system consolidates data in the reporting currency for standardized reporting and analysis.
32. Explain the role of Smart View in Hyperion Planning.
Ans:
Smart View is an Excel add-in that allows users to interact with Hyperion Planning data directly within the familiar Excel interface. It facilitates tasks such as data entry, ad-hoc analysis, and report creation. Smart View enhances user productivity by providing a seamless connection between Excel and Hyperion Planning, allowing users to work with planning data in a familiar environment.
33. What is the importance of the “Version” dimension in Hyperion Planning?
Ans:
The “Version” dimension in Hyperion Planning represents different stages of the planning process, such as working drafts, approved budgets, and final forecasts. It allows users to create and manage different versions of the plan simultaneously. This is valuable for tracking changes, maintaining historical data, and supporting audit trails throughout the planning lifecycle.
34. How does Hyperion Planning support data forms and data grids?
Ans:
- Data forms and data grids in Hyperion Planning provide interfaces for users to input and review data
- Data Forms: Customizable templates for data input, validation, and submission.
- Data Grids: Grid-based views of data for easy manipulation and analysis.
- Slice and Dice: Users can interactively slice and dice data within forms and grids to focus on specific subsets.
- Cell Text and Annotations: Users can add comments or annotations to explain data entries.
35. What is the purpose of the “Scenario” dimension in Hyperion Planning?
Ans:
The “Scenario” dimension allows users to model different planning scenarios or assumptions. It is useful for performing what-if analysis and evaluating the impact of various business conditions on the financial plan. Scenarios can represent best-case, worst-case, or most likely outcomes, helping organizations make informed decisions in dynamic environments.
36. How does Hyperion Planning handle data validation and data integrity?
Ans:
Hyperion Planning includes robust features for ensuring data quality and integrity:
- Data Validation Rules: Administrators can define rules to validate data entries, ensuring accuracy and consistency.
- Cell Level Security: Controls access to individual data cells based on user roles, preventing unauthorized changes.
- Audit Trails: Tracks changes to data, providing a comprehensive history for audit and compliance purposes.
- Error Messaging: Provides informative messages for users to address validation errors during data entry.
37. Explain the concept of “ASO” (Aggregate Storage Option) in Hyperion Planning.
Ans:
ASO is a storage option in Hyperion Planning that leverages Essbase technology for optimized storage and retrieval of aggregated data:
- Aggregated Storage: ASO databases store pre-aggregated data for faster query performance.
- Large Data Sets: Suitable for handling large volumes of data, such as detailed transactional data.
- Query Optimization: Improves response times for complex queries, enhancing overall system performance.
- Designed for Read-Only Access: Typically used for reporting and analysis rather than data entry.
38. What are scenarios and versions used for?
Ans:
Scenarios allow simulation of different financial outcomes (optimistic, pessimistic, etc.). Versions track and store historical data or interim forecasts alongside the current active version.
39. Can you elaborate on the capabilities of Hyperion Planning in handling scenario analysis for risk management?
Ans:
Hyperion Planning excels in scenario analysis, providing organizations with a powerful tool for risk management. Users can create various planning scenarios, modeling different business conditions, and assessing the potential impact on financial outcomes. This feature is invaluable for risk mitigation, allowing organizations to proactively plan for various contingencies. Scenario analysis within Hyperion Planning aids in understanding how changes in assumptions or external factors influence financial projections. By evaluating a range of scenarios, organizations can make informed decisions, enhancing their resilience and adaptability in the face of uncertainty, a critical aspect of modern risk management.
40. What are Dynamic Calc scripts and their uses?
Ans:
- Scripts executed automatically upon data changes to perform complex calculations or update other members.
- Useful for automating recurring tasks, enforcing business rules, and ensuring data consistency.
41.Describe the concept of data locks and their importance in Planning.
Ans:
- Prevent simultaneous editing of data by different users, safeguarding data integrity and avoiding conflicts.
- Granularity can be set on specific cells or entire dimensions for controlled collaboration
42. Can you elaborate on the significance of the “Plan Type” dimension in Hyperion Planning?
Ans:
The “Plan Type” dimension in Hyperion Planning holds significant importance in organizing and managing different versions of the financial plan. It allows organizations to concurrently handle various planning scenarios, such as budgeting, forecasting, and actuals. Each Plan Type can have its unique set of dimensions, data, and business rules, providing a structured approach to scenario planning and analysis. This feature facilitates a dynamic and versatile environment where users can seamlessly switch between different planning perspectives and evaluate the financial impact of diverse business conditions, contributing to a more comprehensive and flexible planning framework.
43. Explain the use of substitution variables in Planning.
Ans:
- Placeholder values are replaced dynamically during calculations or data loading for flexibility and reusability.
- Reduce redundancy and simplify model maintenance by storing common values in variables.
- What are some best practices for designing user-friendly forms in Planning?
- Intuitive layout, clear labeling, validation rules, and efficient navigation.
- Context-sensitive menus, data visualization options, and user-defined filters for enhanced usability.
44. How does Hyperion Planning address the challenge of handling multiple currencies in global organizations?
Ans:
For global organizations dealing with diverse currencies, Hyperion Planning provides robust support through its currency conversion functionality. Administrators can define exchange rates for different currencies, ensuring accurate conversion of financial data. Data can be stored in local currencies, and Hyperion Planning automatically converts it to a reporting currency for standardized analysis and reporting. This feature streamlines the complexities associated with multi-currency environments, offering a unified and consistent view of financial information. It’s particularly valuable for organizations operating across borders, providing a comprehensive solution for managing and analyzing global financial data.
45. How does Hyperion Planning handle data integration with external systems?
Ans:
- Hyperion Planning supports data integration through various methods:
- Data Import/Export: Users can import and export data using flat files, facilitating integration with external systems.
- Data Maps: Define mappings between external data sources and Hyperion Planning dimensions for seamless integration.
- Integration with ERP Systems: Hyperion Planning can integrate with ERP systems to automatically pull in financial data.
- Data Load Rules: Administrators can create data load rules to automate the loading of data from external sources.
46. How does Hyperion Planning facilitate data integration with external systems?
Ans:
Hyperion Planning supports seamless data integration through multiple avenues. One method involves leveraging data import/export capabilities, allowing users to efficiently move data between Hyperion Planning and external systems using flat files. Furthermore, administrators can establish data maps, facilitating a smooth connection by defining mappings between external data sources and Hyperion Planning dimensions. This flexibility extends to integrating with ERP systems, enabling automatic retrieval of financial data for a more cohesive planning process. Data Load Rules can also be employed, providing a structured approach to automating data loading from diverse external sources, contributing to a consolidated and accurate dataset within the planning environment.
47. Explain the purpose and functionality of the “Task Lists” feature in Hyperion Planning.
Ans:
Task Lists in Hyperion Planning enable users to automate and schedule routine tasks:
- Automation: Users can schedule data imports, calculations, and other tasks to run at specific times.
- Dependency Management: Task Lists allow for the definition of task dependencies to ensure a logical execution sequence.
- Notification: Users receive notifications upon task completion, ensuring that they stay informed about the status of automated processes.
- Efficiency: Automating routine tasks improves efficiency and reduces the manual effort required for planning processes.
48. What role does “Task Lists” play in Hyperion Planning?
Ans:
Task Lists in Hyperion Planning serve as a valuable tool for automating and scheduling routine tasks, contributing to enhanced efficiency in the planning process. By allowing users to schedule specific tasks like data imports, calculations, and validations to run at predefined intervals, Task Lists streamline the workflow. They also incorporate dependency management, ensuring a logical sequence of task execution, and notify users upon task completion. This automation not only reduces manual effort but also ensures that critical planning processes are executed systematically, contributing to a more organized and time-effective planning cycle.
49. What are the key considerations in designing efficient business rules using Calculation Manager in Hyperion Planning?
Ans:
Designing efficient business rules in Hyperion Planning using Calculation Manager involves several considerations. Firstly, administrators should carefully define the scope of the business rule, specifying the members and dimensions it applies to. Optimizing the calculation order is crucial, ensuring that calculations are performed in a logical sequence. Leveraging conditional logic and dynamic member formulas can enhance the flexibility of business rules. Additionally, considering the impact of the business rules on system performance and data accuracy is vital. A well-designed business rule in Calculation Manager contributes to streamlined data calculations and supports the overall accuracy of the planning process.
50. What is the role of “Financial Reporting Studio” in Hyperion Planning?
Ans:
Financial Reporting Studio is a reporting tool in Hyperion Planning that allows users to create highly formatted financial reports:
- Drag-and-Drop Interface: Users can design reports using a user-friendly, drag-and-drop interface.
- Pixel-Perfect Formatting: Financial Reporting Studio provides precise control over formatting for professional-looking reports.
- Integration: Reports created in Financial Reporting Studio can be integrated into Hyperion Planning for comprehensive financial analysis.
- Dynamic Reporting: Users can create dynamic reports that update automatically with changes in planning data.
51. How does the “Financial Reporting Studio” enhance reporting capabilities in Hyperion Planning?
Ans:
The Financial Reporting Studio in Hyperion Planning plays a pivotal role in elevating reporting capabilities. With a user-friendly, drag-and-drop interface, users can design highly formatted financial reports with pixel-perfect precision. This studio provides a seamless integration of dynamic reports into the Hyperion Planning environment, offering a robust platform for professional-looking reports. Its dynamic reporting features enable users to create reports that automatically update with changes in planning data, ensuring that financial reports are always reflective of the latest data. This tool empowers users to present financial information in a visually appealing and insightful manner, crucial for effective decision-making.
52. How does Hyperion Planning handle metadata management?
Ans:
Metadata management in Hyperion Planning involves the administration of dimensions, hierarchies, and member properties:
- Dimension Editor: Administrators can use the Dimension Editor to create, modify, and manage dimensions.
- Member Properties: Define properties for individual members to capture additional information.
- Data Relationship Management (DRM): Integrates with DRM for centralized management of metadata.
- Versioning: Supports versioning of metadata, allowing for changes to be tracked and audited.
53. How is metadata management handled in Hyperion Planning?
Ans:
Metadata management in Hyperion Planning encompasses the administration of dimensions, hierarchies, and member properties, ensuring the accuracy and relevance of planning data. Administrators utilize the Dimension Editor to create, modify, and manage dimensions effectively. Member properties can be defined to capture additional information related to specific members. Hyperion Planning seamlessly integrates with Data Relationship Management (DRM), offering a centralized platform for managing metadata across various dimensions. Furthermore, the system supports versioning, allowing changes to be tracked and audited, ensuring a transparent and well-documented evolution of metadata.
54. How does Hyperion Planning support rolling forecasts for organizations adapting to dynamic market conditions?
Ans:
Rolling forecasts in Hyperion Planning allow organizations to adapt to dynamic market conditions by providing a mechanism for continuous planning beyond the traditional fiscal year. Users can define rolling forecast scenarios, allowing for the inclusion of additional periods or adjustments to existing plans. This flexibility is crucial for organizations in rapidly changing industries where traditional annual planning may not suffice. Rolling forecasts enable companies to continuously update and refine their financial projections based on the latest market insights, fostering adaptability and agility in financial planning processes within Hyperion Planning.
55. Explain the role of “Scenario Planning” in Hyperion Planning.
Ans:
Scenario Planning in Hyperion allows organizations to model and analyze different business scenarios:
- Multiple Scenarios: Users can create various scenarios to assess the impact of different business conditions on the financial plan.
- Sensitivity Analysis: Helps organizations understand how changes in assumptions affect financial outcomes.
- Risk Mitigation: Enables proactive planning for potential risks by evaluating the financial impact of various scenarios.
- Strategic Decision Making: Facilitates informed decision-making by providing insights into the potential outcomes of different scenarios.
56. Elaborate on the significance of “Scenario Planning” in Hyperion Planning.
Ans:
Scenario Planning in Hyperion Planning holds immense importance for organizations seeking a dynamic approach to financial forecasting and decision-making. By allowing users to create and analyze different business scenarios, it provides a strategic tool for risk mitigation and opportunity identification. Multiple scenarios can be modeled, each representing a unique set of assumptions or conditions, enabling users to understand the potential impact on financial outcomes. This sensitivity analysis aids in informed decision-making by offering insights into possible outcomes under varying circumstances. Overall, Scenario Planning is a crucial feature for organizations navigating complex and dynamic business environments.
57. How does Hyperion Planning address the needs of multi-user collaboration in the planning process?
Ans:
Hyperion Planning provides collaborative features to support multiple users working on the same plan:
- User Locking: Prevents conflicts by allowing users to lock specific plan elements during data entry.
- Annotations and Comments: Users can add comments and annotations to provide context and explanations for data entries.
- Workflow Approval: Streamlines the approval process by automating the flow of plans through different stages.
- Real-time Updates: Supports real-time updates, ensuring that users see the latest changes made by others
58. How does Hyperion Planning handle dynamic member formulas?
Ans:
Dynamic member formulas in Hyperion Planning play a crucial role in allowing users to create calculated members based on evolving business requirements. These formulas provide a flexible and adaptable approach to data calculations. Users can define dynamic calculations through the Formula Editor, a user-friendly interface that facilitates the creation and management of these formulas. Dynamic member formulas are particularly useful for scenario planning, allowing users to assess the impact of changes on calculations and outcomes. The system tracks changes to dynamic member formulas, ensuring a clear audit trail for compliance and transparency. This feature enhances the precision and agility of calculations within Hyperion Planning.
59. How does Hyperion Planning support multi-user collaboration in planning processes?
Ans:
Hyperion Planning recognizes the importance of collaboration in the planning process and incorporates features to ensure a seamless and efficient collaborative environment. Through user locking mechanisms, conflicts are prevented by allowing users to lock specific plan elements during data entry. Annotations and comments can be added directly to the data, providing context and explanations for data entries, enhancing communication among users. The workflow approval system automates the flow of plans through different stages, streamlining the approval process. Real-time updates are supported, ensuring that users have access to the latest changes made by their collaborators. These collaborative features enhance transparency and efficiency in the planning cycle.
60. Can you explain the role of “Forms Designer” in Hyperion Planning?
Ans:
Forms Designer in Hyperion Planning allows users to customize the layout and appearance of data input forms:
- Layout Customization: Users can design forms with specific labels, data input fields, and validation controls.
- User-Friendly Interface: Forms can be tailored to the needs of different users, making data entry more intuitive.
- Data Validation Rules: Implement validation rules directly within forms to ensure data accuracy.
- Dynamic Forms: Create dynamic forms that adjust based on user input or selections.
61. What role does “Forms Designer” play in enhancing the user experience in Hyperion Planning?
Ans:
Forms Designer in Hyperion Planning serves as a pivotal tool for enhancing the user experience by allowing users to customize the layout and appearance of data input forms. Through the Forms Designer, users can design forms with specific labels, data input fields, and validation controls, tailoring them to the unique needs of different user groups. This customization extends to creating dynamic forms that adjust based on user input or selections, providing a personalized and intuitive interface for data entry. The Forms Designer contributes to an improved user experience, making the planning process more user-friendly and aligned with the diverse requirements of different stakeholders.
62. How does Hyperion Planning support the creation of ad-hoc reports?
Ans:
Hyperion Planning enables users to create ad-hoc reports for on-the-fly analysis:
- Smart View Integration: Ad-hoc analysis can be performed seamlessly using the Smart View Excel add-in.
- Data Exploration: Users can interactively explore and analyze data by dragging and dropping dimensions.
- Dynamic Data Slicing: Ad-hoc reports allow users to dynamically slice and dice data for a deeper understanding.
- Graphical Representation: Supports the creation of charts and graphs within ad-hoc reports for visual analysis.
63. How does Hyperion Planning support the creation of ad-hoc reports?
Ans:
Hyperion Planning empowers users with the ability to generate ad-hoc reports for on-the-fly analysis, fostering a more flexible and responsive approach to reporting. The integration with Smart View, an Excel add-in, facilitates ad-hoc analysis seamlessly within the familiar Excel environment. Users can interactively explore and analyze data by dragging and dropping dimensions, enabling dynamic data slicing for a deeper understanding. Ad-hoc reports also allow for the creation of charts and graphs, aiding visual analysis. This feature ensures that users can quickly adapt to changing reporting needs and extract valuable insights from the planning data in real-time.
64. Explain the role of “Security Classes” in Hyperion Planning.
Ans:
Security Classes in Hyperion Planning help administrators define security based on user roles:
- User Role Mapping: Security classes can be mapped to specific user roles, controlling access to data.
- Granular Control: Administrators can set different security classes for various aspects, such as data entry or report viewing.
- Data Visibility: Enhances data confidentiality by restricting access to sensitive information based on security classes.
- Role-Based Access: Ensures that users have access to only the data relevant to their roles.
65. How does Hyperion Planning integrate with other Oracle EPM tools for end-to-end financial processes?
Ans:
Hyperion Planning seamlessly integrates with other Oracle EPM tools, facilitating end-to-end financial processes. Data integration is achieved through the extraction and loading of data from various sources. Reporting integration involves the use of tools like Hyperion Financial Reporting, enabling the creation of comprehensive financial reports. Data synchronization capabilities ensure that data is consistent across Hyperion Planning and Essbase databases, providing a unified platform for analysis. Additionally, Hyperion Planning integrates with Oracle Workflow, automating approval processes and workflow management. This comprehensive integration supports a seamless and streamlined financial management ecosystem.
66. Explain the role of “Security Classes” in managing access control in Hyperion Planning.
Ans:
Security Classes in Hyperion Planning play a crucial role in managing access control and ensuring data confidentiality. By allowing administrators to define security classes based on user roles, granular control over data access is achieved. These security classes can be mapped to specific user roles, determining the level of access users have, be it data entry, report viewing, or other aspects. Security Classes enhance data visibility by restricting access to sensitive information, contributing to a robust security infrastructure. This role-based access control ensures that users can only access the data relevant to their roles, promoting data integrity and security
67. How does Hyperion Planning handle dynamic member formulas?
Ans:
Dynamic member formulas in Hyperion Planning allow for the creation of calculated members based on business rules:
- Flexible Calculations: Users can define dynamic calculations based on changing business requirements.
- Formula Editor: Provides a user-friendly interface for creating and managing dynamic member formulas.
- Scenario Analysis: Dynamic member formulas are useful for scenario planning and assessing the impact of changes on calculations.
- Auditability: Changes to dynamic member formulas are tracked for audit and compliance purposes.
68. What is the purpose of the “Partitioning” feature in Hyperion Planning?
Ans:
The “Partitioning” feature in Hyperion Planning serves the purpose of dividing data based on specific criteria, contributing to enhanced efficiency and focused analysis. Users can create partitions to segment data according to dimensions or other defined criteria, allowing for a more targeted approach to planning and reporting. This segmentation aids in performance optimization by narrowing down queries to specific subsets of data, improving overall system responsiveness. Additionally, partitions facilitate scenario isolation, enabling users to analyze different planning scenarios in isolation for accurate and insightful analysis. Administrators can leverage partitioning for security purposes, restricting access to specific data subsets based on user roles and responsibilities.
69. Explain the role of Aggregate Storage Option (ASO) in Hyperion Planning.
Ans:
Aggregate Storage Option (ASO) in Hyperion Planning leverages Essbase technology to optimize the storage and retrieval of aggregated data. ASO databases store pre-aggregated data, enhancing query performance, especially for large datasets. It is designed for read-only access, making it suitable for reporting and analysis rather than data entry. ASO enhances the overall system performance by improving response times for complex queries, contributing to a more efficient and responsive planning environment. This storage option is particularly beneficial when dealing with extensive datasets or scenarios where fast query performance is crucial for effective analysis.
70. Can you explain the purpose of the “Partitioning” feature in Hyperion Planning?
Ans:
Partitioning in Hyperion Planning allows organizations to divide data based on specific criteria:
- Data Segmentation: Users can create partitions to segment data based on dimensions or other criteria.
- Performance Optimization: Partitioning can improve query performance by focusing on specific subsets of data.
- Scenario Isolation: Partitions enable the isolation of different planning scenarios for accurate analysis.
- Security Management: Administrators can use partitioning for security purposes, restricting access to specific data subsets.
71. How does Hyperion Planning handle data validation and ensure data integrity?
Ans:
In Hyperion Planning, data validation is a critical aspect of ensuring accuracy and reliability. The system employs data validation rules that administrators can define to enforce data integrity. These rules can encompass a range of conditions, from numerical thresholds to logical consistency checks. During data entry, users are guided by these rules, preventing erroneous or inconsistent data submissions. This robust validation mechanism enhances the overall quality of the planning data. Additionally, administrators can set up cell-level security, ensuring that only authorized users have access to specific data cells, adding an extra layer of control to maintain data confidentiality and integrity.
72. Explain the role of “Security Filters” in row-level security in Hyperion Planning.
Ans:
Security Filters in Hyperion Planning play a key role in implementing row-level security, allowing administrators to control data access based on specific criteria. These filters enable the restriction of access to specific rows of data, ensuring that users only see the data relevant to their roles or responsibilities. Security Filters can be dynamic, adjusting based on user attributes or changing conditions, providing an adaptive security mechanism. This granular control enhances data confidentiality and ensures that sensitive information is accessible only to authorized users. Row-level security through Security Filters is a crucial component of maintaining a secure and compliant planning environment.
73. How does Hyperion Planning handle Multi-Currency scenarios?
Ans:
- Hyperion Planning allows administrators to define exchange rates for different currencies.
- Data can be stored in local currencies, and automatic currency conversion is performed for standardized reporting.
- This feature ensures accurate financial consolidation in organizations with diverse currency requirements.
- Exchange rates can be updated regularly, providing flexibility to adapt to changing currency values.
- Multi-Currency support in Hyperion Planning streamlines global financial planning and reporting.
74. What is the role of “Calculation Scripts” in Hyperion Planning?
Ans:
- Calculation Scripts in Hyperion Planning define custom calculations and business rules for data manipulation.
- They allow for sophisticated calculations such as allocations, custom consolidations, and data transformations.
- Calculation Scripts provide a powerful tool for tailoring the planning application to specific business requirements.
- Administrators can design scripts to execute complex calculations during the planning process.
- The flexibility of Calculation Scripts contributes to a more adaptable and dynamic planning environment.
75. What is the role of “Data Forms” in Hyperion Planning, and how do they enhance the user experience during the planning process?
Ans:
Data Forms in Hyperion Planning serve as interactive interfaces that enable users to input, review, and manipulate planning data. These forms provide a structured layout for users to enter data, ensuring consistency and accuracy. One of the key advantages is the user-friendly interface, allowing for intuitive data entry and validation. Users can customize forms based on their specific needs, tailoring the layout and appearance to enhance usability. Data Forms support dynamic calculations and conditional formatting, further contributing to an enriched user experience. Overall, they play a crucial role in streamlining the planning process and ensuring that users can efficiently engage with planning data.
76. How does Hyperion Planning facilitate the creation and management of “Smart Lists”?
Ans:
Smart Lists in Hyperion Planning are predefined lists of values that users can utilize within dimensions, providing a standardized approach to data entry and analysis. Administrators can create and manage Smart Lists, defining the permissible values for specific members or elements. These lists enhance data integrity by restricting data entry to predefined values, reducing errors and ensuring consistency. Users can easily select values from Smart Lists during data input, simplifying the process and contributing to a more controlled and accurate planning environment. Smart Lists streamline data management by offering predefined, validated options within the planning application.
77. Explain the benefits of using “Web Forms” in Hyperion Planning.
Ans:
- Web Forms provide a user-friendly, web-based interface for data input and review in Hyperion Planning.
- Users can access and interact with forms directly through a web browser, enhancing accessibility.
- Web Forms support dynamic data validations and conditional formatting, ensuring data accuracy.
- They contribute to a seamless and responsive user experience, facilitating efficient data entry.
- The availability of Web Forms extends the reach of Hyperion Planning, enabling users to participate in the planning process from various locatio
78. How does Hyperion Planning handle “Consolidation” processes?
Ans:
- Hyperion Planning automates the consolidation of financial data from various entities and departments.
- Administrators can define consolidation rules to aggregate data based on specific criteria.
- Intercompany eliminations are supported, preventing double-counting of transactions within the consolidated results.
- The consolidation process ensures a unified and accurate view of the organization’s financial performance.
- Hyperion Planning’s consolidation features are integral for generating consolidated financial statements.
79. Can you explain the role of “Attribute Dimensions” in Hyperion Planning, and how do they contribute to detailed analysis?
Ans:
Attribute Dimensions in Hyperion Planning provide additional descriptive information about members in a dimension, enhancing the level of detail available for analysis. These attributes can include characteristics like product descriptions, employee details, or geographical information. By associating attributes with dimension members, users can perform more detailed analysis and gain deeper insights into the planning data. Attribute Dimensions contribute to improved reporting, allowing users to include additional contextual information in their analyses. This feature is particularly valuable when organizations need to perform granular analysis or when there is a requirement for detailed reporting on specific dimension members.
80. How does Hyperion Planning support the incorporation of “Scenario Planning” for strategic decision-making?
Ans:
Hyperion Planning’s Scenario Planning functionality allows organizations to model and analyze different business scenarios, providing a powerful tool for strategic decision-making. Users can create multiple scenarios, each representing a unique set of assumptions or conditions. This capability is instrumental in assessing the potential impact of various business conditions on financial outcomes. Scenario Planning aids in sensitivity analysis, enabling organizations to understand how changes in assumptions affect the financial plan. By exploring different scenarios, decision-makers can make informed choices, enhancing their ability to navigate uncertainties and formulate resilient strategies in dynamic business environments.
81. What is the role of “Member Formulas” in Hyperion Planning, and how do they contribute to dynamic calculations?
Ans:
Member Formulas in Hyperion Planning allow users to define dynamic calculations for members within dimensions. These formulas are particularly useful for scenarios where calculations need to adapt based on changing business requirements. Users can create calculations that dynamically respond to alterations in data or assumptions, providing flexibility and agility in the planning process. The Formula Editor in Hyperion Planning simplifies the creation and management of these formulas, offering a user-friendly interface. Member Formulas play a pivotal role in scenario planning, allowing users to assess the impact of changes on calculations and outcomes, contributing to a more adaptive and responsive planning environment.
82. Explain the role of “Business Rules” in Hyperion Planning.
Ans:
- Business Rules in Hyperion Planning define the logic and calculations applied to planning data.
- They encompass calculations, aggregations, allocations, and other data manipulation processes.
- Business Rules are created using Calculation Manager, providing a centralized platform for rule management.
- The flexibility of Business Rules allows for customization to suit specific business requirements.
- They play a crucial role in automating and streamlining complex calculations within the planning application.
83. How does Hyperion Planning handle “Data Synchronization” with Essbase databases?
Ans:
- Hyperion Planning seamlessly integrates with Essbase, offering a multidimensional storage option.
- Data Synchronization ensures consistency between planning data in Hyperion Planning and Essbase databases.
- Changes made in one environment are reflected in the other, maintaining data integrity.
- Essbase databases can be leveraged for additional analysis and reporting beyond the planning application.
- Data Synchronization is essential for organizations seeking a unified platform for planning and analysis.
84. How does Hyperion Planning support the creation of “KPIs” (Key Performance Indicators) for performance tracking and analysis?
Ans:
Hyperion Planning provides robust support for the creation and tracking of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), essential metrics that organizations use to measure performance. Users can define KPIs within the planning application, associating them with specific measures or metrics. KPIs can be linked to operational drivers and financial outcomes, enabling a comprehensive view of performance. Hyperion Planning allows for dynamic tracking and analysis of KPIs, aiding organizations in monitoring and evaluating their performance against strategic objectives. This feature is instrumental in aligning financial planning with key business goals, fostering a data-driven approach to performance management.
85. How does Hyperion Planning handle the integration of “Custom Dimensions” for diverse planning needs?
Ans:
Hyperion Planning supports the integration of Custom Dimensions, providing organizations with the flexibility to extend planning beyond standard financial metrics. Users can create custom dimensions to represent non-financial aspects such as units, quantities, or any other relevant business metrics. This feature allows organizations to tailor planning to their specific needs, ensuring a comprehensive representation of business activities. Custom Dimensions seamlessly integrate with the planning environment, enabling users to incorporate diverse data into their analyses. This flexibility is crucial for organizations with unique planning requirements, offering a robust solution for aligning financial and operational planning seamlessly.
86. What role does “Security Filters” play in Hyperion Planning’s security model?
Ans:
- Security Filters in Hyperion Planning provide row-level security, restricting data access based on specified criteria.
- They can be applied dynamically, adjusting based on user attributes or changing conditions.
- Security Filters ensure that users only see the data relevant to their roles or responsibilities.
- Granular control is achieved by implementing Security Filters at different levels, enhancing data confidentiality.
- Row-level security through Security Filters contributes to a secure and compliant planning environment.
87. How does Hyperion Planning handle “Workflow Automation” for plan approvals?
Ans:
- Hyperion Planning includes workflow automation for the systematic review and approval of plans.
- Users can configure workflow rules, defining the sequence of approvals and responsible individuals.
- Notifications are sent at each stage, providing transparency and accountability in the approval process.
- Workflow automation streamlines the approval cycle, reducing manual intervention and potential errors.
- It ensures that plans progress through defined stages efficiently, aligning with organizational governance.
88. Can you elaborate on the significance of “Data Maps” in Hyperion Planning and how they contribute to data integration?
Ans:
Data Maps in Hyperion Planning play a crucial role in facilitating data integration by defining mappings between external data sources and Hyperion Planning dimensions. Administrators can create Data Maps to streamline the import and export of data, ensuring a seamless connection between Hyperion Planning and external systems. These mappings contribute to data accuracy by aligning external data with the specific dimensions and structures defined within Hyperion Planning. Data Maps enhance efficiency in data integration processes, offering a standardized and controlled approach.
89. How does Hyperion Planning handle “Attribute Dimensions” for additional information?
Ans:
- Attribute Dimensions in Hyperion Planning provide descriptive information about members.
- These attributes can include additional details such as product descriptions, employee information, etc.
- Attribute Dimensions enhance the level of detail available for analysis and reporting.
- Users can associate attributes with dimension members, providing a more comprehensive view of planning data.
- This feature is particularly beneficial for organizations requiring granular insights into dimension members.
90. Explain the concept of “Smart Push” in Hyperion Planning.
Ans:
- Smart Push in Hyperion Planning allows users to push data changes from one version to another.
- It streamlines the process of moving data between different planning scenarios or versions.
- Users can selectively push data for specific members or entire dimensions, providing flexibility.
- Smart Push is valuable for scenario planning, enabling quick comparisons between different plan versions.
- This feature enhances efficiency in managing multiple planning scenarios.






