
- Introduction
- Definition of HRM
- Importance in Organizations
- HR Functions Overview
- Recruitment & Selection
- Training and Development
- Performance Management
- Compensation and Benefits
- Employee Relations
- HR Technologies
- Challenges in HRM
- Conclusion
Introduction
Human Resource Management (HRM) is the backbone of any organization, responsible for managing its most valuable asset: people. In the dynamic and competitive landscape of modern business, organizations need more than just capital and technology to succeed; they need a motivated, Resume Screening, skilled, and aligned workforce. HRM bridges the gap between strategic goals and employee performance. Over the years, HRM has evolved significantly. From administrative functions like hiring and payroll to strategic tasks like talent development, organizational culture, and employee engagement, HRM plays a central role in organizational success. It ensures that companies are staffed and staffed right with employees who are trained, motivated, and aligned with business goals.
To Explore PMP in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive PMP Certification Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Definition of HRM
- Talent Acquisition & Retention: Ensures the right people are hired and retained.
- Employee Development: Supports training programs for skill enhancement.
- Legal Compliance: Keeps organizations aligned with labor laws and policies.
- Cultural Alignment: Promotes organizational values and ethical behavior.
- Strategic Growth: Aligns HR strategies with business objectives.
- Recruitment & Selection
- Training and Development
- Performance Management
- Compensation and Benefits
- Employee Relations
- HR Compliance
- Organizational Development
- Succession Planning
- Job Analysis and Role Definition
- Posting Job Openings
- Resume Screening and Shortlisting
- Interviews and Assessments
- Reference Checks and Final Selection
- Goal Setting (SMART Goals)
- Periodic Performance Reviews
- 360-Degree Feedback
- Performance Improvement Plans
- Promotions and Career Development
- Base Salary and Bonuses
- Health Insurance and Retirement Plans
- Paid Time Off and Leave Policies
- Employee Assistance Programs
- Wellness and Perks (e.g., gym memberships, meal vouchers)
- Developing a clear HR policy framework
- Managing workplace disputes
- Encouraging employee engagement
- Promoting diversity, equity, and inclusion
- Enforcing workplace ethics and conduct
- HRIS (Human Resource Information Systems)
- Payroll Software
- Learning Management Systems (LMS)
- Performance Management Tools
- Recruitment Platforms and ATS
- Employee Self-Service Portals
- Talent Shortage: Difficulty in finding skilled professionals.
- Remote and Hybrid Workforces: Managing productivity and engagement across geographies.
- Changing Labor Laws: Adapting to evolving legal requirements.
- Diversity and Inclusion: Creating a truly inclusive workplace.
- Employee Well-being: Addressing stress, burnout, and mental health.
- Technology Adoption: Implementing and managing digital HR tools.
Human Resource Management is the strategic and coherent approach to managing people within an organization. It includes the processes involved in hiring, developing, motivating, and retaining employees while ensuring compliance with labor laws and alignment with the organization’s overall objectives. According to the Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM), HRM is “the process of employing people, training them, compensating them, developing policies relating to them, and developing strategies to retain them.” This broad definition highlights that HRM is not just about managing headcount—it’s about optimizing human capital.
Importance in Organizations
The significance of HRM in today’s organizations cannot be overstated. Its contributions extend across every department and level, influencing productivity, culture, compliance, and innovation. Key Reasons HRM Is Crucial:
Effective HRM fosters a positive work environment, drives high performance, reduces employee turnover, and builds a resilient workforce ready to face future challenges.
HR Functions Overview
Human Resource Management includes a wide range of strategic and operational functions. These functions are interrelated and collectively contribute to achieving business goals through people. Major HR Functions:
Each of these areas plays a vital role in shaping an organization’s ability to attract, develop, and retain top talent. Together, they form a robust HR framework that supports sustainable business growth.
Are You Interested in Learning More About PMP? Sign Up For Our PMP Certification Training Today!
Recruitment & Selection
Recruitment and selection are the first and most essential steps in building a high-performing workforce. This function involves attracting qualified candidates and selecting the most suitable individuals based on the organization’s needs.
Key Steps in the Recruitment Process:Modern recruitment also leverages technology through Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS), online assessments, and AI-driven screening tools. A strong recruitment process ensures that the right talent joins the organization and aligns with the culture and long-term vision.
Performance Management
Performance management involves setting employee goals, evaluating outcomes, providing Feedback, and fostering career progression. It aligns individual performance with organizational objectives.
Key Elements:A robust performance management system motivates employees, Human Capital Management identifies top performers, and addresses underperformance. It ensures that recognition and rewards are merit-based and everyone works toward common goals.
Are You Preparing for PMP Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Project Management Interview Questions & Answer to Boost Your Preparation!
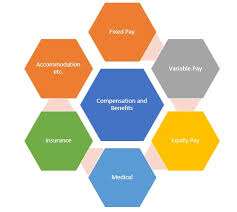
Compensation and Benefits
Compensation and benefits are central to employee satisfaction and retention. HR professionals design fair, competitive pay structures and benefit programs that attract and retain top talent.
Components Include:Strategic compensation helps reduce turnover, boost morale, and reinforce a performance-driven culture. It also ensures compliance with minimum wage laws and equal pay standards.
Employee Relations
Employee relations involve maintaining a positive and productive relationship between the organization and its workforce. It encompasses communication, conflict resolution, Talent Acquisition, grievance handling, and workplace culture.
Key Activities:Good employee relations result in a motivated workforce, reduced absenteeism, and higher retention. They also help create a psychologically safe work environment where employees feel valued and heard.
HR Technologies
The role of technology in HR has expanded significantly. HR Tech, often called Human Capital Management (HCM) systems, automates and streamlines various HR functions, making them more efficient and data-driven.
Popular HR Technologies:Technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and data analytics transform HR into a more strategic and predictive function. These tools provide insights into workforce trends, Job Analysis , attrition risks, and employee engagement levels.
Are You Considering Pursuing a Master’s Degree in PMP? Enroll in the PMP Masters Program Training Course Today!
Challenges in HRM
Despite its importance, HRM faces several challenges in modern organizations. The dynamic nature of work, evolving employee expectations, and regulatory complexities make HR a demanding function.
Common Challenges:Addressing these challenges requires HR professionals to be adaptable, forward-thinking, and proactive in their approach to people management.
Conclusion
Human Resource Management is no longer confined to back-office functions. It has become a strategic partner in driving business success through people-centric practices. By managing the employee lifecycle—from hiring to retirement—HRM ensures that the Organizational Development attracts top talent, develops their potential, and fosters a culture of performance and Talent Acquisition.The growing complexity of business environments makes effective HRM, Human Capital Management more critical than ever. With the right strategies, tools, Job Analysis and mindset, HR professionals can help organizations navigate challenges, enhance employee satisfaction, and achieve long-term goals.





