
SAS Business Intelligence (BI) is a comprehensive suite of tools designed to facilitate data management, analysis, and reporting for organizations seeking to leverage data-driven insights. It integrates various components, including SAS Enterprise Guide, SAS Visual Analytics, SAS Data Integration Studio, and SAS Web Report Studio, to enable users to collect, manage, and analyze data from diverse sources.
1. What is SAS BI and SAP BO are contrasted.
Ans:
SAS BI vs. SAP BO
Reviewers found SAS Business Intelligence to be more user-friendly, easier to administer, and provide a better overall experience compared to SAP BusinessObjects Business Intelligence (BI). However, they preferred SAP BusinessObjects Business Intelligence’s (BI) setup simplicity. Ultimately, the choice between the two often hinges on specific organizational needs and user familiarity.
2. What is the function of TRANSLATE?
Ans:
- A translation table that matches each character with its equivalent replacement character is required as input for the translate() method.
- The Maketrans () function requires two arguments to construct this table: the set of characters to be replaced and the set of replacement characters.
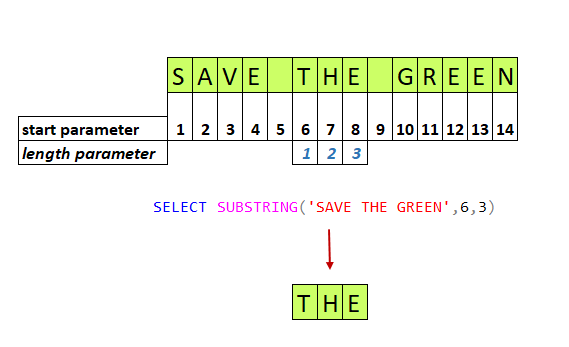
3. What is the function of SUBSTR?
Ans:
- A translation table that matches each character with its equivalent replacement character is required as input for the translate() method.
- The Maketrans () function requires two arguments to construct this table: the set of characters to be replaced and the set of replacement characters.
4. What is the APPEND process?
Ans:
- Lisp is the programming language from which the idea of Append originated.
- The append process returns the concatenation of these elements after receiving zero or more linked lists as parameters.
- However, if applied carelessly, it might result in inefficient code.
5. What distinguishes a format from an informant?
Ans:
| Aspect | Format | Informat |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | specifies the printing or presentation of data. | describes the reading or input of data. |
| Application | utilized while producing output, including printing or presenting data. | utilized while doing input operations, including reading data from outside sources. |
| Syntax | starts with either the user-defined format name or the dollar sign ($). | begins with the format name and a period (.). |
| Functionality | converts values, either textual or numeric, to a certain display format. | transforms raw data during input into character or numeric values. |
6. What is BY-group Processing, and how is it utilized in SAS?
Ans:
BY-group Processing:
BY-group Processing refers to the method in SAS where observations from one or more datasets are sorted or grouped based on shared variable values. This technique is primarily used to combine two or more SAS datasets during the DATA phase, allowing for efficient data manipulation and analysis. Additionally, it facilitates the processing of data in a way that maintains the relationships between grouped observations.
7. Why is the DIVIDE function used?
Ans:
Purpose of the DIVIDE function:
- SAS’s DIVIDE function makes division operations easier by streamlining the syntax.
- It simplifies division computations within SAS applications or procedures by providing a clear method for dividing one numerical expression by another.
- By doing away with the need for extra mathematical operators or complicated formulations, this function simplifies the procedure.
8. What do you mean by the CALL PRXFREE Routine?
Ans:
CALL PRXFREE Routine:
The CALL PRXFREE function in SAS releases memory set aside for Perl regular expression (PRX) patterns. Computed regular expression patterns are stored in memory when using PRX functions such as PRXPARSE or PRXMATCH. This memory is deallocated by calling the CALL PRXFREE procedure, which helps with memory management, especially when working with large datasets or repetitive pattern-matching jobs.
9. Describe the function ANYDIGIT.
Ans:
ANYDIGIT function:
- SAS’s ANYDIGIT function looks throughout a character string to determine where the first digit is encountered.
- It is useful for finding the presence of digits in a string or extracting numerical segments from alphanumeric sequences.
- For example, if YOU applied ANYDIGIT(‘abc123’) on ‘abc123’, the result would be 4 since ‘1’ is the first digit in the string.
10. What does the CALL MISSING Routine mean to you?
Ans:
CALL MISSING Routine:
What do you mean by the CALL MISSING Routine, which is used to assign missing values to specific variables in SAS? This procedure is often utilized in DATA steps or macros to initialize variables or restore them to missing values, making it useful for data manipulation tasks that require variables to be cleared or reset to their initial states. How does this fit into your data processing workflow?
11. What does the VFORMATX function do?
Ans:
- There seems to be some misunderstanding.
- According to what I’ve learned recently, VFORMATX is not a predefined SAS function.
- To properly explain its purpose, I would need more information or context surrounding the precise capability of the function or format you refer to, whether it is custom or user-defined.
- Please specify if you meant something different, and I’ll be happy to help further.
12. What is the purpose of the FILECLOSE data set option?
Ans:
When the FILECLOSE dataset option is used in SAS during the DATA step, it closes a file that was opened earlier with the FILENAME statement or the FILE statement. Its use is limited to managing external files (text, raw data, etc.) by shutting them after processing in order to preserve data integrity and free up system resources. When a DATA step has FILECLOSE specified, SAS automatically closes the associated file when the phase is finished. This function helps prevent possible issues such as file locks or partial data writes resulting from unneeded file retention.
13. What is Debugging?
Ans:
The process of locating, examining, and fixing mistakes or defects in software code is known as debugging. It entails executing the code, analyzing it to identify the problems, and making the required adjustments to guarantee the software functions properly and effectively. Effective debugging not only enhances software quality but also improves overall development efficiency.
14. Which technique is applied for copying data blocks?
Ans:
- You can use an EXCLUDE or SELECT query to make duplicates of particular SAS files.
- Refer to the sections on Specifying Member Types When Copying or Moving SAS Files and Manipulating SAS Files for an example of how to use the COPY statement in conjunction with a SELECT or EXCLUDE statement.
- For more details, also refer to the sections on the SELECT and EXCLUDE statements.
15. What is the acronym for ODS?
Ans:
Exit Delivery System is referred to as ODS. The output from SAS processes and data stages can be managed, formatted, and customized by users using this component of SAS software. Results can be presented and shared more easily thanks to ODS’s ability to create a variety of output formats, including HTML, PDF, Excel, and more. This flexibility makes it an essential tool for generating reports tailored to different audiences and purposes.
16. How does one go about making a complete duplicate of a library?
Ans:
To create a full replica of a library in SAS, utilize the PROC COPY procedure as follows:
- PROC COPY IN=sourceLib OUT=targetLib;
- RUN;
Substitute `sourceLib` with the source library’s name you wish to duplicate and `targetLib` with the designated name for the new library. This procedure duplicates all datasets and additional objects from the source library to the target one.
17. What tasks does SAS carries out?
Ans:
Activities are easy-to-use tools that resemble wizards; they generate SAS code for typical activities such as creating boxplots and doing statistical analyses. Conversely, snippets are short bursts of code that can be quickly added to a program. Users can customize tasks and snippets to meet their requirements, enhancing productivity and streamlining the coding process.
18. What Is DATA Step?
Ans:
- The DATA step is a fundamental component of SAS programming used for data manipulation and processing.
- It allows users to create, modify, and manipulate SAS datasets.
- Within a DATA step, you can read data from external sources, manipulate variables, apply conditional logic, compute new variables, and write the resulting dataset to an output.
- It serves as the building block for data preparation, analysis, and reporting in SAS.
19. Which statement in SAS doesn’t carry out comparisons with automatic conversions?
Ans:
In the WHERE statement, SAS does not immediately change the data types to be compared. As a result, SAS does not perform automated data type conversions when using the WHERE statement to filter data based on circumstances. It is essential to confirm that the data types being compared are compatible or explicitly converted using SAS procedures such as PUT and INPUT. This method guarantees accurate filtering according to predetermined standards, avoiding unexpected behavior resulting from automated conversions.
20. Why is the function PROC SUMMARY used?
Ans:
- In SAS, PROC SUMMARY computes descriptive metrics such as mean, median, min, max, total, standard deviation, and quartiles for numeric variables inside a dataset.
- Large datasets are summarised effectively, providing insights into the distribution and properties of the data.
- Moreover, it supports variable grouping, enabling the computation of summary statistics for discrete data subsets based on categorical variables.
- In general, PROC SUMMARY facilitates better data analysis and decision-making by helping to understand statistical features.
21. What is the purpose of PROC PRINT and PROC CONTENTS?
Ans:
- SAS’s PROC PRINT displays a dataset’s contents in a tabular format, making it easy to examine variables, values, and observations.
- PROC CONTENTS, on the other hand, provides detailed information about the dataset’s properties and structure. It displays metadata like counts of observation variables, attributes of the variant, indexes, and other aspects of the dataset.
22. What are the functions for input and doing?
Ans:
- When reading raw data files or changing character variables into numeric ones within a DATA phase, the INPUT function is usually used to convert character data to numeric data.
- As an example, consider this: {{{sas numeric_variable = INPUT(character_variable, informat.);^
- The PUT function, on the other hand, transforms numeric data into character data and is frequently used to prepare numeric values into certain character formats for output.
- As an illustration, consider this: {{{sas character_variable = PUT(numeric_variable, format.); {}}
23. What distinguishes VAR B1 — B3 from VAR B1 — B3?
Ans:
The representation of variables is where “VAR B1 – B3” and “VAR B1 — B3” differ from one another. A single dash “-” indicates a series of variables, and a double dash “–” indicates a subset of the variables in the dataset. Understanding this distinction is crucial for accurately defining variable groups in analyses. This clarity helps prevent errors in data manipulation and ensures that analyses yield the intended results.
24. What unique input delimiters are there?
Ans:
- SAS features multiple specific input delimiters to facilitate the extraction of data from external sources:
- Column Input: Using this technique, data values are read based on the corresponding column positions.
- For instance, INPUT var1 $1–10, var2 $12–15;
- List Input: Data values are retrieved using spaces to divide them according to the variable order.
25. What is a single SAS function.
Ans:
A SAS function is a pre-defined procedure created to carry out particular operations on data; these operations can include text manipulation and mathematical calculations. SAS systems use these functions to expedite data transformation or analysis procedures efficiently, allowing users to harness powerful analytical capabilities with minimal coding effort.
26. How does SAS get used?
Ans:
- SAS is an all-inclusive solution for data management, sophisticated analytics, and business intelligence facilitation.
- It is skilled in a variety of tasks, including statistical analysis, data processing, predictive modeling, and reporting.
- SAS is widely used in a variety of areas, including marketing, finance, and healthcare, where it is essential for directing decision-making processes and revealing insightful information.
27. How may a Compressed Observations SAS data set be created?
Ans:
You can use the COMPRESS= dataset option in a DATA step or a PROC step to create a SAS dataset of compressed observations. Here’s an example: Your data step code is entered here / RUN; {{{sas DATA CompressedDataSet (COMPRESS=YES); Here, adding {COMPRESS=YES causes the observations in the generated SAS dataset to be compressed. This option can be used when creating a new dataset or when using PROC COPY and the OUT= option to duplicate an existing dataset.
28. What strategies can be used to minimize the size of a large dataset in SAS for Windows?
Ans:
Using the COMPRESS data set option, eliminating extraneous variables or observations, and storing the information in a compressed format like SAS7BDAT, you can minimize the size of a large dataset in SAS for Windows. For effective data access, think about utilizing segmentation or indexing as well. Additionally, consider implementing segmentation or indexing for more efficient data access. What other techniques could help optimize data storage further?
29. What Is SAS Business Intelligence?
Ans:
- The goal of SAS commercial Intelligence (BI) is to assist organizations in deriving insights from data, making wise decisions, and achieving commercial success.
- It gives users the ability to examine data, generate interactive reports, and share insights throughout the company.
- These capabilities include data integration, visualization, reporting, and analytics.
30. Where to Use SAS Business Intelligence?
Ans:
Retail, healthcare, and finance are just a few industries that use SAS analytics software. It is employed in corporate intelligence, data management, and advanced analytics. SAS is a major player in the healthcare industry and holds a substantial market position in the analytics software market, driving innovation and insights that enhance decision-making across various sectors.
31. What is Business intelligence?
Ans:
SAS manages corporate intelligence by offering a full range of software tools for reporting, sophisticated analytics, and data management. Effective data collection, integration, analysis, and visualization empower decision-makers with practical insights that propel corporate success, enabling organizations to respond swiftly to market changes and optimize their strategies.
32. What is Metadata?
Ans:
- Data that provides details about other data is called metadata.
- The information environment of an organization’s processes, datasets, data pieces, and other resources are described together with their properties, linkages, and organizational structure.
- Information like as ownership, usage rights, formats, data definitions, and security settings can all be included in metadata.
- For the efficient management, comprehension, and governance of data assets, it is an indispensable tool.
33. What is SAS Metadata Repository?
Ans:
The SAS Metadata Repository is a centralized location within the SAS environment that is used to manage and store metadata on SAS resources, such as programs, libraries, datasets, users, and permissions. With its comprehensive view of each SAS asset and its relationships, it serves as an all-in-one metadata management solution. The Metadata Repository enables features such as version control, lineage tracking, version querying, and browsing of metadata.
34. What is SAS Enterprise Intelligence Architecture?
Ans:
The architecture developed by SAS for implementing and overseeing business intelligence solutions is known as SAS Enterprise Intelligence Architecture. In order to facilitate data integration, analytics, reporting, and decision-making within enterprises, it includes hardware, software, and procedures, providing a comprehensive framework that supports scalability and adaptability to evolving business needs.
35. What is SAS Application Server?
Ans:
- The SAS Application Server is one part of the SAS architecture responsible for running SAS applications and offering client services.
- It controls how SAS code is executed, handles data processing, and helps SAS clients and other environment components communicate with one another.
- In essence, it allows users to engage with SAS software and utilize its features by acting as the runtime environment for SAS applications.
36. What components make up a SAS BI dashboard?
Ans:
Dashboard for SAS® BI. Monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) with dashboards to see how well your company is doing. The SAS Information Delivery Portal is one web-based interface that is easy to use for creating, managing, and viewing dashboards, offering customizable options that allow users to tailor their visualizations for deeper insights into performance trends.
37. Where are the components of the dashboard developed and maintained?
Ans:
Typically, SAS Business Intelligence (BI) tools like SAS Visual Analytics or SAS Dashboard are used to design and maintain the dashboard’s components. The dashboard component design, creation, and management interface offered by these technologies is easy to use, enabling users to quickly adapt their dashboards to meet changing business requirements and enhance data-driven decision-making.
38. Which components make up a range?
Ans:
- Typically, a range includes the following elements:
- lowest possible number
- Maximum amount
- Step or increment value
39. What many display types does the SAS BI dashboard offer?
Ans:
Numerous display options are available in SAS BI dashboards, including:
- Bar graphs
- Line diagrams
- Pie charts
- Tables Measurements
- Heat maps
- Dispersion charts
- Tree Maps
- Graphs with bullets
- geographical atlases
40. Which kinds of interactive displays are there?
Ans:
Interactive displays in business intelligence typically include:
- Filter panels: Let users dynamically filter data according to predefined standards.
- Drill-down capabilities: Let users go from summary views to detailed levels in order to investigate data hierarchies.
- Hover-over tooltips: When users hover over data points, provide them with more context or information.
- Options for selection: Give consumers the ability to choose and contrast several categories or subsets of data.
Sliders, dropdown menus, and checkboxes are examples of interactive widgets that allow user involvement.
41. What are the principles and functions of business intelligence?
Ans:
- The principles of business intelligence revolve around the following:
- Using data to inform and direct company goals and actions is known as “data-driven decision-making.”
- Providing timely and pertinent information access: Ensuring that decision-makers have access to accurate and current data.
- Analyzing and interpreting data involves using analytical methods to derive meaning from the information.
42. What does the business intelligence dashboard mean?
Ans:
A business intelligence dashboard is a visual depiction of key performance indicators (KPIs) and other pertinent metrics. It usually shows in a single interface and gives users a quick overview of an organization’s performance. It allows users to spot patterns, pinpoint opportunities or areas for improvement, and make well-informed decisions. To make data exploration and analysis easier, interactive features like drill-down capabilities and filters are frequently included in business intelligence dashboards.
43. What is SAS Business Intelligence, please?
Ans:
The SAS Institute created a suite of corporate solutions known as the Statistical Analysis System (SAS) for various analytics applications. Numerous business intelligence functions are included in the systems, such as data management, multivariate analysis, predictive analytics, and advanced analytics, providing organizations with comprehensive tools to transform raw data into actionable insights and informed decision-making.
44. What are the capabilities and ideas of Business Objects?
Ans:
Business Objects: Business Objects: SAP provides a business intelligence platform called Business Objects. Its features include data visualization, reporting, ad hoc analysis, and dashboards. Business Objects facilitates business decision-making processes by enabling users to access, alter, and analyze data from multiple sources, thereby promoting a data-driven culture within organizations and enhancing overall operational efficiency.
45. What is a broadcast agent?
Ans:
Broadcast Agent: A broadcast agent is a component in data management systems that facilitates the automated distribution of reports and notifications to designated users or groups. It ensures timely delivery of critical information, allowing organizations to keep stakeholders informed and engaged, while also streamlining communication processes across various departments.
46. What is a universe? What kinds of universes are there in business objects?
Ans:
- A universe in Business Objects is a semantic layer that translates a database’s structure into business terminology, facilitating data analysis and querying for non-technical users.
- Relational universes, which query relational databases directly, and OLAP universes, which query multidimensional databases, are the two primary categories of universes.
47. Which programs and applications do SAS application developers use the most frequently?
Ans:
SAS BI Applications Developers: When creating and implementing BI solutions, SAS BI application developers frequently make use of tools like SAS Enterprise Guide, SAS Visual Analytics Designer, SAS Studio, and SAS Web Report Studio. These tools enable them to design intuitive dashboards, perform advanced analytics, and deliver interactive reports, enhancing the overall effectiveness of business intelligence initiatives within organizations.
48. Which apps are most frequently utilized by business analysts?
Ans:
Business Analysts: For data analysis, reporting, and visualization, business analysts commonly use BI products like SAS Visual Analytics, SAS Enterprise Guide, Microsoft Power BI, Tableau, and QlikView. These tools empower them to uncover insights, create compelling visualizations, and communicate findings effectively to stakeholders. By leveraging these BI solutions, analysts can drive data-driven decision-making and support strategic initiatives across the organization.
49. Where are the SAS platform applications going to be located?
Ans:
Location of SAS Platform apps: SAS Platform apps can be hosted in the cloud, such as on SAS Viya, a SAS cloud-based analytics platform, or on-premises within an organization’s own data center. This flexibility allows organizations to choose the deployment option that best aligns with their operational needs, security requirements, and scalability goals.
50. How will you find the SAS platform apps that are accessible through a web browser?
Ans:
Go to the SAS portal or web interface that your company offers to locate SAS platform apps that can be accessed via a web browser. Usually, you can use the URL that your SAS administrator sent you to open these programs in the address bar of your web browser. Once logged in, you’ll find a user-friendly dashboard that provides easy navigation to the various applications and tools available for your analytics needs.
51. Why can’t I find the SAS Add-in for Microsoft Office from the Windows Start menu’s SAS group?
Ans:
If you are unable to locate the SAS Add-in for Microsoft Office within the SAS group of the Windows Start menu, it might not have been installed or set correctly on your system. Reinstalling the SAS Add-in for Microsoft Office is one option; alternatively, ask your IT administrator for help. They can assist with troubleshooting the installation process or provide guidance on ensuring that all necessary components are properly configured for use.
52. What is the worksheet’s maximum number of rows and columns that can be used?
Ans:
Depending on the software version being used, there may be a maximum amount of rows and columns in the worksheet. The maximum number of rows in most SAS versions is approximately 10 million, and the maximum number of columns is approximately 32,767. It’s important to be aware of these limitations when designing your datasets, as exceeding these thresholds may result in errors or data truncation.
53. Which choices are available in Web Report Studio for creating reports?
Ans:
The options provided in Web Report Studio for report creation consist of:
- Use a blank template to start fresh while creating reports.
- Utilizing report styles or pre-made templates.
- Importing pre-made templates or reports.
- Producing reports using databases, OLAP cubes, and SAS datasets as data sources.
54. What is the WRS’s main source of data?
Ans:
SAS datasets or relational databases that are accessible to the SAS server where WRS is installed are usually the primary sources of data used in Web Report Studio (WRS). By choosing information from various sources and creating report layouts with the WRS interface, users can generate reports. This flexibility allows for the integration of diverse data sets, enabling more comprehensive analysis and richer insights in the final reports.
55. How many different kinds of prompts exist?
Ans:
- In SAS, various types of prompts are provided, such as:
- Date-based prompts
- Text-based instructions
- List of instructions
- Range cues
- prompts with a hierarchy
56. How many different kinds of prompting frameworks are there?
Ans:
The two different types of prompting frameworks in SAS are the base SAS prompting framework and the stored process prompting framework. Each framework provides a unique set of features and functionalities for generating and controlling prompts in SAS applications, allowing users to customize their data interactions effectively. Understanding these frameworks can enhance user experience and streamline the data analysis process.
57. What is the distinction between the CLASS and BY statements in a procedure?
Ans:
In SAS, BY-group processing is done with the BY command, whereas classification variables are defined for analysis using the CLASS statement. Procedures like PROC SORT or PROC MEANS use the BY statement to specify variables for BY-group processing. In contrast, procedures like PROC MEANS or PROC GLM use the CLASS statement to specify categorical variables for analysis.
58. What are the core functions of SAS?
Ans:
- These are some of SAS’s primary duties:
- Handling and modifying data
- Analytical statistics
- Visualization and reporting
- Modeling that predicts
- Analytics and business intelligence
59. What does the TABLES statement’s CROSSLIST option mean?
Ans:
Using the CROSSLIST option, a cross-tabulation or contingency table of the variables listed in the TABLES statement is produced. For every set of values for the variables, it shows the frequency or count of observations. This allows analysts to easily identify relationships and patterns within the data, facilitating deeper insights into variable interactions.
60. What is the purpose of a SAS program’s output statement?
Ans:
Output Statement Purpose:
Writing data observations to an output dataset is the goal of the OUTPUT statement in a SAS program. It lets you designate which observations, according to conditional logic or other program-defined criteria, you wish to output. When developing customized datasets or subsets of data that satisfy unique requirements for analysis or reporting needs, this statement is especially helpful.
61. Describe the purpose of an SAS program’s stop statement.
Ans:
Stop Statement Purpose:
- The STOP statement in a SAS program terminates the program’s execution prematurely.
- It is typically used within conditional logic to exit a loop or stop processing when certain conditions are met.
- This statement is helpful for controlling the program’s flow and preventing unnecessary processing when further execution is no longer required.
62. What is the way to determine which variables the FREQ method will process?
Ans:
Variables Processed by FREQ Method:
When a program in SAS is executed prematurely, it can be stopped with the STOP command. To break out of a loop or cease processing when specific criteria are satisfied, conditional logic usually uses this technique. When further execution is no longer essential, this statement helps to control the program’s flow and avoid processing that isn’t necessary.
63. What is the distinction between the data statement and the set statement when using the drop data set option?
Ans:
Data Statement vs. Set Statement with DROP Option:
The variables provided in the VAR statement within the PROC FREQ function determine which variables the FREQ technique will process. For each variable specified in the VAR declaration, frequency counts and additional statistics are computed. The FREQ method will process only the variables listed in the VAR statement, ensuring that the analysis focuses exclusively on the selected variables of interest.
64. What are some common mistakes made in SAS programming?
Ans:
- Common Errors Made When Programming SAS:
- Typical errors made when writing SAS include:
- Failing to use a semicolon to finish sentences.
- Spelling errors in function or variable names.
- Misusing variables or datasets as references.
- Not formatting data correctly before analysis.
- Need to handle missing values properly.
65. Which SAS programming techniques are there for creating microvariables?
Ans:
SAS Programming Techniques for Micro Variables: Array processing, macro variables, or a combination of DATA step functions and operators are some methods that SAS programmers use to generate or manipulate data at the micro level. These techniques allow for efficient handling of small-scale data tasks, enabling programmers to streamline their code and enhance data processing capabilities.
66. Describe the input and put functions in brief.
Ans:
Functions for Input and Output In a nutshell:
In SAS, the INPUT function converts character data to numeric data, and the PUT function converts numeric data to character data. These functions are frequently utilized in data manipulation tasks to guarantee data consistency and carry out necessary transformations.
67. What are the few functions of SAS.
Ans:
SAS’s functions include:
- Among SAS’s capabilities are the following:
- Data transformation and manipulation.
- Modeling and statistical analysis.
- Reporting together with visual aids.
- Analytics and business intelligence.
- Natural language processing and text mining.
- Both optimization and forecasting.
68. Which SAS system settings are available for use in troubleshooting SAS micros?
Ans:
- Configuring the SAS System to Troubleshoot Micros:
- When debugging SAS macros, some useful SAS system parameters are as follows:
- The MPRINT option allows the log to show macro code.
- To see the resolution of a macro variable in the log, use the SYMBOLGEN option.
- MERROR option to halt processing in the event of a macro error.
69. What are the different categories of data in SAS?
Ans:
- Data Categories in SAS: There are two primary data categories in SAS:
- Numerical quantities that can be utilized in arithmetic computations are represented by numerical data.
- Textual values, such as letters, numerals, and special characters, are represented by character data.
70. If a variable has digits in it, can it still be a character data type?
Ans:
Yes, in SAS, a variable can be stored as a character data type even if it consists solely of digits. The data type of a variable is determined by the definition within the SAS program, not by the values it contains. This allows for greater flexibility in handling data that may require alphanumeric treatment, such as ZIP codes or phone numbers, which should not be subjected to numerical operations.
71. What could be the biggest dataset in SAS in terms of size?
Ans:
The operating system and file system being utilized in SAS typically dictate the greatest dataset size. SAS datasets can generally hold up to about 2 billion rows and 32,767 columns for 64-bit platforms, with a maximum file size of about 2 terabytes. On the other hand, depending on system resources, configurations, and performance factors, the real restrictions might differ.
72. What happens if a variable contains special characters or letters—can it still be a numeric data type?
Ans:
SAS variable cannot be stored as a numeric data type if it contains special characters or letters. Numerical variables are limited to representing only numerical values; no non-numeric characters may be used. This ensures that numerical operations and analyses remain accurate and reliable, preventing potential errors in calculations. Understanding this limitation is crucial for proper data management and analysis in SAS.
72. What distinguishes PROC SUMMARY from PROC MEANS?
Ans:
Numeric Data Type with Special Characters or Letters: If a SAS variable has special characters or letters in it, it cannot be saved as a numeric data type. Numeric variables may represent only numerical values; non-numeric characters are not permitted. This restriction is essential to maintain the integrity of data processing and ensure that calculations are performed correctly without interference from non-numeric entries.
73. What is the BMDP procedure?
Ans:
This article explains the BMDP technique in SAS. The BMDP statistical software tool is used for data analysis. It offers a range of statistical analysis methods, such as non-parametric testing, regression, and analysis of variance. SAS users can access and use the statistical features of the BMDP program within the SAS environment by following the BMDP method.
74. Which SAS functions are used in character processing?
Ans:
- Functions Used in Character Processing: The following SAS functions are utilized in character processing:
- SCAN: Takes a character string and pulls out words or substrings.
- TRIM: Takes the leading and trailing white spaces out of a string of characters.
- UPCASE: This keystroke encrypts data.
- LOWCASE: Lowercase the characters.
- CAT: Joins several character strings together to form a single string.
75. What is the process of a call exchange?
Ans:
Description of the Call Execute Process: In SAS, the CALL EXECUTE process is used to produce and run SAS code dynamically from within a macro or DATA step. It is frequently employed to produce code that is repeated or to carry out conditional processing in response to data values. Dynamic code creation and execution are made possible via the CALL EXECUTE instruction, which queues the created SAS code for execution at the conclusion of the DATA step or macro.
76. What is the definition of State RUN-group Processing?
Ans:
State RUN-group processing in SAS explains that it is the process of running code inside a single DATA step or procedure. Until an RUN statement is issued or the step or procedure’s conclusion is achieved, the code is processed in sequential order. Thanks to state RUN-group processing, which enables the execution of several statements or processes within a single processing block, complex data manipulation or analysis routines can be created.
77. What is the operation of the BOR?
Ans:
Operation Description for BOR: Reports, universes, and user security settings are just a few examples of the metadata objects that can be stored and managed in the Business Objects environment’s central repository, or BOR. The Business Objects Repository (BOR) serves as a central location for storing and retrieving all assets related to Business Objects.
78. What is the function of DIVIDE used for?
Ans:
DIVIDE Function Use: In SAS, division operations on numerical values are carried out using the DIVIDE function. It yields the quotient as the result of dividing one numeric expression by another. When performing data analysis and reporting activities, the DIVIDE function comes in handy for determining ratios or percentages, making it an essential tool for financial calculations and statistical analyses.
79. What is the operation of the PRXFREE CALL routine?
Ans:
The PRXFREE CALL routine in SAS releases memory allocated for processing regular expressions created by the PRXPARSE function. This helps effectively manage memory utilization within SAS programs by freeing up resources associated with compiled regular expressions. By optimizing memory usage, it contributes to overall program efficiency and performance.
80. What is the operation of the ANYDIGIT function?
Ans:
- A SAS function called ANYDIGIT determines whether a character string contains any digit characters.
- It gives back a Boolean value (0 or 1), where 1 denotes the presence of at least one character in the string that is a number, while 0 denotes the absence of any digit characters.
- When processing or validating character data that might contain numeric values, this function comes in handy.
81. Describe BY-group Processing
Ans:
In SAS, a technique called BY-group processing is used to group data according to the values of one or more variables, or BY variables. The technique entails first grouping the dataset according to the BY variables and then processing observations inside each unique group independently. When using programs like PROC MEANS or PROC SORT, BY-group processing is frequently utilized to carry out computations or analyses inside of particular groups that are defined.
82. What is Program Data Vector, or PDV?
Ans:
Program Data Vector (PDV) Definition:
The Program Data Vector (PDV) is a temporary area in memory used by SAS during data step processing. It holds the current values of variables being processed in the DATA step. The PDV allows SAS to perform data manipulation operations and apply transformations to variables as the DATA step executes.
83. What is the handling of variable formats by PROC COMPARE?
Ans:
Handling of Variable Formats by PROC COMPARE:
- SAS uses a temporary memory region known as the Program Data Vector (PDV) for data step processing.
- It contains the current values of the variables that the DATA phase is processing.
- As the DATA phase runs, SAS is able to manipulate data and apply transformations to variables thanks to the PDV.
84. What is the purpose of SAS’s Retain?
Ans:
Purpose of SAS’s Retain:
In SAS, PROC COMPARE compares the variable values between two datasets. When comparing values, it only looks at the actual data values and ignores variable forms. This means that regardless of how the values are structured for presentation, PROC COMPARE compares the underlying data, ensuring accurate assessments of differences or similarities between datasets without being affected by formatting. This functionality is essential for data validation and quality checks.
85. What is your level of familiarity with the SAS data set?
Ans:
Extent of Familiarity with SAS Data Set:
I have experience with the SAS data set, which is a structured data collection used in SAS (Statistical Analysis System) software environments for business intelligence, data management, and statistical analysis applications. My familiarity includes understanding its structure, how to manipulate it, and utilizing various procedures to analyze and extract meaningful insights from the data.
86. What is the aim of VFORMATX?
Ans:
- Aim of VFORMATX: There is no standard SAS term or function for VFORMATX.
- If you’re talking about a particular SAS topic or function, please explain more, and I’ll be pleased to help you further.
87. What is the purpose of an STD?
Ans:
Purpose of STD:
In statistical terms, STD usually refers to “Standard Deviation.” With SAS, you may use functions like PROC MEANS or PROC STDIZE to determine a variable’s standard deviation. The standard deviation measures a dataset’s dispersion or spread of values around the mean, which sheds light on the data’s variability. Understanding standard deviation is crucial for assessing the reliability of statistical conclusions and for comparing different datasets effectively.
88. When performing comparisons, which SAS command does not automatically convert values?
Ans:
SAS Command Not Automatically Converting Values:
- The COMPRESS dataset option does not immediately convert values when making comparisons in SAS.
- This option accomplishes character variable compression in SAS datasets; it has no effect on the way comparisons are made on the data values themselves.






