If you’re getting ready for an interview focused on SAP Business One, you’ve landed in the right spot. In today’s discussion, we’ll go through some commonly asked SAP Business One interview questions designed to enhance your confidence. SAP Business One functions as a web application firewall (WAF), safeguarding web applications and APIs against various attacks, both known and unknown. It also aids in ensuring compliance with regulations. As a result, individuals in SAP Business One roles may come across interview questions tailored to their specific enterprise SAP Business One positions. The following overview delves into different categories of interview questions related to SAP Business One, aiming to assist individuals aspiring to excel in enterprise SAP Business One roles.
1. Which DLLs are incorporated within the SAP Business One SDK?
Ans:
SAP Business One SDK uses two: Interop.SAPbouiCOM.dll and Interop.SAPbobsCOM.dll. To access the user controls shown over the form, utilize Interop.SAPbouiCOM.dll. Interop.SAPbouiCOM.dll provides access to several controls, including label, Combobox, matrix, and more.
2. What occurs if we take off the EventFilters?
Ans:
Every event will fire if we remove the EventFilters. Unnecessary events should be ignored when programming in SDK since they will reduce the application’s performance. Events will occur by the SAPbouiCOM.The application object’s settings once EventFilter is implemented, improving the application’s performance and meeting the user’s needs.
3. What does the SDK utilize when creating a form?
Ans:
The SAP Business One SDK develops forms using the screen painter. SAP offers screen painter as an add-on that may be used for form development and design. The screen painter produces files with the srf extension; to deploy them in SAP Business One, these files must be renamed to XML.
4. What is the tool that SAP offers for event tracking?
Ans:
- SAP provides an event tracking tool called SAP Business One Event Logger.
- It is best to run SAP Business One and event logger simultaneously. Using the event logger, you may see a comprehensive list of all the events that occurred using SAP.
- The event logger isa beneficial tool for SDK add-on development. The events displayed in the event logger can be coded by.
5. Can SDK change SAP Business One’s default behavior be used?
Ans:
SAP Business One’s default behavior and workflow cannot be changed with SDK. Errors will happen, and there will be some errors. Therefore, it is best to avoid using SDK to tamper with SAP Business One’s standard flow.
6. In the SAP Business One SDK, what does the et_FORM_DATA_ADD event mean?
Ans:
When the add button is hit, the et_FORM_DATA_ADD event is triggered. In SAP, this event creates a new record. The input that the user has provided can be verified using this event. There are two sessions to this event. An event occurs in the first session before the action’s success or the successful execution of the event.
The code appears as,
- code Injector = SAPbouiCOM.BoEventTypes.et_FORM_DATA_ADD
- ANDBusinessObjectInfo = BusinessObjectInfo.EventType.ActivitySuccess = Invalid
- SAPbouiCOM.BoEventTypes.et_FORM_DATA_ADD
- ANDBusinessObjectInfo.ActionSuccess = True
7. How is SAP Business One put into practice?
Ans:
Two layers of architecture are used to implement SAP Business One. Data is centrally kept in a Microsoft SQL Server database, the system’s foundation. Most of the business logic processing occurs on the client program (fat client).
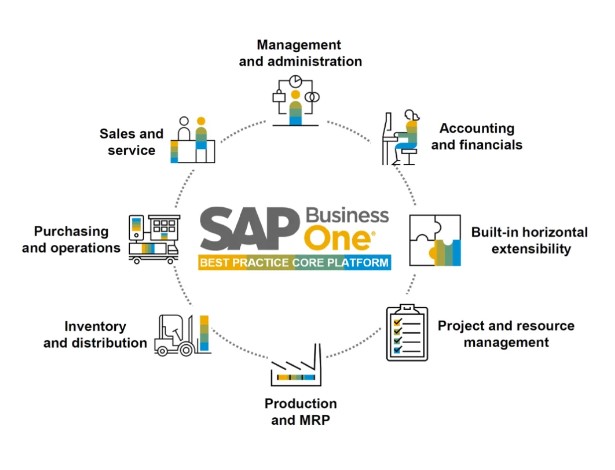
8. What are the various SAP Business One client software components?
Ans:
The various parts of SAP Business One client software are the graphical user interface and the business object classes communicating with the database.
9. In SAP Business One, what is a DI Server?
Ans:
Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP)-packed XML data is accepted by SAP Business One’s DI Server, a DCOM service that operates on the SAP Business One server.
10. What is the purpose of the User Interface API, or UI API?
Ans:
User Interface Application Program is referred to as UI API.SAP provides Interop.SAPbouiCOM.dll, which is the DLL. To access this DLL within a project, add its reference to the project. The controls shown on the form can be accessed via the UI API. The UI API’s functions are as follows:
- Offers items and ways to interact with the UI’s screen components.
- Provides access to the user interface’s internal system events.
- Provides the option to add or change windows, fields, or menus.
- Provides a single, unified user interface.
11. Which kinds of ERP are there?
Ans:
- SAP
- Baan JD Edwards, which Oracle has now purchased
- Oracle has now bought Siebel Peoplesoft
- Microsoft Dynamics
12. How does SAP Business One’s business object get used?
Ans:
Uses for company objects in SAP Business One include the following:
- Obtain information from a SAP Business One database.
- Establish and break connections with the customer database.
- Initiate and terminate international trade.
- Utilise XML information.
13. What kinds of data sources are there?
Ans:
The many categories of data sources are as follows:
1. Tables of Data
2. Sources of DB Data
3. Sources of User Data
14. What purposes does the Data Interface API (DI API) serve?
Ans:
- The DI API offers methods and objects, such as add, update, and remove, to perform different data-level actions. You don’t need to install the SAP Business One client.
- Business items, such as master data and transactional data, are accessible through DI API.
- Development tools that support COM, such as Microsoft Visual Studio, can use the DI API. Data level actions can be carried out simply by referencing the DLL SAPbobsCOM.dll, which SAP supplies.
15. What kinds of objects are there in the DI API?
Ans:
The various DI API objects are as follows:
1. Business Items
2. Items of Infrastructure
3. Particular Items
16. What kinds of transactions may I make using the DI API?
Ans:
The many transaction types that DI API supports are as follows:
- One-to-one Transaction
- One to many Transaction
- Many to many Transaction
- International Transaction
17. When do you create the document automatically in Sb 1?
Ans:
When you create the document, Businesses that import goods automatically determine the cost of purchasing the imported goods, including customs, insurance, transportation, and other expenses, thanks to the landed cost functionality. Landed cost is immediately reported when you create a document in SAP Business One 2007. The landed cost was initially provided as an estimate, which you are free to change at a later time.
18. How does it work with aggregates?
Ans:
The performance of our queries that read attributes frequently will be enhanced if we establish aggregates on Infocube. When we run the query, these are the steps we take:
- The query first searches the cache for pertinent data; if not, it fetches it.
- It enters the BiA Accelerator.
- Compilations
- If the data is unavailable in the first three phases, it finally enters IC.
19. Explain the BubbleEvent.
Ans:
The BubbleEvent property indicates whether SAP Business One will handle the event. SAP Business One will hold the event if BubbleEvent=True; otherwise,
the operation will end. For instance,
- If BoEventTypes.et_CLICK = pVal.EventType pVal.Action_Success = True as well.
- pVal.FormUID = “F_32”
- pVal.ItemUID = “btnSave”
- BubbleEvent=False
After that, End If the save button click event is handled in the code above.
20. Define DBDataSource?
Ans:
Data from the database is stored using DBDataSource.A database is connected to the DBDataSource table, displaying facts in tabular form. Every form in the system uses DBDataSource. DBDataSource is available as follows: I’m assuming that I’ve opened the sales order form and want to retrieve the sales order’s database details. ORDR is the table name. As SAPbouiCOM, Dim objDS.DBDataSource SBO_Application.Forms are obj.ActiveForm.Information Sources.Database Data Sources.Item (“ORDER”)
21. Compare SAP Business One and SAP Business ByDesign.
Ans:
| Feature | |||
| Target Market | Small to Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs) | Mid-market companies | |
| Deployment | On-premise or hosted | Cloud-based | |
| Customization | More flexibility | Standardized, scalable solution | |
| Implementation Speed | Quick implementation | Comprehensive, may take longer | |
| Modules and Functionality | Comprehensive business management solution | End-to-end ERP solution with integrated modules | |
| Integration Capabilities | Supports integration with other applications | Integrated suite with built-in functionalities | |
| Cost Structure | Generally more cost-effective for SMEs | Subscription-based pricing |
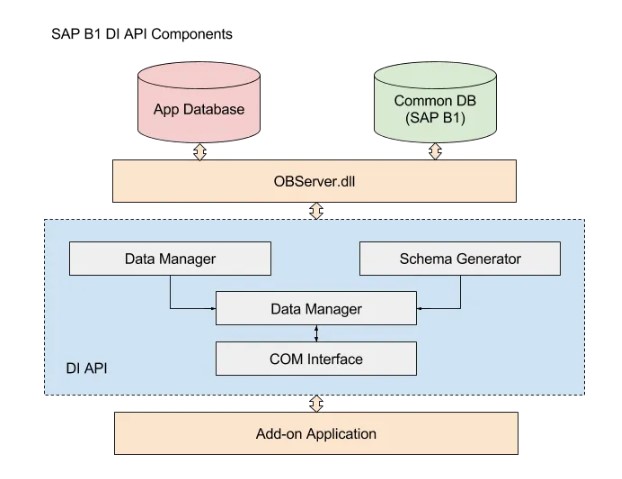
22. What components make up the DI API?
Ans:
Here are the many components of the DI API:
- COM Interface: The add-on application’s interface is provided by the COM Interface.
- DI Core: The DI Core, the primary part of the DI API, carries out all data logic operations.
- Data Manager: The Data Manager obtains data from the database, saves temporary object data, transforms object data into internal data formats, and manages database transactions.
- Schema Generator: This tool uses object interface descriptions to generate XML schemas. Moreover, object validation lists are produced by the schema generator.
23. What kinds of SAP products are there?
Ans:
SAP R/3 is the industry leader in ERP and replaces SAP R/2. Three-tier architecture, or Presentation, Logic, and Data tiers are called R/3. Its numerous modules cover practically all company divisions, including SD, FI, HR, and others. In addition to SAP R/3, the mySAP suite of SAP solutions includes SRM, PLM, CRM, and SCM.
24. What is NetWeaver?
Ans:
Because NetWeaver is an integrated technology platform, SAP Web Application Servers (SAP WEBAs)—the one NetWeaver instance on which all the products in the mySAP suite run—can operate simultaneously. Using NetWeaver has the benefit of enabling mobile and web (HTTP protocol) access to SAP data. As a result, you can reduce the price of user training for the SAP Client-side GUI.
25. What DI server or API is best for heavy-duty operations?
Ans:
DI servers work well for heavy-duty operations. The DI Server includes a connection pooling approach to boost the performance and scalability of the server. DI Server is a SOAP-based interface; it does not confine the client to a COM interface but offers a wide range of viable client technologies.
26. Why do you limit an InfoCube to 16 Dim tables and an ODS to 16 essential fields?
Ans:
The maximum number of fields that can be used to generate a primary key (composite key) in any database system is 16, when retrieving a single record from a cube, a mixture of all dimensions is utilized. This explains why there can only be a maximum of 16 dimensions in the cube.
27. What DLLs are included with the SAP Business One SDK?
Ans:
The two Dells used in the SAP Business One SDK are Interop.SAP bobs COM.dll and Interop.SAP bouiCOM.dll. To access the user controls shown over the form, utilize Interop.SAPbouiCOM.dll. Interop.SAPbouiCOM.dll can access various controls, like labels, combo boxes, matrices, etc. The Interop.SAPbobsCOM.dll file is to get SAP objects—for example, Dim objItem As SAPbobsCOM.Items are the way to access the item objects.
28. Explain SAP and ERP to me.
Ans:
The firm provides industry-leading ERP software, known as SAP BW, SAP ERP, and numerous additional SAP programs. Enterprise Resource Planning is referred to by the acronym ERP. ERP solutions give an organization a real-time picture of its essential business operations to monitor and effectively manage those operations.
29. Why is a cube containing only 16 Dimension tables? Is there a rationale? Is there anything limited?
Ans:
The answer is that the SAP BI InfoCube can have a maximum of 16 dimensions. This is because a standard database table can only have 16 key fields, and a cube form can only have 16. Tables like the F-table and E-table will be created when the InfoCube system is built. We should adhere to that database design as the InfoCube has only sixteen dimensions.
30. What justifies our decision to customize? Give me an example.
Ans:
For Company Requirements and Module Reporting, Eliminate Complexity for the End User and your procedure, including the standards, information, techniques, and instruments you employed to assess the possibilities.
31. In BI 7.0, where is the master data stored?
Ans:
In contrast to the previous iteration, BI 7.0 uses the extended star schema instead of BW, which uses star schema. Master data is kept outside of the cube in this case. Both transaction and master data are housed inside the cube in the star architecture, which presents several issues, including limited analysis, non-reusable master data, and difficulty computing alphanumeric values.
32. How does it benefit aggregates?
Ans:
If our query uses attribute data frequently, query performance will be enhanced if we generate aggregates on InfoCube. When we run the query, these are the steps we take:
- The query first goes into the cache.
- If pertinent data is found there, it will retrieve it.
- If not, it moves to the BI ACCELERATOR (BIA) Aggregates.
If the data is unavailable in the first three phases, it finally enters IC. There is no need to visit IC if we maintain aggregates or BIA OLAP.
33. What tool does the SDK utilize to create forms?
Ans:
The SAP Business One SDK uses Screen Painter to create forms. SAP offers the screen painter as an add-on and helps create and design forms. The screen painter produces files with the srf extension; to use them in SAP Business One, these files must be renamed to XML.
34. What is the tool that SAP offers for event tracking?
Ans:
SAP offers a product called SAP Business One Event Logger to track events. It is best to run SAP Business One and event logger simultaneously. Using the event logger, you may see a comprehensive list of all the events that occurred using SAP. A beneficial tool for creating SDK add-ons is the event logger. The events displayed in the event logger can be coded by. Since all of the programming in SAP Business One SDK is event-driven, an event logger is a helpful tool for creating solid apps.
35. Is using the SDK to change SAP Business One’s default behavior feasible?
Ans:
The SDK cannot change the SAP Business One standard behavior or conventional flow. Errors will happen, and there will be some errors. Therefore, it is best to avoid using SDK to tamper with SAP Business One’s standard flow.
36. What does the SAP Business One SDK’s et_FORM_DATA_ADD event mean?
Ans:
When the add button is hit, the et_FORM_DATA_ADD event is triggered. In SAP, a new record is added by this event. The input that the user has provided can be verified using this event. This occurrence burns through in two sessions. Before the event, I.e., ActionSuccess is successfully executed in the first session, an event triggers.
37. How is SAP Business One implemented?
Ans:
The two-layer design used to implement SAP Business One is the answer. Data is centrally kept in a Microsoft SQL Server database, the system’s foundation. Most of the business logic processing occurs on the client program.
38. What are the different components of SAP Business One client software?
Ans:
The various parts of SAP Business One client software are the graphical user interface and the business object classes that connect to the database.
39. Describe the distinction between update rules and transfer rules.
Ans:
Rules for transfers:
It maps the fields in the data source to the info objects in the Info source or target fields. It aids in identifying which fields in the data source are necessary for the information objects in the data source.
Modify the rules:
To bring things up to date. Here, the focus is on a source (the information source) and a target (the data target). The data targets are updated via update rules. You must build update rules if you feed a data target with a flexible update from an Info-Source.
40. What is the purpose of the User Interface API, or UI API?
Ans:
The acronym for User Interface Application Program is UI API.SAP provides Dll.SAPbouiCOM.dll Interop. To access this DLL, a reference to it has been added to the project. The controls shown on the form can be accessed via the UI API.
41. What does SAP Business One’s company object mean?
Ans:
The uses of company objects in SAP Business One are as follows:
- Obtain information from a SAP Business One database.
- Establish and break contact with the client database.
- Launch and terminate international transactions.
- XML-based data.
42. Which SAP BW transport faults are frequently encountered?
Ans:
Anytime we modify a cube’s structure with Business Warehouse Accelerator Indexes built for it. A simple modification, like adding a navigational attribute, could result from a change in structure. Solution: First delete the BWA indexes, then move the data, and finally recreate the indexes Info Object unavailable in an inactive state. Reason: When we attempt to transfer the info object catalogs without first transferring the info objects, we receive this problem. Solution: Move the info objects and then the info object catalogs as a necessary step first.
43. What kinds of data sources are there?
Ans:
Tables of Data DB Q21:
- Data Sources – User DataSources
- Databases.
- Flat files.
- Internet-based services.
- Other sources such as RSS feeds.
44. What uses does the Data Interface API (DI API) fulfill?
Ans:
The functions of the Data Interface API (DI API) are as follows:
- The DI API offers methods and objects to perform different data-level actions, such as add, update, and remove.
- Access to business objects, such as master data and international data, is made possible by DI API.
- Development tools that support the COM interface, like Microsoft Visual Studio, can use the DI API. SAP provides Dll SAPbobsCOM.dll. Data-level actions can be carried out simply by referencing this dll.
45. What is an API for transactions?
Ans:
The many transaction types that DI API supports are listed below. This DI API Transaction allows programs to perform distributed transactions, that is, the transactions that access and update data on two or more networked computer resources.
46. What is a Bubble Event in a Single Transaction?
Ans:
The Bubble Event indicates whether SAP Business One will handle the event.SAP Business One will hold the event if Bubble Event=True; otherwise, the execution will end.
For instance,
- If pVal.InputType = “btnSave” and pVal.Action_Success = True, and
- pVal.FormUID = “F_32” and pVal.ItemUID = “btnSave,” then
- If BubbleEvent: False
47. What is DBDataSource?
Ans:
The answer is that data from the database is stored using DBDataSource. Tabular data is represented by DBDataSource, which is connected to a database table. Every Form in the system uses DBDataSource. DBDataSource is available as follows:
As SAPbouiCOM, Dim objDS.DBDataSource SBO Application.Forms.ActiveForm is obj. Information Sources.”ORDER” in DBDataSources.Item
48. How can I attach a data source to a textbox?
Ans:
In SAP Business One, you can attach a data source to a textbox by accessing the UI Configuration settings for the form, selecting the desired textbox, and specifying the data source through properties or settings related to data binding. This is typically done using the SAP Business One SDK or the built-in customization features available in the user interface.
49. What are the DI server’s limitations?
Ans:
The DI server’s constraints are as follows:
- Metadata operations are not supported.
- It’s no different from basic DI API with transaction handling support
50. What is OBServerDLL.DLL used for?
Ans:
SkyMap Software produced the DLL file observer.dll. The method is currently being examined. Observer.dll and other non-system processes result from installed software on your computer. Most apps store data in the registry and on your hard drive, so your computer may have amassed invalid entries and experienced fragmentation, which might impair your machine’s efficiency.
51. What components make up the DI API?
Ans:
Below are the many components of the DI API.
COM Interface:
The add-on application’s interface is provided by the COM Interface.
DI Core:
All data logic operations are carried out by the DI Core, which is the primary part of the DI API.
Data Manager:
The Data Manager obtains data from the database, saves transient object data, transforms object data into internal data formats, and manages database transactions.
Schema Generator:
The Schema Generator uses object interface specifications to generate XML schemas. Moreover, object validation lists are produced by the schema generator.
52. When will Business One be made available for purchase?
Ans:
In 2002, a business named Top Manage Financial System developed Business One, which SAP was able to purchase.
53. What kinds of businesses make Use of SAP Business One?
Ans:
To manage MSME (Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises) kind of firms, Business One is an ERP software.
54. What are end users in SAP Business One, and how are they managed?
Ans:
End users are a subset of users with assigned tasks within a specific functional module. They can be managed within the human resource module, and their roles can be set within the administration module under authorizations.
55. What kind of partners are you looking for, and how do you find them?
Ans:
In SAP B1, there are three different kinds of business partners.
- Suppliers Clients Leads
- All of them are created in the business partner module’s business partner master data.
56. What does a “blanket agreement” mean?
Ans:
An arrangement your company enters with a vendor to pre-plan the acquisition of goods or services is known as a blanket contract. These contracts usually have several delivery dates spread across time and are frequently structured to benefit from fixed prices.
57. How is payment made?
Ans:
The four payment methods are bank transfer, check, cash, and credit card. Payment means is used to process both incoming and outgoing payments.
58. What are the various forms of master data in B1, and what is master data?
Ans:
The data records kept in the system for an extended time are known as master data. In Business One, the master data are
- Master data for employees
- Master data for business partners
- Master data for items
- Master data for resources
59. What is the purpose of the internal bank?
Ans:
The top five advantages of an internal bank (IHB), Like commercial banks, in-house banks offer numerous subsidiaries of big international organizations payment processing, liquidity management, and collection services. One major factor supporting in-house banking (IHB) is technology.
60. How can I make several payments at once?
Ans:
The feature that allows you to make many payments at once is called the Automatic Payment Program (APP). Under banking setups, we can specify requirements for APP in payment methods.
61. Which 25 SAP modules are there?
Ans:
- Modules of SAP ERP that are functional:
- Management of Human Capital (SAP HCM)
- Planning for Production (SAP PP)
- Material Administration (SAP MM)
- SAP FSCM stands for Financial Supply Chain Management.
- Distribution and Sales (SAP SD)
- SAP PS (Project System)
62. What is the purpose of Material Requirement Planning (MRP)?
Ans:
To forecast future material demand and help schedule the manufacturing and procurement processes appropriately, MRP is employed in SAP B1. Three goals are intended to be met simultaneously by an MRP system:
- Guarantee that products and materials are available for production and delivery to customers.
- Maintain the lowest possible level of inventory.
- Plan purchasing, delivery, and manufacturing activities.
63. Why do we keep the Financial Module’s Recurring Postings up to date?
Ans:
We can easily publish frequent journal entry transactions by using recurring postings. We can keep templates for these types of transactions and execute them as needed.
64. How can I access the company’s balance sheet in SAP B1?
Ans:
- Financial
- Balance sheet
- Financial Reports
65. Which function can transfer Stock/Inventory from one warehouse to another?
Ans:
The transportation of actual inventory items from one warehouse site to another is referred to as an inventory transfer, stock transfer, or warehouse transfer. In the following situations, shops must transfer inventory: Increase inventory availability when you offer products through various channels and retailers.
66. What is the purpose of the approval procedure?
Ans:
An end user may utilize the approval procedure to obtain authorization from the employer when an end user needs permission from his consultant to do an action to which he lacks access.
67. What is the Use of form settings?
Ans:
We can update the fields to input or show data in any document that is available in SAP Business One. You can turn some form-level and application-wide features on and off using the Form features tab on the Form Profile form. For instance, you can modify the Form’s default Rows display per page. Additionally, you can allow hours to be entered directly onto the timecard.
68. How can we use SAP Business One to verify the stock?
Ans:
There are two methods available to check inventory in SAP B1. “Inventory item data” typically refers to information on a specific inventory item or category of inventory item. In contrast, “item master data” refers to the information included in one or more item masters. Item master data’s locate mode.
- Select Inventory
- Reports on Inventory
69. Why is pick and pack used in inventory status?
Ans:
To automate the process, they are:
- Sales orders
- Inventory transfer requests
- Production orders
- Pick and pack.
70. What does the term “landed cost” mean?
Ans:
The function is utilized to include extra costs
- Carriage
- Customs
- Transportation
71. Which three aspects does SAP offer?
Ans:
Given that SAP InfoCube has three distinct dimensions Those are.
Data Packet Dimension:
This will contain technical data, such as the request number.
One internal reconciliation process:
Reconciliations under Business Partners > Internal Reconciliations.
72. What steps are involved in implementing SAP Business One?
Ans:
An architecture with two layers is commonly used to execute SAP Business One. The system’s main component is a Microsoft SQL Server database on which all the data is kept in one location. The client program (fat client) typically processes the business logic.
73. Which parts make up the SAP Business One client software?
Ans:
The two main parts of the SAP Business One client software are the graphical user interface and the business object classes that connect to the database.
74. What does SAP Business One’s company object mean?
Ans:
The company object represents the SAP Business One database. It is used to establish a connection to a Microsoft SQL Server database. The object clause defines the permissible business operations of a firm. It limits the company’s operating parameters and prohibits it from participating in unspecified activities.
75. What is the function of the company object in SAP Business One?
Ans:
The different applications The following is a list of the different ways that SAP Business One uses the business object:
- Obtain information from a SAP Business One database.
- Establish and break a connection to the customer database.
- Launch and terminate international transactions.
- Utilise XML-based data.
76. How does SAP Business One define DI Server?
Ans:
The DI Server in SAP Business One is a DCOM service that runs on the SAP Business One server and can receive XML data compressed into SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol) packets.
77. Can the SDK change SAP Business One’s default behavior?
Ans:
With SDK, altering SAP Business One’s default behavior or flow is impossible. Errors will occur in any case. As a result, users are advised to refrain from interfering with SAP’s standard workflow using SDK for Business One.
78. Which DI server or API is best for demanding operations?
Ans:
A DI server is appropriate for carrying out demanding operations. The DI Server uses a connection pooling approach to improve server performance and scalability. DI Server is a SOAP-based interface; it does not confine the client to a COM interface but offers a wide range of viable client technologies.
79. Describe A/R Invoice.
Ans:
Account Receivable Invoice is the acronym for A/R Invoice. The following invoices are added to SAP Business One for product sales. Sales Order Delivery; Sales Quotation and A/R BillConsequently, the sales department’s final step is the A/R Invoice. The corresponding accounting entries are added when the A/R Invoice is added. The document from the A/R Invoice is delivered as a bill with the merchandise.
80. Describe A/P Invoice.
Ans:
Account Payable Invoice is the abbreviation for A/P Invoice. The following invoices have been added to SAP Business One to purchase the products.
- Purchase Order
- Goods Receipt
- Purchase Quotation
A/P Invoice For the purchasing department, the A/P Invoice is the final step in the process. The accounting impact is evident when A/P Invoice is included.
81. What is the customer relationship management module?
Ans:
Customer relationship management, including complaint and satisfaction handling, is the main focus of the customer relationship management module.
82. How can SAP Business One be with machine learning?
Ans:
Machine learning can be used with SAP Business One to make product recommendations based on user behavior and previous purchases.
Predictive Analytics: SAP Business One HANA uses machine learning algorithms to analyze historical data to find patterns, trends, and correlations. This makes it possible for the system to accurately forecast future occurrences, including client demand, sales trends, and inventory levels.
83. How may SAP Business One be utilized with IoT?
Ans:
IoT can gather unprocessed data and analyze statistics, problem areas, and novel vaccines. Integrating IoT technology to monitor consumer behavior and facilitate better decision-making can enhance Alexa and other SAP business solutions.
84. What does SAP Business One aim to achieve?
Ans:
Machine-related data can be integrated into production processes without requiring manual entry using SAP Business One, an open and adaptable software. The item is intended to be a basic accounting system readily linked to production operations.
85. What does SAP Business One’s resources module entail?
Ans:
SAP Business One’s resources module maintains enterprise resources, such as labor, vehicles, equipment, and fixed assets. Most businesses’ departments, including operations, finance, human resources, sales and marketing, and quality control, employ these SAP modules. These modules help to streamline all activities by lowering the amount of human labor required.
86. What is SAP Business One’s production module?
Ans:
SAP Business One’s production module manages the manufacturing process, integrating labor, materials, and resources like OAS. The material needs plan manages the procurement and preservation of the required components and establishes production orders.
87. What is SAP Business One’s service module?
Ans:
SAP Business One’s service module manages client maintenance, warranties, and post-purchase support. A single, affordable ERP solution to handle your complete small business – from accounting and financials, purchasing, inventory, sales, and customer interactions to reporting and analytics.
88. What is SAP Business One’s human resources module?
Ans:
SAP Business One’s human resource module manages all human resources, including salespeople, area managers, and representatives. SAP human capital management (HCM) solutions provide strategic, innovative solutions for core HR and payroll, time and attendance, talent management, employee experience management, and people analytics to address your critical workforce transformation needs.
89. What is SAP Business One’s project management module?
Ans:
The robust project management feature of SAP Business One makes it possible for the construction sector to maintain long-standing projects. SAP Business One Project Management combines planning, data entry, release, invoicing, and financial analysis into a consistent user interface. Users of authorized SAP Business One project management have complete access to all data and can make decisions based on their needs.
90. What does SAP Business One’s dashboard look like?
Ans:
- The general manager or financial manager can access the dashboard in SAP Business One, which is in the center of the screen.
- Using this dashboard, users can obtain pertinent data, like gross profit, net profit, and balance payables.
- Additionally, users can alter dashboards to show more pertinent information like profitability, graphs, sales, band balances, top five customers, and working capital.
91. How does SAP Business One’s dashboard customization process work?
Ans:
SAP Business One has three tabs for dashboard customization: myKPI, my dashboard, and my advanced dashboard. Customizing a dashboard is an easy process. Users can alter the graph design, add clients, and update their dashboard. For convenient access, they can also store these charts in their cockpit.
92. What is SAP Business One’s customer 360 analysis feature?
Ans:
SAP Business One’s customer 360 analytics capability thoroughly views all client data, including unfulfilled orders and sales. A picture of the clients from every angle. Information is produced in place of just a number through the system’s evaluation and analysis of pertinent data.
93. What is SAP Business One’s business partner module?
Ans:
Users of SAP Business One can manage leads, vendors, and customers through the business partner module. By establishing new vendors and beginning trade, transactions can be started. The Business Partners module conducts and oversees internal reconciliations for business partners and manages all the data pertinent to your interactions with leads (interested parties), vendors, and consumers.
94. What does SAP Business One’s inventory module entail?
Ans:
With the inventory module, users of SAP Business One can keep track of inventory codes, descriptions, item types, groupings, and various units of measurement. It maintains track of product inventory, quantity at each warehouse, item movement history, and stock status, in addition to providing trustworthy information about shipments both inbound and outbound.
95. What is SAP Business One’s warehouse management system?
Ans:
With SAP Business One’s warehouse management solution, users can track lead times and reorder levels while storing things in numerous locations.
96. Which are SAP’s two primary modules?
Ans:
There are two primary categories of SAP modules: functional and technical. Business functions, including order processing, business information, and human resources, are accessed through available modules. SAP’s back end uses specialized modules to manage your environment, development, and updates.
97. Which SAP Business One valuation techniques are available?
Ans:
- Standard costing
- Stock valuation techniques
- Moving averages
98. What does item master data mean?
Ans:
Only when an item has no open documents and zero total amount may it be converted from an inventory item to a non-inventory item and vice versa. Particularly when it comes to item master data, SAP Business One has been restricted or constrained. This is to ensure that inventory and non-inventory item management is under control.






