
We’ve put together a helpful collection of SIEBEL Business Analyst Interview Questions and Answers to assist you in getting ready for potential questions during your interview. As the demand for skilled SIEBEL business analysts continues to grow, there are plenty of opportunities available at well-known companies globally. Research indicates that SIEBEL Business Analyst holds a market share of approximately 3.25%, highlighting the importance of this role in the business analysis field. With these interview questions, you can enhance your preparation and seize the chance to advance your career in SIEBEL Business Analysis. Whether you are an experienced professional or just starting, ACTE offers straightforward SIEBEL Business Analyst Interview Questions to guide you in succeeding in your interview and achieving your goals as a SIEBEL Business Analyst Developer.
1. What is Siebel and its primary purpose?
Ans:
Oracle developed the Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software program known as Siebel. Its primary purpose is to help organizations manage and enhance customer relationships by providing tools for sales, marketing, and customer service.
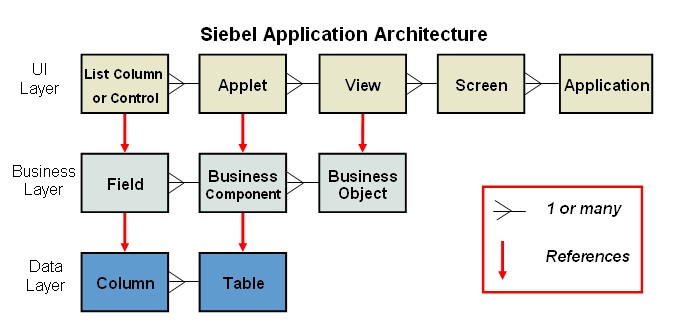
2. Explain the concept of a flowchart and its significance.
Ans:
A flowchart is a visual representation of a process, illustrating the steps and decision points involved. It helps in understanding, analyzing, and improving processes by providing a clear and structured overview of the workflow. Flowcharts are significant for process documentation, analysis, and communication.
3. Define the link specification.
Ans:
- The link specification in Siebel refers to the rules defined for associating records between different business components.
- It outlines the conditions under which records from one business component are linked to records in another, facilitating data relationships and integrity in the application.
4. How do inbound and outbound differ in a picklist?
Ans:
In a Picklist, “inbound” refers to the process of bringing data into the system, while “outbound” pertains to the process of sending data out of the system. In the context of a picklist, inbound may involve importing data from external sources, while outbound may involve exporting data to external systems.
5. Expand UML.
Ans:
UML stands for Unified Modeling Language. It is an industry-standard modeling language used in software engineering to graphically depict the architecture of a system. UML includes various diagram types to depict different aspects of a system, such as class diagrams, use case diagrams, and sequence diagrams.
6. Name two heavily used diagrams in your field.
Ans:
In the field of business analysis, two heavily used diagrams are the Use Case Diagram, illustrating system functionality from a user’s perspective, and the Activity Diagram, depicting the flow of activities within a business process.
7. As a business analyst, which tools are most helpful?
Ans:
Business analysts often find tools like Microsoft Visio, Lucidchart, and draw.io helpful for creating diagrams. Additionally, tools like Jira, Confluence, and Microsoft Excel aid in requirements management, collaboration, and data analysis.
8. List documents prepared by a Business Analyst.
Ans:
Business analysts prepare various documents, including,
- Business Requirements Documents (BRD)
- Functional Requirements Documents (FRD)
- Use Case Documents
- User Stories
- Process Flow Diagrams
- Test Plans
9. What is the maximum number of applets possible in a view?
Ans:
In Siebel, the maximum number of applets possible in a view is 64. This limitation is important to consider when designing and configuring views to ensure optimal performance.
10. Explain the process of data cleansing in EIM.
Ans:
In EIM (Enterprise Integration Manager), data cleansing involves transforming and standardizing data to improve its quality. The process includes identifying and correcting errors, removing duplicates, and ensuring data consistency before integrating it into the Siebel database. Techniques such as validation rules and transformation scripts are used in EIM for data cleansing.
11. Define Siebel Admin Mode View and discuss its creation.
Ans:
In Siebel, an Admin Mode View is a specialized view used by administrators to configure the Siebel application. It allows direct access to configuration elements for customization. To create an Admin Mode View, a Siebel administrator can use Siebel Tools to design the view layout, determine applets and controls, and configure properties tailored explicitly for administrative tasks.
12. Compare the MVG applet and a Pick Applet.
Ans:
MVG (Multi-Value Group) applet and Pick Applet in Siebel serve different purposes. MVG applets are used for displaying and managing related records in a list format, allowing users to select multiple values. Pick Applets, on the other hand, are used to present a list of values for a specific field, allowing users to choose a single value. MVG applets handle one-to-many relationships, while Pick Applets facilitate selection from predefined values.
13. Outline the steps needed to develop a product from an idea.
Ans:
The steps to develop a product from an idea include:
- Idea Generation
- Market Research
- Concept Development and Testing
- Business Analysis
- Product Development
- Market Testing
- Commercialization
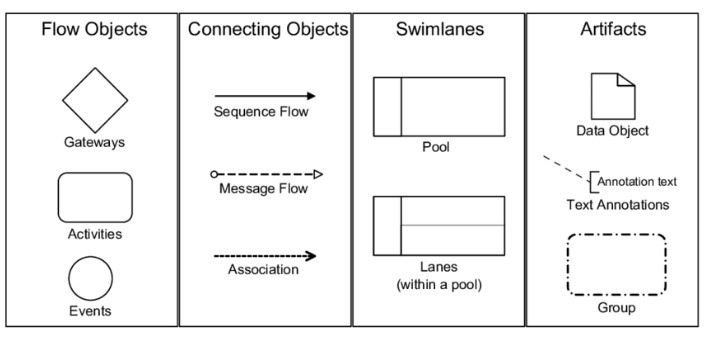
14. What does BPMN stand for?
Ans:
BPMN is nothing but a Business Process Model and Notation. It is a standardized graphical notation for representing business processes in a visual manner, facilitating clear communication and understanding of business processes across different stakeholders.
15. Name the five essential elements’ categories in BPMN.
Ans:
- Flow Objects
- Connecting Objects
- Swimlanes
- Artifacts
- Data
16. Define KANO analysis and share your experience with it.
Ans:
KANO analysis is a technique used to prioritize and understand customer needs and preferences. It categorizes features into five types: Basic Needs, Performance Needs, Excitement Needs, Indifferent Needs, and Reverse Needs. My experience with KANO analysis involves applying it to product development, ensuring a balanced focus on meeting essential requirements, and delighting customers with innovative features.
17. Identify the three key areas in a Kano Analysis.
Ans:
The three key areas in a Kano Analysis are:
- Basic Needs (Must-haves)
- Performance Needs (Linear correlation with satisfaction)
- Excitement Needs (Unexpected delights)
18. Compare the Fish Model and the V Model.
Ans:
The V Model is a software development model that shows the relationship between each phase of the development life cycle and its corresponding testing phase. At the same time, the Fish approach is a project management approach that emphasizes flexibility and iteration. The Fish Model is more iterative, allowing for feedback and adjustments throughout the project, whereas the V Model follows a sequential and linear approach.
19. Can you specify the complete form of PEST?
Ans:
PEST expands for Political, Economic, Social, and Technological factors. PEST analysis is a strategic management tool used to assess and evaluate external macro-environmental factors that can impact an organization.
20. What does Symbolic URL mean in Siebel?
Ans:
In Siebel, a Symbolic URL is a hyperlink that dynamically references data values from Siebel fields to construct URLs. It allows users to navigate to external web pages or launch external applications with specific parameters based on the data in Siebel fields. Symbolic URLs enhance integration and provide contextual links within the Siebel application.
21. How can an external webpage be accessed from a Siebel application?
Ans:
External web pages can be accessed from a Siebel application by defining a Symbolic URL. This involves configuring a hyperlink in Siebel Tools that dynamically constructs URLs based on Siebel data. Users can then click on the hyperlink to open the external webpage with parameters derived from Siebel fields.
22. Define a detailed category in configuration and its purpose.
Ans:
In Siebel configuration, a detailed category is a classification for items such as views, applets, and fields. It helps organize configuration elements for easier management. The purpose of a detailed category is to group related items together, simplifying navigation and ensuring a logical structure within Siebel Tools.
23. What tasks can Siebel perform in terms of functionalities?
Ans:
Siebel can perform a range of functionalities, including:
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
- Sales Force Automation
- Marketing Automation
- Service and Support
- Order Management
- Workflow Automation
- Analytics and Reporting
24. Distinguish between join specification and join definition.
Ans:
| Criteria | |||
| Definition | Specifies the conditions for joining tables during a query. | Defines the relationships between tables in the Siebel database. | |
| Implementation | Utilizes SQL expressions to set conditions for joining tables. | Implemented through relationships defined in the repository. | |
| Flexibility | Provides more flexibility in specifying join conditions. | Offers less flexibility, as it’s configured within Siebel Tools. | |
| Configuration Tool | Not configured directly but expressed in SQL within queries. | Configured using the Siebel Tools application. | |
| Dynamicity | More dynamic, allowing for dynamic modification based on queries. | Static, as it’s set in the Siebel repository during design. | |
| Example | SQL Query: SELECT * FROM Table1 INNER JOIN Table2 ON Condition | Siebel Tools: Configure a relationship between Business Components. |
25. Share the methods for validations in escripts and configuration.
Ans:
Validations in Siebel can be achieved through:
eScripts:
Custom scripts using Siebel eScript language.
Configuration:
Configuring Siebel Validation rules in Siebel Tools to enforce data integrity and business rules.
26. How do you execute Genbscript.exe?
Ans:
Genbscript.exe is executed in the command line or through a script to generate business service scripts in Siebel. The syntax is:
genbscript /c <Connection String> /u <Username> /p <Password> /d <Database> /g <Business Service Name>
27. Identify the out-of-the-box (OOTB) functionality in Siebel.
Ans:
Out-of-the-box (OOTB) functionality in Siebel includes standard features and processes that come pre-built with the application. Examples include lead management, account management, opportunity management, and predefined reports.
28. Elaborate on the creation of an Event Handler.
Ans:
An Event Handler in Siebel is created using Siebel Tools. It involves defining an event, specifying conditions that trigger the event, and associating a script or workflow to be executed when the event occurs. Event Handlers are used to respond to specific events within the Siebel application.
29. Discuss the Audit Trail feature in Siebel.
Ans:
The Audit Trail feature in Siebel enables tracking changes made to data, providing a historical record of modifications. Configuration settings define which fields are audited. The Audit Trail captures details such as who made the change, when it occurred, and the previous and new values of the modified data.
30. Provide a brief overview of siebmtsh.exe.
Ans:
Siebmtsh.exe is a command-line utility used for Siebel Mobile Web Client deployment. It assists in creating and maintaining Siebel Remote databases for mobile applications. The utility helps synchronize data between the Siebel Server and remote clients, facilitating offline usage and data consistency.
31. Explore the concepts of Caching and Purging in Siebel.
Ans:
In Siebel, caching involves storing frequently accessed data temporarily to improve application performance. It reduces the need to retrieve the same data repeatedly from the database. Purging, on the other hand, is the process of removing outdated or unnecessary cached data to ensure the system operates with the latest and most accurate information. These concepts play a crucial role in optimizing Siebel application performance and maintaining data integrity.
32. What is the procedure for configuring Siebel 8 Web Virtual Server?
Ans:
Configuring Siebel 8 Web Virtual Server involves several steps:
- Install the Siebel software and configure the Siebel Gateway Name Server.
- Create a new Siebel Enterprise and configure the Siebel Server.
- Configure the Siebel Web Server Extension (SWSE) for the desired web server.
- Set up the Siebel Web Virtual Server parameters, including parameters for authentication, caching, and session management.
- Configure Siebel Server components and tasks.
- Test the configuration to ensure proper functionality.
33. How is session persistence applied in Siebel?
Ans:
Session persistence in Siebel ensures that user sessions are maintained and do not get lost during interactions with the application. This is achieved through mechanisms such as session cookies, URL rewriting, or IP affinity. The Siebel application server maintains session information, allowing users to seamlessly navigate between different views and perform transactions without losing their session context.
34. Outline the steps for creating a dynamic drill-down.
Ans:
- Identifying the source applet where the drill-down will be initiated.
- Configure the Drilldown Object Type field in the applet to specify the type of drill-down.
- Defining the drill-down applet and associating it with the desired business component.
- Configuring the Drilldown Object field to dynamically set the destination applet based on runtime conditions.
- Testing the dynamic drill-down to ensure it functions as intended.
35. What are the distinctions between Static and Dynamic Drilldowns?
Ans:
Static Drilldowns: Predefined drill-downs that are configured during design time and remain constant. They navigate to a fixed destination applet when clicked.
Dynamic Drilldowns: Configured to determine the destination applet dynamically based on runtime conditions. The target applet may change based on user actions or data values, providing flexibility in the navigation flow.
36. Explain the significance of Business Components in Siebel.
Ans:
Business Components in Siebel represent entities in the underlying database and define the structure of data used in the application. They play a pivotal role in data manipulation, providing a logical abstraction for interacting with database tables. Business Components define fields, joins, and other properties that govern how data is retrieved, displayed, and manipulated in Siebel applications.
37. How are Pick Lists used in Siebel?
Ans:
Pick Lists in Siebel are used to provide predefined values for a specific field. They streamline data entry, ensuring consistency and accuracy by limiting users to selecting values from a predefined list. Pick Lists are configured in Siebel Tools and associated with fields in business components, influencing data entry and promoting standardized data across the application.
38. Define Multi-Value Groups (MVGs) in Siebel.
Ans:
Multi-Value Groups (MVGs) in Siebel allow users to associate multiple records from a related business component with a single record in the primary business component. MVGs are typically represented as lists or applets within the primary applet, enabling users to view, select, and manage related records in a convenient manner. They enhance the flexibility and usability of Siebel applications.
39. What is the purpose of a Business Object in Siebel?
Ans:
In Siebel, a Business Object serves as a logical representation of a business entity, encapsulating data and business rules. It defines the structure and behavior of data within the Siebel application. Business Objects are associated with business components and enable the definition of relationships, methods, and other properties that govern data interaction and manipulation in the system.
40. Explain the concept of drilldowns in Siebel.
Ans:
Drilldowns in Siebel refer to the navigation from one view or applet to another for detailed information. They provide a way to explore related data or perform specific actions by clicking on a hyperlink or a control configured to trigger the drill-down. Drilldowns enhance the user experience by offering seamless access to additional details and functionality within the Siebel application.
41. How does Siebel support workflow automation?
Ans:
Siebel supports workflow automation through its Workflow Process Designer. Users can design and deploy workflows to automate business processes. Workflows in Siebel define the flow of tasks, activities, and decisions, streamlining and optimizing business processes such as sales, marketing, and customer service.
42. Define repository in the context of Siebel.
Ans:
In Siebel, a Repository refers to the set of definitions and metadata that define the configuration of a Siebel implementation. It includes information about applets, views, business components, fields, and other objects. The Repository is stored in the Siebel database and is used by the Siebel Server to render the application for end-users.
43. What is the role of Integration Objects in Siebel?
Ans:
Integration Objects in Siebel facilitate the integration of Siebel applications with external systems. They define the structure of data to be exchanged between Siebel and other applications, ensuring seamless data flow. Integration Objects specify the format, transformation rules, and behavior of data during integration processes.
44. Explain the concept of User Interface (UI) in Siebel.
Ans:
- Visual elements and controls for user interaction.
- Includes views, applets, screens, and controls.
- Configured using Siebel Tools for an intuitive user experience.
45. What is the significance of the Siebel Data Model?
Ans:
The Siebel Data Model is a foundational component that defines the structure and relationships of data within the Siebel application. It includes entities such as tables, columns, relationships, and indexes. The Data Model is crucial for data retrieval, storage, and manipulation, ensuring data consistency and integrity across the Siebel system.
46. How does Siebel handle data validation?
Ans:
Siebel handles data validation through various mechanisms such as configuration, scripting, and workflow policies. Validation rules can be configured in Siebel Tools to enforce data integrity by defining conditions and criteria that must be met before data is accepted or processed. Additionally, scripting languages like eScript or JavaScript can be employed for custom data validation logic.
47. Describe the role of Workflow Policies in Siebel.
Ans:
Workflow Policies in Siebel automate business processes by defining conditions and triggering actions based on specified criteria. They are used to monitor changes in data and initiate predefined workflows when specified events occur. Workflow Policies enhance efficiency by automating routine tasks and ensuring timely responses to critical events.
48. What are the key features of Siebel Assignment Manager?
Ans:
Siebel Assignment Manager automates the assignment of business entities (such as leads, opportunities, or service requests) to users or teams based on predefined criteria. Key features include dynamic assignment rules, workload distribution, skills-based routing, and the ability to prioritize and balance workload among users or teams.
49. Explain the purpose of Business Services in Siebel.
Ans:
Business Services in Siebel provide reusable, modular components that encapsulate business logic and functionality. They offer a set of methods that can be invoked from various components within the Siebel application, promoting code reuse and maintaining consistency. Business Services enhance the extensibility and flexibility of Siebel applications.
50. How is Siebel involved in mobile application development?
Ans:
Siebel supports mobile application development through its Siebel Mobile Web Client. This allows users to access Siebel applications on mobile devices, providing a responsive and tailored user experience. Siebel Mobile applications support offline capabilities, allowing users to work in disconnected environments and synchronize data when a connection is reestablished.
51. What is the role of Siebel Remote in distributed environments?
Ans:
Siebel Remote is a component in Siebel that enables the distribution and synchronization of data between the central Siebel Server and remote clients in a disconnected mode. It allows users to work offline and later synchronize their changes with the central server, supporting scenarios where continuous network connectivity is not guaranteed.
52. Describe Siebel Workflow Monitor and its functionalities.
Ans:
Siebel Workflow Monitor is a tool that provides visibility into the execution and status of workflows in the Siebel application. It allows administrators to monitor workflow processes, view running instances, analyze performance, and troubleshoot any issues. Workflow Monitor facilitates efficient management and optimization of workflow processes.
53. How does Siebel handle security and access control?
Ans:
Siebel employs a comprehensive security model to control access to data and functionality. It includes user authentication, authorization profiles, and role-based access control. Siebel Security ensures that users can only access the data and perform actions relevant to their roles and responsibilities, maintaining data integrity and confidentiality.
54. What is the purpose of Siebel Tools in the development process?
Ans:
Siebel Tools serves as the integrated development environment for customizing, configuring, and extending the functionality of the Siebel CRM application. Administrators to design, modify, and deploy various components, including applets, views, business components, workflows, and more. Siebel Tools plays a crucial role in the entire software development lifecycle of Siebel applications, enabling users to tailor the CRM system to meet specific business needs, industry requirements, and user preferences.
55. How are workflow policies and workflow processes related in Siebel?
Ans:
- Workflow policies and workflow processes are closely related in Siebel, forming integral parts of the automation framework.
- Workflow policies define conditions that trigger the execution of specific workflow processes.
- The relationship is established through associating workflow processes with corresponding workflow policies.
- Workflow processes, consisting of predefined steps and actions, get executed automatically based on the specified conditions outlined in the associated workflow policies.
- This relationship ensures that business processes are automated in response to relevant events or criteria.
56. How does Siebel handle user authentication and authorization?
Ans:
Siebel employs a robust system for user authentication and authorization to ensure secure and controlled access to the CRM application. User authentication is achieved through various methods such as Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP), database authentication, or Single Sign-On (SSO). Once authenticated, Siebel utilizes a role-based authorization model. Users are assigned specific roles, and access to functionalities is granted or restricted based on these roles. User profiles and responsibilities in Siebel dictate the level of access and permissions for each user.
57. Explain the use of Views and Applets in Siebel User Interface.
Ans:
Views and applets are foundational elements in the Siebel User Interface, contributing to the overall user experience. Views define the structure and layout of screens, determining how applets are arranged and displayed to users. Applets, in turn, represent individual sections within views and are responsible for displaying and interacting with data. By configuring views and applets, Siebel allows users to navigate seamlessly through the application, interact with data, and perform various tasks in an organized and user-friendly manner.
58. How does Siebel handle data deduplication and cleansing?
Ans:
- Siebel provides robust tools and processes for managing data quality, including deduplication and cleansing.
- Data deduplication involves identifying and managing duplicate records in the system, preventing data redundancy.
- Data cleansing ensures data accuracy and consistency by validating and standardizing information.
- Siebel achieves these through features like duplicate record identification, merging capabilities, validation rules, and integration with external data quality tools.
59. Describe the role of Siebel eScript in customization.
Ans:
Siebel eScript serves as a powerful scripting language within the Siebel CRM platform, providing developers with the ability to customize and extend the application’s functionality. It is used for creating both client-side and server-side scripts, enabling the implementation of custom business logic, automation of processes, and enhancement of Siebel applications. With Siebel eScript, developers can respond to specific events, validate data, and implement complex business rules to tailor the CRM system according to the unique requirements of the organisation.
60. How is Siebel involved in customer relationship management (CRM)?
Ans:
Siebel is a leading solution in the field of Customer Relationship Management (CRM). It provides a complete suite of tools and functionalities designed to manage and optimise interactions with customers throughout the entire customer lifecycle. Siebel CRM encompasses modules for sales automation, marketing automation, service and support, order management, and analytics.
61. Explain the significance of Siebel Product Configurator.
Ans:
The Siebel Product Configurator is a crucial module within Siebel CRM that empowers organisations to configure complex products and services based on customer requirements. The Product Configurator ensures accurate configuration, pricing, and quoting, allowing businesses to meet the specific needs of customers while maintaining efficiency in order management and fulfilment.
62. How does Siebel handle error handling and logging?
Ans:
- Siebel incorporates robust error handling and logging mechanisms to ensure the reliability and stability of the CRM application.
- When errors occur, Siebel logs relevant information such as error messages, timestamps, and user details.
- Error handling in Siebel may involve presenting user-friendly messages, redirecting workflows, or triggering custom scripts to gracefully manage exceptions and maintain a positive user experience.
63. Describe the role of Siebel Analytics in reporting and analysis.
Ans:
Siebel Analytics, now known as Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition (OBIEE), is seamlessly integrated into Siebel CRM to provide advanced reporting and analysis capabilities. This module allows users to create, customise, and share interactive reports and dashboards, transforming raw data into meaningful insights.
64. What is Siebel eService, and how does it enhance customer service?
Ans:
Siebel eService is a module within the Siebel CRM suite designed to streamline and enhance customer service through web-based self-service portals. eService improves customer service by providing 24/7 accessibility, reducing service costs, and allowing customers to find answers and resolve issues independently.
65. Explain the concept of Siebel Web Services.
Ans:
Siebel Web Services enable seamless integration between Siebel applications and external systems by providing a standardized way to exchange data and invoke business processes. Using industry-standard protocols such as SOAP and REST, Siebel Web Services facilitate communication, allowing organizations to extend the functionality of their Siebel CRM applications and integrate with other systems.
66. What is the process of upgrading Siebel applications to newer versions?
Ans:
The process of upgrading Siebel applications involves several key steps:
- Assessment: Evaluate the existing environment, databases, and customizations.
- Backup: Ensure a comprehensive backup of databases, configurations, and custom code.
- Upgrade Planning: Plan for compatibility, data migration, and system testing.
- Upgrade Execution: Perform the actual upgrade, including software installation and data migration.
- Testing: Conduct thorough testing to validate the upgraded system’s functionality.
- Deployment: Roll out the upgraded application to production, ensuring a smooth transition.
67. How does Siebel handle data synchronization between local and server databases?\
Ans:
Siebel uses Siebel Remote or Mobile Web Client to handle data synchronisation between local and server databases. These components allow remote users to work offline, and changes made locally are synchronised with the central server when a connection is reestablished. This ensures consistency between local and server databases, supporting a distributed and mobile workforce.
68. Explain the purpose of Siebel Repository File System (SRF) and Web Template File System (SWT).
Ans:
The Siebel Repository File System (SRF) stores compiled information about the Siebel application, including applet definitions, business components, and views. The Web Template File System (SWT) stores HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files used to render the user interface. Together, SRF and SWT contribute to the Siebel application’s structure, behaviour, and presentation.
69. What are Siebel’s Responsibilities, and how are they configured?
Ans:
- Siebel Responsibilities define a user’s access rights and permissions within the application.
- They determine which views, applets, and functionalities a user can access.
- Configuring Siebel Responsibilities involves associating them with specific roles, views, and applets, and then assigning these responsibilities to users based on their roles and responsibilities within the organization.
70. Describe the role of Siebel Business Services in integration scenarios.
Ans:
Siebel Business Services plays a vital role in integration scenarios by providing reusable units of functionality that external applications can invoke. Business Services encapsulate business logic and expose it as services, facilitating seamless integration with other systems. They allow organizations to extend and customize Siebel functionality while maintaining interoperability with external applications.
71. What is the significance of the Siebel State Model in workflow processes?
Ans:
The Siebel State Model in workflow processes represents the current state of a workflow instance. It defines the different stages or steps a workflow can go through and the conditions under which it transitions from one state to another. The State Model adds flexibility to workflow processes, allowing for dynamic routing and decision-making based on the current state of the workflow.
72. Explain the role of Siebel Assignment Manager in workload distribution.
Ans:
Siebel Assignment Manager automates the distribution of tasks and activities among users or teams based on predefined criteria. It ensures a fair and efficient distribution of workloads by considering factors such as skills, availability, and workload capacity. Assignment Manager optimizes resource allocation, enhancing productivity and responsiveness in customer service and sales scenarios.
73. How does Siebel support customization without modifying the base code?
Ans:
- Siebel supports customization without modifying the base code through configuration tools such as Siebel Tools.
- Using configuration rather than coding, administrators can modify applets, views, business components, and other elements to meet specific business requirements.
- This approach ensures easier upgrades, reduces the risk of introducing errors, and allows organizations to adapt the Siebel application to their unique needs without altering the underlying codebase.
74. Describe the role of Siebel Server Administration in system management.
Ans:
Siebel Server Administration plays a crucial role in the overall management of the Siebel CRM system. It involves tasks such as configuring server components, monitoring system performance, managing server processes, and ensuring the reliability and availability of the Siebel application.
75. What is Siebel Loyalty Management, and how does it enhance customer loyalty programs?
Ans:
Siebel Loyalty Management is a module within Siebel CRM that enables organizations to design, execute, and manage customer loyalty programs effectively. It enhances loyalty programs by allowing businesses to define rules, rewards, and promotions based on customer behavior and preferences.
76. How does Siebel handle data migration and data quality assurance?
Ans:
Siebel handles data migration through the use of Enterprise Integration Manager (EIM). EIM allows organizations to import, update, and migrate large volumes of data into the Siebel database. Data quality assurance is achieved by defining data validation rules within Siebel Tools, ensuring that imported data meets predefined standards. Additionally, EIM provides logging and error handling features to identify and rectify data quality issues during migration.
77. Explain the concept of Siebel Business Rules and their impact on system behavior.
Ans:
- Siebel Business Rules are predefined rules that govern the behavior of the Siebel application.
- These rules are configured using Siebel Tools and can enforce data validation, automation of business processes, and customization of user interfaces.
- The impact of Siebel Business Rules is significant as they ensure consistency, accuracy, and adherence to business logic, ultimately shaping the behavior of the CRM system.
78. What is Siebel Open UI, and how does it improve user experience?
Ans:
Siebel Open UI is a user interface framework that enhances the user experience by providing a responsive, customizable, and modern interface for the Siebel application. It allows users to access Siebel CRM from a variety of devices and browsers, offering a consistent and user-friendly experience.
79. How does Siebel handle concurrent updates to the same record?
Ans:
Siebel employs record locking mechanisms to handle concurrent updates to the same record. When a user starts editing a record, Siebel locks it, preventing other users from making conflicting updates simultaneously. This ensures data consistency and prevents conflicts arising from multiple users attempting to modify the same record concurrently.
80. Explain the significance of Siebel eMarketing in customer communication.
Ans:
- Siebel eMarketing is a module designed to facilitate targeted and personalized customer communication.
- It enables organizations to create, execute, and analyze marketing campaigns across various channels.
- The significance lies in its ability to tailor communication based on customer preferences, behaviors, and segmentation.
81. Describe the process of configuring Siebel CTI (Computer Telephony Integration).
Ans:
- Installing and configuring CTI middleware.
- Defining CTI server profiles in Siebel Tools.
- Configuring CTI data mapping for screen pops and call logging.
- Implementing business logic for call handling and routing.
- Test and validate the CTI integration to ensure seamless interaction between telephony and Siebel CRM.
82. How does Siebel handle workflow exceptions and error recovery?
Ans:
Siebel Workflow includes mechanisms for handling exceptions and error recovery. Administrators can configure error-handling steps within workflows to address potential issues. Error recovery typically involves defining alternative paths or actions to take when a workflow encounters an exception, ensuring that critical business processes can recover gracefully from unexpected errors.
83. Explain the role of Siebel eCommunication in managing customer interactions.
Ans:
Siebel eCommunication is a module focused on managing customer interactions through various communication channels. The module enhances customer service by providing a centralized view of communication history, allowing for more informed and personalized interactions with customers.
84. How does Siebel support integration with third-party reporting tools?
Ans:
Siebel supports integration with third-party reporting tools through the use of standard protocols such as ODBC (Open Database Connectivity) and JDBC (Java Database Connectivity). This allows external reporting tools to connect to the Siebel database, extract relevant data, and generate reports.
85. What is the significance of Siebel Personalization in tailoring user experiences?
Ans:
Siebel Personalization enables organisations to tailor the user experience by customising the content, layout, and behavior of the Siebel application for individual users or groups. It allows users to define rules and conditions for personalization, ensuring that users see relevant information, layouts, and functionalities based on their roles, preferences, and behaviours.
86. How does Siebel handle data encryption and security during transmission?
Ans:
Siebel ensures data encryption and security during transmission by employing industry-standard protocols such as HTTPS (HTTP Secure) to encrypt data exchanged between the client and server. This encryption ensures that sensitive information, including login credentials and customer data, remains secure during communication over networks. Siebel also supports integration with SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) and TLS (Transport Layer Security) protocols to enhance data security.
87. Describe the role of Siebel SmartScripts in automating complex business processes.
Ans:
Siebel SmartScripts play a pivotal role in automating complex business processes, particularly in customer interactions. SmartScripts guide users through a series of dynamically generated questions and responses based on predefined rules.
88. What is Siebel Order Management, and how does it streamline sales processes?
Ans:
Siebel Order Management encompasses quote generation, order creation, pricing, and order fulfilment. By consolidating these functions, Siebel Order Management enhances efficiency, reduces order processing time, and ensures accuracy in sales transactions. It supports configuration rules, pricing models, and workflows to streamline and automate the sales order process.
89. How does Siebel handle versioning and release management of configuration changes?
Ans:
Siebel employs a robust versioning and release management system for configuration changes. Administrators use Siebel Tools to manage configurations, and each change is tracked with a version number. Siebel supports the creation of repository snapshots, facilitating rollback to previous versions if needed.
90. Describe the process of configuring Siebel CTMS (Clinical Trial Management System).
Ans:
- Defining Study and Site Management
- Setting Up Investigator and Monitor Workflows
- Managing Clinical Data
- Configuring Monitoring and Site Visit Schedules
- Implementing Safety Reporting
- Testing and Validation
91. How does Siebel handle multi-language support for global deployments?
Ans:
Siebel provides robust multi-language support for global deployments through the use of language-specific packs. Administrators can configure the application to support multiple languages, allowing users to interact with Siebel in their preferred language. The multi-language support includes translation of user interface elements, data values, and error messages, ensuring a consistent and localized user experience across diverse regions.
92. Describe the role of Siebel eChannel in enabling multi-channel customer interactions.
Ans:
Siebel eChannel enables multi-channel customer interactions by providing a unified platform for managing customer interactions across various channels, including web, mobile, and social media. It allows organizations to deliver a consistent and personalized customer experience regardless of the channel chosen.
93. What is Siebel Open UI’s impact on cross-browser and cross-device compatibility?
Ans:
Siebel Open UI significantly improves cross-browser and cross-device compatibility by using standard web technologies such as HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScript. This allows users to access the Siebel application from various browsers and devices, ensuring a responsive and consistent user experience. Siebel Open UI’s flexibility in design and layout contributes to enhanced compatibility across different platforms and devices.
94. Explain the significance of Siebel Smart Inventory Management in logistics.
Ans:
In logistics, Siebel Smart Inventory Management is essential for streamlining inventory procedures. It improves demand forecasting, streamlines reorder procedures, and offers real-time visibility into inventory levels. Stockouts and excess inventory are reduced thanks to smart inventory management, which makes sure that inventory is handled effectively.






