
A complete software platform called Splunk is made for managing, analyzing, and visualizing data produced by machines. It performs exceptionally well at giving businesses a reliable solution for managing various data kinds, such as logs, events, and metrics. The primary functions of the platform comprise the assimilation and organization of data from diverse origins, permitting users to execute intricate searches and acquire significant understanding of their operational and business intelligence. The real-time monitoring capabilities of Splunk enable organizations to promptly identify and address problems, guaranteeing optimal system security and performance.
1. What is Splunk?
Ans:
Splunk is a real-time software platform designed to search, analyze, and visualize machine-generated data. It provides a scalable and versatile solution for collecting, indexing, and correlating data from various sources, making it valuable for monitoring, troubleshooting, and gaining insights into the performance and security of IT systems.
2. What is the purpose of the Splunk Indexer?
Ans:
The Splunk Indexer is responsible for indexing and storing the data that is ingested by the forwarders. It makes the data searchable and enables users to run fast and efficient searches, create reports, and generate visualizations.
3. How does Splunk handle data ingestion?
Ans:
Data ingestion in Splunk involves the use of forwarders, which are lightweight agents that collect and forward data to the indexer. The forwarders can handle various data sources, formats, and protocols, ensuring flexibility in data collection.
4. Explain the main components of Splunk.
Ans:
The main components of Splunk include:
- Forwarders: Agents installed on data sources to collect and forward data to the Splunk indexer.
- Indexer: Receives and indexes the data, making it searchable and available for analysis.
- Search Head: The user interface allows users to search, analyze, and visualize the indexed data.
- Deployer: Manages the configuration and deployment of Splunk components.
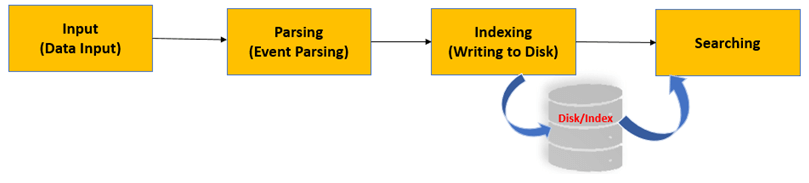
5. Explain the difference between a report and dashboard in Splunk.
Ans:
- Report: A report in Splunk is a saved search with specific fields and formatting options. It presents data in a tabular format and can be scheduled to run at specific intervals.
- Dashboard: A dashboard is a collection of visualizations, reports, and other elements that provide a consolidated data view. Dashboards allow users to customize and arrange visual components to gain insights at a glance.
6. What is the Splunk Universal Forwarder?
Ans:
The Splunk Universal Forwarder is a standalone, lightweight version of Splunk that only performs the task of forwarding data to the Splunk indexer. It doesn’t index or store data locally, making it suitable for resource-constrained systems.
7. What is the Splunk Deployment Server?
Ans:
Centralized management and configuration distribution amongst several Splunk instances in an environment are made possible in large part by the Splunk Deployment Server. Central to Splunk’s deployment architecture is the Deployment Server, which automates configuration management and guarantees consistency and uniformity across the Splunk farm. For companies with multiple installations, Splunk is a vital tool because it allows for the distribution of settings, applications, and other configurations to different Splunk instances.”
8. Describe the architecture of a basic Splunk deployment.
Ans:
A basic Splunk deployment consists of forwarders on data sources, an indexer for data storage and indexing, and a search head for user interaction. This can be expanded to include a deployment server, licence master, and cluster master for larger and more complex deployments.
9. Differentiate between Splunk Free, Splunk Enterprise, and Splunk Cloud.
Ans:
- Splunk Free: A free version of Splunk with limitations on daily data volume and without some advanced features.
- Splunk Enterprise: The full-featured, on-premises version of Splunk with no data volume restrictions, suitable for large-scale deployments.
- Splunk Cloud: A cloud-based offering of Splunk where Splunk manages the infrastructure and maintenance. It is suitable for organizations preferring a cloud-based solution.
10. What is the difference between hot, warm, and cold buckets?
Ans:
- Hot Bucket: Contains the most recent and actively indexed data. This data is frequently updated and is stored in memory for quick access.
- Warm Bucket: Contains data that is less frequently accessed than hot data but is still relevant for searches and analysis. Warm buckets are stored on disk.
- Cold Bucket: Contains older, less frequently accessed data. Cold buckets are typically archived and stored on slower, less expensive storage mediums.
11. Explain the function of the Splunk licence master.
Ans:
The Licence Master manages and distributes Splunk licences across the deployment. It helps control and monitor the usage of the Splunk platform and ensures compliance with licensing agreements. It’s crucial for managing large-scale deployments with multiple instances.
12. How does Splunk handle distributed search?
Ans:
Splunk handles distributed search by allowing users to search across multiple indexers and aggregate results centrally. The search head sends search queries to indexers, which retrieve and return relevant data. This enables efficient searching and analysis of data distributed across a Splunk deployment.
13. What is the difference between a daily indexed volume licence and a term licence?
Ans:
| Aspect | Daily Indexed Volume License | Term License | |
| Duration | Valid every day and usually renewed every day. | Valid for a predetermined period of time. | |
| Billing Cycle | Charged according to the amount of indexed data received each day. | Charged according to the predetermined term (e.g., annually). | |
| Flexibility | Allows for adjustment in accordance with daily requirements. | Gives a set, predefined amount for the duration of the term. | |
| Usage | Suitable for settings with varying amounts of data. | Suitable for scenarios with steady or predictable data volumes. | |
| Renewal Process | Daily renewed, and modifications are possible on a regular basis. | Renewed at the conclusion of the term, with potential modifications. |
14. What is the role of a search head in Splunk?
Ans:
- User Interface: serves as a web-based user interface for searching, analyzing, and visualizing data when interacting with Splunk.
- Process of Searching: coordinates the search process and aggregates results by running queries and searches against indexed data.
- Creating a Dashboard: makes it possible to create reports and dashboards that display insights from Splunk searches.
- Dispersed Exploration: enables scalable and effective processing by coordinating dispersed searches across several indexers.
15. What is the purpose of the transaction command in SPL?
Ans:
- Organizing Events: Events can be grouped in SPL using the transaction command according to shared attributes like a timestamp or shared identifier.
- Correlation of Events: It makes it easier to correlate occurrences that take place within a given time range or have a common field value.
- Time-sensitive Transactions: defines transactions that take place within a given time frame, which is useful for organizing and analyzing events that happen quickly after one another.
16. How can you extract fields in Splunk?
Ans:
Fields can be extracted in Splunk using field extractions, done through configuration files, interactive field extractions, or regular expressions. Field extractions help identify and name fields within the indexed data for better search and analysis.
17. What is a knowledge object in Splunk?
Ans:
A knowledge object in Splunk is a configuration artefact that helps customize and extend Splunk’s functionality. Examples include field extractions, event types, tags, and saved searches. Knowledge objects are used to enhance the way data is indexed, searched, and visualized.
18. How does Splunk handle time-based data?
Ans:
Time-based data is effectively managed by Splunk through a basic architectural feature of arranging it into chronological buckets. In order to precisely index and retrieve information based on time, a time field is an essential part of Splunk’s data model. Trends, patterns, and anomalies over particular time periods can be found by users through time-based searches, analyses, and visualizations.
19. How do you create alerts in Splunk?
Ans:
- Lookup term: Create a search query in SPL (Search Processing Language) to find the conditions that cause the alert to be triggered first.
- Save As Warning: In the Splunk Search & Reporting app, choose “Save As” and then “Alert” to save the search query as an alert.
- Describe the Trigger Conditions: Provide the trigger conditions—a threshold or a pattern, for example—that specify when the alert should go off.
- Decide on Alert Actions: Set up alert actions, which specify what happens, like sending an email, launching a script, or activating a webhook, when the alert goes off.
20. Explain the concept of data rollups in Splunk.
Ans:
In Splunk, data rollups are the results of gathering and condensing data to maximize search efficiency and storage effectiveness. This entails compiling comprehensive event data into condensed formats, which are then usually saved in summary indexes. Data rollups facilitate more efficient reporting and analytics by reducing information while maintaining important insights.
21. How can you configure data retention policies in Splunk?
Ans:
Data retention policies in Splunk are configured through the indexes.conf file. This file allows you to set parameters like maxDataSize, frozenTimePeriodInSecs, and maxHotSpanSecs, which determine how long data is retained, when it rolls from hot to warm or cold buckets, and how much space it can occupy.
22. What is a summary index in Splunk?
Ans:
A summary index in Splunk is a secondary index that stores aggregated or summarised data. It is useful for speeding up searches and reports, especially for frequently accessed, pre-aggregated information. Summary indexing is configured using saved searches that store results in a summary index.
23. What is the purpose of props.conf and transforms.conf?
Ans:
Props.conf:
- Oversees the information extraction and display process for Splunk from event data.
- Actions: Specify timestamp configurations, event line-breaking rules, and field extractions.
Transforms.conf:
- Goal: Provides guidelines for refining and enhancing data while it is being indexed.
- Steps: Use custom scripts or regex to define field extractions and transformations. Set up extractions with complicated logic or spanning several events.
24. Describe the steps involved in setting up a forwarder in Splunk
Ans:
Install and Download:
- Splunk Universal Forwarder can be downloaded from the Splunk website.
- Install the forwarder on the data-sending machine.
Inputs should be configured as follows:
- To define which data sources to monitor, edit inputs.conf.
- For data collection, specify log files, directories, or network ports.
Outputs should be configured as follows:
- Change the outputs.conf file to specify where the forwarder sends data.
- Set the Splunk indexer’s address and port.
25. How do you configure inputs in Splunk?
Ans:
Setting up inputs in Splunk is essential to customizing the platform to gather and index particular data sources. Users can specify parameters for data sources, including sourcetype, index, and source, by using the `inputs.conf` file. This enables flexible data ingestion from different kinds and places. Splunk continuously gathers and indexes the intended data by making regular updates to the `inputs.conf` file, which allows Splunk to adjust to the changing requirements of data monitoring and analysis.
26. Explain the Splunk authentication and authorization process.
Ans:
Authentication in Splunk is the process of verifying user identities, while authorization controls the access rights of authenticated users. Splunk supports various authentication methods such as LDAP, AD, and local authentication. Authorization is managed through roles, and users are assigned roles to determine their access levels.
27. How can you secure Splunk communication?
Ans:
An essential layer of protection for data in transit is provided by SSL/TLS protocols, which are used to secure communication within Splunk. In order to enable encrypted and authenticated communication between components, the configuration entails creating and deploying SSL certificates for every Splunk instance. This security precaution, which guards against unauthorized access and possible tampering, is especially important in settings where sensitive data is handled. Consistent upkeep and upgrades of SSL certificates are part of what makes the Splunk deployment’s security integrity possible.
28. How do you troubleshoot a slow search in Splunk?
Ans:
To troubleshoot a slow search in Splunk, you can:
- Check the search job inspector for detailed information about the search.
- Analyze the performance of individual search commands.
- Review the search log files for errors or warnings.
- Optimise the search query to make it more efficient.
- Ensure that the underlying hardware and infrastructure are performing well.
29. Explain how to optimize a search query in Splunk.
Ans:
To optimize a search query in Splunk:
- Use specific time ranges to narrow down the search scope.
- Limit the fields retrieved using the fields command.
- Optimise regular expressions and searches for better performance.
- Utilise summary indexes for pre-aggregated data.
- Leverage acceleration options like data model acceleration.
30. What is Splunk HEC (HTTP Event Collector)?
Ans:
One useful feature that allows data to be ingested into Splunk via HTTP or HTTPS protocols is Splunk HEC, or HTTP Event Collector. It offers a simple method for sending events into Splunk for indexing from outside sources. This feature makes it easier to integrate Splunk with other apps and systems, facilitating smooth data transfer and analysis.
31. What is the Splunk Common Information Model (CIM)?
Ans:
The Splunk Common Information Model (CIM) is a comprehensive framework that includes best practices and guidelines for standardizing and normalizing various types of data sources. CIM offers a standardized method for classifying and organizing data, promoting compatibility and consistency among various data kinds. Users can streamline the analysis of data from multiple sources by correlating events and conducting searches more quickly by following CIM standards.
32. How does Splunk handle geospatial data?
Ans:
Splunk’s native support and specialized commands enable it to handle geospatial data exceptionally well. The geostats command is a useful tool for comprehending spatial relationships within datasets because it enables users to visualize and analyze data on maps. The iplocation command also makes it possible to derive geographic data from IP addresses, improving the geospatial context of data.
33. How can you monitor Splunk system health?
Ans:
Splunk provides various tools and dashboards for monitoring system health. Key indicators include:
- Monitoring Console: Provides insights into index and search performance.
- Splunk Web Interface: Offers real-time monitoring of various components.
- REST API: Allows for programmatic monitoring and integration with external monitoring tools.
34. Describe best practices for designing a Splunk deployment.
Ans:
Plan for scalability and growth.
- Distribute workloads efficiently across indexers and search heads.
- Implement data lifecycle management and retention policies.
- Regularly monitor and optimize performance.
- Secure the deployment following best practices.
- Document and maintain configurations.
35. What is a Splunk Bucket and how does it impact performance?
Ans:
A bucket is the basic unit of storage for indexed data in Splunk. Because it controls how data is stored, retrieved, and searched within the Splunk environment, it has a significant impact on performance. Performance optimization requires proper bucket management. In order to suit the unique requirements and features of the data being indexed, bucket sizes and storage policies must be configured. In large-scale Splunk deployments, efficient bucket management guarantees effective data retrieval and search operations, which enhances overall system responsiveness and performance.
36. Explain how to use the Splunk REST API.
Ans:
The Splunk REST API allows users to interact with Splunk programmatically. Some everyday use cases include searching and retrieving data, managing configurations, and automating administrative tasks. Authentication is typically done using API tokens or credentials, and responses are in JSON format. The API documentation provides details on available endpoints and functionalities.
37. How do you manage and optimize Splunk licensing?
Ans:
- Monitor licence usage through the Licence Usage Report.
- Implement data volume quotas to control usage.
- Use licence pooling for distributed deployments.
- Understand and optimize licence usage by configuring data inputs and summarization.
38. What are some security best practices for Splunk?
Ans:
- Implement role-based access controls (RBAC).
- Secure communication using SSL/TLS.
- Regularly audit and review access controls.
- Utilise secure deployment practices.
- Keep Splunk software and components up to date.
39. What is the Splunk SDK, and how is it used?
Ans:
To facilitate smooth programmatic integration with the Splunk platform, Splunk offers sets of libraries and tools called Software Development Kits (SDKs). Many programming languages, such as Python, Java, JavaScript, and others, are supported by these SDKs. Developers are able to customize apps, automate processes, and expand Splunk’s functionality to suit their own requirements by utilizing the Splunk SDKs.
40. Explain the use of the “search” command in SPL.
Ans:
The search command in SPL is used to initiate a search in Splunk. It is often the first command in a search query and is followed by search criteria. For example, index=main sourcetype=access_combined | stats count by the client initiates a search for events in the “main” index with the “access_combined” source type.
41. How can you use the “eval” command in Splunk?
Ans:
The evaluation command in SPL is used to create or modify existing fields in search results. It allows for mathematical operations, string manipulations, and conditional evaluations. For example, … | eval total_bytes = bytes_in + bytes_out creates a new field called “total_bytes.”
42. How can you integrate Splunk with external databases?
Ans:
Splunk can be integrated with external databases using various methods:
- DB Connect: Splunk DB Connect allows you to connect to relational databases, execute SQL queries, and index the results.
- Lookup Tables: Splunk can use lookup tables to enrich events with data from external databases.
- Custom Scripts: You can use custom scripts or apps to fetch data from external databases and forward it to Splunk.
43. What is the “rex” command used for?
Ans:
- The rex command in SPL is used for regular expression (regex) extraction. It allows users to extract fields from event data using regular expressions.
- For instance, … | rex field=_raw “error message:(?
.+)” extracts the error message from the raw event data.
44. How does Splunk handle large datasets?
Ans:
Splunk employs various strategies to handle large datasets, including data indexing, compression, and bucketing. It utilizes efficient search algorithms, distributed search, and summary indexing. Proper configuration of data retention policies and data model acceleration also contribute to handling large datasets effectively.
45. What is the role of Hadoop in Splunk?
Ans:
Hadoop can be integrated with Splunk to provide additional storage for historical data. Splunk Hadoop Connect allows you to export and archive data to Hadoop, enabling long-term storage and analysis while reducing the storage burden on the Splunk indexer.
46. Can Splunk be integrated with machine learning algorithms?
Ans:
- Splunk can be integrated with machine learning algorithms through custom scripts, external machine learning frameworks, or apps.
- The Machine Learning Toolkit is an add-on for Splunk that provides a user-friendly interface for applying machine learning algorithms to data. It includes pre-built algorithms, visualizations, and tools
47. What’s the differences between single-instance, distributed, and clustered deployments in Splunk.
Ans:
- Single-Instance Deployment: A standalone installation where all Splunk components (indexer, search head, and forwarder) reside on a single server.
- Distributed Deployment: Components are distributed across multiple servers for scalability. Indexers store data, search heads provide the interface, and forwarders collect and forward data.
- Clustered Deployment: A more advanced distributed setup with multiple indexers organized into a cluster. It provides redundancy, load balancing, and high availability.
48. Explain the concept of Splunk search head pooling.
Ans:
Search Head Pooling is a feature that allows multiple search heads to share a common set of search artefacts and configurations. It improves search performance and enables load balancing across multiple search heads. This is especially useful in large-scale deployments with multiple users and concurrent searches.
49. What is the Splunk SmartStore feature, and how does it work?
Ans:
Splunk SmartStore is a feature designed to enhance storage scalability and efficiency in large-scale deployments. It allows Splunk indexers to offload and retrieve data from external object storage systems, such as Amazon S3 or Dell EMC ECS. This enables organizations to manage massive amounts of data without the need for expensive local storage, improving cost-effectiveness and scalability.
50. How does Splunk support high availability and disaster recovery?
Ans:
High availability in Splunk can be achieved through clustering, where multiple indexers or search heads work together to provide redundancy. Disaster recovery involves regularly backing up configurations and data and having standby systems ready to take over in case of a failure. Regularly testing and updating the disaster recovery plan is crucial.
51. Describe the process of setting up a Splunk indexer cluster.
Ans:
Setting up a Splunk indexer cluster involves several steps:
- Install Splunk Enterprise on each indexer.
- Configure the server. conf and indexes.conf files.
- Establish communication between cluster peers.
- Configure replication factor and search factor for data redundancy.
- Add each indexer to the cluster using the clustering commands.
- Start the cluster master and enable clustering on each indexer.
52. You notice a sudden spike in licence usage. How would you troubleshoot this issue?
Ans:
To troubleshoot a sudden spike in licence usage:
- Examine the Licence Usage Report.
- Check which sources or source types are contributing to the end.
- Review configurations to ensure no unexpected increase in data volume.
- Inspect the Search Job Inspector for searches consuming excessive resources.
- Investigate for any unusual activities or unexpected data influx.
53. A user reports that a specific search takes too long. How would you approach this problem?
Ans:
To troubleshoot a slow search reported by a user:
- Check the search job inspector for details on the search execution.
- Examine the search query for complexity and efficiency.
- Review the underlying data model and indexes for optimization opportunities.
- Analyze system resource usage on the search head and indexers.
- Consider using summary indexes or data model acceleration for better performance.
54. How does Splunk address compliance requirements such as PCI-DSS or HIPAA?
Ans:
Splunk can be configured to meet compliance requirements like PCI-DSS or HIPAA by implementing security best practices, access controls, encryption, and audit logging. Additionally, organizations can use Splunk’s reporting and alerting features to monitor and demonstrate compliance.
55. What are Splunk roles, and how are they assigned?
Ans:
Splunk roles control user permissions and access levels. Roles include admin, power user, and user, among others. Roles are assigned to users based on their responsibilities and required access levels.
56. Describe a situation where you had to optimize a poorly performing Splunk query.
Ans:
To optimize a poorly performing Splunk query:
- Simplify and streamline the search query.
- Optimise regular expressions and search terms.
- Leverage summary indexing or data model acceleration.
- Review index configurations and field extractions for efficiency.
- Ensure hardware resources are adequate and distributed appropriately.
57. How would you handle a Splunk forwarder not sending data to the indexer?
Ans:
To handle a situation where a Splunk forwarder is not sending data:
- Check the forwarder’s logs for errors or connection issues.
- Verify network connectivity between the forwarder and indexer.
- Inspect the inputs. Configure the forwarder for correct configurations.
- Ensure the forwarder is running and properly configured to monitor the data source.
58. What is SPL (Search Processing Language)?
Ans:
Splunk’s core query language, known as SPL, or Search Processing Language, makes it easier to search and analyze data on the platform. This language offers a strong framework for extracting, transforming, and visualizing data while enabling users to create complex and flexible queries. By utilizing a syntax that is both strong and adaptable, users of SPL can conduct intricate searches to find insightful information.
59. Explain the Splunk licensing model.
Ans:
Splunk’s licensing model is based on the volume of data ingested (Daily Indexed Volume). Users purchase licences to index a certain amount of data per day. The model can be adjusted based on the organization’s needs.
60. Explain the use of Splunk apps and add-ons.
Ans:
Splunk apps are pre-packaged collections of dashboards, reports, and settings tailored for specific use cases. Add-ons extend functionality by providing configurations for ingesting and parsing data from diverse sources, enhancing Splunk’s adaptability to different needs.
61. Explain how you would design a Splunk deployment for a large-scale environment.
Ans:
For a large-scale environment:
- Implement a distributed deployment with separate indexers, search heads, and forwarders.
- Use clustering for high availability and load balancing.
- Utilise summary indexing, data model acceleration, and SmartStore for scalability.
- Implement proper data lifecycle management and retention policies.
- Scale hardware resources according to the anticipated data volume and user load.
62. when did you had to troubleshoot a critical issue in a Splunk deployment.
Ans:
To troubleshoot a critical issue in a Splunk deployment:
- Gather information on the symptoms and impact of the issue.
- Review logs, including Splunk logs, system logs, and configuration files.
- Use monitoring tools and dashboards to identify performance bottlenecks.
- Check for recent changes or updates that might have triggered the issue.
- Engage Splunk support or consult the documentation and community forums for assistance.
63. How would you handle version upgrades in a production Splunk environment?
Ans:
- Review Release Notes: Understand changes, new features, and potential impact.
- Test in a Sandbox: Validate the upgrade in a non-production environment.
- Backup Configuration: Ensure a backup of configurations and data.
- Coordinate Downtime: Plan a maintenance window for the promotion.
- Upgrade Forwarders First: Upgrade universal forwarders before indexers/search heads.
64. How does Splunk handle different types of data sources (logs, metrics, etc.)?
Ans:
Splunk uses add-ons to manage a variety of data sources, including metrics and logs. Specialized configurations known as add-ons specify data inputs, field extractions, and other settings required for efficient data ingestion and analysis. Through the utilization of customized add-ons that are matched to the features of every data source, Splunk guarantees precise information parsing, indexing, and correlation, allowing users to extract valuable insights from a variety of data kinds.
65. Describe the process of configuring Splunk to monitor a new data source.
Ans:
The configuration process in Splunk requires the specification of the data source type, location, and extra settings in order to monitor a new data source. Users can achieve this by directly editing configuration files like `inputs.conf` to define the parameters for the new data source, or by using Splunk Web’s “Add Data” feature. By completing this configuration step, you can be sure that Splunk will detect, gather, and index data from the recently added source, enabling search and analysis within the Splunk platform.
66. How does Splunk process events during indexing?
Ans:
Splunk creates metadata, extracts important information, and breaks down events into searchable fields during indexing. In order to enable temporal analysis and correlation, Splunk timestamps events as they are ingested and arranges them in chronological order. By using timestamps, search parameters, and extracted fields, this indexing process improves Splunk’s search capabilities and makes it possible for users to quickly retrieve and examine particular events.
67. Explain how to secure sensitive information in Splunk.
Ans:
To secure sensitive information in Splunk:
- Use encryption for data in transit and at rest.
- Implement access controls and role-based permissions.
- Mask or anonymize sensitive fields using field transformations.
- Use Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) for secure communication.
68. How can Splunk be integrated with cloud services like AWS or Azure?
Ans:
Splunk can be integrated with cloud services by:
- Installing Splunk directly on cloud instances.
- Using Splunk Connect for AWS/Azure for log ingestion.
- Utilising add-ons or apps specific to the cloud platform.
- Configuring inputs to collect data from cloud services.
69. Explain the role of timestamps in event processing.
Ans:
Splunk’s event processing relies heavily on timestamps because they give events a chronological sequence. A timestamp is assigned to each event, enabling correlation, analysis, and time-based searches. Users can precisely order events, recognize temporal patterns, and gain understanding of data trends over time when timestamps are present. Timestamps are essential for understanding the temporal context of events and improve search and analysis performance on the Splunk platform.
70. How can Splunk be used in an IoT (Internet of Things) environment?
Ans:
Splunk is used in IoT environments to analyze and derive insights from the vast amounts of data generated by connected devices. It enables monitoring of device performance, detection of anomalies, and proactive decision-making based on real-time data.
71. Describe the considerations for deploying Splunk in a cloud environment.
Ans:
Considerations for deploying Splunk in a cloud environment include:
- Network connectivity and bandwidth.
- Storage performance and scalability.
- Security measures for data protection.
- Compliance with cloud provider guidelines.
- Integration with cloud-native services.
72. How do you add and manage users in Splunk?
Ans:
Users are added and managed in Splunk through the following steps:
- Use the web interface or command line to add users.
- Assign roles to control access privileges.
- Manage user passwords and authentication methods.
- Configure user preferences and settings.
73. How can you customize the Splunk user interface?
Ans:
Splunk’s user interface can be customized by:
- Creating custom dashboards with specific visualizations.
- Modifying CSS styles to change the look and feel.
- Developing custom apps or add-ons.
- Configuring user-specific settings and preferences.
- Utilising SimpleXML to design custom views and forms.
74. Explain the role of timestamps in event processing.
Ans:
Splunk’s event processing relies heavily on timestamps because they give events a chronological sequence. A timestamp is assigned to each event, enabling correlation, analysis, and time-based searches. Users can precisely order events, recognize temporal patterns, and gain understanding of data trends over time when timestamps are present.
75. Describe a scenario where you would use the KV Store in Splunk.
Ans:
The Splunk KV Store can be used in a situation where the list of authorized users or devices is dynamic and subject to change over time. The KV Store offers a centralized repository for managing information about authorized entities, enabling users to store and update this reference data efficiently. This makes it possible for Splunk lookups and validations to function smoothly, guaranteeing that the most recent data is always available for correlation and analysis.
76. What is the Splunk KV Store, and how is it used?
Ans:
- The Splunk KV Store is a key-value store within Splunk.
- Usage: Used for storing and retrieving arbitrary data in key-value pairs.
- Applications: Commonly used for reference data, lookups, and custom configurations.
- Splunk offers a flexible way to manage and access structured data.
- Integration: Allows users to create and manage key-value data collections.
77. How can Splunk be integrated into a DevOps workflow?
Ans:
- Data Ingestion: A range of DevOps tools, logs, and metrics can provide data for Splunk to process.
- Centralized Monitoring: Offers a platform that is centralized for keeping an eye on infrastructure, logs, and application performance.
- Automation: Works with automation tools to set up conditions that cause alerts and actions to be triggered.
- Encourages cooperation between teams working on development, operations, and quality assurance.
78. Describe the challenges and considerations for monitoring IoT data in Splunk.
Ans:
Challenges in monitoring IoT data with Splunk include handling large-scale data volumes, real-time processing requirements, ensuring data security and privacy, and dealing with diverse data formats from different IoT devices.
79. Explain how Splunk can be used for application monitoring in a DevOps environment.
Ans:
Splunk is used in DevOps for real-time application monitoring by ingesting and analyzing log data, providing insights into performance, error rates, and user experiences. Custom dashboards and alerts enable proactive issue detection and resolution, improving overall application reliability.
80. How would you use the REST API to retrieve data from Splunk?
Ans:
Using the REST API to retrieve data from Splunk entails making HTTP requests to the appropriate endpoints and specifying search criteria via parameters. The Splunk REST API is a powerful interface for interacting with Splunk programmatically, allowing users to query and retrieve data based on their specific needs.
81. What are the benefits of using search head clustering?
Ans:
- High Availability: Ensures that search functionality is always available in the event of a search head failure.
- Horizontal scaling is possible by adding more search heads to distribute the load.
- Improves search performance by dividing search and reporting workloads.
- Failover: Provides failover capabilities to ensure continuous search services during node failures.
82. Explain the importance of field extractions in search queries.
Ans:
- Structured Data Analysis: Field extractions convert unstructured data into structured fields, allowing for more organized and meaningful log event analysis.
- Extracted fields provide a foundation for more precise and targeted search queries, allowing users to focus on specific aspects of the data.
- Fields act as building blocks for visualizations and reports, allowing users to create meaningful charts and dashboards.
83. What is a data model in Splunk, and how is it created?
Ans:
A data model in Splunk is a structure that defines relationships and hierarchies between fields in events. It is created using the Splunk Web interface, allowing users to define and explore the relationships between different data elements.
84. How can Splunk be used for business intelligence purposes?
Ans:
Splunk’s capacity to compile and examine a wide range of data sources makes it a potent business intelligence tool. It offers instantaneous insights into user behavior, trends, and operational data. Organizations can monitor key performance indicators, identify patterns that support strategic planning, and make well-informed decisions thanks to Splunk’s analytics capabilities.
85. Describe a scenario where you used Splunk to provide business insights.
Ans:
In one particular case, a business wanted to improve user interaction with their web portal. To examine the log data produced by user interactions, Splunk was used. Splunk’s analysis yielded valuable insights that allowed for a thorough understanding of user behavior, preferences, and pain points. This data made it easier to optimize the user experience, which raised customer satisfaction and enhanced engagement metrics, all of which helped the business succeed.
86. How can PowerShell scripts be integrated with Splunk?
Ans:
Scripted inputs allow PowerShell scripts to be easily integrated with Splunk. Automation of a number of processes, such as alerting, system monitoring, and data collection, is made possible by this integration. Administrators can run PowerShell scripts at predetermined intervals or in response to predefined events by setting up scripted inputs in Splunk. Through this integration, businesses can use PowerShell’s capabilities for tasks like log extraction, system health monitoring, and custom data collection, all while centralizing and analyzing the data that is gathered inside the Splunk platform.
87. Describe the process of troubleshooting forwarder connectivity issues.
Ans:
- Verify the Status of the Forwarder: Make sure the source machine’s Splunk Universal Forwarder is up and running.
- Examine the logs: Check the forwarder logs (splunkd.log) for any messages indicating errors or problems with connectivity.
- Setting up a firewall: Make sure that firewalls are set up to permit communication between the Splunk indexer and the forwarder.
- Network Interconnectivity: Check that the forwarder and the indexer are connected to the same network. Test connectivity using programs like telnet or ping.
88. Explain the benefits of using data models in Splunk.
Ans:
- Structured Data Analysis: By defining relationships and hierarchies between fields, data models give users an organized method to organize and analyze data.
- Unified Schema: Data models facilitate the development of a single, unified schema that serves as a representation of the data’s underlying structure and encourages consistency between searches and reports.
- Field aliasing improves readability and streamlines intricate searches by enabling users to specify alternate names for fields inside a data model.
89. How can PowerShell scripts be integrated with Splunk?
Ans:
Scripted inputs allow PowerShell scripts to be easily integrated with Splunk. Automation of a number of processes, such as alerting, system monitoring, and data collection, is made possible by this integration. Administrators can run PowerShell scripts at predetermined intervals or in response to predefined events by setting up scripted inputs in Splunk. Through this integration, businesses can use PowerShell’s capabilities for tasks like log extraction, system health monitoring, and custom data collection, all while centralizing and analyzing the data that is gathered inside the Splunk platform.
90. Explain how Splunk can be used to monitor and analyze network data.
Ans:
Splunk is a potent platform for network data monitoring and analysis that offers insights into the functionality, security, and well-being of a company’s network infrastructure. Splunk allows for real-time visibility into network activity by ingesting logs from networking devices, including switches, routers, firewalls, and other network components.
91. How do you configure data forwarding in a distributed Splunk environment?
Ans:
Setting up data forwarding is essential in a distributed Splunk environment to consolidate log data from multiple sources onto a central indexer for analysis and storage. The `outputs.conf` configuration file on the forwarder must be edited during this procedure.
92. Explain the concept of search head clustering in Splunk.
Ans:
- High Availability: By splitting up the workload between several search heads, search head clustering provides high availability.
- Fault Tolerance: This feature ensures that search functionality is available continuously even in the event of a failure of one of the cluster’s search heads.
- Scalability: Organizations can add more search heads to meet growing search and reporting demands because search head clustering facilitates horizontal scaling.
- Consistent Configuration: To guarantee consistency, configuration modifications made on one search head instantly spread to the other search heads in the cluster.
93. Describe a situation where you had to troubleshoot issues related to data forwarding.
Ans:
In a situation where data forwarding issues arise, troubleshooting involves:
- Checking network connectivity and.
- Validating configuration settings in outputs. Conf. review
- Reviewing the forwarder and indexer logs to identify and resolve any communication problems.
94. How does Splunk support data rollbacks?
Ans:
Splunk does not support traditional data rollbacks in the sense of reverting changes. However, it has mechanisms like bucket replication and disaster recovery options to ensure data availability and recoverability in case of failures.
95. Explain the role of the Splunk Deployment Monitor.
Ans:
The Splunk Deployment Monitor is an app that provides insights into the health and performance of a Splunk deployment. It allows administrators to monitor the status of indexers, search heads, forwarders, and other components, providing visibility into resource usage and potential issues in the deployment.






