
WHEN IS ROM USED?
ROM estimate is used
At Project Initiation: to screen/prioritize for final decision making as to which project to choose among available options.
During the Project Life Cycle: To estimate the final cost to conclude the project and are reviewed and refined as more and more information is gathered during the project execution phase.
HOW TO MAKE ROM ESTIMATE?
- Developing a ROM estimate takes a lot of skill and experience.
- You’ll always need to involve relevant stakeholders and subject matter experts for their opinion on the required level of estimation to complete certain milestones.
- And as the term itself describes, it is a rough order magnitude, i.e., there will be a chance of inaccuracies, or the estimations will have limited accuracy.
- It all depends on the experience and the information received from subject matter experts, ROM can have accuracy level -50% to +50% (As per PMBOK6).
- Ultimately we get roughly estimated information regarding the schedule and effort required to complete a milestone.
- ROM estimates can also be made from the available references of similar projects from the past. For example, the total cost to establish a new plant with 100 metric tons capacity will almost two times of the old plant with 50 metric tons capacity.
TOOLS USED IN ROM ESTIMATE
In general, the following are the main tools & techniques to get to ROM estimate.
- Ball Park estimate
- Top-down estimation
- Historical data and expert opinion
- It is recommended to make an estimate in terms of time and cost. It helps the subject experts to provide their expert opinions in a most efficient and precise manner.
- As at the early stages, there is very limited information available, so it wouldn’t be possible to provide an accurate estimate of time and cost, so what we can do here is divide the estimates into three categories. i.e., Low, Medium, and High. It could look like as below
ROM ESTIMATE CATEGORIES
ROM estimates can be categorized into these activities. This is based on the level of effort.
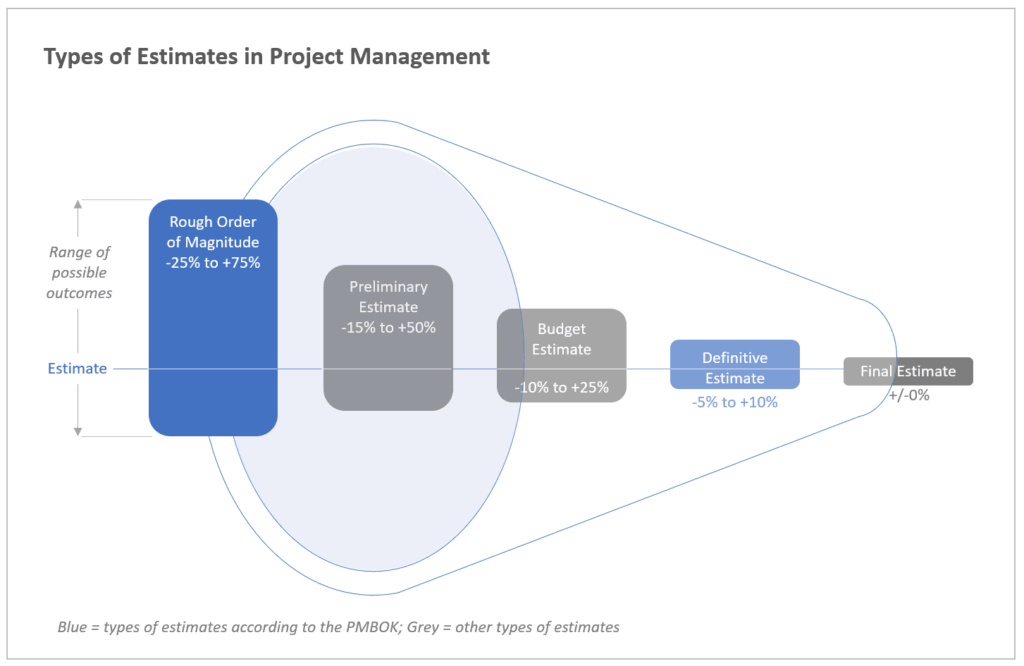
LOW EFFORT
- Hours: 30 to 50 hours for completion
- Cost: $1500 to $4500 dollars
- Duration: 1 to 2 weeks
- Number of Resources: 1 to 2 Resources
MEDIUM EFFORT
- Hours: 50 to 250 hours for completion
- Cost: $4500 to $10,000 dollars
- Duration: 1 to 3 months
- Number of Resources: 3 to 5 Resources
HIGH EFFORT
- Hours: 300 to 1000 hours for completion
- Cost: $15,000 to $50,000 dollars
- Duration: 4 to 6 months
- Number of Resources: 5 to 15 Resources
- This kind of category, as listed above, makes life easier for everyone by breaking down the work into every possible manner at the early stages of the project.
- Similarly, subject experts would be more comfortable in providing the estimates with this kind of model.
Inaccurate cost estimation and budgeting
- Inaccurate cost estimation and budgeting is one of the main root causes of project cost overruns. Once the budgeted costs are lower than what is really required, the recovery is very difficult.
- The only way out is re-estimation, and re-budgeting, which is a long drawn out process, especially for infrastructure projects based on fixed price bids. Why is this so?.
- Projects are progressively elaborated, so are budgets. The expected accuracy of estimates increases as the project progresses. When the project is in evaluation stage a Rough Order of Magnitude estimate (ROM) will serve the purpose. The expected accuracy levels of rough order of magnitude estimates are between -15 to +75 percentage. During project portfolio planning a Budgetary estimate is required. The expected accuracy level of budgetary estimates are between -15 to +15 percentage.
- During the planning phase of the project, one need the most accurate estimates known as Definitive estimates whose expected accuracy level is between -5 to +5 percentage. Definitive estimates are based on detailed Work Breakdown Structures (WBS).
- While budgetary estimates are possible with high levels of work breakdown structures, for definitive estimates one need detailed work breakdown structures meeting the 8-80 rule. Unfortunately, fixed price contracts are signed much before the preparation of the detailed work breakdown structures with the required granularity.
- Hence budgetary estimates gets labelled as definitive estimates.
- Very often, estimation team fails to factor in appropriate overheads into the engineering and construction costs before finalizing the project budget.
- One has to bear in mind the following while estimating cost and budgeting. Error in judgment of any of these components will impact the budgeting process negatively.
Cost + Contingency costs + Management reserves = budgetBudget + Profit = Price (quoted)
If the quoted price itself is lower than the budget, then it is only a matter of time before the actual cost exceeds the planned cost.
Root cause#2. Inadequate cost monitoring and control systems
- Recently, I was shocked to see the pathetic state of spread sheet based planning and tracking system of a very large infrastructure project where well known global giants are stakeholders.
- Automated real time progress monitoring based on earned value management principles is what is needed.
Root cause#3. Improper vendor selection
- If the scope is absolutely clear, then fixed price contracts will work perfectly. For this we need definitive estimates based on work breakdown structures of high level of detail.
- If the scope is not very clear, then cost reimbursable contracts are a better choice.
Root cause#5. Lack of professional ethics
- Lack of professional ethics is a milder way of addressing ‘CORRUPTION’ which shadows every aspect of many projects which are lagging behind both schedule wise and cost wise.
- Having said that, let us focus on how to improve the accuracy of project cost estimation and budgeting.
ROM Estimate vs Definitive Estimate
- Rough Order of Magnitude (ROM) Estimate: the differences between estimates and actual figures may be as large as 75% more or 25% less
- used in early stage of the project when things are not very solid/clear and/or for projects that span a lengthy period
- Definitive Estimate: the differences between estimates and actual figures may be within the range of -5% to + 10% (more or less)
- used in latter stage of the project and/or the project is simple to estimate
In addition to the ROM Estimate and Definitive Estimate, there are some more estimation ranges:
- Preliminary estimate: within the range of -15% to +50%
- Budget estimate: within the range of -10% to +25%
- Final estimate: 100% accurate
The degree of accuracy of the estimations will become more accurate as the project proceed as many unknowns at the beginning of the project will become known later on.
ROM Estimate vs Definitive Estimate Illustrated
- Let’s take the project of PMP Exam study and preparation again for the illustration of the degree of accuracy of estimation.
- At the very beginning of the exam preparation, the Aspirants may have little or no previous knowledge about the exam syllabus and the PMBOK.
- The actual period of time required for the studies may not be known accurately. The only way to estimate the study period is through the lessons learned of other exam takers.
- And as a rule of thumb, the estimated preparation period for the exam is roughly 3 months of part-time study, which is considered a Rough Order of Magnitude (ROM) Estimate.
- But after going through the exam prep course, the PMP Aspirant will then be able to understand the topics for the exam and their knowledge gaps.
- Hence a more accurate estimate can be made (e.g. 100 days — more like a Definitive Estimate). And at that time, it is often advisable to book the exact date of the exam, which can also act as a driving force for the PMP study.
Mock Exam Question
- The project is working into 3/4 of project duration and the final component is to be built to improve the accuracy of the system. The project manager is updating the cost of the whole system.
- What is the degree of accuracy of the estimate?
- Preliminary Estimate
- Rough Order of Magnitude Estimate
- Budget Estimate
- Definitive Estimate
Rough Order of Magnitude
- When it is very early in the project or you have little information available for a project, and management has asked you to provide them with a budget estimate quickly, you will provide the ROM of the budget estimate.
- The accuracy of this estimate is low. It varies between -25% to +75%.
- You find this value by looking any past similar types of projects or just have an overlook of the broad scope of work and then decide on it.
- Here, the time required to calculate the cost estimate is the least.
Definitive Estimate
- You use this metric when management needs a more accurate cost or time estimate and you have enough project information.
- This estimate requires more time than the ROM technique; however, its accuracy is between -5% to +10%.
- With definitive estimate the management can be sure about the project or any bid they are going to participate in.
- You will get the definitive estimate when you have a detailed scope of work or if the project is already running.
Now we will study estimation techniques and their accuracy.
Estimation Techniques
There are four techniques for estimation:
- Analogous Estimation
- Parametric Estimation
- Three Point Estimation
- Bottom Up Estimation
- In an analogous estimation, you compare the cost of the project with any past similar projects and come up with an estimation of the project. You use this technique when you have little information about the project.
- The cost estimate of this technique can be considered a rough order of magnitude as the accuracy of the estimate is not good. This estimation is also known as a ballpark estimate.
- In parametric estimation, you take statistical data from any past projects and apply it to the current project. For example, the cost of painting per square foot.
- The accuracy of this estimation is better than analogous. The estimation of this technique can be definitive or ROM depending on the quality of data and effort involved.
- In three point estimating, you find three estimates and take an average to remove the bias. The accuracy of this estimate is better than the two discussed above.
- The bottom up estimation technique gives the most accurate result and is also known as the “definitive estimation technique”.
- In this technique you find the cost of each activity and add them up to get the cost of the project. Though this technique is time consuming, it provides the best results.
- The estimation values obtained from three point estimating and bottom up estimating are the most accurate, and you can say that these estimates are definitive.





