
A burndown chart shows the amount of work that has been completed in an epic or sprint, and the total work remaining. Burndown charts are used to predict your team’s likelihood of completing their work in the time available.
- Introduction To Learn Burndown Charts
- How are Burndown Charts calculated
- Components of a burndown chart Chart
- How to create a burndown chart?
- How to view and understand the burndown chart
- Types of Burndown Charts
- Burn up vs. burn down charts
- What Are the Limitations of a Burndown Chart?
- Benefits of Learn Burndown Charts
- Conclusion
- Collecting project data and helping teams understand how to proceed with sprint
- Communicate project objectives clearly
- Allowing teams to better organize their run
- Separate tasks more accurately
- Jira Burndown Chart Study
Introduction To Learn Burndown Charts:
Jira burndown charts are like project trackers. They are visual aids that help to visualize project progress and help plan and track runners. Indicates the number of tasks already completed in the race and the number of tasks to be completed.
Burndown charts can be used by teams to determine if they will be able to reach their tops and complete the task on time. Burndown charts also assist the team in identifying scope creep that may occur during the sprint.
They help with:
Let’s start with the Jira heat chart tutorial by first understanding some of the basics:
What is Scrum? Scrum is a dynamic and flexible Agile project management framework. It is the most widely used Agile framework and emphasizes collaboration, planning, and communication.
What is Epic? A scrum works by breaking down large projects into smaller pieces. Each of these small episodes is called Epic, which can be further subdivided.
What is Sprint? Epics are subdivided into Sprints, which are short-lived, time-bound boxes that are assigned to complete certain tasks. The active product is delivered at the end of each sprint.
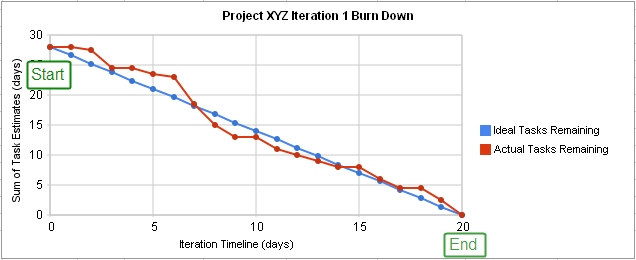
- The burn chart helps to measure the daily activity left in the sprint. By using the burn chart, we can determine the amount of effort made compared to the amount of work submitted in each repetition.
- The burning speed represented by the slope reflects the production rate reached each day and can be calculated by comparing the number of hours worked compared to the initial project rate.
- This helps teams understand if the project is up to date, early or late. Team members can refer to the hot chart and make any changes to their operating system.
How are Burndown Charts calculated:
Components of a burndown chart Chart:
The hot chart has many parts. Its axes are used to display time / multiplication (horizontal) and user story points (vertical). The first area of the project is located on the left, which is also the highest part of the relevant fire chart. The far right point of your graph shows the end of your project or sprint.
On most hot charts, you will see the appropriate left-hand line for a dot or use a different color. This line uses group past performance to measure their performance and gives you a rating stick to judge your performance. One distinguishing feature of the relevant work line is its continuous tendency. In fact, teams work at different speeds throughout the project.
The actual work line in the hot chart shows the actual continuation of the project. Real and relevant work lines share the same origin, but the real line goes above or below the ideal line depending on the situation. If the actual line is above the appropriate line, your project is still in the background. Similarly, a real line of descent means that your project is ahead of schedule.
- You need to set up rating statistics to find out how much work your team has completed. Evaluation metrics are a unit of measurement used to measure activity, such as news points, hours, user stories etc.
- This unit can be selected by the team. Evaluation statistics help calculate the speed of the group for each sprint, which is the sum of the calculations for the completed news.
- Speed helps during sprint planning.
- Setting balance statistics in Jira software (Atlassian source)
- Navigate to the board or backlog, then select more (Ellipses button)> Board settings.
- News scaling helps determine how much time it will take to complete certain tasks in a sprint.
- Before the start of the sprint, you need to enter a measure.
- This could be in news articles or other ratings of your choice.
- Go to Back Logo for your Scrum project.
- Select a problem. Once the issue is selected you can see its details on the right.
- Rate it in Story points or in the actual rating field, depending on what you choose as your rating figures.
How to create a burndown chart?
Compiling a burn chart requires a few things to consider. These are:
1. Set rating statistics:
2. Establishing scales:
3. Rating:
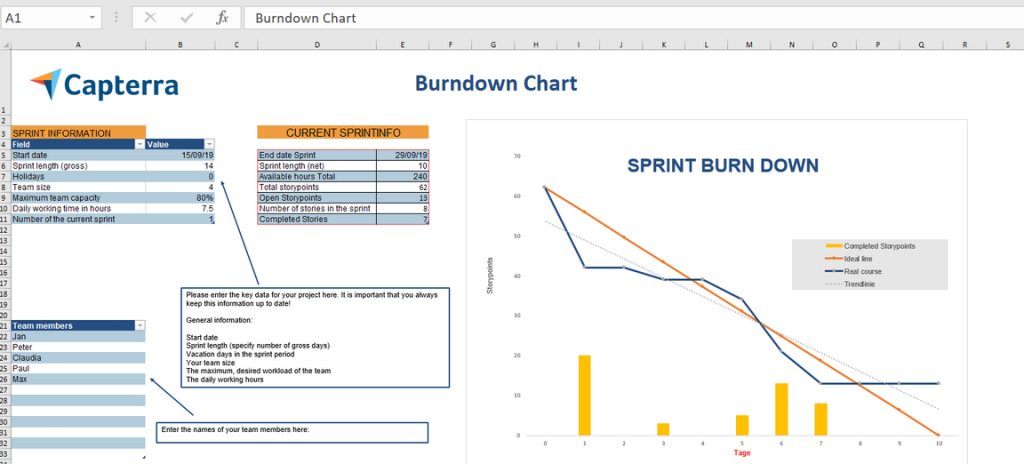
- Navigate to your scrum project.
- Choose Backlog Or Active sprint.
- Click Reports, then select Burndown Chart.
- Your burn chart will look like below:
- Understanding your burn chart:
How to view and understand the burndown chart:
You can track your team’s progress with a sprint burn chart. Since the burn chart shows the amount of work left to be done in the sprint, it can be used to estimate whether a running goal can be achieved within a set time. By tracking the amount of work left in the entire sprint, the team can better organize themselves to achieve the goal. Let’s see how we can look at it and explain the burn chart.
- Go to your Scrum project and select Backlog or Active Sprint.
- Then click on “Reports” followed by “Burndown Chart”.
- Epic Burndown Charts.
- The Epic Burndown Chart allows Scrum Groups to show their progress during the Sprint. This is a chart that shows you how the team performed on Epic. Teams can see how much Epic is left, as well as the impact of changes during Sprint.
- Go to your Scrum project.
- Click on Backlog or Active Sprint.
- Then click on Messages and select Epic Burndown.
- You will notice a selection of landmarks near the Epic Burndown theme, with options depending on what is set.
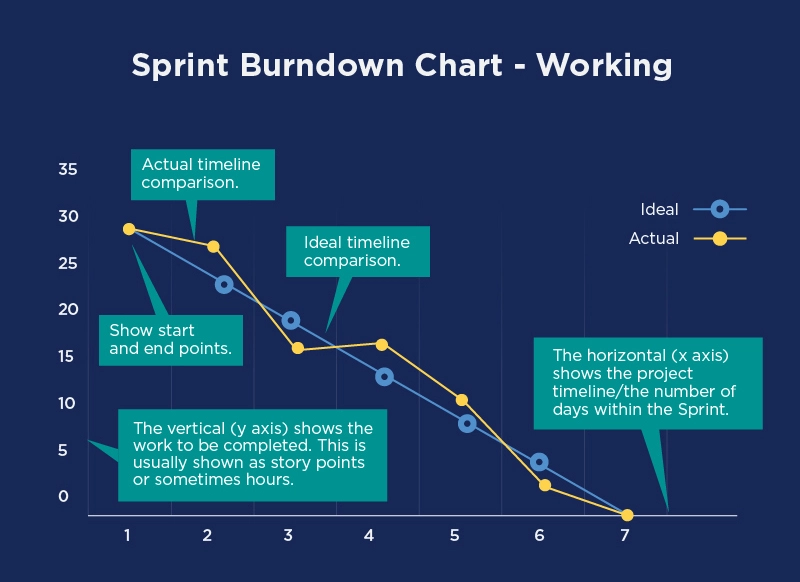
- Reading Burndown Charts.
- The x-axis is for days on the run.
- The y-axis depends on how much effort you put into it.
- The correct line shows how much progress you should make each day.
- And the actual line shows how much progress you are making each day.
Types of Burndown Charts:
Sprint burn charts
The Sprint Burndown Chart is used to track the amount of work remaining in the Sprint Project, and measures the chances of achieving a specified goal. It shows the completed work per day compared to the estimated completion rate for each runner. By tracking this information throughout a given sprint, teams can manage their progress very effectively.
To view the Sprint Burndown Chart, do the following:
Epic Burndown Chart View:
Burndown charts are easy to draw, and easy to read and understand. To learn, you need to know:
Types of Sprint Burn charts
What makes the chart an effective reporting tool is that it shows the progress of the team towards the Sprint Goal and not just in terms of time spent but how much work is left.
1st Sprint Burning Chart: Sprint Goal Met
A sample from the Burned Chart “Sprint Commitment Met” is shown above. Progress has been steady during this period, with no increase in performance or declining output which may indicate project problems.
Sprint Burndown 2 Chart: Running Goal Not Achieved
Teams are still committed to completing the Sprint as planned, but are unable to maintain their true speed. So, that means any work left at this point will be further developed in the future Sprints and may end up being more important than ever!
Sprint Burndown Chart 3: Running Goal Met Together Early
Here, the team works very well and can finish faster than expected. The team may be overly sensitive to the complexity of these issues, which explains why they are able to complete tasks so quickly.
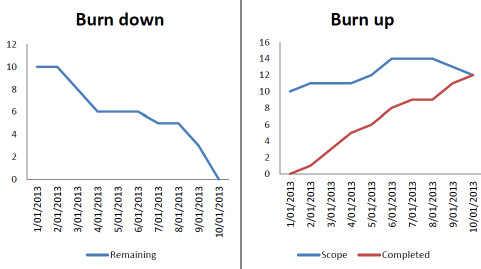
- Burnup charts are another well-liked possibility for visualizing a project. Burnup charts are unit-like hot charts as they share an identical linking system. However, the burn chart shows all the remaining work and therefore the temperature charts tell you how abundant you have gotten to date.
- Unlike rising temperature charts, temperature charts begin from very cheap and rise. Burnup charts even have a separate scope line showing however much your product and demand are. For a made project, the progress line of the burn chart meets the scope line at the tip.
- Simply put, burnout charts win owing to their vogue. Burnup charts, however, show a lot of details and might tell you concerning changes in scope earlier. Burndown charts can solely register changes in size and scope when completion of duplication. With temperature charts, you’ll be able to schedule changes in scope and increase your efforts to fulfill deadlines.
- Burndown charts are a vital tool for project managers owing to their options and adaptability. They are accustomed to being specialized in older commencement teams however currently they need to go on the far side of the commencement and are employed by any manager in spite of the tactic.
- Burndown charts are simply the start. Any made manager uses plenty of project management tools to examine a project and create the task as simple and attainable as attainable.
Burn up vs. burn down charts:
What Are the Limitations of a Burndown Chart?
The burn chart doesn’t reveal everything. for instance, it solely shows the quantity of points within the story completed. The burndown chart doesn’t show any changes, for instance, within the scope of labor as measured by the quantity of points within the backlog.
Therefore, it may be troublesome to mention that the changes within the burn chart square measure thanks to backlogs that are completed or thanks to a rise or decrease in story points. Having a burnup chart will solve this drawback by having a separate line within the graph of the whole backlog size.
However, there’s no burn or burn chart that offers a sign of what product square measure is left behind. Therefore, a hot chart will show progress however not whether or not the team is functioning on the correct factor. So, these charts square measure the simplest way to indicate trends instead of a team delivering the correct product log material.
Rely on smart Values
Another drawback with hot charts is the accuracy of the relevant work line. Whether or not the road of the actual activity is on top of or below the acceptable task line depends on the accuracy of the period of time estimates of tasks. Therefore, if the party overreacts to the time necessities, progress is created with a lot of accuracy if it’s not accessible before the point in time. however if they appear down on the necessities of the time, it’ll appear that they’re belated.
There is the simplest way to resolve this drawback, which is by inserting a good part into the new chart. Therefore, when the initial duplication of the project, the potency issue is recalculated to permit for a lot of accuracy.
- The most important feature of the burn chart is simplicity and flexibility. With this chart, you can get a lot of information even if things are not right for your project.
- The chart also provides direct comparisons between planned and actual progress, so you can quickly see if things are not going according to your plan.
- The provision of visual representation charts is a great help in maintaining effective collaboration. Managers need to keep everyone informed and on the same page.
- The burndown chart provides status reports and does not take much time to practice and read, so everyone can easily track.
- A hot chart can also be an excellent motivating tool for team members. It keeps everyone involved and regular comparisons and good performance on the graph encourage members to act consistently.
- In many fast-paced workplaces, the burn chart is especially important and is often the focus of the room as it keeps everyone informed and focused on their tasks.
Benefits of Learn Burndown Charts:
Conclusion:
As projects are so important and expansive as Scrum Master or Product Owner you may be frustrated by the lack of planning and team communication. Burndown charts are the perfect solution for this and will allow teams to better plan their run, which will improve productivity and ensure customer satisfaction. Jira software from Atlassian has a large number of tools including a Jira burn chart that will help the Scrum team on its journey to success.





