
- Introduction to Financial Management
- Financial Planning
- Capital Budgeting
- Capital Structure Decisions
- Working Capital Management
- Risk Management
- Dividend Decision
- Profit Planning and Control
Introduction to Financial Management
Financial management is a critical component of any business that involves the strategic planning, organizing, directing, and controlling of financial resources to achieve organizational goals. It ensures that an enterprise uses its financial assets efficiently to generate value and maintain economic stability. The core objective of financial management is to maximize shareholder wealth while maintaining adequate liquidity and risk control. Central to this discipline are the functions of financial management, which provide a framework for making sound financial decisions. These include investment decisions, financing decisions, dividend distribution, working capital management, and strategic planning often enhanced through PMP Training Each of these functions plays a vital role in supporting a company’s growth and long-term financial sustainability. By thoroughly understanding the functions of financial management, businesses can allocate resources wisely, forecast financial performance accurately, and adapt to changing market conditions. Furthermore, the functions of financial management enable financial managers to assess risks, control costs, and ensure that the company remains on a path of steady growth. In a dynamic economic environment, effective financial management is essential not just for survival but for gaining a competitive edge in the marketplace.
To Explore PMP in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive PMP Certification Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
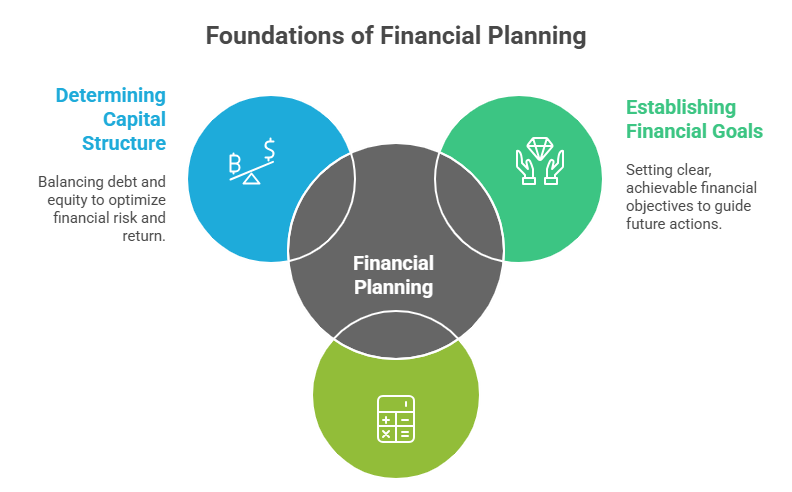
Financial Planning
- Establishing Financial Goals: Financial planning starts with setting short-term and long-term financial goals that align with the overall vision of the organization or individual.
- Estimating Capital Requirements: It involves assessing how much capital is needed for operations, expansion, and contingencies, helping avoid shortages or excesses a process that can be greatly supported by applying Key Tools and Techniques in Management Accounting.
- Determining Capital Structure: Financial planning helps decide the proportion of debt and equity in financing, balancing risk and return effectively.
Financial planning is the process of estimating the capital required and determining its composition to ensure a business has adequate funds to meet its goals. It involves setting financial objectives, developing budgets, forecasting future financial needs, and managing financial resources effectively. Proper financial planning helps organizations allocate resources efficiently, reduce financial risks, and ensure long-term sustainability.
- Framing Financial Policies: It includes creating clear policies related to cash control, credit, investment, and procurement of funds to guide financial decision-making.
- Ensuring Liquidity: A well-prepared financial plan ensures the business maintains sufficient liquidity to meet day-to-day expenses and obligations without stress.
- Monitoring and Reviewing: Continuous monitoring of financial performance against the plan allows timely adjustments and ensures the organization stays on track financially.
- Debt vs. Equity Financing: The primary decision involves determining the right balance between debt (loans, bonds) and equity (shares, retained earnings). Each has its advantages and risks.
- Cost of Capital: The goal is to minimize the company’s overall cost of capital, which is the weighted average of the cost of debt and equity, ensuring that financing is as cost-effective as possible an objective that can be better supported when you Achieve Goals with AI Powered Learning Tools
- Risk Management: Companies need to assess the financial risk associated with high levels of debt, including interest payments and the possibility of financial distress, while balancing the potential for higher returns.
- Control Considerations: Issuing equity can dilute ownership and control, whereas debt financing allows the existing owners to retain control of the company. This must be factored into capital structure decisions.
- Tax Implications: Debt financing offers tax benefits because interest payments are tax-deductible. This can make debt more attractive, especially for companies in higher tax brackets.
- Market Conditions and Economic Factors: Capital structure decisions are influenced by external factors such as interest rates, market conditions, and economic stability, which impact the availability and cost of both debt and equity.
- Risk Identification: The first step in risk management is identifying potential risks, whether financial, operational, market-related, or regulatory, that could impact the business.
- Risk Assessment and Evaluation: After identification, risks are assessed based on their likelihood and potential impact. This helps prioritize which risks need immediate attention and which can be managed over time.
- Risk Control Strategies: Businesses use various strategies to control risks, including avoidance, reduction, transfer (e.g., through insurance), or acceptance, depending on the nature and severity of the risk factors that can also influence roles and compensation, such as the Product Managers salary in India.
- Risk Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of identified risks ensures that the business stays alert to any changes in the risk landscape and can adapt strategies accordingly.
- Contingency Planning: Developing contingency plans ensures that the organization is prepared for unforeseen risks, helping to minimize the impact if adverse events occur.
- Employee Involvement and Training: Effective risk management involves employees at all levels, ensuring they are trained to recognize risks, follow procedures, and respond appropriately to mitigate potential threats.
Capital Budgeting
Capital budgeting is the process by which businesses evaluate and decide on long-term investments in assets and projects that are expected to generate future returns. It involves analyzing potential expenditures or investments such as purchasing new machinery, expanding operations, or launching new products. The goal of capital budgeting is to allocate resources efficiently by selecting projects that will maximize the firm’s value and contribute to long-term profitability. This process typically includes estimating future cash flows, assessing project risks, and applying evaluation techniques such as Net Present Value (NPV), Internal Rate of Return (IRR), Payback Period, and Profitability Index all of which are critical skills along the Product Manager Career Path A sound capital budgeting decision ensures that a company commits funds to projects that offer the best potential for growth and return on investment while minimizing financial risk. Effective capital budgeting also helps companies avoid over-investing in unprofitable ventures or under-investing in high-potential opportunities. By prioritizing projects based on strategic fit, financial viability, and expected return, businesses can maintain financial stability and drive sustainable growth. Since capital budgeting decisions often involve significant amounts of money and affect the company’s financial health for years, careful analysis and planning are essential. In today’s competitive market, effective capital budgeting is a cornerstone of sound financial management and strategic planning.
Are You Interested in Learning More About PMP? Sign Up For Our PMP Certification Training Today!
Capital Structure Decisions
Capital structure decisions refer to the choices made by a company regarding the mix of debt and equity financing used to fund its operations and growth. These decisions are crucial because they affect the company’s financial risk, cost of capital, and overall value. An optimal capital structure ensures that a company can finance its activities effectively while maintaining financial stability and maximizing shareholder wealth.
Are You Preparing for PMP Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Project Management Interview Questions & Answer to Boost Your Preparation!
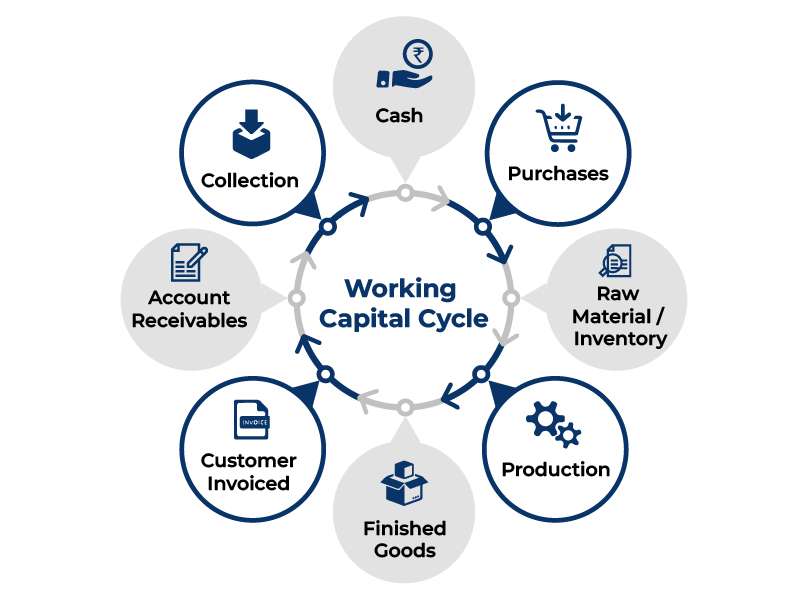
Working Capital Management
Working capital management is the process of managing a company’s short-term assets and liabilities to ensure smooth day-to-day operations and maintain financial stability. It involves efficiently managing the company’s current assets, such as cash, inventory, and receivables, along with current liabilities like accounts payable and short-term debts. The main goal of working capital management is to ensure that the company has enough liquidity to meet its short-term obligations while avoiding excess capital tied up in unproductive assets. Proper working capital management helps improve cash flow, reduce financing costs, and prevent financial distress. Key elements of working capital management include managing inventory levels to avoid overstocking or stockouts, optimizing the collection of receivables to maintain cash flow, and negotiating favorable terms with suppliers to extend accounts payable without harming relationships all of which can be streamlined through PMP Training. Effective management also involves monitoring cash flow closely and ensuring that there is an adequate cash balance to cover unexpected expenses or fluctuations in revenue. Inadequate working capital management can lead to operational inefficiencies, liquidity problems, and an increased risk of insolvency. On the other hand, overly conservative management can result in missed opportunities for growth and profitability. Therefore, striking the right balance in working capital management is essential for maintaining operational efficiency and financial health.
Risk Management
Risk management is the process of identifying, assessing, and prioritizing potential risks that could affect a company’s operations, finances, or reputation, followed by the implementation of strategies to minimize, monitor, and control these risks. Effective risk management helps businesses anticipate challenges, mitigate losses, and ensure long-term stability. It is essential for protecting assets, maintaining business continuity, and achieving organizational goals.
Dividend Decision
Dividend decision refers to the process by which a company determines the amount of profit to distribute to shareholders in the form of dividends versus retaining it for reinvestment in the business. This decision is crucial as it affects the company’s capital structure, stock price, and shareholder satisfaction. The dividend decision is influenced by various factors such as the company’s profitability, growth opportunities, cash flow situation, and the preferences of its shareholders.If the company is experiencing steady profits and limited investment opportunities, it may opt to distribute a larger portion of its profits as dividends. Conversely, if the company is focusing on expansion or has high-growth opportunities, it might retain earnings to finance these activities decisions that often align with strategic planning within Product Manager Roles Another important consideration is the company’s financial stability. Businesses with a stable cash flow are more likely to offer regular dividends, while those with volatile earnings may reduce or eliminate dividends to maintain financial flexibility. Tax considerations also play a role, as dividends are often taxed at different rates than capital gains. Ultimately, the dividend decision involves balancing the need for reinvestment with providing shareholders with a return on their investment. An optimal dividend policy ensures both short-term shareholder satisfaction and long-term business growth.
Are You Considering Pursuing a Master’s Degree in PMP? Enroll in the PMP Masters Program Training Course Today!
Profit Planning and Control
Profit planning and control is the process by which businesses set profit goals and devise strategies to achieve and monitor those goals over a specified period. It involves forecasting revenues, estimating expenses, and determining the necessary actions to maximize profitability. Profit planning begins with setting clear financial objectives based on market conditions, company resources, and growth targets. It requires the development of detailed budgets, cost control mechanisms, and performance metrics to track progress, all of which can be effectively managed with the help of PMP Training. Control mechanisms are implemented to compare actual performance against planned outcomes, allowing managers to identify variances and take corrective actions if needed. Effective profit planning ensures that resources are allocated efficiently, costs are managed, and revenue targets are met. It also provides a framework for decision-making, helping businesses prioritize investments, manage cash flow, and assess risk. Regular monitoring and analysis of profit performance are essential for identifying trends, making timely adjustments, and ensuring long-term financial sustainability. In addition to maximizing short-term profits, profit planning and control focus on the strategic alignment of financial goals with overall business objectives. By creating a structured approach to both planning and control, organizations can improve profitability, maintain competitiveness, and achieve consistent financial growth.





