
- Introduction: Understanding Projects in Project Management
- Defining a Project: Key Characteristics
- The Project Lifecycle
- Types of Projects in Project Management
- Project Features: Elements That Make a Project Successful
- The Role of a Project Manager
- Project Management Methodologies
- Challenges in Project Management
- The Importance of Projects in Achieving Organizational Goals
- Conclusion
Introduction: Understanding Projects in Project Management
In the field of project management, a project is defined as a temporary endeavor undertaken to create a unique product, service, or result. Projects are distinct from ongoing operations because they are finite, with defined start and end points. They also require resources such as time, money, and personnel and often involve complex coordination and planning. Whether in the corporate world, government, or nonprofit sectors, successful project management is critical to ensuring that goals are met within the given constraints of time, budget, and quality. In this blog, we’ll explore what constitutes a project, break down the key characteristics of projects, highlight the different types of projects, and discuss the features that contribute to successful project management. Additionally, if you’re looking to further develop your skills, PMP Training can be an excellent opportunity to expand your knowledge and expertise in project management.
Defining a Project: Key Characteristics
A project is not just any task or set of activities it is defined by certain characteristics that set it apart from routine, ongoing operations. Let’s take a look at the key characteristics of a project.
2.1 Unique PurposeEvery project has a unique purpose or objective. This purpose typically involves creating something new or making a significant change. Whether it’s building a new software application, constructing a bridge, or launching a marketing campaign, the end result should provide a new product, service, or outcome that hasn’t been achieved before. For those interested in exploring a structured approach to managing projects, Traditional Project Management offers a well-established methodology to guide projects from start to finish.
2.2 Defined Start and End DatesOne of the most important characteristics of a project is that it has defined start and end dates. Unlike ongoing operations that run indefinitely, projects have a clear timeline. This timeline might range from a few weeks to several years, depending on the complexity and scope of the project. The defined timeline is crucial for setting expectations, allocating resources, and measuring progress.
2.3 Limited ResourcesEvery project operates under constraints, which means that resources such as time, money, and personnel are limited. One of the roles of the project manager is to efficiently utilize these resources to complete the project successfully. Budget constraints and time limitations are often key drivers in project planning.
2.4 Specific DeliverablesA project is expected to produce specific deliverables, tangible or intangible outcomes that meet the requirements of stakeholders. These deliverables could be anything from a completed construction project, a software product, or a marketing report. The deliverables are what define the project’s success and are typically outlined in the project scope.
2.5 Progressive ElaborationA project often requires progressive elaboration, which means that details are refined and developed as the project progresses. This process allows teams to adjust plans based on new information, changing requirements, or unexpected challenges. Progressive elaboration helps ensure the project is aligned with its objectives and constraints.
Become a Project Management expert by enrolling in this PMP Training Online Course today.
The Project Lifecycle
The project lifecycle refers to the series of phases a project goes through from start to finish. The lifecycle provides a structured approach to managing the project and ensures that all necessary activities are completed in the correct order.
3.1 InitiationDuring the initiation phase, the project’s feasibility is assessed, and key stakeholders are identified. A project charter or a similar document is created to formally authorize the project. This phase sets the direction for the entire project and aligns stakeholders on goals and expectations. To help organize and break down the project’s scope, the Work Breakdown Structure can be a valuable tool for ensuring that all deliverables are clearly defined and manageable.
3.2 PlanningThe planning phase involves creating detailed plans for executing the project. This includes defining the scope, budget, timeline, resources, and risks. A detailed project management plan is developed, outlining how each aspect of the project will be managed throughout its lifecycle.
3.3 ExecutionThe execution phase is where the project work takes place. The project team carries out the tasks defined in the planning phase to produce the deliverables. This phase typically requires coordination, communication, and resource management to ensure that everything runs smoothly.
3.4 Monitoring and ControllingThe monitoring and controlling phase runs concurrently with the execution phase. During this phase, the project manager tracks progress against the plan, identifies any variances, and takes corrective action when necessary. Monitoring and controlling ensure the project stays on track to meet its objectives.
3.5 ClosingThe closing phase occurs once all the project deliverables are completed. In this phase, the project is formally closed, and any final documentation or approvals are completed. The project manager reviews the entire project to ensure that all objectives have been met, and a post-project evaluation may be conducted to learn from the project experience.
Advance your Project Management career by joining this PMP Training Online Course now.
Types of Projects in Project Management
There are different types of projects based on industry, scope, and purpose. Let’s look at some common project types in project management.
4.1 Construction ProjectsConstruction projects include building infrastructure such as roads, bridges, buildings, and other physical structures. These projects are highly complex, with significant resource allocation, safety considerations, and regulatory compliance. Construction projects often involve a wide range of stakeholders, including contractors, architects, engineers, and government agencies.
4.2 IT ProjectsIT projects involve developing, implementing, or maintaining information technology systems or solutions. These projects may include building new software applications, integrating systems, or upgrading IT infrastructure. IT projects require specialized knowledge and often face challenges like rapidly changing technologies and evolving stakeholder needs.
4.3 Research and Development ProjectsResearch and development (R&D) projects aim to create new products, services, or technologies through research and innovation. These projects often involve experimentation and exploration, with an emphasis on discovering new possibilities. R&D projects can be long-term and carry a higher level of uncertainty and risk. Effective Supply Chain Management is essential in ensuring that the necessary resources and materials are available for successful execution of these projects.
4.4 Event Management ProjectsEvent management projects focus on planning and executing events such as conferences, weddings, corporate gatherings, or concerts. These projects typically involve detailed logistical planning, managing multiple vendors, and ensuring a seamless experience for participants. Event management projects are time-sensitive and require careful coordination.
4.5 Organizational Change ProjectsOrganizational change projects aim to improve or transform aspects of an organization, such as implementing new systems, processes, or business models. These projects often require managing change resistance, communication with stakeholders, and careful planning to ensure successful implementation.
4.6 Product Development ProjectsProduct development projects involve designing, creating, and launching new products. These projects require collaboration across various departments such as marketing, design, engineering, and manufacturing. Product development projects can be iterative and often follow a structured process to ensure the product meets market needs.
Project Features: Elements That Make a Project Successful
Several key features contribute to the success of a project. Let’s explore some of these elements.
5.1 Clear ObjectivesHaving clear, well-defined objectives is essential for a successful project. These objectives should align with the project’s goals and the organization’s strategic vision. Clear objectives help guide decision-making and provide focus for the project team.
5.2 Effective Project PlanningEffective planning is at the heart of successful project management. A detailed project plan should outline tasks, milestones, timelines, budgets, and risks. Proper planning ensures that resources are allocated efficiently and that the team is aligned on project goals and expectations.
5.3 Resource ManagementManaging resources, such as time, budget, and personnel, is a crucial aspect of project success. Resource management ensures that resources are allocated to the right tasks, that there is minimal waste, and that the project stays within budget and timeline constraints. Applying quality control principles like the Rule of Seven can help project managers identify patterns or issues early, allowing for timely adjustments and better resource utilization.
5.4 Risk ManagementEvery project involves risks, and proactive risk management is vital to success. By identifying potential risks early on, assessing their impact, and creating contingency plans, project managers can mitigate negative outcomes and ensure that the project stays on track.
5.5 Stakeholder EngagementEngaging with stakeholders throughout the project is essential for ensuring that their needs are met and that the project remains aligned with their expectations. Stakeholder engagement fosters communication, builds trust, and minimizes misunderstandings during the project.
The Role of a Project Manager
The project manager plays a crucial role in overseeing the entire project, from initiation to closing. Their responsibilities span planning, executing, monitoring, and controlling the project to ensure it meets its goals, stays on track, and is completed on time. During the planning phase, the project manager defines objectives, allocates resources, and establishes timelines. They then execute the plan, ensuring tasks are carried out as planned. Throughout the project, the manager monitors progress, addresses issues, and makes adjustments as needed. Effective communication with stakeholders is key, keeping them informed and ensuring their expectations are met. Additionally, the project manager is responsible for identifying and managing risks to minimize potential disruptions. They also ensure that resources, such as time, money, and team efforts, are utilized efficiently to optimize performance and deliver value. PMP Training can be an excellent resource for those looking to enhance their project management skills. Overall, the project manager ensures that all aspects of the project align with the desired outcomes and business objectives.
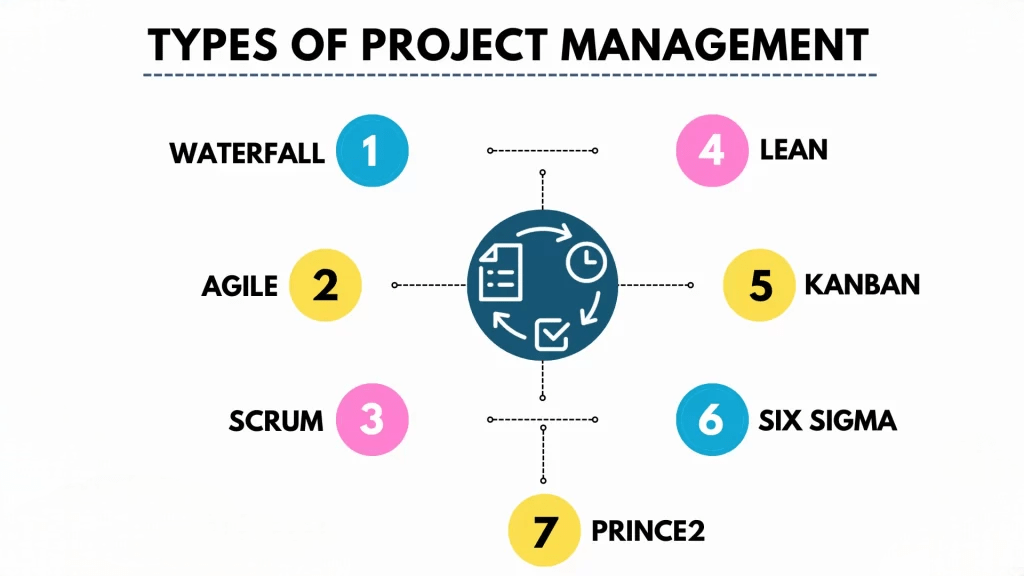
Project Management Methodologies
There are several methodologies for managing projects, and the right one depends on the project type, scope, and objectives.
7.1 Waterfall MethodologyThe Waterfall methodology is a linear, sequential approach where each phase of the project is completed before moving on to the next. It’s best suited for projects with well-defined requirements and low uncertainty.
7.2 Agile MethodologyThe Agile methodology focuses on iterative development, where the project is broken down into smaller phases or sprints. Agile is best for projects with evolving requirements and a need for flexibility, such as IT and software development projects.
7.3 Hybrid MethodologyThe Hybrid methodology combines elements of both Waterfall and Agile, allowing project managers to adjust their approach depending on the specific needs of the project.
Are you getting ready for your PMP interview? Check out our blog on PMP Interview Questions and Answers!
Challenges in Project Management
Project management comes with its share of challenges, including scope creep, budget overruns, team conflicts, and time constraints. Scope creep occurs when the project’s scope expands beyond the initial plan, leading to delays and increased costs. Budget overruns are often a result of poor estimation, unforeseen changes, or inadequate resource allocation. Team conflicts can arise due to differing opinions, miscommunication, or unclear roles, which can hinder progress. Time constraints are another common challenge, often leading to rushed work and compromised quality. To address these challenges, effective communication is crucial, keeping all team members and stakeholders informed and aligned on expectations. Strong stakeholder management ensures that their needs are understood and prioritized without derailing the project’s goals. Robust planning, including clear milestones, risk management strategies, and realistic timelines, helps anticipate and mitigate potential issues before they impact the project’s success. Additionally, using techniques like Structured Brainstorming can help generate creative solutions to complex problems and foster collaboration among team members. By tackling these challenges head-on, project managers can steer projects toward successful completion.
The Importance of Projects in Achieving Organizational Goals
Projects are vital to achieving an organization’s strategic objectives, as they serve as the means to execute specific initiatives that drive innovation, improvement, and growth. By focusing on defined tasks with clear outcomes, projects help translate long-term goals into actionable steps. They enable organizations to introduce new products, enhance existing services, streamline processes, and adapt to changing market conditions. Each project, whether large or small, contributes to the organization’s ability to stay competitive and meet evolving customer demands. By carefully managing projects to align with strategic priorities, organizations ensure that resources are used effectively, risks are minimized, and value is delivered. Ultimately, successful projects are crucial for realizing the organization’s vision and fostering continuous growth and improvement.
Conclusion
Understanding what constitutes a project and recognizing its key features is essential for successful project management. A project is a temporary endeavor with a specific objective, a defined start and end, and the goal of producing a unique product, service, or result. To drive success, projects require clear objectives that align with organizational goals, effective planning, and proper resource management. Engaging stakeholders throughout the project ensures alignment with their needs and expectations, contributing to project success. Project management methodologies, such as Agile, Waterfall, or Scrum, provide structured frameworks for organizing tasks, managing risks, and ensuring efficient resource utilization. These methodologies help guide project managers in tracking progress, adjusting plans when necessary, and maintaining focus on delivering value. By using these tools and techniques, project managers can increase the likelihood of achieving successful outcomes, driving innovation, and meeting both customer and organizational expectations. Additionally, PMP Trainingcan provide valuable knowledge and skills to further enhance your project management capabilities.





