
- Definition
- Types of CSR
- Importance in Business
- CSR Laws in India
- Role in Brand Building
- Reporting & Auditing
- Criticisms of CSR
- Conclusion
Definition
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is a business approach where companies voluntarily integrate social and environmental concerns into their everyday operations and relationships with stakeholders. Unlike traditional business models focused primarily on maximizing profits, CSR emphasizes a balanced approach that considers the broader impact a company has on society and the environment. This self-regulating framework encourages organizations to be accountable not only to their shareholders but also to employees, customers, communities, and the planet. By adopting CSR, businesses demonstrate a commitment to ethical practices that go beyond legal compliance, reflecting values of fairness, sustainability, and respect. CSR initiatives can take many forms depending on a company’s goals and industry. Common activities include charitable donations, community engagement, implementing fair labor policies, reducing environmental impact through sustainable resource use and minimizing waste, and promoting diversity and inclusion within the workforce. These efforts help improve the quality of life for employees, their families, and the wider community. Moreover, CSR fosters long-term economic development by building trust and goodwill among customers and stakeholders, which can translate into stronger brand reputation and customer loyalty. In today’s globalized world, companies face increasing pressure from consumers, regulators, and investors to operate responsibly. Businesses that embrace CSR not only contribute positively to society but also gain competitive advantages by attracting talent, improving operational efficiencies, and mitigating risks. Ultimately, CSR reflects a holistic vision where economic success goes hand-in-hand with social progress and environmental stewardship, shaping a sustainable future for all.
To Explore PMP in Depth, Check Out Our Comprehensive PMP Certification Training To Gain Insights From Our Experts!
Types of CSR
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) activities are commonly grouped into four main categories: environmental responsibility, ethical responsibility, philanthropic responsibility, and economic responsibility. Environmental responsibility focuses on efforts to minimize a company’s ecological footprint. This includes actions like adopting renewable energy sources, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, managing waste effectively, and sourcing materials sustainably. These initiatives help preserve natural resources and combat climate change, aligning business practices with global environmental goals. Ethical responsibility centers on maintaining high standards of fairness and integrity within the workplace and supply chains. It involves ensuring fair labor practices, protecting human rights, promoting workplace safety, and combating corruption or unethical behavior. Companies committed to ethical responsibility strive to create safe and inclusive work environments while respecting the rights of all stakeholders. Philanthropic responsibility refers to voluntary efforts aimed at giving back to society. This can take the form of charitable donations, supporting education and healthcare initiatives, volunteering programs, and community development projects. These activities demonstrate a company’s dedication to social welfare and help build stronger ties with the communities where they operate. Economic responsibility involves adopting business practices that promote sustainable economic growth without exploiting stakeholders.

This includes transparent financial reporting, fair trade, supporting local businesses, and creating jobs. By ensuring economic responsibility, companies contribute to the financial well-being of their employees, customers, suppliers, and the wider community. Organizations may prioritize one or more of these CSR categories based on their size, industry, values, and strategic goals. Together, these dimensions form a comprehensive framework for businesses to operate responsibly and contribute positively to society and the environment.
Importance in Business
- Enhances Brand Reputation and Customer Loyalty: Companies that engage in CSR build a positive public image. Consumers are more likely to trust and stay loyal to brands that actively demonstrate concern for social and environmental issues.
- Attracts and Retains Talent: A strong CSR commitment appeals to today’s workforce, particularly millennials and Gen Z, who seek employers with values that align with their own. CSR initiatives contribute to a sense of purpose and employee satisfaction.
- Leads to Cost Savings: CSR encourages sustainable practices such as reducing energy usage, minimizing waste, and optimizing resource consumption. These practices can significantly lower operational costs over time.
- Improves Access to Capital: Investors increasingly look for socially responsible companies when making investment decisions. Strong CSR performance can lead to higher investor confidence and better access to funding opportunities.
- Ensures Legal and Regulatory Compliance: With growing environmental and labor regulations, CSR helps businesses stay compliant, reducing the risk of legal penalties and reputational damage.
- Strengthens Stakeholder Relationships: CSR fosters trust and engagement with key stakeholders, including customers, employees, governments, and local communities. Strong relationships improve cooperation and long-term success.
- Supports Long-Term Sustainability: Companies that integrate CSR into their core operations are more adaptable to change and resilient in the face of global challenges, ultimately positioning themselves for long-term growth and stability.
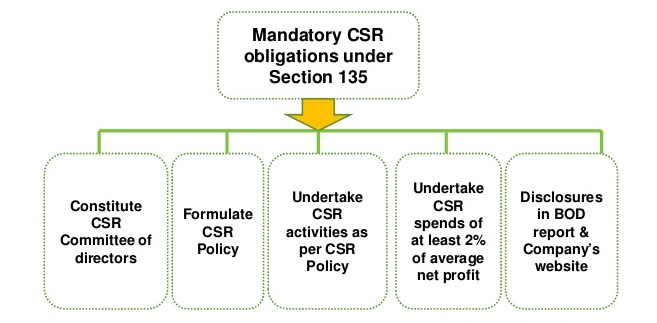
- Mandatory CSR Spending: As per Section 135 of the Companies Act, 2013, companies meeting certain financial thresholds must spend at least 2% of their average net profits from the past three financial years on CSR activities, making India one of the first countries to legally mandate CSR contributions.
- Eligibility Criteria: The CSR requirement applies to companies with a net worth of ₹500 crore or more, turnover of ₹1,000 crore or more, or net profit of ₹5 crore or more during any financial year. This ensures that only sizable, profit-making companies are obligated to participate.
- CSR Committee Requirement: Eligible companies must form a CSR committee consisting of at least three board members. This committee is responsible for developing, implementing, and monitoring the company’s CSR policy and activities.
- Defined Areas for CSR Investment: Schedule VII of the Companies Act provides a clear list of focus areas where CSR funds can be allocated. These include education, healthcare, gender equality, environmental sustainability, protection of national heritage, and rural development, among others.
- Mandatory Compliance: Amendments introduced in 2021 made CSR spending mandatory rather than voluntary. Companies that fail to comply with these requirements may face financial penalties and must disclose reasons for any shortfall.
- Impact on Corporate Strategy: The legal framework has pushed companies to align their business strategies with social goals, leading to more structured and impactful CSR initiatives.
- Boost to Social Development: By enforcing CSR as a statutory obligation, India has seen a significant increase in corporate contributions to social causes, thereby enhancing the role of businesses in national development.
- Mandatory Disclosure in India: Under the Companies Act, 2013, Indian companies falling under CSR requirements must disclose CSR activities and expenditures in their annual reports and on their websites, ensuring regulatory compliance and public transparency.
- Detailed Reporting Requirements: CSR reports must include specific details such as the composition of the CSR committee, total amount spent, reasons for any unspent funds, and comprehensive descriptions of CSR projects and outcomes.
- Global Reporting Standards: Many companies worldwide adopt established frameworks like the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), Integrated Reporting (IR), and Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) to structure and standardize their CSR disclosures, improving clarity and comparability.
- Independent Auditing: External audits of CSR initiatives help verify that allocated funds are used efficiently and that reported activities and results are accurate. This enhances the credibility of CSR efforts and promotes accountability.
- Third-Party Verification: Increasingly, companies are employing independent third parties to assess and validate their CSR claims. This adds an additional layer of trust and helps prevent misleading information or “greenwashing.”
- Measuring Social Impact: Transparent reporting serves not only compliance purposes but also allows companies to measure the social and environmental impact of their initiatives, which is essential for long-term strategy and improvement.
- Stakeholder Trust and Engagement: Consistent, transparent CSR reporting builds trust with stakeholders, customers, investors, employees, and communities by demonstrating a company’s genuine commitment to social responsibility and ethical practices.
Are You Preparing for PMP Jobs? Check Out ACTE’s Project Management Interview Questions & Answer to Boost Your Preparation!
CSR Laws in India
Role in Brand Building
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) plays a crucial role in shaping a company’s brand identity and enhancing its reputation in the marketplace. When a business actively demonstrates its commitment to social and environmental causes through well-planned CSR initiatives, it sets itself apart from competitors by highlighting its core values, ethics, and dedication to making a positive impact. This approach helps humanize the brand, allowing customers and communities to form emotional connections based on shared concerns and principles. For example, companies that focus on environmental sustainability often attract eco-conscious consumers who prefer to support businesses aligned with their values. In addition to building customer loyalty, CSR activities often lead to positive media attention and favorable word-of-mouth promotion. These benefits contribute to a stronger public image and increased visibility, which can translate into higher sales and market share. Internally, CSR strengthens organizational culture by fostering employee pride, satisfaction, and engagement. Employees tend to feel more motivated and committed when they work for socially responsible companies, which enhances productivity and reduces turnover. During times of crisis or controversy, companies with a solid CSR reputation are better positioned to maintain customer trust and goodwill, helping them recover more quickly. Overall, CSR is much more than a philanthropic obligation; it serves as a strategic tool that enhances brand equity, attracts investors, and boosts employee morale. By integrating CSR into their core business strategies, companies can create lasting value for both society and themselves, ensuring sustainable success over the long term.
Reporting & Auditing
Are You Considering Pursuing a Master’s Degree in PMP? Enroll in the PMP Masters Program Training Course Today!
Criticisms of CSR
Despite its positive goals, Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) has faced significant criticism on multiple fronts. One major issue is “greenwashing,” where companies exaggerate or falsely advertise their environmental or social efforts to appear more responsible than they actually are. Critics argue that in some cases, CSR is used primarily as a marketing tool to distract from unethical business practices or to improve a company’s public image without making real, meaningful changes. This undermines the credibility of CSR initiatives and can mislead consumers and stakeholders. Another common criticism is the lack of standardization in CSR reporting and practices. Because there are no universally accepted metrics or frameworks, it becomes difficult to measure the true impact of CSR activities or to compare performance between companies. This inconsistency creates confusion and sometimes skepticism about the actual benefits of CSR programs. Some critics also argue that CSR diverts focus from a company’s primary objective of generating profits and maximizing shareholder value. They contend that CSR should be voluntary and driven by genuine commitment rather than regulatory mandates. For example, in India, where CSR spending is legally required, there is concern that such enforcement leads to token gestures rather than meaningful, sustainable development. Additionally, CSR efforts can sometimes create dependency among beneficiary communities instead of empowering them to become self-sufficient. For CSR to be truly effective, it must be authentic, transparent, and deeply integrated with a company’s core values and long-term business strategy. Only then can CSR move beyond superficial efforts and contribute to real social and environmental progress.
Are You Interested in Learning More About PMP? Sign Up For Our PMP Certification Training Today!
Conclusion
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) has become an essential component of sustainable and ethical business practices. It represents a company’s dedication to acting as a responsible corporate citizen, contributing positively to society and the environment. Originally viewed as a voluntary and philanthropic effort, CSR has evolved into a strategic priority and, in many cases, a legal requirement that influences how companies conduct their operations. In today’s world, where businesses face pressing challenges such as climate change, social inequality, and resource scarcity, CSR provides a framework for companies to actively participate in creating solutions that benefit not only their stakeholders but society at large. When CSR is implemented authentically and strategically, it delivers multiple benefits. Beyond helping communities and protecting the environment, CSR initiatives enhance a company’s brand reputation, build stakeholder trust, and support long-term business growth. Customers are increasingly favoring brands that demonstrate social responsibility, employees seek workplaces aligned with their values, and investors are focusing more on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria when making decisions. This shift in expectations means that CSR is no longer an optional add-on but a vital part of corporate strategy that drives competitive advantage. As the global economy continues to evolve, the importance of CSR will only increase. Companies that embrace their social and environmental responsibilities will be better positioned to thrive in a world demanding transparency, accountability, and positive impact. Ultimately, CSR stands as a cornerstone for businesses committed to sustainable success and meaningful contributions to the world.





