
- Overview of Indian Stock Market
- Key Exchanges (BSE, NSE)
- Regulatory Bodies (SEBI)
- Types of Securities Traded
- Market Participants
- Investment Instruments
- Trading Mechanisms
- Risk Management
Overview of Indian Stock Market
The Indian stock market is one of the most dynamic and fast-growing markets in the world, offering a wide range of investment opportunities for individuals and institutions alike. At its core, the market operates through major stock exchanges in India such as the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) and the National Stock Exchange (NSE), where shares of publicly listed companies are traded daily. The Indian stock market index, including benchmarks like the Sensex and Nifty 50, reflects the overall performance and health of the market, guiding investors in their decisions. These indices track the movement of top-performing companies and are key indicators of market trends. For investors seeking to make informed choices, tools like stock screener India platforms are essential. These screeners help filter stocks based on various financial metrics such as market capitalization, price-to-earnings ratio, volume, and more, enabling smarter investment strategies. Whether you’re a seasoned trader or a beginner, understanding the Indian stock market’s structure, indices, and analytical tools is crucial to navigating its complexities and seizing potential gains. With increasing digital access and regulatory support, more people are now entering the stock market, making it an integral part of India’s economic growth and financial future.
Do You Want to Learn More About Database? Get Info From Our Database Online Training Today!
Key Exchanges (BSE, NSE)
- Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE): Established in 1875, BSE is Asia’s oldest stock exchange and home to Sensex India, the benchmark index tracking 30 financially strong companies.
- National Stock Exchange (NSE): Launched in 1992, NSE introduced fully automated electronic trading and is widely used for its Nifty 50 index, representing top 50 companies.
- Sensex and Nifty: Both indices serve as barometers for market sentiment and are key indicators for identifying the best share in India to invest in.
India’s equity market operates primarily through two major platforms the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) and the National Stock Exchange (NSE). These key exchanges play a critical role in the growth of the share bazar India, offering transparent and regulated environments for trading securities. They facilitate various trading mechanisms such as intraday, delivery, futures, and options trading. Understanding these exchanges is essential for anyone aiming to invest in the best share in India or explore global connections like Nasdaq India. Here’s a closer look at both exchanges:
- Trading Mechanisms: BSE and NSE support modern trading mechanisms including algorithmic and high-frequency trading.
- Global Integration: Initiatives like Nasdaq India reflect increasing globalization and foreign investor interest.
- Retail Participation: With easier digital access, more retail investors are entering the share bazar India, boosting liquidity and market depth.
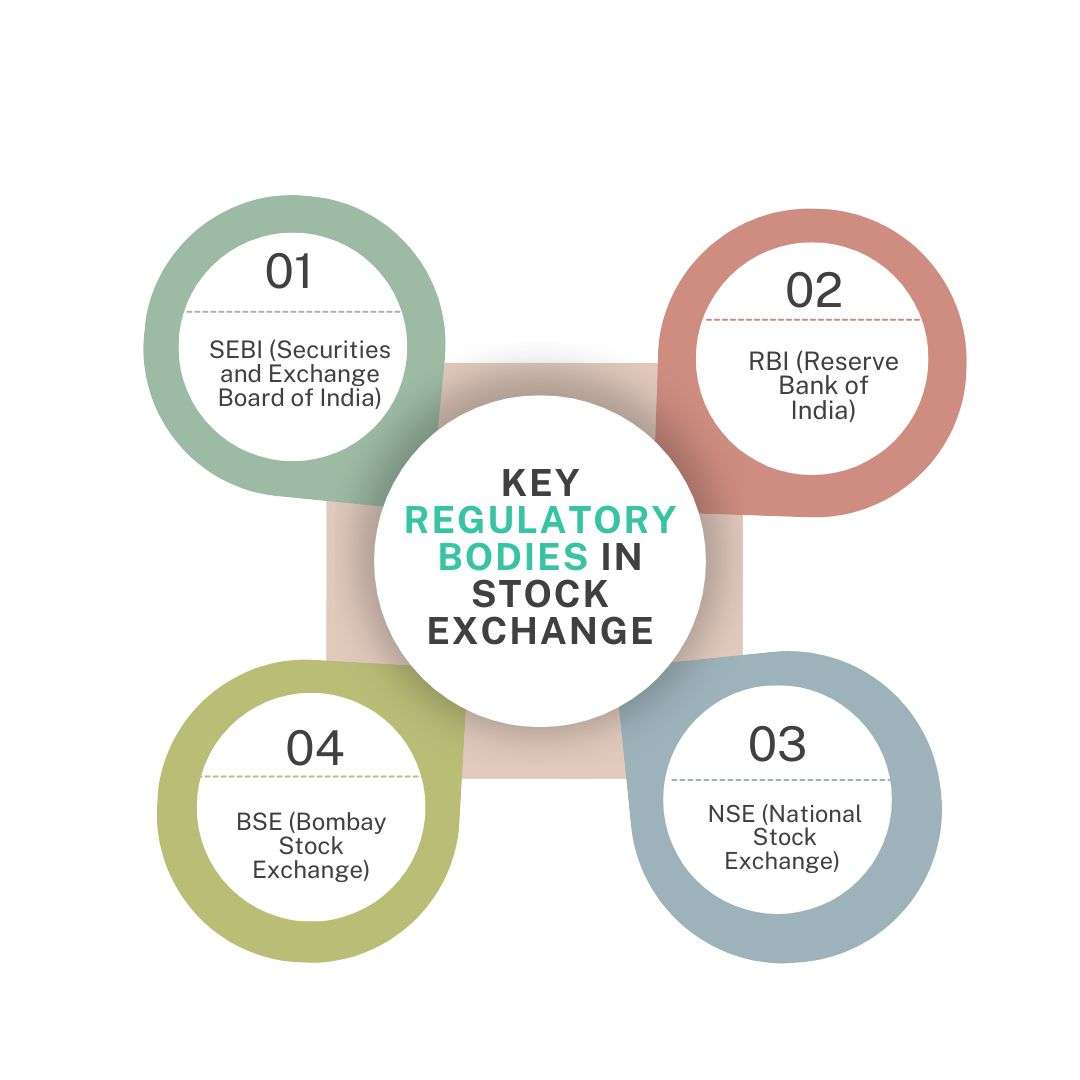
Regulatory Bodies (SEBI)
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) serves as the primary regulatory body overseeing the functioning of the Indian capital markets, ensuring transparency, investor protection, and fair practices across all trading activities. Established in 1992, SEBI plays a pivotal role in regulating the operations of every stock exchange in India, including major ones like the NSE and BSE, and supervises all market intermediaries such as brokers, mutual funds, and portfolio managers. By setting guidelines and enforcing compliance, SEBI maintains the integrity of the Indian stock market index, including benchmarks like the Sensex and Nifty, which are widely followed by investors. It also ensures that corporate disclosures and trading activities adhere to strict legal and ethical standards. SEBI’s initiatives promote market education, awareness, and accessibility, especially for retail investors. In the digital age, SEBI supports tools like stock screener India platforms that help investors make informed decisions by offering data-driven insights into company performance and market trends. With SEBI’s proactive surveillance and governance, the Indian stock market continues to evolve as a robust and investor-friendly ecosystem, playing a crucial role in the nation’s economic development and wealth creation.
Would You Like to Know More About Database? Sign Up For Our Database Online Training Now!
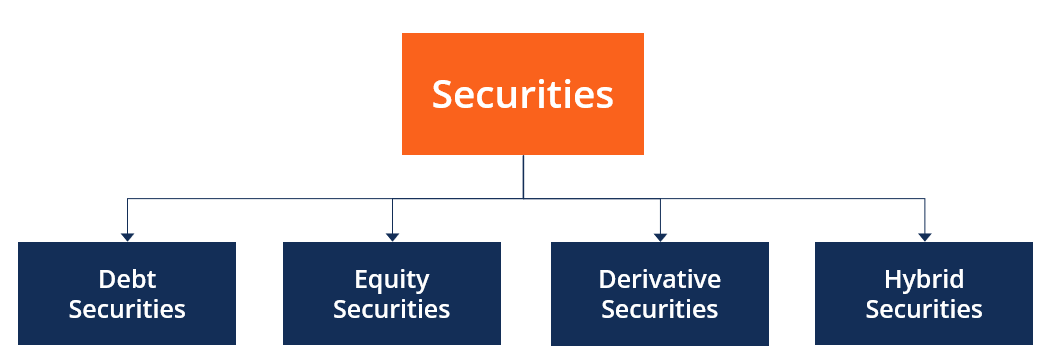
Types of Securities Traded
- Equity Shares: These represent ownership in a company and entitle investors to dividends and voting rights. They are the most commonly traded securities and form the basis of key indices like the Sensex and Nifty.
- Preference Shares: These offer fixed dividends and have priority over equity shares in the event of liquidation but usually lack voting rights.
- Debentures and Bonds: These are fixed-income instruments issued by companies or the government to raise capital, offering regular interest payments.
The Indian stock market offers a diverse range of securities for trading, catering to various investor profiles and risk appetites. These instruments are traded across every major stock exchange in India, such as BSE and NSE, and are key components of the Indian stock market index, which reflects overall market performance. To analyze and choose the right investment opportunities, tools like stock screener India platforms are commonly used. Here’s an overview of the main types of securities traded:
- Derivatives: Instruments like futures and options are traded for hedging or speculative purposes, often based on underlying assets like stocks or indices.
- Mutual Funds and ETFs: These pooled investment vehicles allow investors to gain exposure to a diversified portfolio, including those that mirror the Indian stock market index.
- Government Securities (G-Secs): These are low-risk instruments issued by the government, ideal for conservative investors looking for stability in their portfolio.
- Equity Shares: Representing ownership in a company, equity shares are the most popular investment instrument and are heavily weighted in the Indian stock market index.
- Mutual Funds: These are professionally managed funds that pool money from various investors to invest in diversified portfolios, including equities, bonds, and other assets.
- Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs): ETFs are similar to mutual funds but are traded like stocks on a stock exchange in India, often tracking specific indices or sectors.
- Debentures and Bonds: These fixed-income instruments offer regular interest payments and are ideal for conservative investors seeking predictable returns.
- Derivatives (Futures and Options): Used for hedging or speculation, derivatives derive value from underlying assets like stocks or indices.
- Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs): These offer exposure to real estate without owning property directly and are becoming an emerging choice for portfolio diversification.
Market Participants
The Indian stock market is a vibrant ecosystem driven by a diverse group of market participants, each playing a unique role in shaping the dynamics of the share bazar India. These participants include retail investors, institutional investors, foreign portfolio investors (FPIs), mutual funds, brokers, and market makers. Retail investors form a growing segment, actively trading and investing in the best share in India using both traditional and digital platforms. Institutional investors and FPIs bring in large-scale capital and often influence market trends and liquidity. Brokers and sub-brokers act as intermediaries, facilitating transactions on key stock exchanges like NSE and BSE, while market makers help maintain liquidity by continuously quoting buy and sell prices. These participants engage using a range of trading mechanisms, including intraday, delivery-based, and derivatives trading, tailored to different risk appetites and investment goals. Benchmark indices like Sensex India not only guide investment decisions but also reflect the overall market sentiment and performance. With global integration on the rise, links to platforms like Nasdaq India are fostering cross-border opportunities and investor confidence. Together, these market players ensure the smooth functioning, depth, and resilience of India’s financial markets, making them more accessible, efficient, and robust than ever before.
To Earn Your Database Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Blockchain Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Database Online Training Today!
Investment Instruments
The Indian stock market offers a wide array of investment instruments that cater to different financial goals, risk tolerances, and investment horizons. These instruments are traded across every major stock exchange in India such as NSE and BSE, and many of them are key contributors to the Indian stock market index, which tracks market performance. For selecting suitable investments, tools like stock screener India help investors analyze and compare options effectively. Here are six common investment instruments in the Indian market:
Trading Mechanisms
Trading mechanisms in the Indian stock market have evolved significantly over the years, offering investors efficient, transparent, and technology-driven platforms for buying and selling securities. These mechanisms are the backbone of the share bazar India, enabling seamless transactions across key exchanges like BSE and NSE. The most common types include intraday trading, delivery-based trading, derivatives trading (futures and options), and algorithmic trading. Intraday trading involves buying and selling stocks within the same day, while delivery trading focuses on holding shares for the long term. Derivatives are used by traders to hedge risk or speculate on price movements, often linked to key indices like Sensex India. Algorithmic and high-frequency trading, driven by pre-set strategies and technology, are gaining traction among institutional investors. These trading mechanisms help investors identify and act on opportunities quickly, especially when seeking the best share in India to invest in. With global markets becoming increasingly interconnected, platforms like Nasdaq India are influencing trading behavior and offering access to international exposure. Whether you’re a retail trader or an institutional investor, understanding and leveraging the right trading mechanism is essential for success in the modern financial landscape of India’s dynamic stock market.
Preparing for a Database Job? Have a Look at Our Blog on Database Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Risk Management
Risk management is a crucial aspect of investing in the stock market, helping investors protect their capital and make informed decisions in a volatile environment. In the context of the Indian financial ecosystem, effective risk management begins with understanding market dynamics and utilizing tools that support strategic planning. Investors closely monitor the Indian stock market index, such as the Sensex and Nifty, which reflect the overall market sentiment and help gauge potential risks associated with macroeconomic or sector-specific trends. Being aware of these indices enables investors to adjust their portfolios accordingly and avoid excessive exposure to market downturns. Trading on any stock exchange in India involves inherent risks, including price fluctuations, liquidity issues, and unforeseen economic events. To mitigate these risks, investors use tools like stock screener India platforms, which help filter stocks based on key financial metrics like earnings, debt levels, and market volatility. Diversification, stop-loss orders, position sizing, and staying updated on global and domestic news are additional techniques commonly employed. By integrating these strategies and tools, investors can manage risks more effectively and enhance their chances of achieving long-term financial goals while navigating the ever-changing landscape of the Indian stock market.




