
- What is Credit Management?
- Types of Credit (Personal, Business)
- Credit Policy Formation
- Credit Analysis
- Credit Scoring Models
- Credit Risk Assessment
- Collections and Recoveries
- Bad Debts and Provisions
- Role in Banking and NBFCs
- Legal and Regulatory Aspects
- Technology in Credit Management
- Conclusion
What is Credit Management?
Credit management is the process by which businesses and financial institutions grant credit, monitor credit risk, and ensure timely collection of payments from borrowers or customers. It plays a vital role in maintaining healthy cash flow and minimizing financial losses related to defaults and bad debts. Effective credit management balances the need to support sales and business growth through credit extension with the imperative to mitigate credit risk and protect the lender’s or company’s financial health. In essence, credit management involves setting credit policies, evaluating creditworthiness, granting credit limits, monitoring outstanding receivables, and managing collections and recoveries. For banks, non banking financial companies (NBFCs), and businesses that extend trade credit, an efficient credit management system is indispensable to sustaining profitability and liquidity.
Do You Want to Learn More About Database? Get Info From Our Database Online Training Today!
Types of Credit (Personal, Business)
Credit can be broadly classified based on the borrower type and purpose: Personal credit is a flexible financial tool that meets the needs of consumers at different life stages. These credit options include a variety of financing solutions, such as personal loans for unexpected expenses like medical bills or school costs, credit cards with flexible borrowing limits, auto loans for buying vehicles, home mortgages for real estate purchases, and loans for essential electronics and appliances. Lenders look at personal credit applications by assessing an individual’s financial profile. They carefully consider factors like income stability, ability to repay, existing credit history, and potential collateral.
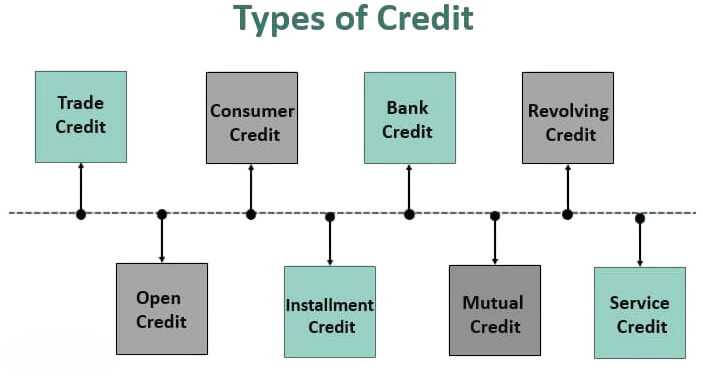
This careful approach ensures that credit options are tailored to fit the specific financial situations and risk levels of individual borrowers. It provides accessible and structured financial support for their personal and professional goals. Business credit is an essential financial resource for companies looking to fund their operations, expand, and manage cash flow well. This flexible tool includes various lending options, such as working capital loans for daily expenses, term loans for buying assets, and trade credit that allows businesses to delay payments to suppliers. Companies can also use flexible choices like overdrafts and cash credit secured by collateral. Additionally, they can access specialized tools like letters of credit and bank guarantees for international trade finance. Lenders evaluate business credit applications by looking at several important factors, including financial statements, cash flow stability, the strength of the business model, industry risks, and overall management quality. By understanding and effectively using these different credit options, organizations can make the most of their financial resources, support growth efforts, and stay nimble in a competitive business environment.
Credit Policy Formation
A credit policy is a formal set of guidelines that defines how credit is extended, managed, and recovered within an organization. It acts as a blueprint ensuring consistency, risk control, and regulatory compliance.
- Credit Eligibility Criteria: Defines who qualifies for credit based on creditworthiness, financial health, and history.
- Credit Limits: Establishes maximum exposure per customer or borrower.
- Payment Terms: Specifies repayment schedules, grace periods, and interest rates.
- Documentation Requirements: Lists necessary paperwork for credit approval.
- Collection Procedures: Details steps for follow-ups, reminders, and actions in case of delayed payments.
- Risk Management Guidelines: Outlines credit risk mitigation strategies such as collateral or guarantees.
- Delegation of Authority: Assigns approval powers at different organizational levels.
- Monitoring and Reporting: Defines frequency and format of credit reviews and reports.
Importance
A well-structured credit policy ensures disciplined credit granting, reduces defaults, and supports business objectives. It also helps standardize processes, train staff, and maintain customer relationships.
Would You Like to Know More About Database? Sign Up For Our Database Online Training Now!
Credit Analysis
Credit analysis is the evaluation process to determine the creditworthiness of a borrower or customer before granting credit. It aims to assess the likelihood that the borrower will fulfill their debt obligations timely.
- Financial Statement Analysis: Examines profitability, liquidity, leverage, and cash flow of the borrower.
- Credit History and Score: Reviews past repayment behavior, defaults, and credit bureau ratings.
- Industry and Market Analysis: Considers the borrower’s industry dynamics and competitive position.
- Management Assessment: Evaluates the competence and integrity of the borrower’s management team.
- Collateral Evaluation: Assesses the value and quality of security offered.
- Purpose and Amount of Credit: Checks if the loan amount is reasonable and intended use is sound.
Credit Scoring Models
Credit scoring models are detailed tools that evaluate credit risk by assigning scores to borrowers through careful analysis. These models use different methods, including statistical techniques like logistic regression, machine learning algorithms such as decision trees and neural networks, and behavioral scoring methods that track customer payment habits. By looking at important factors like payment history, debt levels, length of credit history, types of credit, recent inquiries, and income status, these models help financial institutions make quick, efficient, and consistent credit decisions. The main goal of credit scoring models is to create a standard way to assess risk, reduce human bias, and provide a trustworthy framework for evaluating borrowers’ creditworthiness. With their thorough and data-driven approach, these models have changed lending practices. They offer a clearer and more accurate way to assess credit risk while simplifying the decision-making process for financial institutions.
To Earn Your Database Certification, Gain Insights From Leading Blockchain Experts And Advance Your Career With ACTE’s Database Online Training Today!
Credit Risk Assessment
Credit risk assessment is an important financial process that evaluates the chances of a borrower defaulting by analyzing several key components. This method involves determining the probability of default (PD), estimating potential loss given default (LGD), and calculating exposure at default (EAD). Together, these elements help financial institutions assign accurate credit risk ratings from AAA to D. Through careful data collection, thorough stress testing under different bad scenarios, and continual monitoring of credit quality, organizations can identify and prioritize potential financial risks. The main goal of this approach is to help banks and non banking financial companies (NBFCs) set aside the right amount of capital and create effective risk management strategies. By using a structured framework, financial institutions can make better lending decisions, reduce potential losses, and stay financially healthy in a complicated economic environment.
Collections and Recoveries
Collections and recoveries are crucial components of credit management focused on obtaining overdue payments and minimizing losses:
Collections Process
- Reminder Communications: Calls, emails, and letters to prompt payment.
- Negotiations: Restructuring payment plans or settlements.
- Legal Notices: Issuing formal warnings as per legal guidelines.
- Escalation: Involving higher authorities or credit agencies.
Recoveries
When debts become non-performing, recovery efforts include.
- Asset Liquidation: Selling collateral or guarantees.
- Debt Restructuring: Modifying terms to facilitate repayment.
- Legal Actions: Filing suits, initiating insolvency proceedings.
Effective collections improve cash flows and reduce write-offs.
Preparing for a Database Job? Have a Look at Our Blog on Database Interview Questions and Answers To Ace Your Interview!
Bad Debts and Provisions
Despite best efforts, some credits may turn irrecoverable, classified as bad debts:
- Bad Debts: Amounts that are deemed uncollectible due to borrower insolvency, disputes, or other reasons. Written off from books after all recovery attempts fail.
- Provisions: Accounting for anticipated losses from doubtful debts by creating provisions. Helps in realistic profit reporting and complies with accounting standards.
Proper management of bad debts and provisions safeguards the financial statements’ integrity.
Role in Banking and NBFCs
Credit risk assessment is an important financial process that evaluates the chances of a borrower defaulting by analyzing several key components. This method involves determining the probability of default (PD), estimating potential loss given default (LGD), and calculating exposure at default (EAD). Together, these elements help financial institutions assign credit risk ratings from AAA to D. Through careful data collection, stress testing under different challenging scenarios, and ongoing monitoring of credit quality, organizations can identify and prioritize potential financial risks. The main goal of this approach is to help banks and non banking financial companies (NBFCs) set aside the right amount of capital and develop effective risk management strategies. By using a clear and structured framework, financial institutions can make better lending choices, reduce potential losses, and maintain strong financial health in a complex economic environment.
Legal and Regulatory Aspects
Credit management must comply with various laws and regulations to ensure ethical lending and protect stakeholder interests:
- Reserve Bank of India (RBI) Guidelines: Define provisioning norms, classification of assets, and credit appraisal processes.
- Securitization and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest (SARFAESI) Act: Provides tools for recovery of secured debts.
- Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC): Governs resolution of defaulting borrowers.
- Consumer Protection Laws: Protect borrower rights.
- Data Privacy Laws: Govern handling of credit data.
Adhering to legal frameworks minimizes litigation risks and enhances credibility.
Technology in Credit Management
Technology has revolutionized credit management by improving speed, accuracy, and efficiency:
- Credit Management Software: Automates credit scoring, limit monitoring, and reporting.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Enhance credit risk prediction and fraud detection.
- Blockchain: Improves transparency and security in credit transactions.
- Big Data Analytics: Enables comprehensive borrower profiling.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Streamlines repetitive tasks like reminders and documentation.
- Digital Lending Platforms: Provide quick credit decisions and disbursals.
Technology enables scalable, data-driven credit management aligned with modern business demands.
Conclusion
Credit management is a multifaceted discipline critical to financial institutions and businesses alike. From defining credit types and forming policies to detailed credit analysis, risk assessment, monitoring, and collections, each step is essential to maintaining financial health and supporting business growth. With the integration of advanced technology and adherence to regulatory frameworks, credit management continues to evolve, enabling smarter decision-making and efficient operations. For organizations, mastering credit management means balancing growth aspirations with prudent risk control, thereby ensuring sustainable profitability and stakeholder confidence.



